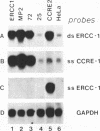
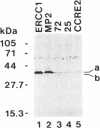
Abstract
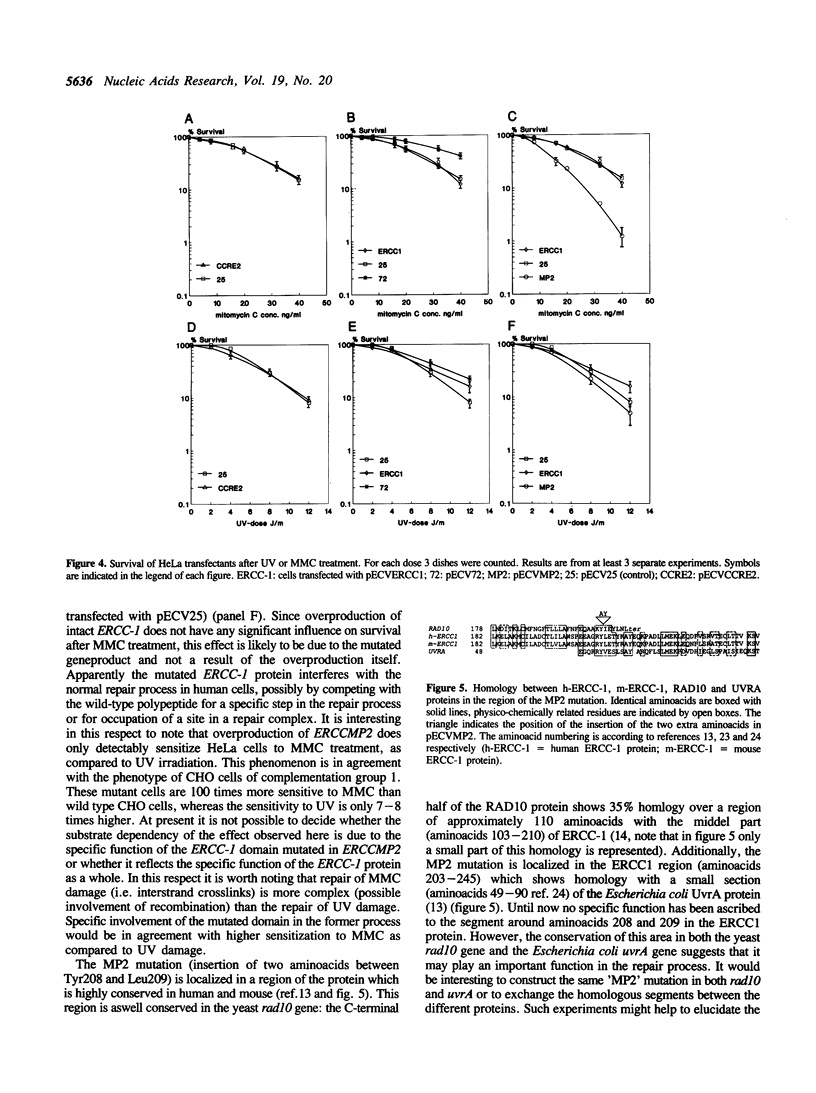
Antisense and mutated cDNA of the human excision repair gene ERCC-1 were overexpressed in repair proficient HeLa cells by means of an Epstein-Barr-virus derived cDNA expression vector. Whereas antisense RNA did not influence the survival of the transfected cells, a mutated cDNA generating an ERCC-1 protein with two extra amino acids in a conserved region of its C-terminal part resulted in a significant sensitization of the HeLa transfectants to mitomycin C-induced damage. These results suggest that overexpression of the mutated ERCC-1 protein interferes with proper functioning of the excision repair pathway in repair proficient cells and is compatible with a model in which the mutated ERCC-1 protein competes with the wild-type polypeptide for a specific step in the repair process or for occupation of a site in a repair complex. Apparently, this effect is more pronounced for mitomycin C induced crosslink repair than for UV-induced DNA damage.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battista J. R., Ohta T., Nohmi T., Sun W., Walker G. C. Dominant negative umuD mutations decreasing RecA-mediated cleavage suggest roles for intact UmuD in modulation of SOS mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7190–7194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belt P. B., Groeneveld H., Teubel W. J., van de Putte P., Backendorf C. Construction and properties of an Epstein-Barr-virus-derived cDNA expression vector for human cells. Gene. 1989 Dec 14;84(2):407–417. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90515-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman L., Yeung A. T. The UvrABC endonuclease system of Escherichia coli--a view from Baltimore. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90006-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Molecular genetics of eukaryotic DNA excision repair. Cancer Cells. 1990 Oct;2(10):311–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Van Houten B., Thomas D. C., Sancar A. Sequences of Escherichia coli uvrA gene and protein reveal two potential ATP binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4895–4901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartasova T., Cornelissen B. J., Belt P., van de Putte P. Effects of UV, 4-NQO and TPA on gene expression in cultured human epidermal keratinocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5945–5962. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola D., Westwick J., Rundell A. Y., Adamson E. D., Edwards S. A. Analysis of a transformed cell line using antisense c-fos RNA. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):253–265. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90151-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudgett J. S., MacInnes M. A. Isolation of the functional human excision repair gene ERCC5 by intercosmid recombination. Genomics. 1990 Dec;8(4):623–633. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90248-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Murray J. M. Antisense RNA of proto-oncogene c-fos blocks renewed growth of quiescent 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):639–649. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P., Prakash L., Dumais D., Perozzi G., Prakash S. Nucleotide sequence of the RAD10 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3549–3552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04115.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby C. P., Sancar A. Structure and function of the (A)BC excinuclease of Escherichia coli. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90005-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Satokata I., Ogita Z., Uchida T., Okada Y. Molecular cloning of a mouse DNA repair gene that complements the defect of group-A xeroderma pigmentosum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5512–5516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troelstra C., Odijk H., de Wit J., Westerveld A., Thompson L. H., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. Molecular cloning of the human DNA excision repair gene ERCC-6. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5806–5813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten B. Nucleotide excision repair in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Mar;54(1):18–51. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.1.18-51.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber C. A., Salazar E. P., Stewart S. A., Thompson L. H. Molecular cloning and biological characterization of a human gene, ERCC2, that corrects the nucleotide excision repair defect in CHO UV5 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1137–1146. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeda G., van Ham R. C., Masurel R., Westerveld A., Odijk H., de Wit J., Bootsma D., van der Eb A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. Molecular cloning and biological characterization of the human excision repair gene ERCC-3. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2570–2581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerveld A., Hoeijmakers J. H., van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Pastink A., Wood R. D., Bootsma D. Molecular cloning of a human DNA repair gene. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):425–429. doi: 10.1038/310425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zdzienicka M. Z., Roza L., Westerveld A., Bootsma D., Simons J. W. Biological and biochemical consequences of the human ERCC-1 repair gene after transfection into a repair-deficient CHO cell line. Mutat Res. 1987 Jan;183(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(87)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., Vredeveldt G., Mayne L. V., Odijk H., Vermeulen W., Klein B., Weeda G., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D., Westerveld A. The cloned human DNA excision repair gene ERCC-1 fails to correct xeroderma pigmentosum complementation groups A through I. Mutat Res. 1989 Mar;217(2):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(89)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Westerveld A., Yasui A., Koken M. H., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Molecular characterization of the human excision repair gene ERCC-1: cDNA cloning and amino acid homology with the yeast DNA repair gene RAD10. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):913–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., van den Tol J., Warmerdam P., Odijk H., Meijer D., Westerveld A., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. Evolution and mutagenesis of the mammalian excision repair gene ERCC-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5305–5322. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]