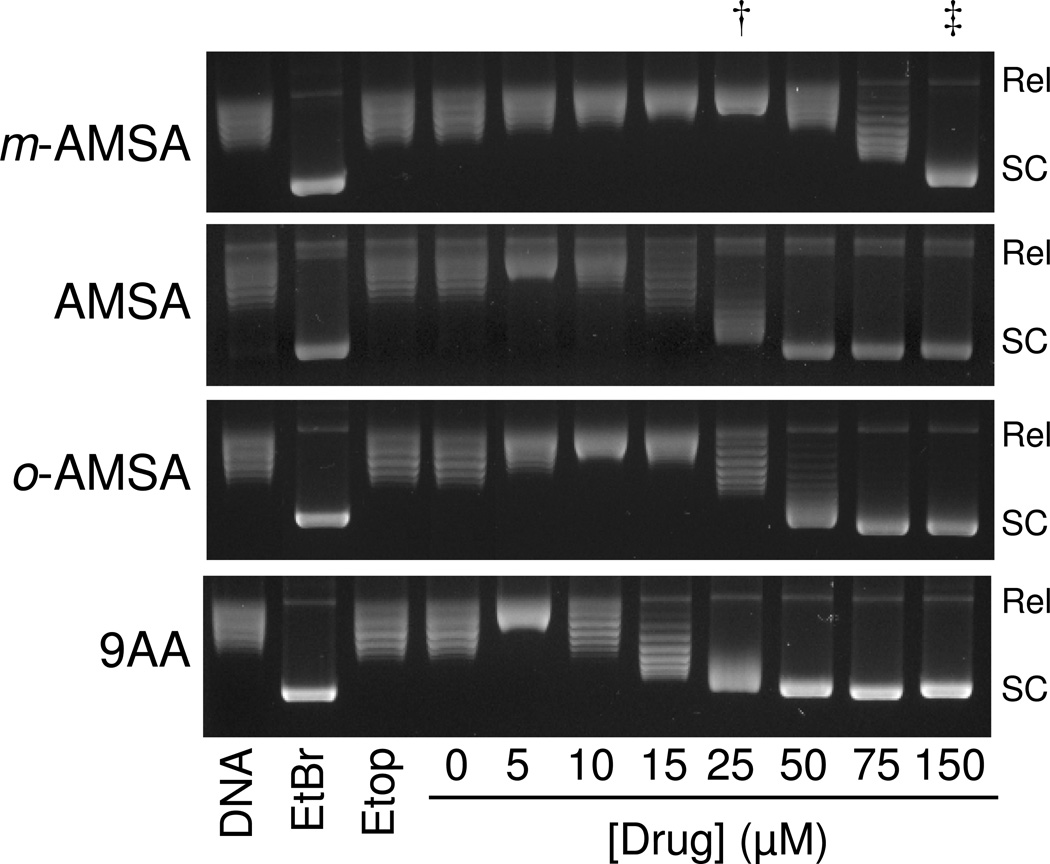
Figure 5.
DNA intercalation by m-AMSA and derivatives. The abilities of 0–150 µM m-AMSA, AMSA, o-AMSA, and 9-aminoacridine (9AA) to intercalate into DNA were determined using a topoisomerase I-based supercoiling assay. Representative ethidium bromide (EtBr)-stained agarose gels are shown. The effects of 10 µM EtBr and 100 µM etoposide (Etop) are included as positive and negative controls, respectively. Relaxed DNA standards (DNA) also are shown. Results are representative of three independent experiments. As described in Table 1, concentrations of intercalators required to yield “fully relaxed” (Rel) and “fully supercoiled” (SC) plasmid are used for comparative purposes. Lanes that include these concentrations for m-AMSA are indicated by a dagger (†) and double dagger (‡), respectively.