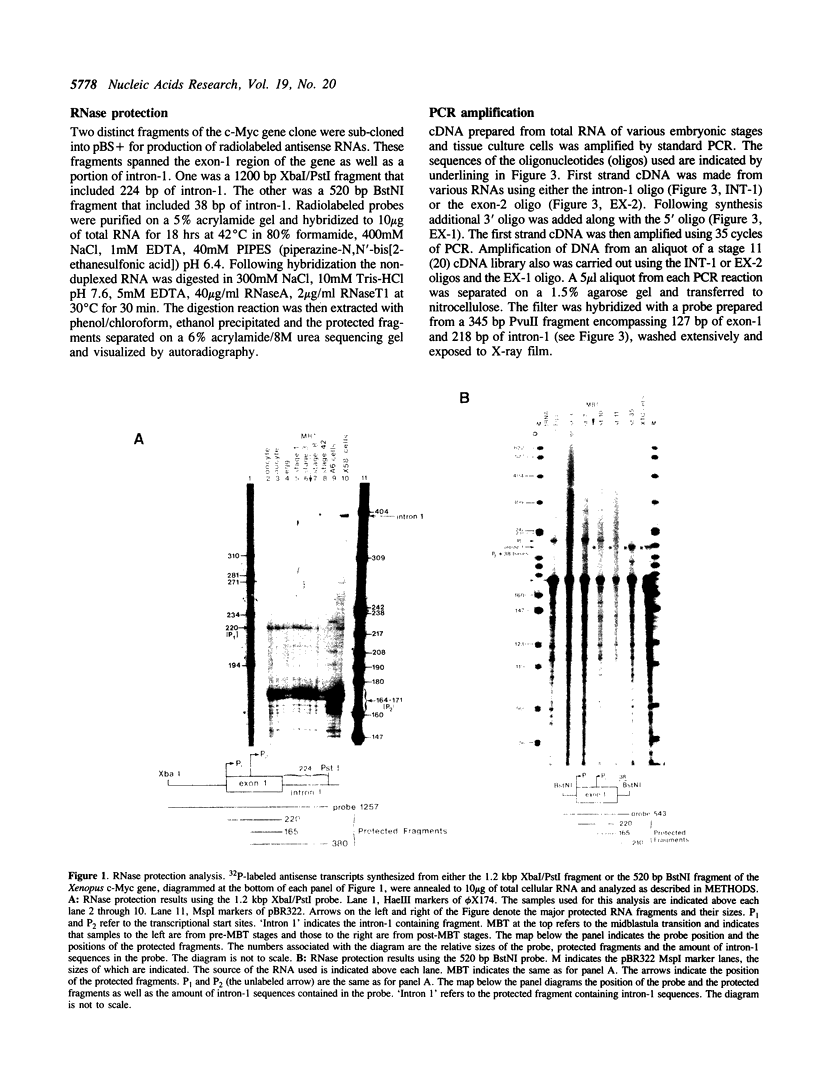
Abstract
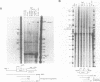
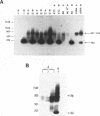
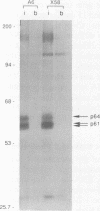
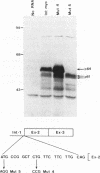
Two distinct c-Myc RNA classes have been identified in Xenopus laevis, presumably expressed from the duplicated c-Myc locus (1, 6). The major Xenopus c-Myc transcripts arise from sites termed P1 and P2 similarly to those of the mammalian c-Myc genes. I have used a cloned Xenopus c-Myc gene to examine the regulated pattern of expression from this gene during early Xenopus embryogenesis. Analysis of the pattern of transcript processing indicates that not only are P1 and P2 differentially active during early development but alternatively spliced c-Myc RNAs are generated which contain sequences of the first intron. These intron-1 containing c-Myc RNAs are generated by alternative splicing of transcripts initiated from the major transcription start site, P2, and are observed only in RNA samples from post-midblastula embryos or Xenopus tissue culture cells. Xenopus tissue culture cells synthesize two major c-Myc proteins (p61 and p64). Xenopus RNAs that do not contain intron-1 sequences synthesize only the p61 species. Two closely spaced ATG codons at the 5' end of exon-2 are utilized equivalently to generate a p61 doublet. Intron-1 containing RNAs utilize an ATG codon in the intron sequences to synthesize the p64 species as well as the exon-2 ATG codons to synthesize the p61 doublet.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Gerondakis S., Webb E., Corcoran L. M., Cory S. Cellular myc oncogene is altered by chromosome translocation to an immunoglobulin locus in murine plasmacytomas and is rearranged similarly in human Burkitt lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1982–1986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J., Moulding C., Taub R., Murphy W., Stewart T., Potter H., Lenoir G., Leder P. The human c-myc oncogene: structural consequences of translocation into the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Adams J. M., Dunn A. R., Cory S. Murine T lymphomas in which the cellular myc oncogene has been activated by retroviral insertion. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Onc gene amplification in promyelocytic leukaemia cell line HL-60 and primary leukaemic cells of the same patient. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):61–63. doi: 10.1038/299061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Greve J., Battey J., Fedorko J., Birrer M., Evan G., Kaye F., Sausville E., Minna J. The human L-myc gene encodes multiple nuclear phosphoproteins from alternatively processed mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4381–4388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosaka-Akita H., Rosenberg R. K., Minna J. D., Birrer M. J. A complex pattern of translational initiation and phosphorylation in L-myc proteins. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):371–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Gilman M. Z., Maruyama M., Weinberg R. A. c-myc and c-fos expression in differentiating mouse primary keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2853–2857. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downs K. M., Martin G. R., Bishop J. M. Contrasting patterns of myc and N-myc expression during gastrulation of the mouse embryo. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):860–869. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godeau F., Persson H., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B. C-myc expression is dissociated from DNA synthesis and cell division in Xenopus oocyte and early embryonic development. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3571–3577. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusse M., Ghysdael J., Evan G., Soussi T., Méchali M. Translocation of a store of maternal cytoplasmic c-myc protein into nuclei during early development. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5395–5403. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., King M. W., Bentley D. L., Anderson C. W., Eisenman R. N. A non-AUG translational initiation in c-myc exon 1 generates an N-terminally distinct protein whose synthesis is disrupted in Burkitt's lymphomas. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourdry J., Brulfert A., Gusse M., Schoevaert D., Taylor M. V., Mechali M. Localization of c-myc expression during oogenesis and embryonic development in Xenopus laevis. Development. 1988 Dec;104(4):631–641. doi: 10.1242/dev.104.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffredo T., Vandenbunder B., Dieterlen-Lièvre F. In situ study of c-myc protein expression during avian development. Development. 1989 Apr;105(4):679–695. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.4.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. A., Street A. J., Fahrlander P. D., Yang J. Q., Eisenman R. N., Marcu K. B. Translocated c-myc genes produce chimeric transcripts containing antisense sequences of the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in mouse plasmacytomas. Oncogene. 1988 May;2(5):469–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. W., Roberts J. M., Eisenman R. N. Expression of the c-myc proto-oncogene during development of Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4499–4508. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. Methylation-sensitive sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc basic region. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):186–189. doi: 10.1126/science.1987636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Principaud E., Spohr G. Xenopus laevis c-myc I and II genes: molecular structure and developmental expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):3081–3088. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.3081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Hamlyn P. H., Baer R. Altered nucleotide sequences of a translocated c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):760–765. doi: 10.1038/306760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid P., Schulz W. A., Hameister H. Dynamic expression pattern of the myc protooncogene in midgestation mouse embryos. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):226–229. doi: 10.1126/science.2911736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbunder B., Pardanaud L., Jaffredo T., Mirabel M. A., Stehelin D. Complementary patterns of expression of c-ets 1, c-myb and c-myc in the blood-forming system of the chick embryo. Development. 1989 Oct;107(2):265–274. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriz S., Taylor M., Méchali M. Differential expression of two Xenopus c-myc proto-oncogenes during development. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4091–4097. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., Reddy E. P., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chicken c-myc gene reveals homologous and unique coding regions by comparison with the transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29, delta gag-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2146–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman K. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Collum R. G., Smith R. K., Kohl N. E., Denis K. A., Nau M. M., Witte O. N., Toran-Allerand D., Gee C. E. Differential expression of myc family genes during murine development. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):780–783. doi: 10.1038/319780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]