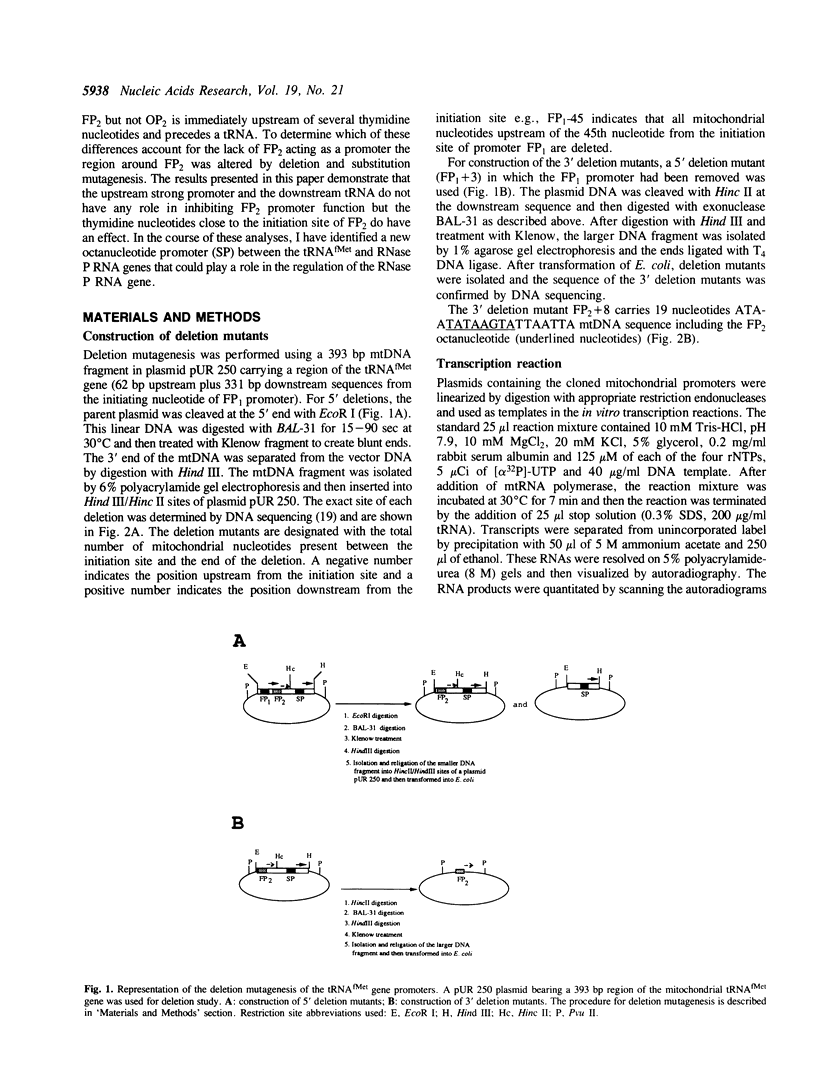
Abstract
Prior work has indicated that an octanucleotide [5'TATAAGTA(+1)3'] sequence is used as a promoter in yeast mitochondria. Two such sequences (FP1 and FP2) are present upstream of the tRNA(fMet)-RNAse P RNA -tRNA(Pro) gene cluster but only the FP1 promoter but not the FP2 appears to be active in vivo and in vitro. The results presented in this paper suggest that the downstream ATTAATT sequence close to the initiation site of FP2 causes premature termination of transcription and effectively inhibits transcription from the FP2 octanucleotide sequence. Thus the different levels of RNA synthesis from these tRNA(fMet) promoters might be determined by variable transcriptional initiation and elongation blockage events. Since FP1 is found to be the only active promoter in this gene cluster, these three genes are thought to be transcribed together from the FP1 promoter. In this study, a new promoter (SP) between the tRNA(fMet) and RNase P RNA genes has been identified which may participate in RNase P RNA gene expression. The sequence of the new promoter does not match perfectly to the mitochondrial conserved promoter sequence but does match to the consensus promoter sequence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biswas T. K. Control of mitochondrial gene expression in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9338–9342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas T. K., Edwards J. C., Rabinowitz M., Getz G. S. Characterization of a yeast mitochondrial promoter by deletion mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1954–1958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas T. K., Getz G. S. A critical base in the yeast mitochondrial nonanucleotide promoter. Abolition of promoter activity by mutation at the -2 position. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):3927–3930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas T. K., Getz G. S. Nucleotides flanking the promoter sequence influence the transcription of the yeast mitochondrial gene coding for ATPase subunit 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):270–274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas T. K., Getz G. S. Promoter-promoter interactions influencing transcription of the yeast mitochondrial gene, Oli 1, coding for ATPase subunit 9. Cis and trans effects. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4844–4851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas T. K., Getz G. S. Regulation of transcriptional initiation in yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19053–19059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas T. K., Ticho B., Getz G. S. In vitro characterization of the yeast mitochondrial promoter using single-base substitution mutants. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13690–13696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson T., Rabinowitz M. Identification of multiple transcriptional initiation sites on the yeast mitochondrial genome by in vitro capping with guanylyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14025–14033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M. C., Fox T. D. Control of mitochondrial gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:91–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth M. J., Martin N. C. RNase P activity in the mitochondria of Saccharomyces cerevisiae depends on both mitochondrion and nucleus-encoded components. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1058–1064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. C., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Two RNA polymerase sigma factors from Bacillus subtilis discriminate between overlapping promoters for a developmentally regulated gene. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):800–804. doi: 10.1038/302800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. Initiation of Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA synthesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5480–5484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Tinoco I., Jr DNA-RNA hybrid duplexes containing oligo(dA:rU) sequences are exceptionally unstable and may facilitate termination of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2295–2299. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osinga K. A., De Vries E., Van der Horst G. T., Tabak H. F. Initiation of transcription in yeast mitochondria: analysis of origins of replication and of genes coding for a messenger RNA and a transfer RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):1889–1900. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.1889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponnambalam S., Busby S. RNA polymerase molecules initiating transcription at tandem promoters can collide and cause premature transcription termination. FEBS Lett. 1987 Feb 9;212(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81549-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Groot Koerkamp M. J., Van der Horst G. T., Touw E. P., Osinga K. A., Van der Bliek A. M., Veeneman G. H., Van Boom J. H., Tabak H. F. Characterization of the promoter of the large ribosomal RNA gene in yeast mitochondria and separation of mitochondrial RNA polymerase into two different functional components. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1041–1047. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04320.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Koerkamp M. J., Touw E. P., Tabak H. F. Specificity factor of yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase. Purification and interaction with core RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12785–12791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticho B. S., Getz G. S. The characterization of yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase. A monomer of 150,000 daltons with a transcription factor of 70,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10096–10103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Myers A. M. Genetics of mitochondrial biogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:249–285. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.001341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettstein-Edwards J., Ticho B. S., Martin N. C., Najarian D., Getz G. S. In vitro transcription and promoter strength analysis of five mitochondrial tRNA promoters in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2905–2911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkley C. S., Keller M. J., Jaehning J. A. A multicomponent mitochondrial RNA polymerase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14214–14223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







