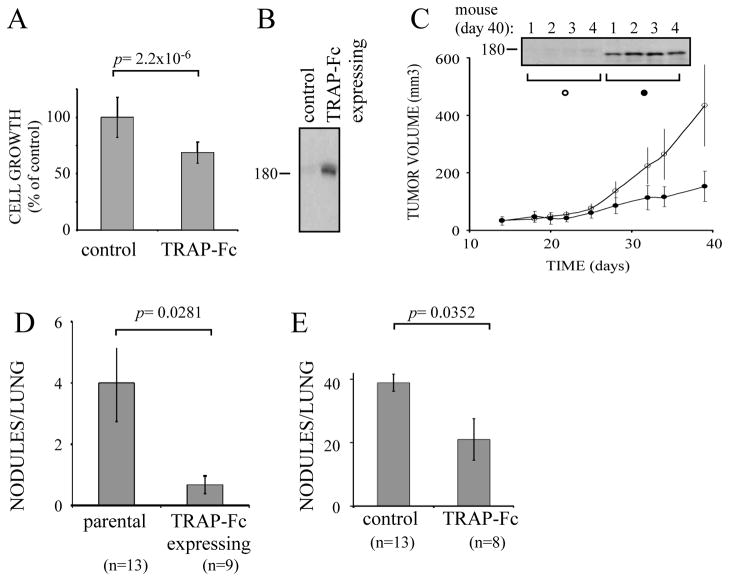
Figure 6. TRAP-Fc inhibits lung metastasis of MDA-MB-231 mammary cancer cell.
(A) MDA-MB-231 cells (2×104) were treated with TRAP-Fc (30 μg/ml) and proliferation was determined in hexaplicates after 5 days, using the MTT assay. (B) Conditioned media collected from parental cells and from MDA-MB-231 cells stably expressing the TRAP-Fc protein were immunoblotted (IB) with an anti-EGFR antibody. (C) Parental MDA-MB-231 and TRAP-Fc-expressing cells (2.5×106) were inoculated into the mammary fat pad of scid mice (6 and 7 mice, respectively). Tumor size was monitored twice a week. Average tumor sizes and standard deviations (bars) are shown. In the end of the experiment (day 40) tumors were removed from 4 mice of each group, homogenized, electrophoresed and immunoblotted with an anti-EGFR antibody. Representative blots are shown. (D) Parental MDA-MB-231 and TRAP-Fc-expressing cells (2.5×106) were injected into the tail vein of scid mice. Nodules in the lungs were counted at day 60 and their averages presented. The control group included 13 mice, and the TRAP-expressing group included 9 mice. (E) MDA-MB-231 cells (1.5×105) were injected into the tail vein of scid mice. TRAP-Fc (100 μg per injection) was injected intraperitoneally (8 mice) on days 1, 3, 6 and 9. Nodules in the lungs were counted at day 60. The control group included 13 mice.