Abstract
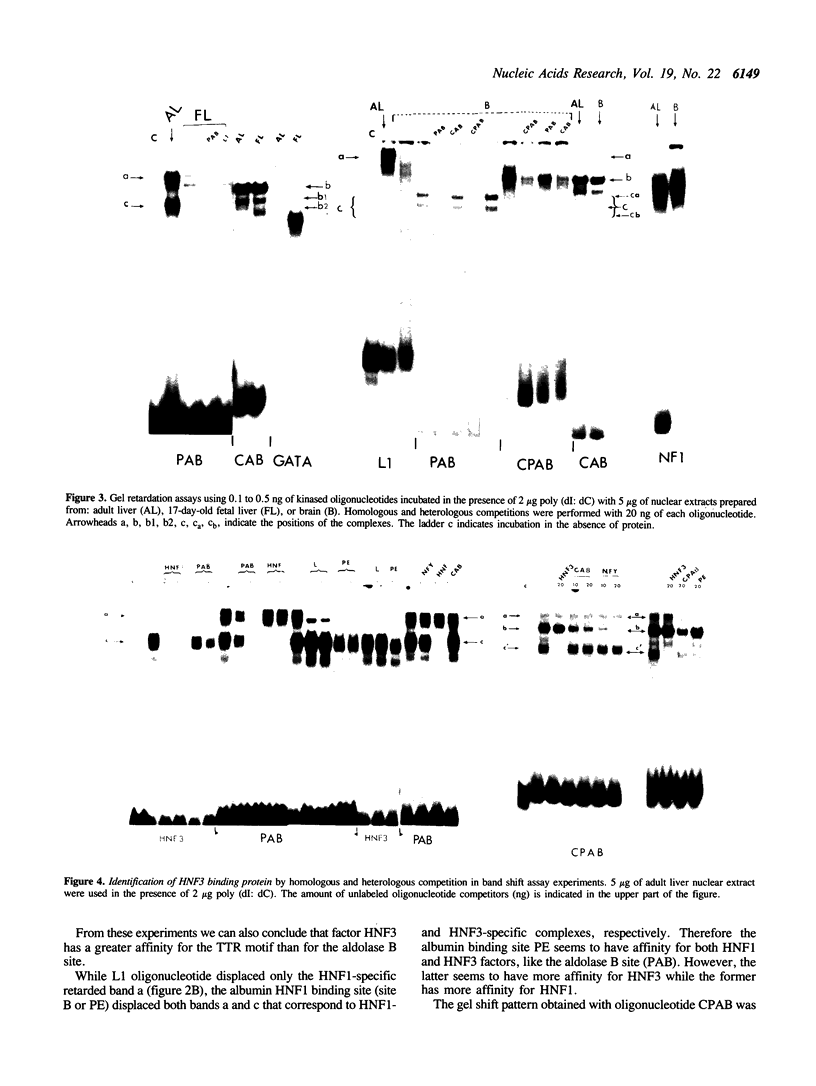
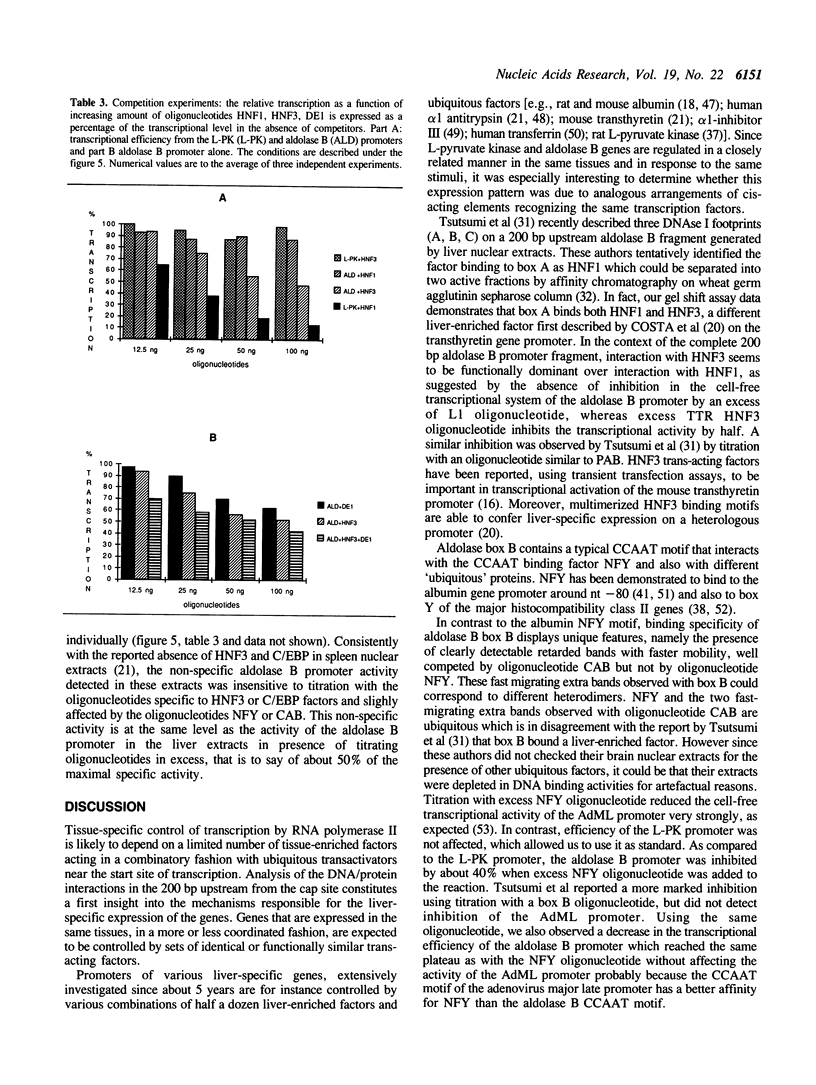
The rat aldolase B 5' flanking region (nucleotides - 194 to +41) contains sufficient information for liver-specific expression. A detailed investigation of factors binding to the rat aldolase B 5' flanking region has allowed us to identify three distinct factors that filled different sites of this region (A, B, C). The liver-enriched C/EBP or related factors bind to box C, as demonstrated by the specific interaction with bacterially expressed C/EBP protein. Box B bearing the CCAAT sequence binds the ubiquitous factor NFY. Surprisingly, Box A is able to bind two liver enriched factors, namely HNF1 and HNF3. However, in the context of the intact promoter, as shown by footprinting competition experiments, HNF3 binds solely to this sequence. HNF3, but not HNF1 is a transcriptional activator as demonstrated in the in vitro transcription assay.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham L. J., Bradshaw A. D., Shiels B. R., Northemann W., Hudson G., Fey G. H. Hepatic transcription of the acute-phase alpha 1-inhibitor III gene is controlled by a novel combination of cis-acting regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3483–3491. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumhueter S., Mendel D. B., Conley P. B., Kuo C. J., Turk C., Graves M. K., Edwards C. A., Courtois G., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1 shares three sequence motifs with the POU domain proteins and is identical to LF-B1 and APF. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):372–379. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada A., Maki R. A. DNA binding of the mouse class II major histocompatibility CCAAT factor depends on two components. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3097–3100. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Raymondjean M., Carranca A. G., Herbomel P., Yaniv M. Factors involved in control of tissue-specific expression of albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. J., Chen T. T., Lei H. Y., Chen D. S., Lee S. C. Molecular cloning of a transcription factor, AGP/EBP, that belongs to members of the C/EBP family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6642–6653. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouard T., Blumenfeld M., Bach I., Vandekerckhove J., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. A distal dimerization domain is essential for DNA-binding by the atypical HNF1 homeodomain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5853–5863. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decaux J. F., Antoine B., Kahn A. Regulation of the expression of the L-type pyruvate kinase gene in adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11584–11590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decaux J. F., Marcillat O., Pichard A. L., Henry J., Kahn A. Glucose-dependent and -independent effect of insulin on gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3432–3438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frain M., Swart G., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Stämpfli S., Frank R., Cortese R. The liver-specific transcription factor LF-B1 contains a highly diverged homeobox DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90877-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., Roux J., Rigaud G., Pictet R. Cell-type specific activity of two glucocorticoid responsive units of rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene is associated with multiple binding sites for C/EBP and a novel liver-specific nuclear factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):131–139. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregori C., Ginot F., Decaux J. F., Weber A., Berbar T., Kahn A., Pichard A. L. Expression of the rat aldolase B gene: a liver-specific proximal promoter and an intronic activator. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 30;176(2):722–729. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80244-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Rollier A., Tronche F., Ott M. O., Yaniv M., Weiss M. C. The rat albumin promoter is composed of six distinct positive elements within 130 nucleotides. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4750–4758. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Li X. Y., Black D., Matthes H., Benoist C., Mathis D. Co-evolution from yeast to mouse: cDNA cloning of the two NF-Y (CP-1/CBF) subunits. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3119–3127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai E., Stromstedt P. E., Quinn P. G., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A., Granner D. K. Characterization of a complex glucocorticoid response unit in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4712–4719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Tanaka T., Tsutsumi R., Ishikawa K., Tsutsumi K. Two different HNF1-like transcription activators in the liver bind to the same region of the rat aldolase B promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1337–1343. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80934-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., Lane M. D. Mouse insulin-responsive glucose transporter gene: characterization of the gene and trans-activation by the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):251–255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. G., Sheffery M. Physical characterization of the purified CCAAT transcription factor, alpha-CP1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13362–13369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm D. J., Roesler W. J., Liu J. S., Park E. A., Hanson R. W. In vitro analysis of promoter elements regulating transcription of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):480–485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Tao W. F., Chen W. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha belongs to a gene family in mammals that is homologous to the Drosophila homeotic gene fork head. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):416–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maire P., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The role of cis-acting promoter elements in tissue-specific albumin gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2711183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maity S. N., Vuorio T., de Crombrugghe B. The B subunit of a rat heteromeric CCAAT-binding transcription factor shows a striking sequence identity with the yeast Hap2 transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5378–5382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Lane M. D., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Is CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein a central regulator of energy metabolism? Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2021–2024. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelzon D., Boissier F., Zakin M. M. The binding site for the liver-specific transcription factor Tf-LF1 and the TATA box of the human transferrin gene promoter are the only elements necessary to direct liver-specific transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5717–5721. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. R., Maire P., Schibler U. DBP, a liver-enriched transcriptional activator, is expressed late in ontogeny and its tissue specificity is determined posttranscriptionally. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90808-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnich A., Besmond C., Darquy S., Reach G., Vaulont S., Dreyfus J. C., Kahn A. Dietary and hormonal regulation of aldolase B gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):1045–1052. doi: 10.1172/JCI111766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsch D., Stewart A. F., Boshart M., Mestril R., Weih F., Schütz G. Chromatin structures of the rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene relate to the function of its cis-acting elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3334–3342. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numazaki M., Tsutsumi K., Tsutsumi R., Ishikawa K. Expression of aldolase isozyme mRNAs in fetal rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 2;142(1):165–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E. A., Roesler W. J., Liu J., Klemm D. J., Gurney A. L., Thatcher J. D., Shuman J., Friedman A., Hanson R. W. The role of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein in the transcriptional regulation of the gene for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6264–6272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramji D. P., Tadros M. H., Hardon E. M., Cortese R. The transcription factor LF-A1 interacts with a bipartite recognition sequence in the promoter regions of several liver-specific genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1139–1146. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangan V. S., Das G. C. Purification and biochemical characterization of hepatocyte nuclear factor 2 involved in liver-specific transcription of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8874–8879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymondjean M., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Several distinct "CCAAT" box binding proteins coexist in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):757–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Platero J. S., Shuman J., Calame K. Ig/EBP-1: a ubiquitously expressed immunoglobulin enhancer binding protein that is similar to C/EBP and heterodimerizes with C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1404–1415. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorpp M., Kugler W., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. Hepatocyte-specific promoter element HP1 of the Xenopus albumin gene interacts with transcriptional factors of mammalian hepatocytes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Zhong W. M., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2353–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Why bend DNA? Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90729-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronche F., Rollier A., Bach I., Weiss M. C., Yaniv M. The rat albumin promoter: cooperation with upstream elements is required when binding of APF/HNF1 to the proximal element is partially impaired by mutation or bacterial methylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4759–4766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi K., Ito K., Ishikawa K. Developmental appearance of transcription factors that regulate liver-specific expression of the aldolase B gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4923–4931. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Munnich A., Decaux J. F., Kahn A. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of L-type pyruvate kinase gene expression in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7621–7625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Puzenat N., Kahn A., Raymondjean M. Analysis by cell-free transcription of the liver-specific pyruvate kinase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4409–4415. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Puzenat N., Levrat F., Cognet M., Kahn A., Raymondjean M. Proteins binding to the liver-specific pyruvate kinase gene promoter. A unique combination of known factors. J Mol Biol. 1989 Sep 20;209(2):205–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90273-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuarin J., Mueller C., Schibler U. A ubiquitous CCAAT factor is required for efficient in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 20;214(4):865–874. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90341-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthopoulos K. G., Prezioso V. R., Chen W. S., Sladek F. M., Cortese R., Darnell J. E., Jr The different tissue transcription patterns of genes for HNF-1, C/EBP, HNF-3, and HNF-4, protein factors that govern liver-specific transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3807–3811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]