Abstract
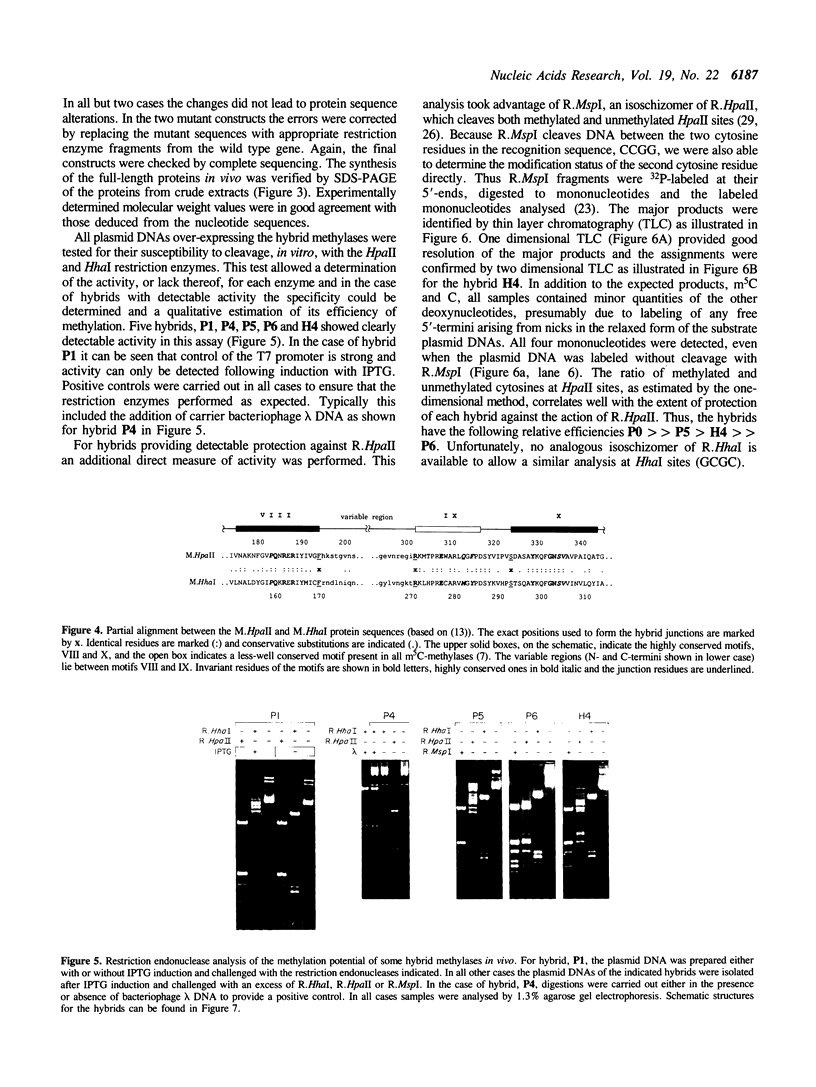
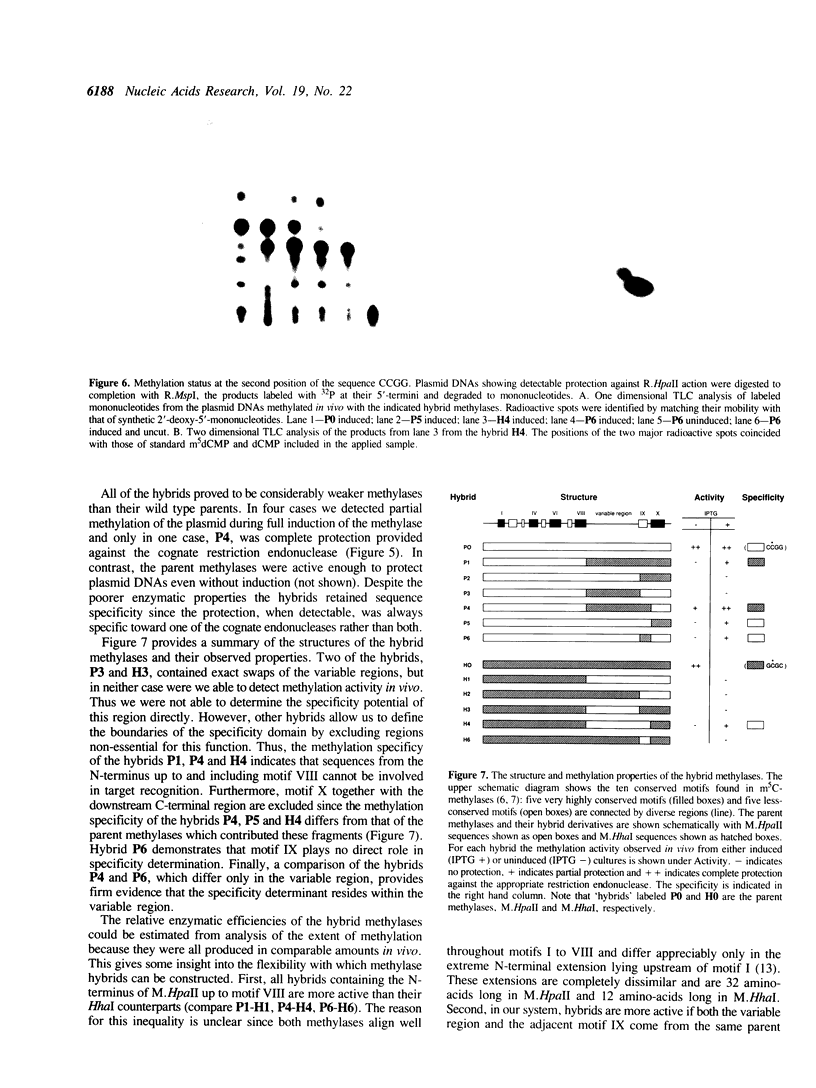
Prokaryotic DNA[cytosine-C5]methyltransferases (m5C-methylases) share a common architectural arrangement of ten conserved sequence motifs. A series of eleven hybrids have been constructed between the HpaII (recognition sequence: Cm5CGG) and HhaI (recognition sequence: Gm5CGC) DNA-methylases. The hybrids were over-expressed in E.coli and their in vivo methylation phenotypes investigated. Six were inactive by our assay while five of them retained partial methylation activity and full specificity. In all five cases the specificity matched that of the parent methylase which contributed the so-called variable region, located between conserved motifs VIII and IX. This was the only sequence held in common between the active hybrids and for the first time provides unequivocal evidence that the specificity determinants of the mono-specific m5C-methylases are located within the variable region. Correlation of the hybrid methylase structure with the efficiency of methylation suggests that conserved motif IX may interact with the variable region whereas motif X most probably interacts with the N-terminal half of the molecule.
Full text
PDF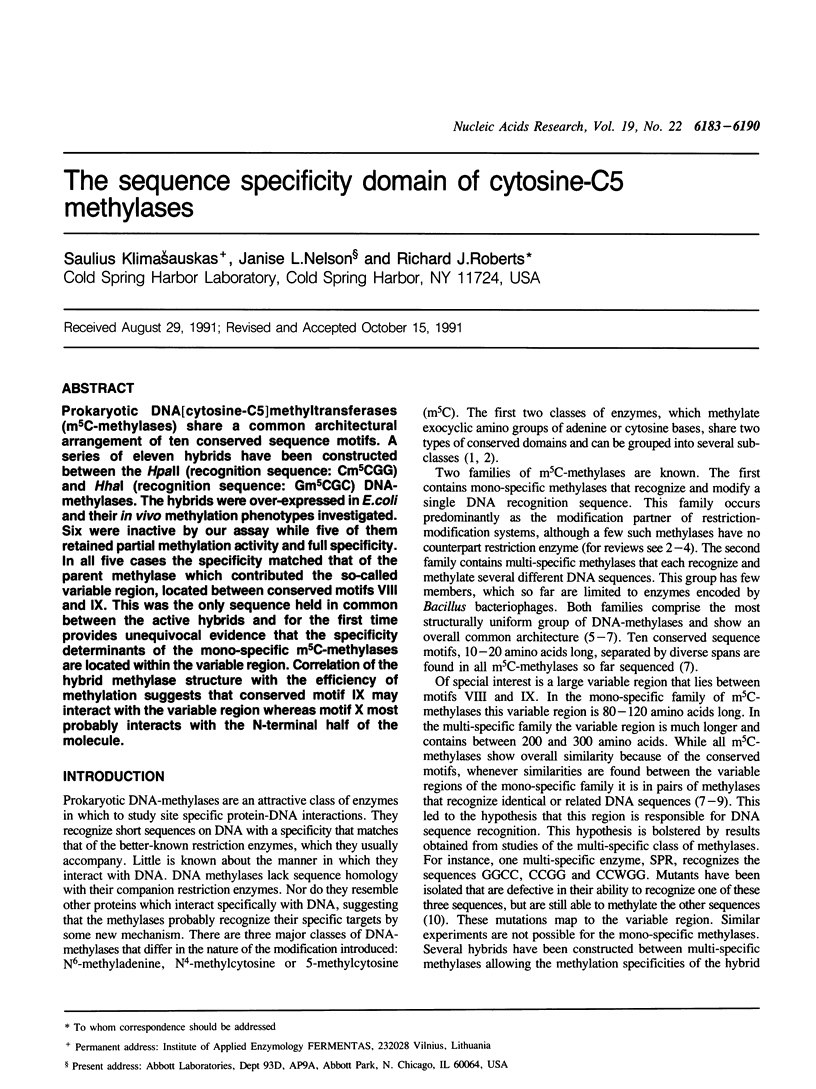





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balganesh T. S., Reiners L., Lauster R., Noyer-Weidner M., Wilke K., Trautner T. A. Construction and use of chimeric SPR/phi 3T DNA methyltransferases in the definition of sequence recognizing enzyme regions. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3543–3549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butkus V., Petrauskiene L., Maneliene Z., Klimasauskas S., Laucys V., Janulaitis A. Cleavage of methylated CCCGGG sequences containing either N4-methylcytosine or 5-methylcytosine with MspI, HpaII, SmaI, XmaI and Cfr9I restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7091–7102. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card C. O., Wilson G. G., Weule K., Hasapes J., Kiss A., Roberts R. J. Cloning and characterization of the HpaII methylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1377–1383. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caserta M., Zacharias W., Nwankwo D., Wilson G. G., Wells R. D. Cloning, sequencing, in vivo promoter mapping, and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene for the HhaI methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4770–4777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Solage A., Glaser G., Razin A. Direct detection of methylated cytosine in DNA by use of the restriction enzyme MspI. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(6):2125–2132. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dila D., Sutherland E., Moran L., Slatko B., Raleigh E. A. Genetic and sequence organization of the mcrBC locus of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4888–4900. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4888-4900.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich M., Wang R. Y. 5-Methylcytosine in eukaryotic DNA. Science. 1981 Jun 19;212(4501):1350–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.6262918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenbaum Y., Cedar H., Razin A. Restriction enzyme digestion of hemimethylated DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2509–2515. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsley A., Arnheim N., Toney M. D., Cortopassi G., Galas D. J. A simple method for site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6545–6551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler C., Manta V. Specificity of restriction endonucleases and DNA modification methyltransferases a review (Edition 3). Gene. 1990 Aug 16;92(1-2):1–248. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90486-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. C., Pósfai G., Szybalski W. A novel gene-fusing vector: construction of a 5'-GGmCC-specific chimeric methyltransferase, M.BspRI/M.BsuRI. Gene. 1991 Apr;100:45–50. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90348-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimasauskas S., Timinskas A., Menkevicius S., Butkienè D., Butkus V., Janulaitis A. Sequence motifs characteristic of DNA[cytosine-N4]methyltransferases: similarity to adenine and cytosine-C5 DNA-methylases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9823–9832. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korch C., Hagblom P. In-vivo-modified gonococcal plasmid pJD1. A model system for analysis of restriction enzyme sensitivity to DNA modifications. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 15;161(3):519–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauster R., Trautner T. A., Noyer-Weidner M. Cytosine-specific type II DNA methyltransferases. A conserved enzyme core with variable target-recognizing domains. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 20;206(2):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pósfai J., Bhagwat A. S., Pósfai G., Roberts R. J. Predictive motifs derived from cytosine methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2421–2435. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Macelis D. Restriction enzymes and their isoschizomers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):2077–2109. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slatko B. E., Croft R., Moran L. S., Wilson G. G. Cloning and analysis of the HaeIII and HaeII methyltransferase genes. Gene. 1988 Dec 25;74(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilák L., Venetianer P., Kiss A. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the genes coding for the Sau96I restriction and modification enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4659–4664. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautner T. A., Balganesh T. S., Pawlek B. Chimeric multispecific DNA methyltransferases with novel combinations of target recognition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6649–6658. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., Flavell R. A. MspI, an isoschizomer of hpaII which cleaves both unmethylated and methylated hpaII sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3231–3236. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter J., Noyer-Weidner M., Trautner T. A. The amino acid sequence of the CCGG recognizing DNA methyltransferase M.BsuFI: implications for the analysis of sequence recognition by cytosine DNA methyltransferases. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1007–1013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08203.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilke K., Rauhut E., Noyer-Weidner M., Lauster R., Pawlek B., Behrens B., Trautner T. A. Sequential order of target-recognizing domains in multispecific DNA-methyltransferases. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2601–2609. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. G. Organization of restriction-modification systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2539–2566. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Santi D. V. High level expression and purification of HhaI methyltransferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):703–717. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Santi D. V. Kinetic and catalytic mechanism of HhaI methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4778–4786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo O. J., Agarwal K. L. Isolation and characterization of two proteins possessing Hpa II methylase activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6445–6449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






