Abstract
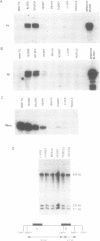
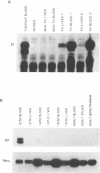
Transgenic mice were generated which carried the adult alpha and beta-globin genes and the major tadpole specific beta-globin gene of Xenopus laevis. The adult specific alpha and beta genes were found to express in erythroid tissues in adult mice, while the major tadpole specific beta gene (beta T1) was expressed in blood from 12.5 day embryos. The pattern of expression of the beta T1 gene during mouse development was consistent with its being regulated as an embryonic globin gene in the mouse. This observation suggests that some of the factors mediating globin switching have been conserved during the evolution of modern amphibia and mammals and raises interesting questions concerning the evolution of vertebrate globin gene switching.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banville D., Kay R. M., Harris R., Williams J. G. The nucleotide sequence of the mRNA encoding a tadpole beta-globin polypeptide of Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7924–7927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banville D., Williams J. G. Developmental changes in the pattern of larval beta-globin gene expression in Xenopus laevis. Identification of two early larval beta-globin mRNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90307-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banville D., Williams J. G. The pattern of expression of the Xenopus laevis tadpole alpha-globin genes and the amino acid sequence of the three major tadpole alpha-globin polypeptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5407–5421. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendig M. M., Williams J. G. Differential expression of the Xenopus laevis tadpole and adult beta-globin genes when injected into fertilized Xenopus laevis eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):567–570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M., Moore G. W., Matsuda G. Darwinian evolution in the genealogy of haemoglobin. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):603–608. doi: 10.1038/253603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorr T., Kleinschmidt T., Fricke H. Close tetrapod relationships of the coelacanth Latimeria indicated by haemoglobin sequences. Nature. 1991 May 30;351(6325):394–397. doi: 10.1038/351394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Kay R. M., Williams J. G. Analysis of Xenopus laevis globins during development and erythroid cell maturation and the construction of recombinant plasmids containing sequences derived from adult globin mRNA. Dev Biol. 1979 Oct;72(2):350–363. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosbach H. A., Wyler T., Weber R. The Xenopus laevis globin gene family: chromosomal arrangement and gene structure. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90495-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Wood D., Simons J. P., Kay R. M., Williams J. G. Linkage of adult alpha- and beta-globin genes in X. laevis and gene duplication by tetraploidization. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):555–564. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollias G., Wrighton N., Hurst J., Grosveld F. Regulated expression of human A gamma-, beta-, and hybrid gamma beta-globin genes in transgenic mice: manipulation of the developmental expression patterns. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90862-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhof W., Klinger-Mitropoulos S., Stalder J., Weber R., Knöchel W. The primary structure of the larval beta 1-globin gene of Xenopus laevis and its flanking regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7705–7719. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patient R. K., Elkington J. A., Kay R. M., Williams J. G. Internal organization of the major adult alpha- and beta-globin genes of X. laevis. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90494-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Lee E., Westphal H., Felsenfeld G. Site-independent expression of the chicken beta A-globin gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):749–752. doi: 10.1038/348749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt K. W., Maruyama T., Riggs A. Hemoglobins of the tadpole of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana. Amino acid sequence of the beta chain of a major component. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3294–3301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw E., Tsai S. F., Hogben P., Orkin S. H. Regulated expression of globin chains and the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 during erythropoiesis in the developing mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6596–6606. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. M., Chung S. W., White J. S., Reicheld S. M., Patterson M., Clarke B. J., Chui D. H. Adult hemoglobins are synthesized in murine fetal hepatic erythropoietic cells. Blood. 1983 Dec;62(6):1280–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]