Abstract
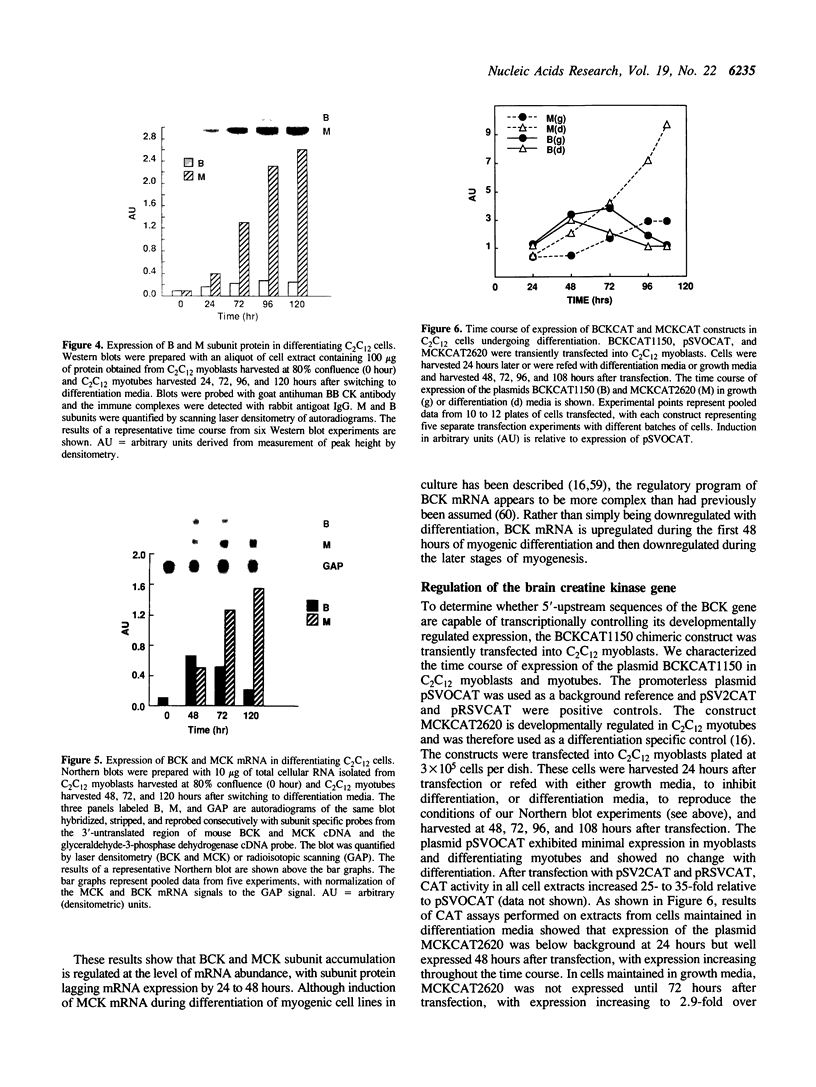
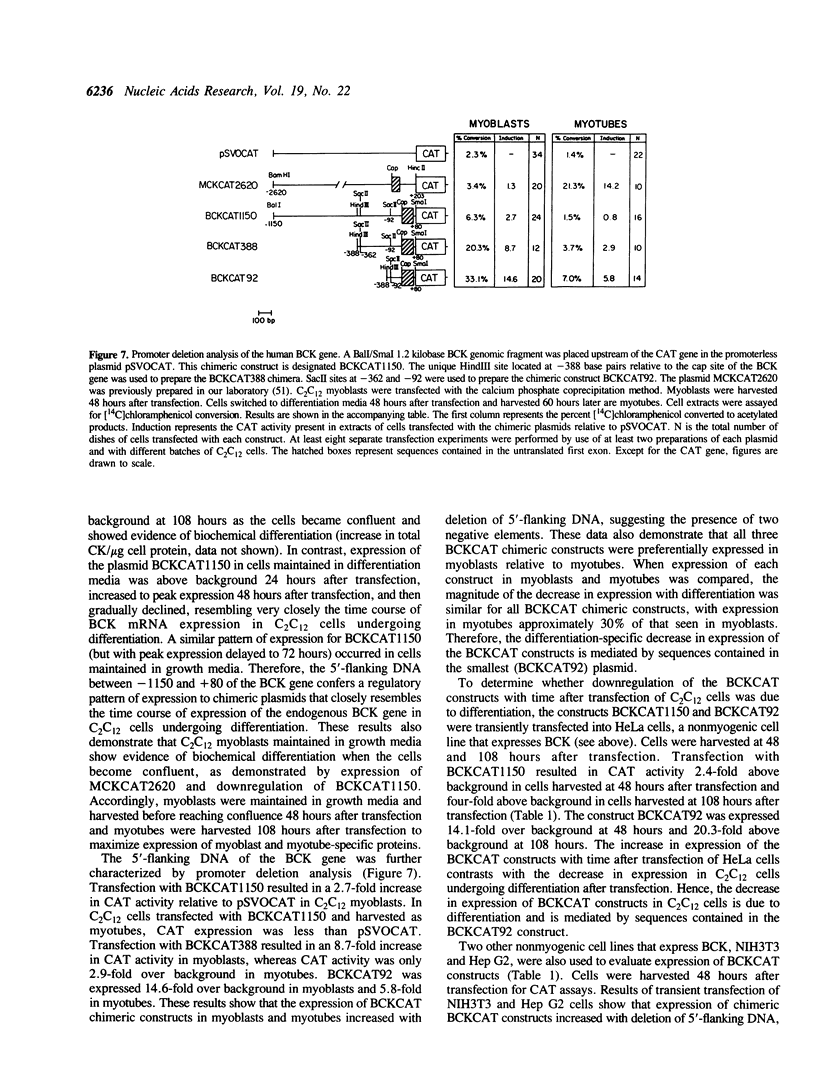
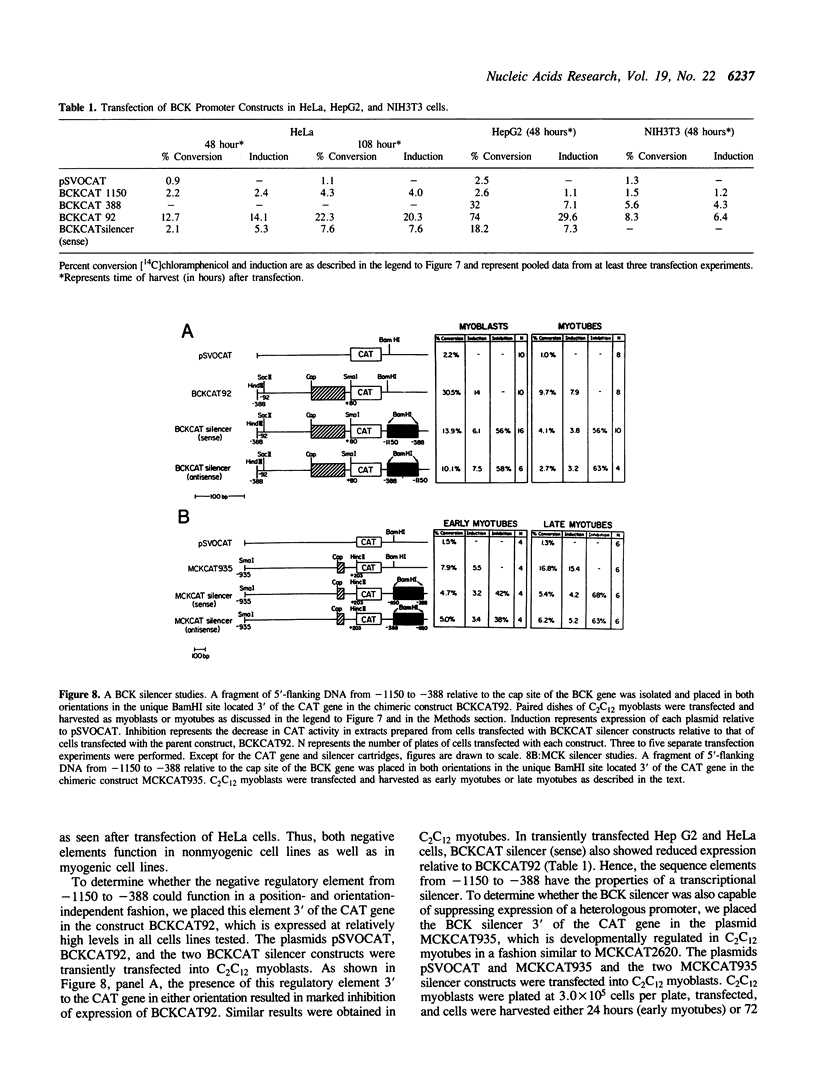
We characterized the developmental expression of the brain creatine kinase (BCK) gene in the C2C12 myogenic cell line with the use of isoenzyme, Western blot, and Northern blot analyses. The results show that both BCK subunit protein and mRNA are upregulated early in myogenesis, and then downregulated in fully differentiated myotubes. To characterize the transcriptional regulatory mechanisms, a chimeric construct containing 1.2 kilobase pairs of 5'-flanking DNA from the human BCK gene placed upstream of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in the promoterless plasmid pSVOCAT was transiently transfected into C2C12 cells. In myoblasts and differentiating myotubes, the time course of expression of the constructs paralleled that of endogenous BCK mRNA. Additional constructs prepared by deleting 5'-flanking DNA were also transfected into C2C12 cells. All constructs were preferentially expressed in myoblasts relative to myotubes with absolute levels of expression increasing with deletion of 5'-flanking DNA. In nonmyogenic cells expression of the plasmids also increased with deletion of 5'-flanking DNA. An element from -1150 to -388 was isolated and found to be capable of suppressing expression of the BCK promoter and of heterologous promoters independent of orientation and position and hence to function as a silencer. Thus, BCK expression is mediated by sequences contained in the 5'-flanking DNA, including negative elements active in both C2C12 cells and nonmyogenic cells and elements that mediate the developmental expression of the BCK gene in C2C12 myogenic cells.
Full text
PDF




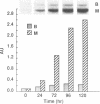
Images in this article
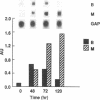
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson E. D. Isoenzyme transitions of creatine phosphokinase, aldolase and phosphoglycerate mutase in differentiating mouse cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1976 Apr;35(2):355–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnsdorf M. F., Bigger J. T., Jr The effect of procaine amide on components of excitability in long mammalian cardiac Purkinje fibers. Circ Res. 1976 Feb;38(2):115–122. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Steiner C., Köhne A. C., Renkawitz R. Modular structure of a chicken lysozyme silencer: involvement of an unusual thyroid hormone receptor binding site. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90532-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billadello J. J., Fontanet H. L., Strauss A. W., Abendschein D. R. Characterization of MB creatine kinase isoform conversion in vitro and in vivo in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1637–1643. doi: 10.1172/JCI114062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billadello J. J., Kelly D. P., Roman D. G., Strauss A. W. The complete nucleotide sequence of canine brain B creatine kinase mRNA: homology in the coding and 3' noncoding regions among species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 16;138(1):392–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Pavlath G. K., Hardeman E. C., Chiu C. P., Silberstein L., Webster S. G., Miller S. C., Webster C. Plasticity of the differentiated state. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):758–766. doi: 10.1126/science.2414846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boam D. S., Clark A. R., Docherty K. Positive and negative regulation of the human insulin gene by multiple trans-acting factors. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8285–8296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvagnet P. F., Strehler E. E., White G. E., Strehler-Page M. A., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Multiple positive and negative 5' regulatory elements control the cell-type-specific expression of the embryonic skeletal myosin heavy-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4377–4389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T. J., Olson E. N. Myogenin resides in the nucleus and acquires high affinity for a conserved enhancer element on heterodimerization. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):582–595. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher E. A., Maisonpierre P. C., Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr Expression of the troponin complex genes: transcriptional coactivation during myoblast differentiation and independent control in heart and skeletal muscles. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4134–4142. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskin J. N., Jaynes J. B., Chamberlain J. S., Hauschka S. D. The mouse muscle creatine kinase cDNA and deduced amino acid sequences: comparison to evolutionarily related enzymes. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(4):334–341. doi: 10.1007/BF02115689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper S. A., Tilghman S. M. Postnatal repression of the alpha-fetoprotein gene is enhancer independent. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):537–546. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao S. X., Gutman P. D., Dave H. P., Schechter A. N. Identification of a transcriptional silencer in the 5'-flanking region of the human epsilon-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5306–5309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caravatti M., Perriard J. C., Eppenberger H. M. Developmental regulation of creatine kinase isoenzymes in myogenic cell cultures from chicken. Biosynthesis of creatine kinase subunits M and B. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1388–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. N., Gazdar A. F., Bepler G., Guccion J. G., Marangos P. J., Moody T. W., Zweig M. H., Minna J. D. Establishment and identification of small cell lung cancer cell lines having classic and variant features. Cancer Res. 1985 Jun;45(6):2913–2923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ch'ng J. L., Mulligan R. C., Schimmel P., Holmes E. W. Antisense RNA complementary to 3' coding and noncoding sequences of creatine kinase is a potent inhibitor of translation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10006–10010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ch'ng J. L., Shoemaker D. L., Schimmel P., Holmes E. W. Reversal of creatine kinase translational repression by 3' untranslated sequences. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1003–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.2343304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., Jaynes J. B., Hauschka S. D. Regulation of creatine kinase induction in differentiating mouse myoblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):484–492. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. A., Ordahl C. P. A single troponin T gene regulated by different programs in cardiac and skeletal muscle development. Science. 1984 Nov 23;226(4677):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.6095446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserjesi P., Olson E. N. Myogenin induces the myocyte-specific enhancer binding factor MEF-2 independently of other muscle-specific gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daouk G. H., Kaddurah-Daouk R., Putney S., Kingston R., Schimmel P. Isolation of a functional human gene for brain creatine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2442–2446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePonti-Zilli L., Seiler-Tuyns A., Paterson B. M. A 40-base-pair sequence in the 3' end of the beta-actin gene regulates beta-actin mRNA transcription during myogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1389–1393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue M., Ernst H., Wentworth B., Nadal-Ginard B., Rosenthal N. A muscle-specific enhancer is located at the 3' end of the myosin light-chain 1/3 gene locus. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1779–1790. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dym H., Yaffe D. Expression of creatine kinase isoenzymes in myogenic cell lines. Dev Biol. 1979 Feb;68(2):592–599. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90229-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPPENBERGER H. M., EPPENBERGER M., RICHTERICH R., AEBI H. THE ONTOGENY OF CREATINE KINASE ISOZYMES. Dev Biol. 1964 Aug;10:1–16. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(64)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell F. X., Sax C. M., Zehner Z. E. A negative element involved in vimentin gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2349–2358. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Zweig M. H., Carney D. N., Van Steirteghen A. C., Baylin S. B., Minna J. D. Levels of creatine kinase and its BB isoenzyme in lung cancer specimens and cultures. Cancer Res. 1981 Jul;41(7):2773–2777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Burstein H., Maniatis T. The human beta-interferon gene enhancer is under negative control. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Boczko E. M., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. The mouse albumin enhancer contains a negative regulatory element that interacts with a novel DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3896–3905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson G. M., Mitchell M. T., Molloy G. R., Pearson M. L., Benfield P. A. Identification of a novel TA-rich DNA binding protein that recognizes a TATA sequence within the brain creatine kinase promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8925–8944. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlick R. A., Hobson G. M., Patterson J. H., Mitchell M. T., Benfield P. A. Brain and muscle creatine kinase genes contain common TA-rich recognition protein-binding regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4826–4836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imler J. L., Lemaire C., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. Negative regulation contributes to tissue specificity of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2558–2567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Promoter region of the human Harvey ras proto-oncogene: similarity to the EGF receptor proto-oncogene promoter. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1378–1381. doi: 10.1126/science.2999983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Xu Y. H., Stratton R. H., Roe B. A., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Characterization and sequence of the promoter region of the human epidermal growth factor receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4920–4924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., MacDonald J. J., Lees-Miller S., Tjian R. GC box binding induces phosphorylation of Sp1 by a DNA-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90296-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., Chamberlain J. S., Buskin J. N., Johnson J. E., Hauschka S. D. Transcriptional regulation of the muscle creatine kinase gene and regulated expression in transfected mouse myoblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2855–2864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., Johnson J. E., Buskin J. N., Gartside C. L., Hauschka S. D. The muscle creatine kinase gene is regulated by multiple upstream elements, including a muscle-specific enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):62–70. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Pastan I. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human DNA binding factor that represses transcription. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye F. J., McBride O. W., Battey J. F., Gazdar A. F., Sausville E. A. Human creatine kinase-B complementary DNA. Nucleotide sequence, gene expression in lung cancer, and chromosomal assignment to two distinct loci. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1412–1420. doi: 10.1172/JCI112969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss I., Bösze Z., Szabó P., Altanchimeg R., Barta E., Deák F. Identification of positive and negative regulatory regions controlling expression of the cartilage matrix protein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2432–2436. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovari L., Sumrada R., Kovari I., Cooper T. G. Multiple positive and negative cis-acting elements mediate induced arginase (CAR1) gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5087–5097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Hammer R. E., Tilghman S. M., Brinster R. L. Developmental regulation of alpha-fetoprotein genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1639–1648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski R. W., Ehrismann R., Schweinfest C. W., Dottin R. P. Accumulation of creatine kinase mRNA during myogenesis: molecular cloning of a B-creatine kinase cDNA. Dev Biol. 1985 Nov;112(1):84–88. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L., Holmgren-König M., Khoury G. Transcriptional "silencer" element in rat repetitive sequences associated with the rat insulin 1 gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3151–3155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lough J., Bischoff R. Differentiation of creatine phosphokinase during myogenesis: quantitative fractionation of isozymes. Dev Biol. 1977 Jun;57(2):330–344. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariman E. C., Broers C. A., Claesen C. A., Tesser G. I., Wieringa B. Structure and expression of the human creatine kinase B gene. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):126–137. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariman E. C., Schepens J. T., Wieringa B. Complete nucleotide sequence of the human creatine kinase B gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6385–6385. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathey-Prevot B., Andrews N. C., Murphy H. S., Kreissman S. G., Nathan D. G. Positive and negative elements regulate human interleukin 3 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Caskey C. T. Structure, expression, and mutation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., Williams T. J., Tjian R. Enhancer binding factors AP-4 and AP-1 act in concert to activate SV40 late transcription in vitro. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):557–561. doi: 10.1038/332557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. T., Benfield P. A. Two different RNA polymerase II initiation complexes can assemble on the rat brain creatine kinase promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8259–8267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muglia L., Rothman-Denes L. B. Cell type-specific negative regulatory element in the control region of the rat alpha-fetoprotein gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7653–7657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat G. E., Kedes L. Multiple 5'-flanking regions of the human alpha-skeletal actin gene synergistically modulate muscle-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4089–4099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohara R., Sobel B. E., Jaffe A. S., Abendschein D. R. Quantitative analysis for isoforms of creatine kinase MM in plasma by chromatofocusing, with on-line monitoring of enzyme activity. Clin Chem. 1988 Feb;34(2):235–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan W. T., Liu Q. R., Bancroft C. Identification of a growth hormone gene promoter repressor element and its cognate double- and single-stranded DNA-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):7022–7028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papenbrock T., Wille W. The 3' non-coding region of the mouse brain B creatine kinase mRNA: a sequence with exceptional homology among species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8690–8690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Bishop J. O. Changes in the mRNA population of chick myoblasts during myogenesis in vitro. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):751–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perriard J. C. Developmental regulation of creatine kinase isoenzymes in myogenic cell cultures from chicken. Levels of mRNA for creatine kinase subunits M and B. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7036–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Functional domains and upstream activation properties of cloned human TATA binding protein. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1625–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.2363050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers E. F., Yang J. Q., Marcu K. B. A negative transcriptional control element located upstream of the murine c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):899–904. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R. Transcriptional repression in eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):192–197. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Basu S. K., Osborne T. F., Chin D. J., Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Luskey K. L. HMG CoA reductase: a negatively regulated gene with unusual promoter and 5' untranslated regions. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg U. B., Eppenberger H. M., Perriard J. C. Occurrence of heterogenous forms of the subunits of creatine kinase in various muscle and nonmuscle tissues and their behaviour during myogenesis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):87–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. Identification of regulatory elements of cloned genes with functional assays. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:704–720. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi A. M., Eppenberger H. M., Volpe P., Cotrufo R., Wallimann T. Muscle-type MM creatine kinase is specifically bound to sarcoplasmic reticulum and can support Ca2+ uptake and regulate local ATP/ADP ratios. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5258–5266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savagner P., Miyashita T., Yamada Y. Two silencers regulate the tissue-specific expression of the collagen II gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6669–6674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Eldridge J. D., Paterson B. M. Expression and regulation of chicken actin genes introduced into mouse myogenic and nonmyogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2980–2984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainberg A., Yagil G., Yaffe D. Alterations of enzymatic activities during muscle differentiation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1971 May;25(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman L. M., Dermer G. B., Zweig M. H., Van Steirteghem A. C., Tökés Z. A. Creatine kinase BB: a new tumor-associated marker. Clin Chem. 1979 Aug;25(8):1432–1435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Das G., Herr W. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1582–1599. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sömjen D., Kaye A. M., Binderman I. Stimulation of creatine kinase BB activity by parathyroid hormone and by prostaglandin E2 in cultured bone cells. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 1;225(3):591–596. doi: 10.1042/bj2250591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask R. V., Billadello J. J. Tissue-specific distribution and developmental regulation of M and B creatine kinase mRNAs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 21;1049(2):182–188. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask R. V., Strauss A. W., Billadello J. J. Developmental regulation and tissue-specific expression of the human muscle creatine kinase gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17142–17149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. C., Brand S. J. Islet cell-specific regulatory domain in the gastrin promoter contains adjacent positive and negative DNA elements. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8908–8914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutzey K. E., Kline R. L., Konieczny S. F. An internal regulatory element controls troponin I gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1397–1405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. X., Kumar V., Rivera R. T., Chisholm J., Biswas D. K. cis-acting negative regulatory element of prolactin gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4785–4788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]