Abstract
Although weight loss ameliorates many of the metabolic abnormalities associated with obesity, there has been reluctance to prescribe weight loss in obese, older individuals because of the fear that it will cause debilitating loss of muscle mass and impair physical function. To gain insight into the mechanisms responsible for the weight loss-induced changes in muscle mass, we measured the rate of muscle protein synthesis (by using stable isotope labeled tracer methodology) during basal, post-absorptive conditions and during mixed meal ingestion in eight obese, older adults: i) before weight loss therapy, ii) ∼3 months after starting the weight loss intervention (i.e., during the active weight loss phase), when subjects had lost ∼7% of their initial body weight and iii) after they had lost ∼10% of their body weight and maintained this new body weight for ∼6 months (∼12 months after starting the weight loss intervention). The basal muscle protein fractional synthesis rate was not affected by weight loss. Mixed meal ingestion stimulated the rate of muscle protein synthesis, and the anabolic response (i.e., increase in the protein synthesis rate above basal values) was greater (P<0.05) during negative energy balance and active weight loss at 3 months (0.033 ± 0.012 %·h-1, mean ± SEM) than during weight maintenance before and at 12 months of weight loss therapy (0.003 ± 0.003 and 0.008 ± 0.012 %·h-1, respectively). We conclude that during dietary calorie restriction and weight loss in older adults, the rate of muscle protein synthesis is not impaired. Thus, the loss of muscle mass must be mediated predominately by adverse effects of dietary calorie restriction on muscle proteolysis.
Keywords: sarcopenia, obesity, calorie restriction
Introduction
The increasing prevalence of obesity in older adults is a major public health problem (1). Not only does obesity cause serious metabolic abnormalities but it also worsens the age-related decline in physical function that leads to frailty (2). Nevertheless, there has been reluctance to prescribe weight loss in obese older individuals because of the fear that it will cause further loss of muscle mass (3). To help design treatment strategies to counteract the weight loss-induced changes in muscle mass, it is necessary to understand the mechanisms responsible for the loss of muscle mass that accompanies the loss of fat mass during dietary energy restriction.
The results from studies in obese rats indicate that both muscle protein synthesis and breakdown are depressed during dietary calorie restriction and muscle loss occurs because protein synthesis is depressed to a greater extent than protein breakdown (4-6). As far as we know, only one study has examined the effect of diet-induced weight loss on muscle protein synthesis in obese human subjects. In contrast to results from the rodent studies, it was reported that 11-weeks of dietary energy restriction increased the rate of muscle protein synthesis (7). Thus, increased muscle protein breakdown must have caused the loss of muscle mass. It is possible, but not known, that the difference in results is due to the fact that, unlike the rodents, the obese human subjects were studied during a short weight maintenance period at their reduced body mass rather than during calorie restriction (negative energy balance).
The purpose of our study therefore was to examine both the effect of negative energy balance during dietary energy restriction and consequent weight loss as well as the effect of energy balance at the reduced body weight on the rate of muscle protein synthesis in obese older adults. To this end, subjects were studied: i) before undergoing weight loss therapy, ii) after ∼3 months of dietary energy restriction, after subjects have lost ∼7% of their body weight and were continuing to lose weight, and iii) after subjects have lost ∼10% of their body weight (which required ∼ 3 additional months of calorie restriction) and have maintained their new weight for ∼6 months (i.e., ∼12 months after the initiation of weight loss therapy). We measured the rate of muscle protein synthesis both during basal, post-absorptive conditions and during mixed meal intake.
Methods and Procedures
Subjects
We studied eight obese men (n = 3) and women (n = 5) between the ages of 65 and 80 y (mean age: 69 ± 2 y, mean ± SEM). All subjects were sedentary (i.e., did not participate in regular exercise for more than 30 min, more than twice a week) and weight-stable (i.e., no more than ± 2 kg change in body weight during the past year). None of the subjects reported excessive alcohol intake or smoked. All participants were considered to be in good health after completion of a comprehensive medical evaluation which included a medical history and physical examination, standard blood and urine tests, and a graded treadmill exercise stress test. None had severe cardiopulmonary disease, neuromuscular impairments, sensory or cognitive deficits, cancer diagnosis within the last 5 years, or had used corticosteroids, or androgen- or estrogen-containing or mimicking compounds within the last year. Subjects who were treated for hypertension and/or hypercholesterolemia had been on a stable drug regimen for at least six months before beginning the study. Written informed consent was obtained from each subject before participation in the study, which was approved by the Human Studies Committee at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, MO.
Experimental protocol
Each subject was scheduled to undergo body composition analyses and muscle protein synthesis rate measurements on three occasions: i) at the beginning of the trial (∼1-3 weeks before starting the weight loss therapy), ii) ∼3 months after starting the weight loss therapy (i.e., during the active weight loss phase), and iii) after they have lost ∼10% of their initial body weight and maintained their new body weight for ∼6 months (∼12 months after starting the weight loss therapy). Two of the eight subjects (1 man and 1 woman) were lost to follow-up for the third protein metabolism study (i.e., weight maintenance phase at 12-months after initiation of the weight loss therapy). Since the results at the 3 month time point were not different irrespective of whether we used n = 6 or n = 8, we decided to present only the data obtained in 6 subjects for all three time points (before, during and after weight loss) in the paper and the data obtained in all 8 subjects before and after 3 months of weight loss in an online supplement.
Body composition analysis
Total body mass, total and trunk fat masses (FM), total fat free mass (FFM) and appendicular lean mass were determined by using DXA (Hologic Delphi 4500/w, Waltham, MA) as previously described (8, 9).
Muscle protein synthesis rate measurements
Subjects were admitted to the Clinical Research Unit on the evening before each protein metabolism study after being instructed to refrain from vigorous exercise or other strenuous activities for at least three days. At 2000 h, they consumed a standard meal providing 12 kcal per kg body mass (55% of the total meal energy as carbohydrates, 30% as fat, and 15% as protein) and then rested in bed and fasted (except for water) until completion of the protein metabolism study the next day. At ∼0600 h on the following morning, a cannula was inserted into an antecubital vein for the infusion of a stable isotope labeled leucine tracer (purchased from Cambridge Isotope Laboratories Inc, Andover, MA); another cannula was inserted into a vein of the contralateral hand for blood sampling. At ∼0800 h, a muscle tissue sample from the quadriceps femoris was obtained to determine the background leucine tracer-to-tracee ratio (TTR) in muscle tissue fluid and muscle protein. Muscle tissue was obtained under local anesthesia (lidocaine, 2%) by using a Tilley-Henkel forceps. Immediately afterward, a primed, constant infusion of [5,5,5-2H3] L-leucine (priming dose: 4.8 μmol·kg body wt-1, infusion rate: 0.08 μmol·kg body wt-1·min-1) was started and maintained until completion of the study ∼6 h later. At 210 min after the start of the leucine tracer infusion, a second muscle biopsy was obtained to determine the basal rate of muscle protein synthesis (as incorporation of [5,5,5-2H3]leucine into muscle protein) as previously described (10, 11). Immediately after the second biopsy, a liquid meal (Ensure®, Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL, USA, containing 15% of energy as protein, 55% as carbohydrate and 30% as fat) was given intermittently in small boluses every 10 minutes for 150 min so that every subject received a priming dose of 23 mg protein·kg FFM-1 and 70 mg protein·kg FFM-1·h-1 during the 2.5 h feeding period (∼10-15 g of protein in total). At the onset of feeding, the infusion rate of labeled leucine was increased to 0.12 μmol·kg body wt-1·min-1 to adjust for the increased plasma leucine availability. A third muscle biopsy was obtained at 360 min (i.e., 150 min after the first meal aliquot) to determine the muscle protein synthesis response to feeding. The second and third biopsies were obtained from the leg contralateral to that biopsied initially - through the same incision, but with the forceps directed in proximal and distal directions, so that the two biopsies were collected ∼5-10 cm apart. Blood samples (4 ml each) were obtained at baseline, before beginning the isotope infusion, and then every 30 min during the entire study period to determine leucine, glucose and insulin concentrations and the α–ketoisocaproic acid (KIC) enrichment in plasma. One milliliter of blood was collected in pre-chilled tubes containing heparin, plasma was separated immediately by centrifugation and plasma glucose concentration was measured; the remaining blood was collected in pre-chilled tubes containing EDTA, plasma was separated by centrifugation within 30 min of collection and then stored at -80°C until final analyses were performed. Muscle tissue was rinsed in ice-cold saline immediately after collection, cleared off all visible fat and connective tissue, and then frozen in liquid nitrogen and later transferred to a -80°C freezer for storage until final analyses were performed.
Sample processing and analyses
Plasma glucose concentration was determined on an automated glucose analyzer (Yellow Spring Instruments, Yellow Springs, OH). Plasma insulin concentration was determined by radioimmunoassay (Linco Research, St. Louis, MO). Plasma leucine concentration, plasma α-KIC tracer-to-tracee ratio (TTR), and the leucine TTR in muscle proteins and muscle tissue fluid were determined by using gas-chromatography/mass-spectrometry (GC-MS; MSD 5973 System, Hewlett-Packard) and standards of known isotope enrichment (10-13). Briefly, a known amount of norleucine was added to the plasma, proteins were precipitated, and the supernatant, containing free amino and keto acids, was collected to prepare the t-butyldimethylsilyl (t-BDMS) and O-t-butyldimethylsilyl quinoxalinols derivatives of leucine and α-KIC, respectively. Muscle samples (∼20 mg) were homogenized in 1 ml trichloroacetic acid solution (3% w/v), proteins were precipitated by centrifugation, and the supernatant, containing free amino acids, was collected. The pellet containing muscle proteins was washed and then hydrolyzed in 6 N HCl at 110 °C for 24 h. Amino acids in the protein hydrolysate and supernatant samples were purified on cation-exchange columns (Dowex 50W-X8-200, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Richmond, CA) to prepare the t-BDMS derivative of leucine.
Calculations
Leucine rate of appearance (Ra) in plasma was calculated by dividing the rate of [5,5,5-2H3]leucine infusion by the average plasma α-KIC TTR during basal, postabsorptive conditions (60 – 240 min) and feeding (270 – 360 min). Leucine Ra during basal, postabsorptive conditions represents the rate of leucine release into plasma from proteolysis; during feeding, leucine Ra represents the sum of the rate of leucine release into plasma from proteolysis plus the rate of transfer of absorbed leucine from the meal into the systemic circulation. The mixed muscle protein fractional synthesis rate (FSR) during basal conditions and mixed meal consumption was calculated based on the incorporation rate of [5,5,5-2H3]leucine into muscle proteins by using a standard precursor-product model as follows: FSR = ΔEp/Eic × 1/t × 100; where ΔEp is the change in enrichment (TTR) of protein-bound leucine in two subsequent biopsies (i.e., the first and second and the second and third, respectively), Eic is the enrichment of the leucine precursor pool (i.e., leucine in muscle tissue fluid of the second [end of basal period] and third [end of feeding] biopsies, respectively), and t is the time between biopsies (14). We also calculated muscle protein FSR values by using the plasma α-KIC TTR as the enrichment of the precursor pool and this did not affect the results from our study. Therefore, we chose to not present these values. The homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) score was calculated as 1/22.5 × [plasma glucose concentration (in mg/dl) × plasma insulin concentration (in μU/mL) during basal, post-absorptive conditions] (15).
Supervised weight loss program
After completion of the initial body composition and muscle protein synthesis rate assessments, subjects underwent a supervised weight loss program and received instructions for an energy-reduced diet and behavior therapy. The goal was to achieve 10% weight loss at 6 months and to maintain the new body weight for an additional 6 months. To achieve this goal, subjects were prescribed a balanced diet (according to the recommendations by the American Heart Association) to provide an energy deficit of 500-750 kcal/day and 1.0 g of protein per kg body weight per day (2). They met weekly as a group with a study dietician to monitor body weight, discuss standard behavioral strategies (problem-solving skills, identification of high-risk situations, and relapse prevention training) aimed at modifying eating habits, to review food diaries, and to adjust their caloric intake to achieve their weight loss target of ∼10% body mass loss within 6 months. After subjects achieved the targeted 10% weight loss, they were prescribed a balanced weight maintenance diet, containing 1.0 g protein per kg body weight per day and continued to meet with the dietician every other week to monitor body weight and ensure weight maintenance. Body weight changes in response to the prescribed energy intakes and targeted weight loss therapy are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
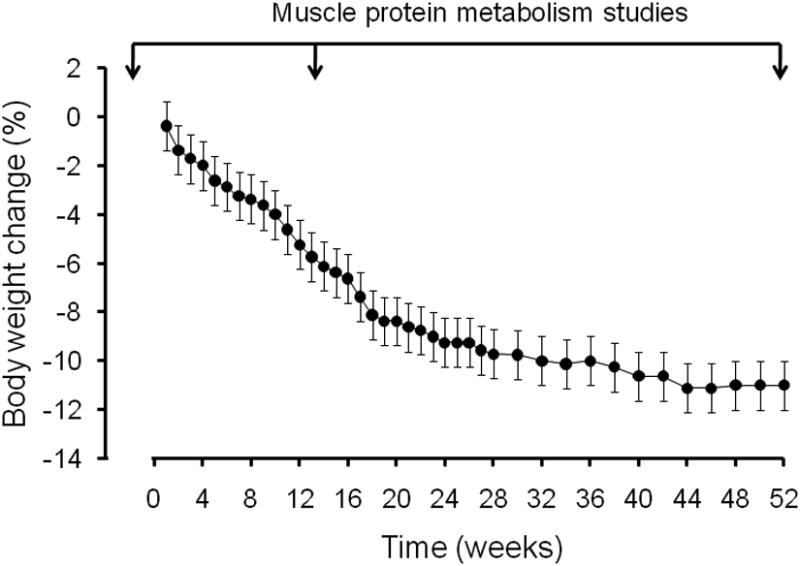
Body weight changes in response to the prescribed energy intakes and targeted weight loss therapy (n = 8 during the first 6 months; n = 6 during the final 6 months). Values are means ± SEM. Arrows on top indicate the time of the muscle protein metabolism studies (before weight loss therapy, after ∼3 months of weight loss therapy during the active weight loss phase, and during weight maintenance at the reduced body weight at 12 months).
Statistical analysis
All data sets were tested for normality and the changes over time in body composition, whole-body leucine Ra, and HOMA-IR were evaluated by using one-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Tukey's post-hoc procedure. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc procedure were used to evaluate changes over time in plasma glucose, insulin, and leucine concentrations, and the mixed muscle protein FSR during basal, post-absorptive and fed conditions. All values are reported as mean ± SEM.
Results
Body weight, body composition and HOMA-IR (Figure 1, Table 1 and Supplemental Table 1)
Table 1.
Subject characteristics before and after weight loss.
| Before weight loss therapy | During and after weight loss therapy | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| 3 months (active weight loss) | 12 months (weight maintenance) | ||
| N (male, female) | 6 (2, 4) | 6 (2, 4) | 6 (2, 4) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 38.3 ± 1.6 | 35.5 ± 1.3* | 34.8 ± 1.6* |
| Body mass (kg) | 107.6 ± 6.4 | 99.9 ± 6.9* | 97.7 ± 7.7* |
| Fat-free mass (kg) | 59.8 ± 5.1 | 57.0 ± 5.2* | 57.6 ± 5.4* |
| Appendicular lean mass (kg) | 26.1 ± 2.7 | 24.1 ± 2.4* | 24.2 ± 2.6* |
| Fat mass (kg) | 47.9 ± 2.4 | 42.9 ± 2.9* | 40.2 ± 3.2* |
| Trunk fat mass (kg) | 24.5 ± 2.1 | 21.1 ± 2.1* | 20.2 ± 2.3* |
| HOMA-IR score | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.5* | 1.3 ± 0.4* |
Values are means ± SEM.
ANOVA revealed a significant main effect of time and Tukey's post-hoc analysis indicated that values marked with an asterisk are significantly different from before weight loss (P < 0.05). HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance.
Subjects progressively reduced their body weight during the first 6 months of weight loss therapy and then maintained their newly reduced body weight for an additional 6 months. After 3 months, they lost an average of ∼7% of their initial body weight; by 6 months, they had further reduced their body weight to ∼90 % of their initial weight. The loss of total body mass included significant decreases in total body and trunk FM, FFM, and appendicular lean mass. The HOMA-IR score decreased by ∼24% after 3 months of weight loss therapy and then remained unchanged until the end of the study at 12 months.
Plasma glucose, insulin and leucine concentrations during basal, post-absorptive conditions and feeding
Plasma glucose concentration was not different before and after weight loss, neither during basal, post-absorptive conditions nor during feeding, which increased plasma glucose concentration by ∼1.5 mM above basal values before, during, and after weight loss therapy (Table 2 and Supplemental Table 2). For plasma insulin concentration (Table 2 and Supplemental Table 2), ANOVA revealed significant main effects of time and feeding (all P < 0.05); i.e., plasma insulin concentrations were greater in the fed state and less during/after than before weight loss. Post-hoc analysis indicated that both the plasma insulin concentrations at 3 months and 12 months were ∼20-30% lower (P < 0.05) compared with the corresponding baseline (before weight loss) values. Plasma leucine concentration was not different before and after weight loss, neither during basal, post-absorptive conditions nor during feeding, which increased plasma leucine concentration by ∼20 μM above basal values (Table 2 and Supplemental Table 2).
Table 2.
Plasma leucine, glucose and insulin concentrations and plasma α-ketoisocaproate (KIC) tracer-to-tracee ratios (TTR) during basal, postabsorptive conditions and during mixed meal consumption before, during and after weight loss (n = 6).
| Time (min) | Concentration | Enrichment (TTR) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leucine (μM) | Glucose (mM) | Insulin (μU/L) | Plasma α-KIC | |||||||||
| 0-MO | 3-MO | 12-MO | 0-MO | 3-MO | 12-MO | 0-MO | 3-MO | 12-MO | 0-MO | 3-MO | 12-MO | |
| Basal state | ||||||||||||
| 0 | 102 ± 9 | 105 ± 13 | 138 ± 17 | 5.5 ± 0.2 | 5.3 ± 0.3 | 5.1 ± 0.1 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| 30 | 103 ± 10 | 111 ± 13 | 133 ± 18 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.0730 ± 0.0040 | 0.0789 ± 0.0075 | 0.0542 ± 0.0053 |
| 60 | 103 ± 10 | 110 ± 15 | 145 ± 19 | 5.5 ± 0.2 | 5.2 ± 0.2 | 5.1 ± 0.1 | --- | --- | --- | 0.0704 ± 0.0052 | 0.0608 ± 0.0129 | 0.0507 ± 0.0029 |
| 90 | 105 ± 10 | 111 ± 14 | 141 ± 17 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.0688 ± 0.0047 | 0.0656 ± 0.0090 | 0.0541 ± 0.0013 |
| 120 | 103 ± 10 | 112 ± 14 | 138 ± 18 | 5.3 ± 0.2 | 5.1 ± 0.2 | 5.0 ± 0.1 | --- | --- | --- | 0.0670 ± 0.0044 | 0.0735 ± 0.0070 | 0.0539 ± 0.0008 |
| 150 | 109 ± 10 | 110 ± 13 | 143 ± 15 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.0703 ± 0.0065 | 0.0738 ± 0.0062 | 0.0569 ± 0.0017 |
| 180 | 106 ± 11 | 113 ± 14 | 143 ± 17 | 5.1 ± 0.2 | 5.1 ± 0.2 | 4.9 ± 0.1 | 8 ± 2 | 6 ± 2 | 5 ± 1 | 0.0691 ± 0.0050 | 0.0796 ± 0.0106 | 0.0566 ± 0.0022 |
| 190 | 107 ± 11 | 114 ± 14 | 145 ± 18 | 5.0 ± 0.2 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 4.8 ± 0.1 | --- | --- | --- | 0.0710 ± 0.0055 | 0.0777 ± 0.0095 | 0.0584 ± 0.0016 |
| 200 | 109 ± 11 | 117 ± 15 | 141 ± 18 | 4.9 ± 0.1 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 4.8 ± 0.1 | --- | --- | --- | 0.0750 ± 0.0084 | 0.0772 ± 0.0087 | 0.0561 ± 0.0019 |
| 210 | 111 ± 12 | 117 ± 15 | 145 ± 16 | 5.0 ± 0.2 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 4.7 ± 0.1 | 8 ± 2 | 5 ± 2 | 6 ± 2 | 0.0737 ± 0.0067 | 0.0727 ± 0.0060 | 0.0582 ± 0.0018 |
| Mean | 106 ± 10 | 112 ± 13 | 141 ± 17 | 5.2 ± 0.2 | 5.1 ± 0.2 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 8 ± 2 | 6 ± 2b | 6 ± 2b | 0.0709 ± 0.0054 | 0.0733 ± 0.0079 | 0.0554 ± 0.0010b |
| During mixed meal feeding | ||||||||||||
| 240 | 131 ± 7 | 136 ± 12 | 172 ± 14 | 6.1 ± 0.3 | 6.2 ± 0.3 | 5.9 ± 0.3 | --- | --- | --- | 0.0842 ± 0.0054 | 0.0886 ± 0.0119 | 0.0653 ± 0.0020 |
| 270 | 128 ± 8 | 132 ± 12 | 172 ± 11 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 6.6 ± 0.2 | 6.6 ± 0.2 | 31 ± 6 | 31 ± 6 | 23 ± 5 | 0.0902 ± 0.0071 | 0.0893 ± 0.0083 | 0.0726 ± 0.0043 |
| 300 | 120 ± 9 | 130 ± 14 | 157 ± 13 | 6.7 ± 0.2 | 6.8 ± 0.2 | 6.4 ± 0.2 | --- | --- | --- | 0.0987 ± 0.0107 | 0.0943 ± 0.0087 | 0.0745 ± 0.0032 |
| 330 | 122 ± 13 | 128 ± 14 | 150 ± 12 | 6.8 ± 0.3 | 6.6 ± 0.1 | 6.6 ± 0.2 | 35 ± 5 | 27 ± 5 | 23 ± 5 | 0.0971 ± 0.0103 | 0.0954 ± 0.0086 | 0.0730 ± 0.0031 |
| 340 | 123 ± 12 | 127 ± 12 | 147 ± 11 | 6.9 ± 0.2 | 6.7 ± 0.1 | 6.6 ± 0.2 | --- | --- | --- | 0.0942 ± 0.0077 | 0.0945 ± 0.0075 | 0.0753 ± 0.0037 |
| 350 | 123 ± 12 | 119 ± 13 | 152 ± 13 | 7.0 ± 0.1 | 6.9 ± 0.2 | 6.4 ± 0.1 | --- | --- | --- | 0.0977 ± 0.0105 | 0.0936 ± 0.0083 | 0.0765 ± 0.0044 |
| 360 | 119 ± 11 | 121 ± 13 | 152 ± 16 | 6.8 ± 0.1 | 6.9 ± 0.2 | 6.7 ± 0.1 | --- | --- | --- | 0.0968 ± 0.0091 | 0.0939 ± 0.0087 | 0.0752 ± 0.0047 |
| Mean | 124 ± 10a | 129 ± 9a | 157 ± 12a | 6.7 ± 0.2a | 6.7 ± 0.3a | 6.5 ± 0.1a | 33 ± 5a | 29 ± 5a,b | 23 ± 5a,b | 0.0942 ± 0.0084a | 0.0878 ± 0.0088a | 0.0732 ± 0.0030a,b |
Values are mean ± SEM.
ANOVA revealed a significant main effect of feeding (P < 0.01).
ANOVA revealed a significant main effect of time and Tukey's post hoc analysis indicated that values marked with a b were significantly different from before weight loss (P < 0.01).
Plasma α-KIC and muscle free leucine enrichments, whole-body leucine Ra and muscle protein synthesis rate during basal, post-absorptive conditions and feeding
Plasma α-KIC enrichments were steady between 60 min and 210 min during the basal state and changed minimally (<15 %) between 240 min and 360 min during feeding (Table 2 and Supplemental Table 2). Average α-KIC enrichments were not different before and after 3 months of weight loss therapy but were ∼20% lower (P < 0.05) at 12 months (i.e., during weight maintenance at the reduced body weight). Accordingly, the muscle free leucine labeling was not different before and after 3 months of weight loss therapy but was ∼20% lower (P < 0.05) at 12 months (muscle free leucine TTR in the 2nd and 3rd biopsies at 0, 3, and 12 months: 0.0511 ± 0.0061 and 0.0741 ± 0.0033; 0.0485 ± 0.0057 and 0.0716 ± 0.0060; 0.0407 ± 0.0044 and 0.0639 ± 0.0028).
Total whole-body leucine Ra (expressed in μmol·min-1) was ∼8% lower after 3 months of weight loss therapy (active weight loss phase), both during basal, postabsorptive conditions and mixed meal feeding; this difference was significant with n = 8 ( Supplemental Table 3) whereas it did not reach statistical significance with n = 6 (Table 3). Whole-body leucine Ra relative to FFM or body mass was not different, neither during basal, postabsorptive conditions nor during mixed meal feeding (Table 3 and Supplemental Table 3). At 12 months, during maintenance of the new reduced body weight, whole body leucine Ra was ∼15% greater than before weight loss, both during basal, postabsorptive conditions and during mixed meal consumption, irrespective of whether it was expressed as total Ra or relative to FFM or body mass (Table 3).
Table 3.
Whole-body leucine rate of appearance (Ra) during basal, post-absorptive conditions and during mixed meal consumption before, during and after weight loss therapy (n = 6).
| Before weight loss therapy | During and after weight loss therapy | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| 3 months (active weight loss) | 12 months (weight maintenance) | ||
| Basal state | |||
| μmol·min-1 | 124 ± 14 | 110 ± 15 | 137 ± 15 a |
| μmol·kg FFM-1·min-1 | 2.07 ± 0.12 | 1.92 ± 0.11 | 2.38 ± 0.06 a |
| μmol·kg BM-1·min-1 | 1.15 ± 0.09 | 1.10 ± 0.10 | 1.39 ± 0.04 a,b |
| Mixed meal feeding | |||
| μmol·min-1 | 152 ± 16 | 143 ± 15 | 170 ± 20 a,b |
| μmol·kg FFM-1·min-1 | 2.57 ± 0.17 | 2.52 ± 0.11 | 2.39 ± 0.08 a,b |
| μmol·kg BM-1·min-1 | 1.42 ± 0.11 | 1.43 ± 0.09 | 1.72 ± 0.08 a,b |
Values are mean ± SEM. ANOVA revealed a significant main effect of time. Tukey's post-hoc analysis indicated the following differences:
Value significantly different from corresponding value at 3 months (P < 0.05).
Value significantly different from corresponding value before weight loss therapy (P < 0.05). BM: body mass; FFM: fat-free mass.
The basal muscle protein FSR was not affected by weight loss (Figure 2 and Supplemental Figure 1). Mixed meal ingestion stimulated the rate of muscle protein synthesis (main effect of feeding, P < 0.05) and the anabolic response (i.e., increase in the protein synthesis rate above basal values) was greater (P<0.05) during negative energy balance and active weight loss at 3 months (0.033 ± 0.012 %·h-1) than before weight loss and during weight maintenance of the reduced body weight at 12 months (0.003 ± 0.003 and 0.008 ± 0.012 %·h-1, respectively).
Figure 2.
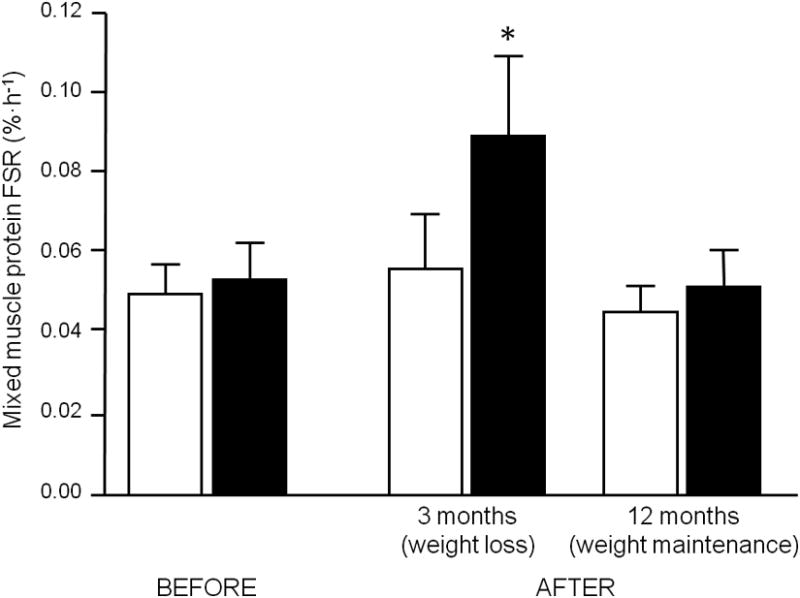
Skeletal muscle protein fractional synthesis rate (FSR) during basal, post-absorptive conditions (white bars) and small bolus feeding of a liquid mixed meal (black bars) in obese older adults before, during and after weight loss (n = 6). Values are means ± SEM. * ANOVA revealed a significant time by feeding interaction and Tukey's post-hoc analysis indicated that this was due to the 3 month fed FSR value, which was significantly different from all other values (P < 0.05).
Discussion
Dietary calorie restriction to induce weight loss is the cornerstone of treatment to improve health in obese persons because it increases insulin sensitivity and reduces cardiovascular risk (16, 17). One of the “side-effects” of calorie restriction, however, is loss of muscle mass. The calorie restriction-induced loss of muscle mass has minimal clinical implications in young obese individuals but it is feared that it may impair physical function and increase the risk of becoming frail in older obese adults because it accelerates the normal age-associated loss of muscle mass and function (3, 18). A better understanding of the mechanisms responsible for the loss of muscle mass during calorie restriction is therefore necessary to devise adequate treatment strategies to overcome this problem. Our results suggest that the root cause for loss of muscle mass during dietary calorie restriction and weight loss lies in accelerated muscle protein breakdown, which results in net negative muscle protein balance, because muscle protein synthesis is either not affected or even increased (i.e., in the fed state during the acute weight loss phase).
These findings are in general agreement with the results obtained in postmenopausal women who underwent weight loss therapy (7), which as far as we can tell is the only other study to date on human subjects to have examined this. However, they contrast those obtained from studies on obese rats in which muscle protein synthesis is depressed during dietary calorie restriction (4-6). The reason(s) for the discrepancy is not clear but may be related to the fact that calorie restriction in the rats was much more severe (i.e., starvation) than in the present study and the study in postmenopausal women by Campbell et al. (7). Nevertheless, it appears that ultimately the loss of muscle mass both in human subjects and rodents is due to inappropriately high rates of proteolysis (relative to the rate of protein synthesis).
Another key finding in our study was that during a state of negative energy balance (acute weight loss phase) but not during energy balance after significant (∼10%) weight loss, the anabolic response to feeding is increased. This suggests that muscle protein synthesis, in particular the response to anabolic stimuli such as feeding, may be sensitive to changes in the cells energy status and changes in energy balance can potentially overcome the age-associated resistance to feeding (11, 19-21). We deliberately provided only a small meal and an amount of protein (∼10-15 g) that would sub-maximally stimulate the rate of muscle protein synthesis (19, 22, 23) to avoid a potential “ceiling effect”. Thus, the anabolic effect of the meal at the beginning of the study was very small and not statistically significant, consistent with the small meal/amount of protein (∼10-15 g) provided and anabolic resistance of muscle in older adults (11, 19-23). It is possible but unlikely that the improved anabolic response to feeding in our study was related to the dietary calorie restriction-induced improvement in insulin sensitivity because plasma glucose and insulin concentrations during basal, postabsorptive conditions and feeding and the HOMA-IR score were not different at the 3- and 12-month time points whereas the anabolic response to feeding was improved only at the 3-month time point, when subjects were studied while actively losing weight. Although, HOMA-IR values provide only a crude measure of whole-body insulin sensitivity and it is possible that we may have missed subtle differences in muscle insulin sensitivity.
There are several limitations that need to be considered when interpreting our results. First, we did not include a control group and as such a potential placebo effect or changes in muscle protein metabolism that may occur over time, independent of weight loss, are not accounted for. However, we consider this an unlikely scenario because we (11) and others (24) have shown that muscle protein metabolism in a placebo/no intervention control group is steady over several weeks to months. Secondly, we did not measure the rate of muscle protein breakdown and therefore can only speculate (on the basis of the observed changes in muscle mass and the muscle protein synthesis rate) how calorie restriction affects it. Consistent with earlier studies, we found that calorie restriction reduced total whole-body leucine Ra (expressed as μmol·min-1 (25-27)), and the reduction in leucine Ra appeared to be proportional to the loss of lean and total body mass. In contrast, maintenance of the newly reduced body weight for several months was associated with an increase in leucine flux, indicative of a greater whole-body proteolytic rate after than before weight loss. However, whole-body leucine flux is not a robust surrogate measure for muscle proteolytic activity because muscle protein breakdown contributes only ∼25-30% to whole-body leucine Ra (28).
In summary, dietary calorie restriction and weight loss in older adults have no adverse effect on the muscle protein synthesis process; in fact, the anabolic response to feeding is improved during the acute weight loss phase. We therefore conclude that the loss of muscle mass must be mediated predominately by adverse effects of dietary calorie restriction and weight loss on muscle proteolysis, which results in net negative muscle protein balance and muscle loss. Furthermore, an increase in the anabolic response to nutritional stimuli during negative energy balance limits the net loss of muscle protein. Therapies to reduce or prevent the loss of muscle mass during dietary calorie restriction should probably focus on limiting proteolysis.
Supplementary Material
Supplemental figure 1. Skeletal muscle protein fractional synthesis rate (FSR) during basal, post-absorptive conditions (white bars) and small bolus feeding of a liquid mixed meal (black bars) in obese older adults before and after 3 months of weight loss therapy (active weight loss phase; n = 8). Values are means ± SEM. * ANOVA revealed a significant time by feeding interaction and Tukey's post-hoc analysis indicated that this was due to the 3 month fed FSR value, which was significantly different from all other values (P < 0.05).
Acknowledgments
The study was designed by DTV and BM; data collection was performed and supervised by DTV, GIS, KS, and BM; data analyses and interpretation were performed by DTV, GIS, KS, and BM; writing was performed by DTV, GIS, KS, and BM. None of the authors had conflicts of interest. This publication was made possible by National Institutes of Health Grants AG 025501, AR 049869, AG 021164, RR 00036 (General Clinical Research Center), RR 00954 (Biomedical Mass Spectrometry Resource), and DK 56341 (Nutrition Obesity Research Center) and a grant from the Longer Life Foundation.
We are grateful to Nicole Wright, Kathie Obert, and the nursing staff of the Clinical Research Unit for their skilled technical assistance in performing this study and to the study subjects for their cooperation.
Footnotes
Disclosures: The authors have no financial or personal interest in any company or organization sponsoring the research, including advisory board affiliations.
References
- 1.van Baak MA, Visscher TL. Public health success in recent decades may be in danger if lifestyles of the elderly are neglected. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;84:1257–8. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/84.6.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Villareal DT, Apovian CM, Kushner RF, Klein S. Obesity in older adults: technical review and position statement of the American Society for Nutrition and NAASO, The Obesity Society. Obes Res. 2005;13:1849–63. doi: 10.1038/oby.2005.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kennedy RL, Chokkalingham K, Srinivasan R. Obesity in the elderly: who should we be treating, and why, and how? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2004;7:3–9. doi: 10.1097/00075197-200401000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dunn MA, Houtz SK, Hartsook EW. Effects of fasting on muscle protein turnover, the composition of weight loss, and energy balance of obese and nonobese Zucker rats. J Nutr. 1982;112:1862–75. doi: 10.1093/jn/112.10.1862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Goodman MN, McElaney MA, Ruderman NB. Adaptation to prolonged starvation in the rat: curtailment of skeletal muscle proteolysis. Am J Physiol. 1981;241:E321–7. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.241.4.E321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Clark AS, Mitch WE. Comparison of protein synthesis and degradation in incubated and perfused muscle. Biochem J. 1983;212:649–53. doi: 10.1042/bj2120649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Campbell WW, Haub MD, Wolfe RR, et al. Resistance training preserves fat-free mass without impacting changes in protein metabolism after weight loss in older women. Obesity. 2009;17:1332–9. doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Villareal DT, Holloszy JO, Kohrt WM. Effects of DHEA replacement on bone mineral density and body composition in elderly women and men. Clin Endocrinol. 2000;53:561–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.2000.01131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Heymsfield SB, Smith R, Aulet M, et al. Appendicular skeletal muscle mass: measurement by dual-photon absorptiometry. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990;52:214–8. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/52.2.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Villareal DT, Smith GI, Sinacore DR, Shah K, Mittendorfer B. Regular multicomponent exercise increases physical fitness and muscle protein anabolism in frail, obese, older adults. Obesity. 2011;19:312–8. doi: 10.1038/oby.2010.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Smith GI, Atherton P, Reeds DN, et al. Dietary omega-3 fatty acid supplementation increases the rate of muscle protein synthesis in older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93:402–12. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.110.005611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Patterson BW, Zhang XJ, Chen Y, Klein S, Wolfe RR. Measurement of very low stable isotope enrichments by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry: application to measurement of muscle protein synthesis. Metabolism. 1997;46:943–8. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(97)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Langenbeck U, Luthe H, Schaper G. Keto acids in tissues and biological fluids: O-t-butyldimethylsilyl quinoxalinols as derivatives for sensitive gas chromatographic/mass spectrometric determination. Biomed Mass Spec. 1985;12:507–9. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200120912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wolfe RR. Radioactive and Stable Isotope Tracers in Biomedicine: Principles and Practice of Kinetic Analysis. Wiley-Liss; New York: 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28:412–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00280883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fabbrini E, Klein S. Fundamentals of cardiometabolic risk factor reduction: achieving and maintaining weight loss with pharmacotherapy or bariatric surgery. Clin Cornerstone. 2008;9:41–8. doi: 10.1016/s1098-3597(08)60027-7. discussion 9-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Aronne LJ, Isoldi KK. Overweight and obesity: key components of cardiometabolic risk. Clin Cornerstone. 2007;8:29–37. doi: 10.1016/s1098-3597(07)80026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rolland Y, Kim MJ, Gammack JK, Wilson MM, Thomas DR, morley JE. Office management of weight loss in older persons. Am J Med. 2006;119:1019–26. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2006.02.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cuthbertson D, Smith K, Babraj J, et al. Anabolic signaling deficits underlie amino acid resistance of wasting, aging muscle. Faseb J. 2005;19:422–4. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-2640fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Guillet C, Prod'homme M, Balage M, et al. Impaired anabolic response of muscle protein synthesis is associated with S6K1 dysregulation in elderly humans. Faseb J. 2004;18:1586–7. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-1341fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rasmussen BB, Fujita S, Wolfe RR, et al. Insulin resistance of muscle protein metabolism in aging. Faseb J. 2006;20:768–9. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-4607fje. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bohe J, Low A, Wolfe RR, Rennie MJ. Human muscle protein synthesis is modulated by extracellular, not intramuscular amino acid availability: a dose-response study. J Physiol. 2003;552:315–24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.050674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Moore DR, Robinson MJ, Fry JL, et al. Ingested protein dose response of muscle and albumin protein synthesis after resistance exercise in young men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89:161–8. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2008.26401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dillon EL, Sheffield-Moore M, Paddon-Jones D, et al. Amino acid supplementation increases lean body mass, basal muscle protein synthesis, and insulin-like growth factor-I expression in older women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:1630–7. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kanaley JA, Haymond MW, Jensen MD. Effects of exercise and weight loss on leucine turnover in different types of obesity. Am J Physiol. 1993;264:E687–92. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.264.5.E687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Welle S, Statt M, Barnard R, Amatruda J. Differential effect of insulin on whole-body proteolysis and glucose metabolism in normal-weight, obese, and reduced-obese women. Metabolism. 1994;43:441–5. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(94)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Henderson GC, Nadeau D, Horton ES, Nair KS. Effects of adiposity and 30 days of caloric restriction upon protein metabolism in moderately vs severely obese women. Obesity. 2010;18:1135–42. doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nair KS, Halliday D, Griggs RC. Leucine incorporation into mixed skeletal muscle protein in humans. Am J Physiol. 1988;254:E208–13. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.2.E208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental figure 1. Skeletal muscle protein fractional synthesis rate (FSR) during basal, post-absorptive conditions (white bars) and small bolus feeding of a liquid mixed meal (black bars) in obese older adults before and after 3 months of weight loss therapy (active weight loss phase; n = 8). Values are means ± SEM. * ANOVA revealed a significant time by feeding interaction and Tukey's post-hoc analysis indicated that this was due to the 3 month fed FSR value, which was significantly different from all other values (P < 0.05).


