Abstract
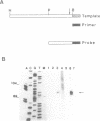
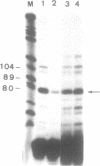
We have isolated the mouse MyoD1 gene flanked by its promoter region by screening a genomic library with synthetic oligonucleotides. The structural gene is interrupted by two G + C rich introns. Transfection of the cloned gene inserted into an expression vector converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Sequence analysis of about 650 bp of the 5' upstream region revealed the presence of several potential regulatory elements such as a TATA-box, an AP2-box, two SP1-boxes and a CAAT-box. In addition, there are three half palindromic estrogen response elements, a potential cAMP response element and various muscle specific elements such as a muscle-specific CAAT-box (MCAT) and four potential binding sites for MyoD1. Using S1 protection analysis the major start site of transcription in muscle and myoblast cells was mapped 3 bp upstream of the published cDNA 5' end. Promoter activity of the 650 bp upstream fragment was tested by in vitro transcription and by transfection analysis of myoblasts and fibroblasts. In all promoter test systems used, MyoD1 promoter activity was detected in myoblasts as well as in fibroblasts. Furthermore, DNA methylation was found to turn off MyoD1 promoter activity both in myoblasts and in fibroblasts.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. L., Bryans M., Rinaldi A., Smart A., Yesufu H. M. Eukaryotic DNA methylases and their use for in vitro methylation. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Jan 30;326(1235):189–198. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1990.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrisani O. M., Hayes T. E., Roos B., Dixon J. E. Identification of the promoter sequences involved in the cell specific expression of the rat somatostatin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5715–5728. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artelt P., Grannemann R., Stocking C., Friel J., Bartsch J., Hauser H. The prokaryotic neomycin-resistance-encoding gene acts as a transcriptional silencer in eukaryotic cells. Gene. 1991 Mar 15;99(2):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90134-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Burden S. J. Muscle-specific gene expression controlled by a regulatory element lacking a MyoD1-binding site. Nature. 1989 Oct 26;341(6244):716–720. doi: 10.1038/341716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyes J., Bird A. DNA methylation inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1123–1134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P. Weight matrix descriptions of four eukaryotic RNA polymerase II promoter elements derived from 502 unrelated promoter sequences. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):563–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Jones P. Determination genes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;1(6):1075–1080. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colmenares C., Teumer J. K., Stavnezer E. Transformation-defective v-ski induces MyoD and myogenin expression but not myotube formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1167–1170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eftimie R., Brenner H. R., Buonanno A. Myogenin and MyoD join a family of skeletal muscle genes regulated by electrical activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1349–1353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson C. P. Myogenesis and developmental control genes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;2(6):1065–1075. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90157-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Schaffner W. CpG methylation of the cAMP-responsive enhancer/promoter sequence TGACGTCA abolishes specific factor binding as well as transcriptional activation. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):612–619. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Le Bail O., Hatat D., Piette J., Kieran M., Logeat F., Wallach D., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. TNF stimulates expression of mouse MHC class I genes by inducing an NF kappa B-like enhancer binding activity which displaces constitutive factors. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3793–3800. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., Wolkowicz M. J., Rideout W. M., 3rd, Gonzales F. A., Marziasz C. M., Coetzee G. A., Tapscott S. J. De novo methylation of the MyoD1 CpG island during the establishment of immortal cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6117–6121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet I., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Cedar H. DNA methylation affects the formation of active chromatin. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E. Transcription control and differentiation: the HLH family, c-myc and C/EBP. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;1(6):1081–1087. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Tsai S. Y., Greene G. L., Clark J. H., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Specific binding of estrogen receptor to the estrogen response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr 5-Azacytidine induction of stable mesodermal stem cell lineages from 10T1/2 cells: evidence for regulatory genes controlling determination. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):791–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Buskin J. N., Lockshon D., Davis R. L., Apone S., Hauschka S. D., Weintraub H. MyoD is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):823–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Paterson B. M., Weintraub H. Transfection of a DNA locus that mediates the conversion of 10T1/2 fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):649–656. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90507-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Thayer M. J., Overell R. W., Weintraub H. Transformation by activated ras or fos prevents myogenesis by inhibiting expression of MyoD1. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley T. J., Anagnou N. P., Pepe G., Nienhuis A. W. RNA processing errors in patients with beta-thalassemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4775–4779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H., Yutzey K. E., Konieczny S. F. Muscle-specific expression of the troponin I gene requires interactions between helix-loop-helix muscle regulatory factors and ubiquitous transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):267–280. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. M-CAT binding factor, a novel trans-acting factor governing muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4271–4283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. J. c-myc inhibition of MyoD and myogenin-initiated myogenic differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2842–2851. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. MyoD family: a paradigm for development? Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1454–1461. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak A., Bryans M., Jost J. P. An avian 40 KDa nucleoprotein binds preferentially to a promoter sequence containing one single pair of methylated CpG. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1029–1034. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. A., Gordon H., Hall Z. W., Paterson B. M., Blau H. M. Negative control of the helix-loop-helix family of myogenic regulators in the NFB mutant. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Bessereau J. L., Huchet M., Changeux J. P. Two adjacent MyoD1-binding sites regulate expression of the acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit gene. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):353–355. doi: 10.1038/345353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. Muscle cell differentiation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;1(6):1094–1101. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli V., Webster K. A., Kedes L. Muscle-specific expression of the cardiac alpha-actin gene requires MyoD1, CArG-box binding factor, and Sp1. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1811–1822. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Cheng P. F., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. MyoD1: a nuclear phosphoprotein requiring a Myc homology region to convert fibroblasts to myoblasts. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):405–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3175662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Bird A. Alternative chromatin structure at CpG islands. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90339-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer M. J., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. Positive autoregulation of the myogenic determination gene MyoD1. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90838-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer M. J., Weintraub H. Activation and repression of myogenesis in somatic cell hybrids: evidence for trans-negative regulation of MyoD in primary fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90285-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaccaro M., Pawlak A., Jost J. P. Positive and negative regulatory elements of chicken vitellogenin II gene characterized by in vitro transcription competition assays in a homologous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3047–3051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya T. B., Rhodes S. J., Taparowsky E. J., Konieczny S. F. Fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor beta repress transcription of the myogenic regulatory gene MyoD1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3576–3579. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Lockshon D., Lassar A. MyoD binds cooperatively to two sites in a target enhancer sequence: occupancy of two sites is required for activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5623–5627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Adam M. A., Lassar A. B., Miller A. D. Activation of muscle-specific genes in pigment, nerve, fat, liver, and fibroblast cell lines by forced expression of MyoD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. M., Donoghue M., Engert J. C., Berglund E. B., Rosenthal N. Paired MyoD-binding sites regulate myosin light chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1242–1246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutzey K. E., Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Differential trans activation associated with the muscle regulatory factors MyoD1, myogenin, and MRF4. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3934–3944. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahradka P., Larson D. E., Sells B. H. RNA polymerase II-directed gene transcription by rat skeletal muscle nuclear extracts. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Nov;185(1):8–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]