Abstract
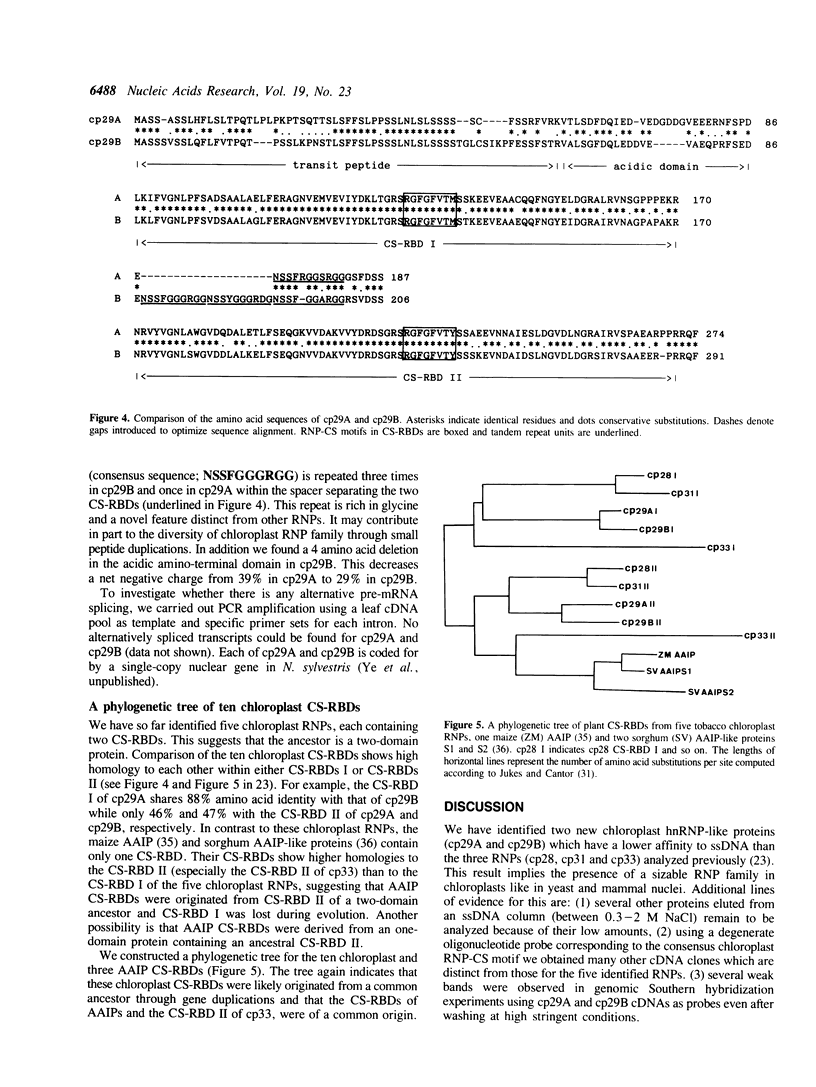
Two new ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) have been identified from a tobacco chloroplast lysate. These two proteins (cp29A and cp29B) are nuclear-encoded and have a less affinity to single-stranded DNA as compared with three other chloroplast RNPs (cp28, cp31 and cp33) previously isolated. DNA sequencing revealed that both contain two consensus sequence-type homologous RNA-binding domains (CS-RBDs) and a very acidic amino-terminal domain but shorter than that of cp28, cp31 and cp33. Comparison of cp29A and cp29B showed a 19 amino acid insertion in the region separating the two CS-RBDs in cp29B. This insertion results in three tandem repeats of a glycine-rich sequence of 10 amino acids, which is a novel feature in RNPs. The two proteins are encoded by different single nuclear genes and no alternatively spliced transcripts could be identified. We constructed a phylogenetic tree for the ten chloroplast CS-RBDs. These results suggest that there is a sizable RNP family in chloroplasts and the diversity was mainly generated through a series of gene duplications rather than through alternative pre-mRNA splicing. The gene for cp29B contains three introns. The first and second introns interrupt the first CS-RBD and the third intron does the second CS-RBD. The position of the first intron site is the same as that in the human hnRNP A1 protein gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biamonti G., Buvoli M., Bassi M. T., Morandi C., Cobianchi F., Riva S. Isolation of an active gene encoding human hnRNP protein A1. Evidence for alternative splicing. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 5;207(3):491–503. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd C. G., Swanson M. S., Görlach M., Dreyfuss G. Primary structures of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2, B1, and C2 proteins: a diversity of RNA binding proteins is generated by small peptide inserts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9788–9792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buvoli M., Biamonti G., Tsoulfas P., Bassi M. T., Ghetti A., Riva S., Morandi C. cDNA cloning of human hnRNP protein A1 reveals the existence of multiple mRNA isoforms. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3751–3770. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buvoli M., Cobianchi F., Bestagno M. G., Mangiarotti A., Bassi M. T., Biamonti G., Riva S. Alternative splicing in the human gene for the core protein A1 generates another hnRNP protein. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1229–1235. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Bravo R., Arenstorf H. P., LeStourgeon W. M. Identification of proliferation-sensitive human proteins amongst components of the 40 S hnRNP particles. Identity of hnRNP core proteins in the HeLa protein catalogue. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 1;194(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A., Dreyfuss G. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins: role in RNA splicing. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1534–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.3952495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher D. A., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal protein operon: a new chloroplast gene for ribosomal protein L5 and description of a novel organelle intron category designated group III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7591–7608. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crétin C., Puigdomènech P. Glycine-rich RNA-binding proteins from Sorghum vulgare. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Nov;15(5):783–785. doi: 10.1007/BF00016128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G. Structure and function of nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:459–498. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Swanson M. S., Piñol-Roma S. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles and the pathway of mRNA formation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Mar;13(3):86–91. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez J., Sánchez-Martínez D., Stiefel V., Rigau J., Puigdomènech P., Pagès M. A gene induced by the plant hormone abscisic acid in response to water stress encodes a glycine-rich protein. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):262–264. doi: 10.1038/334262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. R., Johnson D., Raychaudhuri G., Beyer A. L. The Drosophila Hrb87F gene encodes a new member of the A and B hnRNP protein group. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):25–31. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiratsuka J., Shimada H., Whittier R., Ishibashi T., Sakamoto M., Mori M., Kondo C., Honji Y., Sun C. R., Meng B. Y. The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa) chloroplast genome: intermolecular recombination between distinct tRNA genes accounts for a major plastid DNA inversion during the evolution of the cereals. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):185–194. doi: 10.1007/BF02464880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B. K., Sawhney R. K., Wilson S. H. Potential for two isoforms of the A1 ribonucleoprotein in Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1367–1371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. Q., Sugiura M. Nucleic acid-binding specificities of tobacco chloroplast ribonucleoproteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2893–2896. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. Q., Sugiura M. Three distinct ribonucleoproteins from tobacco chloroplasts: each contains a unique amino terminal acidic domain and two ribonucleoprotein consensus motifs. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3059–3066. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. Q., Ye L. Z., Sugita M., Sugiura M. Tobacco nuclear gene for the 31 kd chloroplast ribonucleoprotein: genomic organization, sequence analysis and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2987–2991. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfioletti G., Schneider C. A new and fast method for preparing high quality lambda DNA suitable for sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):2873–2884. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.2873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami E., Shinohara K., Kuwabara T., Watanabe A. In vitro synthesis and assembly of photosystem II proteins of spinach chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 1;244(2):517–527. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90620-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nietfeld W., Mentzel H., Pieler T. The Xenopus laevis poly(A) binding protein is composed of multiple functionally independent RNA binding domains. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3699–3705. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfo M., Valentini O., Biamonti G., Rossi P., Riva S. Large-scale purification of hnRNP proteins from HeLa cells by affinity chromatography on ssDNA-cellulose. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jan 2;162(1):213–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preugschat F., Wold B. Isolation and characterization of a Xenopus laevis C protein cDNA: structure and expression of a heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein core protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9669–9673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Abelson J. Pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90276-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W., Kornberg R. D. A single domain of yeast poly(A)-binding protein is necessary and sufficient for RNA binding and cell viability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3268–3276. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., Dathan N. A., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. Major determinants of the specificity of interaction between small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1A and U2B'' and their cognate RNAs. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):502–506. doi: 10.1038/345502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., van Venrooij W. J., Dathan N. A., Hamm J., Mattaj I. W. Identification of the RNA binding segment of human U1 A protein and definition of its binding site on U1 snRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4163–4170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Dathan N. A., Boelens W., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. The U2B'' RNP motif as a site of protein-protein interaction. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3675–3681. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster G., Gruissem W. Chloroplast mRNA 3' end processing requires a nuclear-encoded RNA-binding protein. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1493–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada H., Sugiura M. Fine structural features of the chloroplast genome: comparison of the sequenced chloroplast genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):983–995. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierakowska H., Szer W., Furdon P. J., Kole R. Antibodies to hnRNP core proteins inhibit in vitro splicing of human beta-globin pre-mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5241–5254. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M. The chloroplast chromosomes in land plants. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:51–70. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surowy C. S., van Santen V. L., Scheib-Wixted S. M., Spritz R. A. Direct, sequence-specific binding of the human U1-70K ribonucleoprotein antigen protein to loop I of U1 small nuclear RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4179–4186. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Nakagawa T. Y., LeVan K., Dreyfuss G. Primary structure of human nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle C proteins: conservation of sequence and domain structures in heterogeneous nuclear RNA, mRNA, and pre-rRNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Steppuhn J., Herrmann R. G. Domain structure of mitochondrial and chloroplast targeting peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):535–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





