Abstract
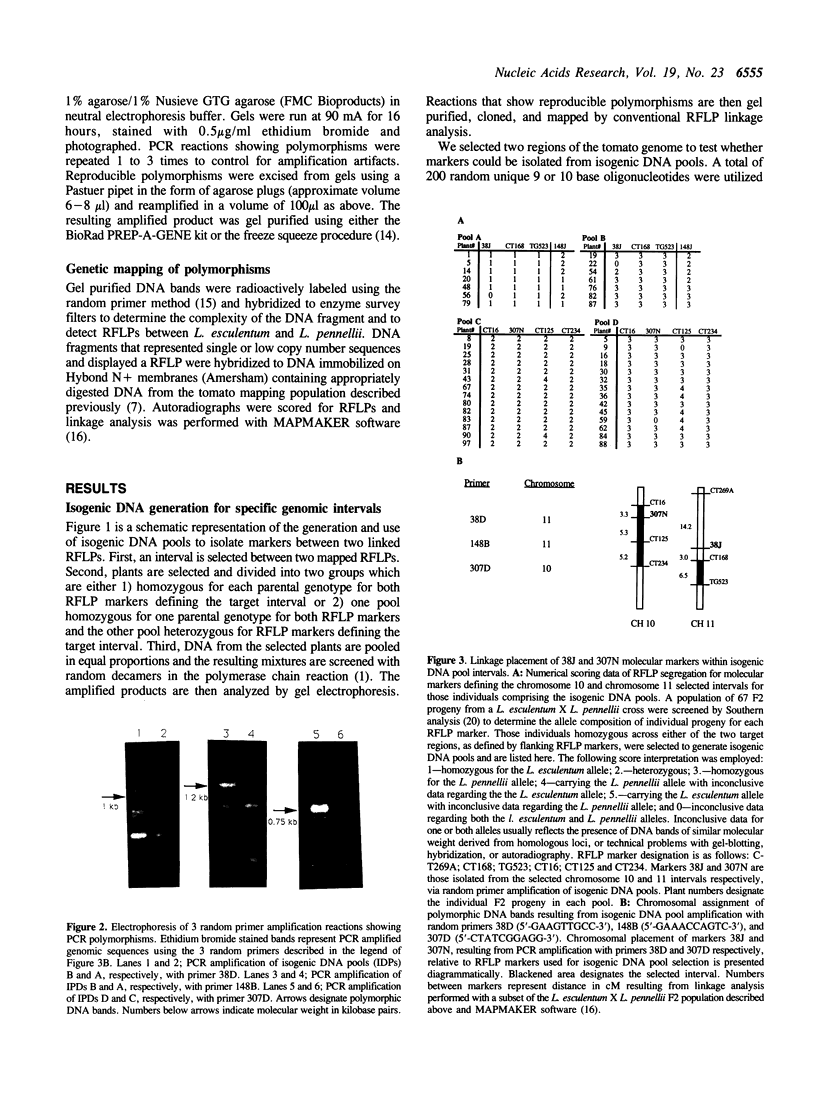
We present a general method for isolating molecular markers specific to any region of a chromosome using existing mapping populations. Two pools of DNA from individuals homozygous for opposing alleles for a targeted chromosomal interval, defined by two or more linked RFLP markers, are constructed from members of an existing mapping population. The DNA pools are then screened for polymorphism using random oligonucleotide primers and PCR (1). Polymorphic DNA bands should represent DNA sequences within or adjacent to the selected interval. We tested this method in tomato using two genomic intervals containing genes responsible for regulating pedicle abscission (jointless) and fruit ripening (non-ripening). DNA pools containing 7 to 14 F2 individuals for each interval were screened with 200 random primers. Three polymorphic markers were thus identified, two of which were subsequently shown to be tightly linked to the selected intervals. The third marker mapped to the same chromosome (11) but 45 cM away from the selected interval. A particularly attractive attribute of this method is that a single mapping population can be used to target any interval in the genome. Although this method has been demonstrated in tomato, it should be applicable to any sexually reproducing organism for which segregating populations are being used to construct genetic linkage maps.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Green P., Abrahamson J., Barlow A., Daly M. J., Lincoln S. E., Newberg L. A., Newburg L. MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):174–181. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry B. S., Kesseli R. V., Farrara B., Michelmore R. W. A Genetic Map of Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) with Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism, Isozyme, Disease Resistance and Morphological Markers. Genetics. 1987 Jun;116(2):331–337. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. B., Williams J. G., Tanksley S. D. Rapid identification of markers linked to a Pseudomonas resistance gene in tomato by using random primers and near-isogenic lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Iannuzzi M. C., Kerem B., Drumm M. L., Melmer G., Dean M., Rozmahel R., Cole J. L., Kennedy D., Hidaka N. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1059–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.2772657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Renz M. An optimized freeze-squeeze method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):14–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90419-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Marchuk D. A., Andersen L. B., Letcher R., Odeh H. M., Saulino A. M., Fountain J. W., Brereton A., Nicholson J., Mitchell A. L. Type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: identification of a large transcript disrupted in three NF1 patients. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):181–186. doi: 10.1126/science.2134734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. D., Zamir D., Ganal M. W., Tanksley S. D. Use of isogenic lines and simultaneous probing to identify DNA markers tightly linked to the tm-2a gene in tomato. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):579–585. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




