Abstract
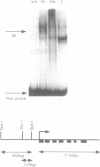
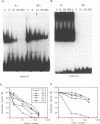
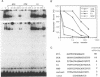
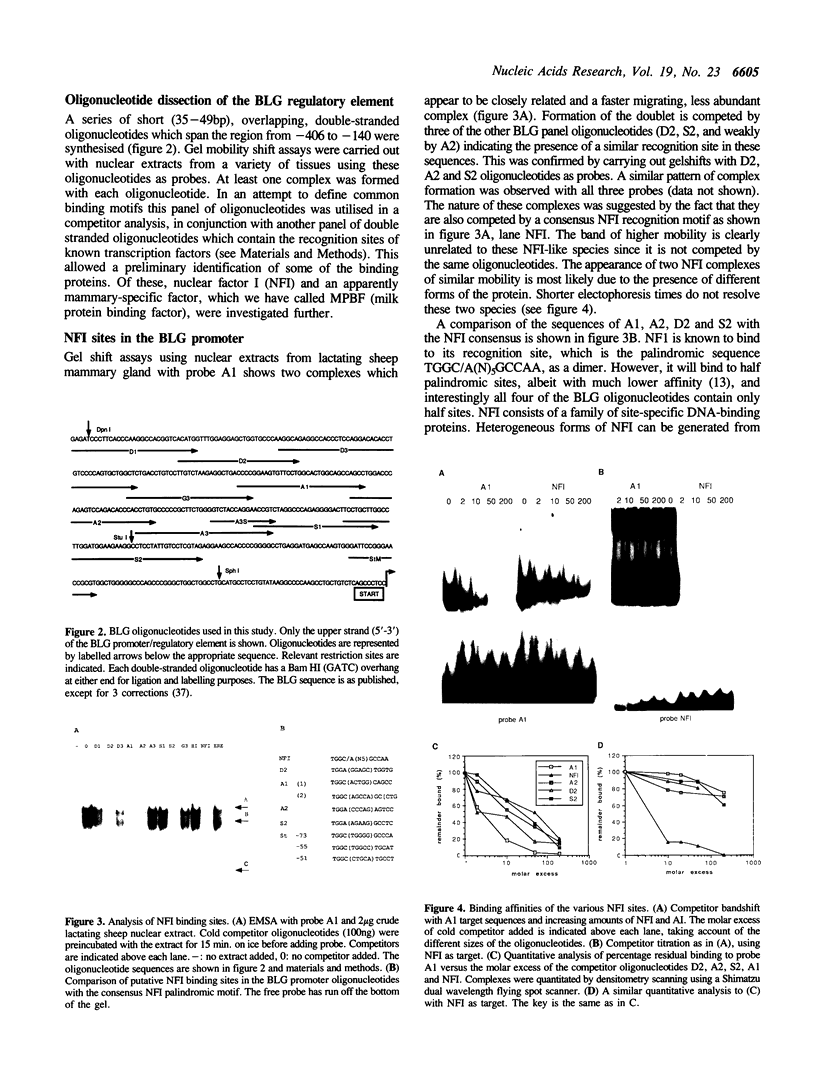
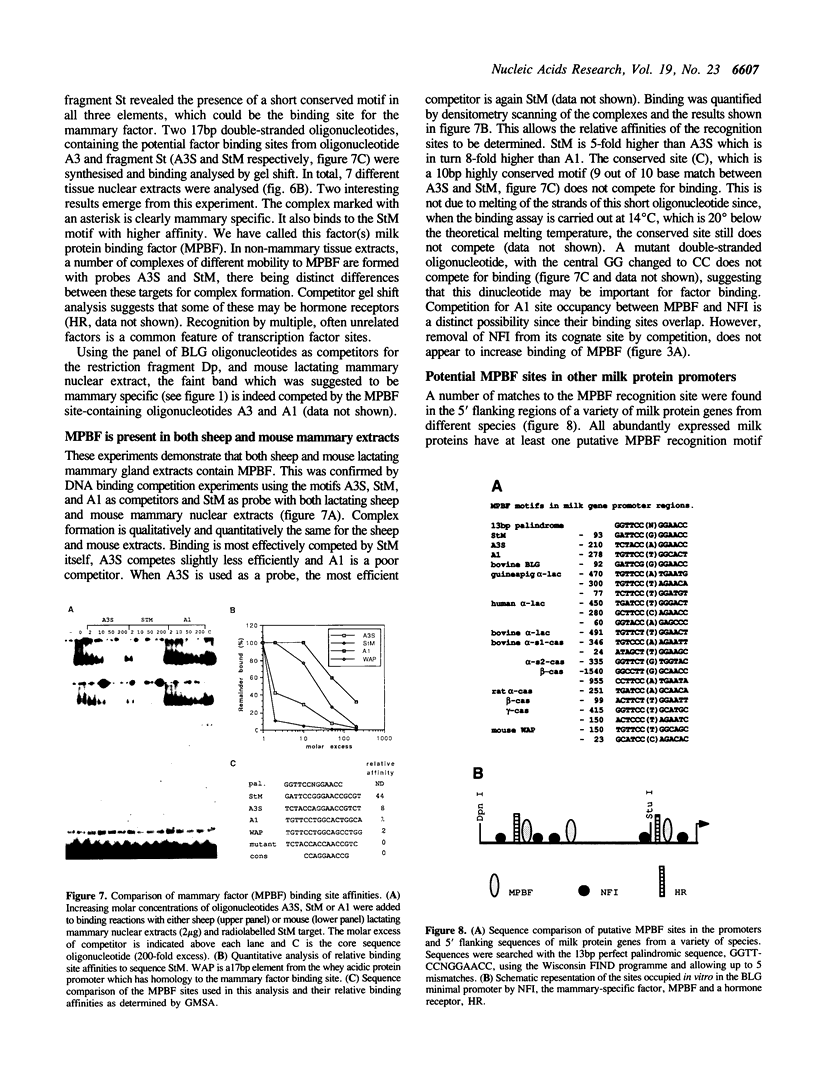
The minimal 5' regulatory region of the sheep beta-lactoglobulin gene (BLG), as defined in transgenic mice, was used to identify nuclear factors which may be involved in milk protein gene expression in the lactating mammary gland. This 406bp promoter region was dissected into short, overlapping, double-stranded oligonucleotides to facilitate identification of the bound proteins. A variety of sites, for both known and previously undescribed DNA-binding proteins, are occupied in vitro. Some of these factors were investigated in detail. Two forms of nuclear factor I (NFI), which have different recognition site affinities, are present in nuclear extracts from lactating mammary gland and bind to at least 5 sites in this BLG control element. In addition, a factor (milk protein binding factor, MPBF) which is specific to extracts from both mouse and sheep lactating mammary gland binds to 3 BLG promoter sites and may be a milk protein gene transcription factor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borellini F., Oka T. Growth control and differentiation in mammary epithelial cells. Environ Health Perspect. 1989 Mar;80:85–99. doi: 10.1289/ehp.898085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L., Beato M. Nuclear factor I acts as a transcription factor on the MMTV promoter but competes with steroid hormone receptors for DNA binding. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2233–2239. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu H. M., Fischer W. H., Osborne T. F., Comb M. J. NF-I proteins from brain interact with the proenkephalin cAMP inducible enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2721–2728. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doppler W., Groner B., Ball R. K. Prolactin and glucocorticoid hormones synergistically induce expression of transfected rat beta-casein gene promoter constructs in a mammary epithelial cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):104–108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil G., Smith J. R., Goldstein J. L., Slaughter C. A., Orth K., Brown M. S., Osborne T. F. Multiple genes encode nuclear factor 1-like proteins that bind to the promoter for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8963–8967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloss B., Yeo-Gloss M., Meisterenst M., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L., Bernard H. U. Clusters of nuclear factor I binding sites identify enhancers of several papillomaviruses but alone are not sufficient for enhancer function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3519–3533. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal N., Knox J., Gronostajski R. M. Analysis of multiple forms of nuclear factor I in human and murine cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1041–1048. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Tontonoz P., Ross S. R., Spiegelman B. M. Identification of a potent adipocyte-specific enhancer: involvement of an NF-1-like factor. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):428–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L., Emery D. C., Davies M. S., Parker D., Craig R. K. Organization and sequence of the human alpha-lactalbumin gene. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):735–742. doi: 10.1042/bj2420735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris S., Ali S., Anderson S., Archibald A. L., Clark A. J. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genomic ovine beta-lactoglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10379–10380. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris S., McClenaghan M., Simons J. P., Ali S., Clark A. J. Developmental regulation of the sheep beta-lactoglobulin gene in the mammary gland of transgenic mice. Dev Genet. 1991;12(4):299–307. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020120407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Tamura T., Furuichi T., Mikoshiba K. Isolation of complementary DNAs encoding a cerebellum-enriched nuclear factor I family that activates transcription from the mouse myelin basic protein promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19065–19070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., Tjian R. O-glycosylation of eukaryotic transcription factors: implications for mechanisms of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox J. J., Rebstein P. J., Manoukian A., Gronostajski R. M. In vivo stimulation of a chimeric promoter by binding sites for nuclear factor I. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):2946–2951. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre P., Berard D. S., Cordingley M. G., Hager G. L. Two regions of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat regulate the activity of its promoter in mammary cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2529–2537. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubon H., Hennighausen L. Conserved region of the rat alpha-lactalbumin promoter is a target site for protein binding in vitro. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 1;256(2):391–396. doi: 10.1042/bj2560391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubon H., Hennighausen L. Nuclear proteins from lactating mammary glands bind to the promoter of a milk protein gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2103–2121. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Dusserre Y., Wahli W., Mermod N. Synergistic transcriptional activation by CTF/NF-I and the estrogen receptor involves stabilized interactions with a limiting target factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):2937–2945. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Givel F., Wahli W. The estrogen-responsive element as an inducible enhancer: DNA sequence requirements and conversion to a glucocorticoid-responsive element. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3719–3727. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Gander I., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L. A quantitative analysis of nuclear factor I/DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4419–4435. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Specific binding of a cellular DNA replication protein to the origin of replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowock J., Borgmeyer U., Püschel A. W., Rupp R. A., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA protein binds to the MMTV-LTR, the adenovirus origin of replication, and the BK virus enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2045–2061. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paonessa G., Gounari F., Frank R., Cortese R. Purification of a NF1-like DNA-binding protein from rat liver and cloning of the corresponding cDNA. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3115–3123. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons F. E., Simons K. J., Chung M., Yeh J. The comparative pharmacokinetics of H1-receptor antagonists. Ann Allergy. 1987 Dec;59(6 Pt 2):20–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons J. P., McClenaghan M., Clark A. J. Alteration of the quality of milk by expression of sheep beta-lactoglobulin in transgenic mice. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):530–532. doi: 10.1038/328530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topper Y. J., Freeman C. S. Multiple hormone interactions in the developmental biology of the mammary gland. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1049–1106. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Cooperative binding of steroid hormone receptors contributes to transcriptional synergism at target enhancer elements. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90919-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Activation domains of stably bound GAL4 derivatives alleviate repression of promoters by nucleosomes. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90237-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries E., van Driel W., van den Heuvel S. J., van der Vliet P. C. Contactpoint analysis of the HeLa nuclear factor I recognition site reveals symmetrical binding at one side of the DNA helix. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):161–168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04734.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]