Abstract
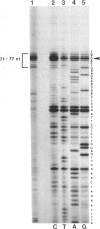
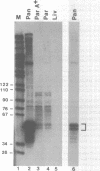
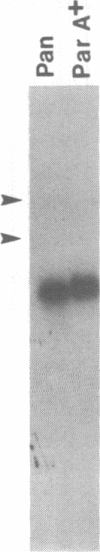
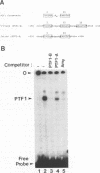
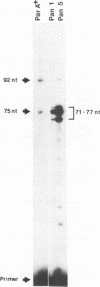
The mouse pancreatic ribonuclease gene Rib-1 was isolated from a library of mouse genomic DNA and sequenced. This small gene contains a nontranslated exon of 52 base pairs, an intron of 791 base pairs, and a coding exon of 741 base pairs. Rib-1 transcripts were detected in parotid gland as well as in pancreas. The abundance of the transcripts were approximately 200-fold greater in pancreatic RNA than in parotid RNA. The sites of transcription initiation were mapped by primer extension and ribonuclease protection assays. One major initiation site and several minor initiation sites were identified in pancreatic RNA. Transcription in parotid appears to be initiated from the same sites. Parotid-specific transcripts were not detected. The data suggest that Rib-1 is transcribed in pancreas and parotid from the same promoter. This is in contrast with the mechanism for production of amylase in pancreas and parotid, which is accomplished by tissue specific expression of different gene copies.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley P. L., MacDonald R. J. Tissue-specific expression of kallikrein-related genes in the rat. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4520–4527. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball W. D., Rutter W. J. The DNase activities of the mouse. J Exp Zool. 1971 Jan;176(1):1–14. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401760102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard E. A. Ribonucleases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:677–732. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.003333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beintema J. J., Fitch W. M., Carsana A. Molecular evolution of pancreatic-type ribonucleases. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 May;3(3):262–275. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulet A. M., Erwin C. R., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific enhancers in the rat exocrine pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3599–3603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carsana A., Confalone E., Palmieri M., Libonati M., Furia A. Structure of the bovine pancreatic ribonuclease gene: the unique intervening sequence in the 5' untranslated region contains a promoter-like element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5491–5502. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle A. M., Castle J. D. The purification and partial characterization of phospholipase A2, a secretory protein of rabbit parotid gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 23;666(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockell M., Stevenson B. J., Strubin M., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K. Identification of a cell-specific DNA-binding activity that interacts with a transcriptional activator of genes expressed in the acinar pancreas. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2464–2476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICHEL H. J., CONGER N., CHERNICK W. S. ACID AND ALKALINE RIBONUCLEASES OF HUMAN PAROTID, SUBMAXILLARY, AND WHOLE SALIVA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Aug;107:197–208. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott R. W., Samuelson L. C., Lambert M. S., Meisler M. H. Assignment of pancreatic ribonuclease gene to mouse chromosome 14. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;42(1-2):110–112. doi: 10.1159/000132261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskola J. U., Nevalainen T. J., Aho H. J. Purification and characterization of human pancreatic phospholipase A2. Clin Chem. 1983 Oct;29(10):1772–1776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullberg U., Widegren B., Arnason U., Egesten A., Olsson I. The cytotoxic eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) has ribonuclease activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1239–1242. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80310-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann K. J., Ten R. M., Loegering D. A., Jenkins R. B., Heise M. T., Schad C. R., Pease L. R., Gleich G. J., Barker R. L. Structure and chromosome localization of the human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin and eosinophil cationic protein genes: evidence for intronless coding sequences in the ribonuclease gene superfamily. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):535–546. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G., Keller P. R., Johnson T. M., Meisler M. H. Binding of a pancreatic nuclear protein is correlated with amylase enhancer activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8185–8195. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M., Keller S. A., Samuelson L. C., Osborn L., Rosenberg M. P., Meisler M. H. A salivary amylase transgene is efficiently expressed in liver but not in parotid gland of transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6613–6623. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn R. C. The comparative biochemistry, physiology, and genetics of animal alpha-amylases. Adv Comp Physiol Biochem. 1978;7:1–103. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-011507-5.50007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse F., Komro C. T., Michnoff C. H., MacDonald R. J. The cell-specific elastase I enhancer comprises two domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):893–902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai H., Yoshihara K., Umemoto M., Igarashi K., Hirose S., Ohgi K., Irie M. Studies on salivary gland ribonucleases. III. Purification and properties of three ribonucleases from bovine parotid gland. J Biochem. 1983 Mar;93(3):865–874. doi: 10.1093/jb/93.3.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W., Strydom D. J., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Sequence of the cDNA and gene for angiogenin, a human angiogenesis factor. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5494–5499. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenstra J. A., Beintema J. J. The amino acid sequence of mouse pancreatic ribonuclease. Extremely rapid evolutionary rates of the myomorph rodent ribonucleases. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):399–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Weinrich S. L., Nelson C., Rutter W. J. The chymotrypsin enhancer core. Specific factor binding and biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20744–20751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., Williams T. J., Tjian R. Enhancer binding factors AP-4 and AP-1 act in concert to activate SV40 late transcription in vitro. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):557–561. doi: 10.1038/332557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri M., Carsana A., Furia A., Libonati M. Sequence analysis of a cloned cDNA coding for bovine seminal ribonuclease. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):275–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinovitch M. R., Sreebny L. M., Smuckler E. A. Ribonuclease and ribonuclease inhibitor of the rat parotid gland and its secretion. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3441–3446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H. F., Ackerman S. J., Tenen D. G. Human eosinophil cationic protein. Molecular cloning of a cytotoxin and helminthotoxin with ribonuclease activity. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):163–176. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H. F., Tenen D. G., Ackerman S. J. Molecular cloning of the human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin: a member of the ribonuclease gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4460–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson L. C., Keller P. R., Darlington G. J., Meisler M. H. Glucocorticoid and developmental regulation of amylase mRNAs in mouse liver cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3857–3863. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson L. C., Wiebauer K., Gumucio D. L., Meisler M. H. Expression of the human amylase genes: recent origin of a salivary amylase promoter from an actin pseudogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8261–8276. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson L. C., Wiebauer K., Snow C. M., Meisler M. H. Retroviral and pseudogene insertion sites reveal the lineage of human salivary and pancreatic amylase genes from a single gene during primate evolution. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2513–2520. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Pittet A. C., Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Tosi M., Gellman S., Wellauer P. K. The mouse alpha-amylase multigene family. Sequence organization of members expressed in the pancreas, salivary gland and liver. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):247–266. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüller C., Nijssen H. M., Kok R., Beintema J. J. Evolution of nucleic acids coding for ribonucleases: the mRNA sequence of mouse pancreatic ribonuclease. Mol Biol Evol. 1990 Jan;7(1):29–44. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slifman N. R., Loegering D. A., McKean D. J., Gleich G. J. Ribonuclease activity associated with human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin and eosinophil cationic protein. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2913–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreebny L. M., Ruark G. W., Tamarin A. The distribution of deoxyribonuclease in the salivary glands and pancreas of various mammals. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Jul;12(7):777–781. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wawrzyniak C. J., Gallagher P. M., D'Amore M. A., Carter J. E., Lund S. D., Rinchik E. M., Ganschow R. E. DNA determinants of structural and regulatory variation within the murine beta-glucuronidase gene complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4074–4078. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weremowicz S., Fox E. A., Morton C. C., Vallee B. L. Localization of the human angiogenin gene to chromosome band 14q11, proximal to the T cell receptor alpha/delta locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Dec;47(6):973–981. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. A single mouse alpha-amylase gene specifies two different tissue-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]