Abstract
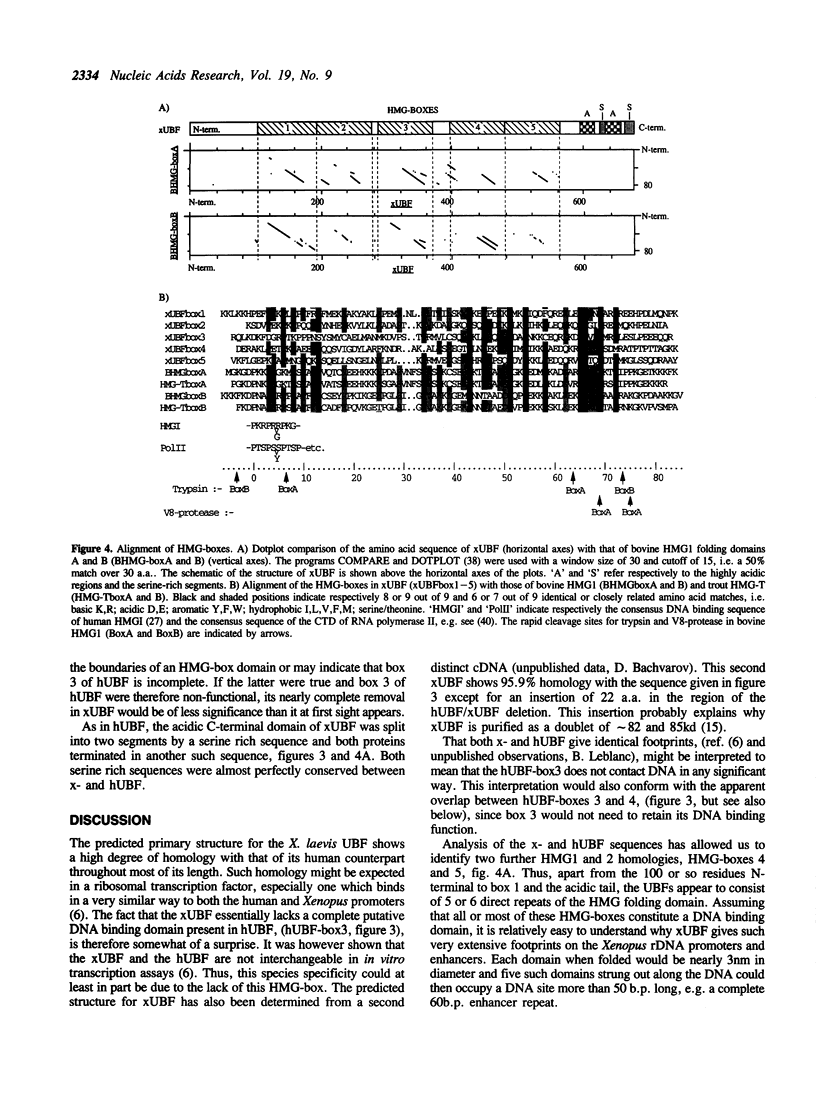
The RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF has been identified in human, mouse, rat and Xenopus and the primary structure of the human protein has been determined. Human UBF was shown to contain four tandem homologies to the folding domains of the HMG1 and 2 proteins and hence to belong to a previously unrecognised family of 'HMG-box' transcription factors. Here, cDNA clones encoding the Xenopus laevis UBF (xUBF) have been isolated and sequenced. Northern and Southern blots revealed that in tissue culture cells, xUBF is coded on a single major mRNA size species by a small number of genes. The deduced primary structure of xUBF is highly homologous with the human protein except for a central deletion which removes most of one HMG-box. This explains the major size difference between the X. laevis and human proteins and may well explain their different transcriptional specificities. It is shown that xUBF contains 5 tandemly repeated HMG-boxes and that by analogy the human protein contains 6.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateman E., Iida C. T., Kownin P., Paule M. R. Footprinting of ribosomal RNA genes by transcription initiation factor and RNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8004–8008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman E., Paule M. R. Events during eucaryotic rRNA transcription initiation and elongation: conversion from the closed to the open promoter complex requires nucleotide substrates. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1940–1946. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman E., Paule M. R. Regulation of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA transcription by RNA polymerase modification. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90601-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Assembly of alternative multiprotein complexes directs rRNA promoter selectivity. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):943–954. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Learned R. M., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1192–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.3413483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H., Tjian R. Molecular mechanisms governing species-specific transcription of ribosomal RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carballo M., Puigdomènech P., Palau J. DNA and histone H1 interact with different domains of HMG 1 and 2 proteins. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1759–1764. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary P. D., Turner C. H., Leung I., Mayes E., Crane-Robinson C. Conformation and domain structure of the non-histone chromosomal proteins HMG 1 and 2. Domain interactions. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 3;143(2):323–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary P. D., Turner C. H., Mayes E., Crane-Robinson C. Conformation and domain structure of the non-histone chromosomal proteins, HMG 1 and 2. Isolation of two folded fragments from HMG 1 and 2. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 15;131(2):367–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill M. E., Suzuki M. 'SPKK' motifs prefer to bind to DNA at A/T-rich sites. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4189–4195. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08604.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J. L. Tails of RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Burgess R. R. Sigma factors from E. coli, B. subtilis, phage SP01, and phage T4 are homologous proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6745–6763. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubbay J., Collignon J., Koopman P., Capel B., Economou A., Münsterberg A., Vivian N., Goodfellow P., Lovell-Badge R. A gene mapping to the sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome is a member of a novel family of embryonically expressed genes. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):245–250. doi: 10.1038/346245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Cordes S., Tjian R. Purification and characterization of a transcription factor that confers promoter specificity to human RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1358–1369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Learned T. K., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. T. Human rRNA transcription is modulated by the coordinate binding of two factors to an upstream control element. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfioletti G., Schneider C. A new and fast method for preparing high quality lambda DNA suitable for sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):2873–2884. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.2873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., McStay B., Schultz M. C., Bell S. P., Reeder R. H. The Xenopus ribosomal gene enhancers bind an essential polymerase I transcription factor, xUBF. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1779–1788. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., Smith S. D., Reeder R. H., Rothblum L. rUBF, an RNA polymerase I transcription factor from rats, produces DNase I footprints identical to those produced by xUBF, its homolog from frogs. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3810–3812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Nissen M. S. The A.T-DNA-binding domain of mammalian high mobility group I chromosomal proteins. A novel peptide motif for recognizing DNA structure. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8573–8582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D. E. Very rapid nucleotide sequence analysis of improved, double-stranded minipreps. Gene. 1989 Jan 30;75(1):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90396-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Clos J., Hädelt W., Schreck R., Cvekl A., Grummt I. Isolation and functional characterization of TIF-IB, a factor that confers promoter specificity to mouse RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1385–1393. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. H., Berta P., Palmer M. S., Hawkins J. R., Griffiths B. L., Smith M. J., Foster J. W., Frischauf A. M., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):240–244. doi: 10.1038/346240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh J., Dixon G. H. High mobility group proteins 1 and 2 function as general class II transcription factors. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 3;29(26):6295–6302. doi: 10.1021/bi00478a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Oriahi E., Lowe D., Yang-Yen H. F., O'Mahony D., Rose K., Chen K., Rothblum L. I. Characterization of factors that direct transcription of rat ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3105–3116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Oriahi E., Yang-Yen H. F., Xie W. Q., Chen C., Rothblum L. I. Interaction of RNA polymerase I transcription factors with a promoter in the nontranscribed spacer of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1677–1685. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M. SPKK, a new nucleic acid-binding unit of protein found in histone. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):797–804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03440.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M. SPXX, a frequent sequence motif in gene regulatory proteins. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 5;207(1):61–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M. The heptad repeat in the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II binds by intercalating into DNA. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):562–565. doi: 10.1038/344562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Kato H., Ishikawa Y., Hisatake K., Tashiro K., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Sequence-specific binding of a transcription factor TFID to the promoter region of mouse ribosomal RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13836–13842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Culotta V. C., Sollner-Webb B. Factors and nucleotide sequences that direct ribosomal DNA transcription and their relationship to the stable transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3451–3462. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]