Abstract
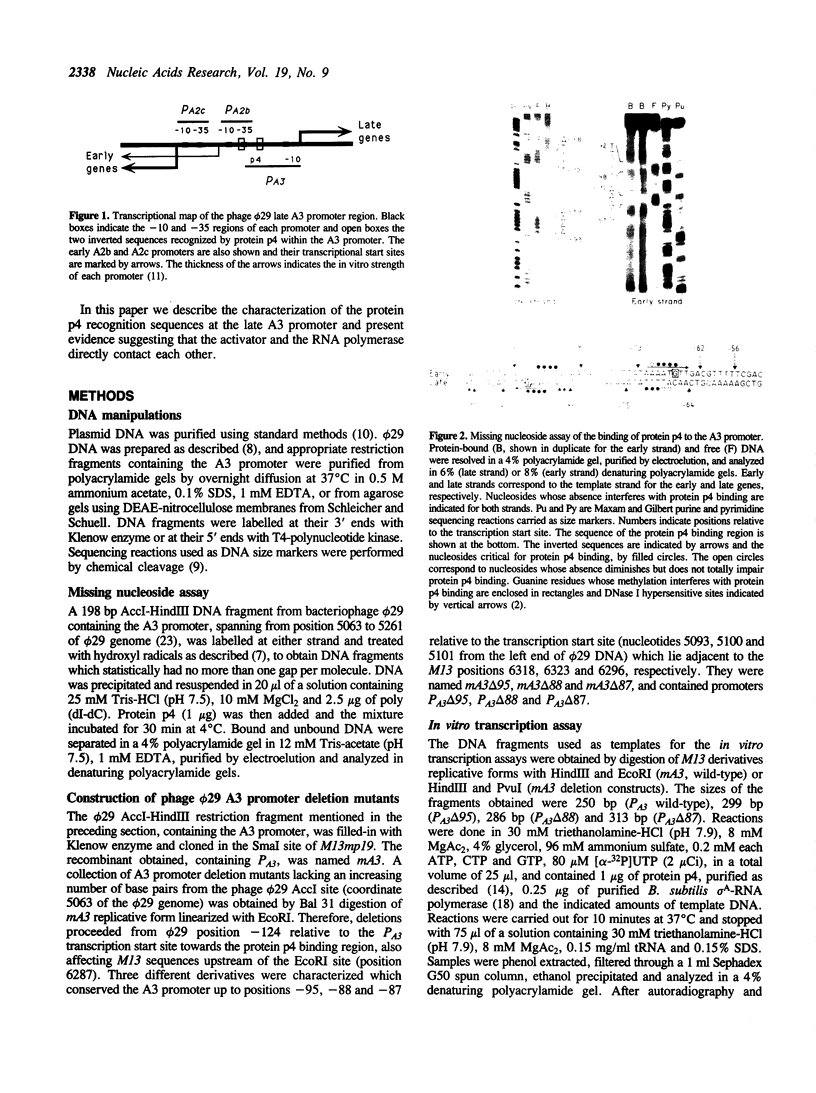
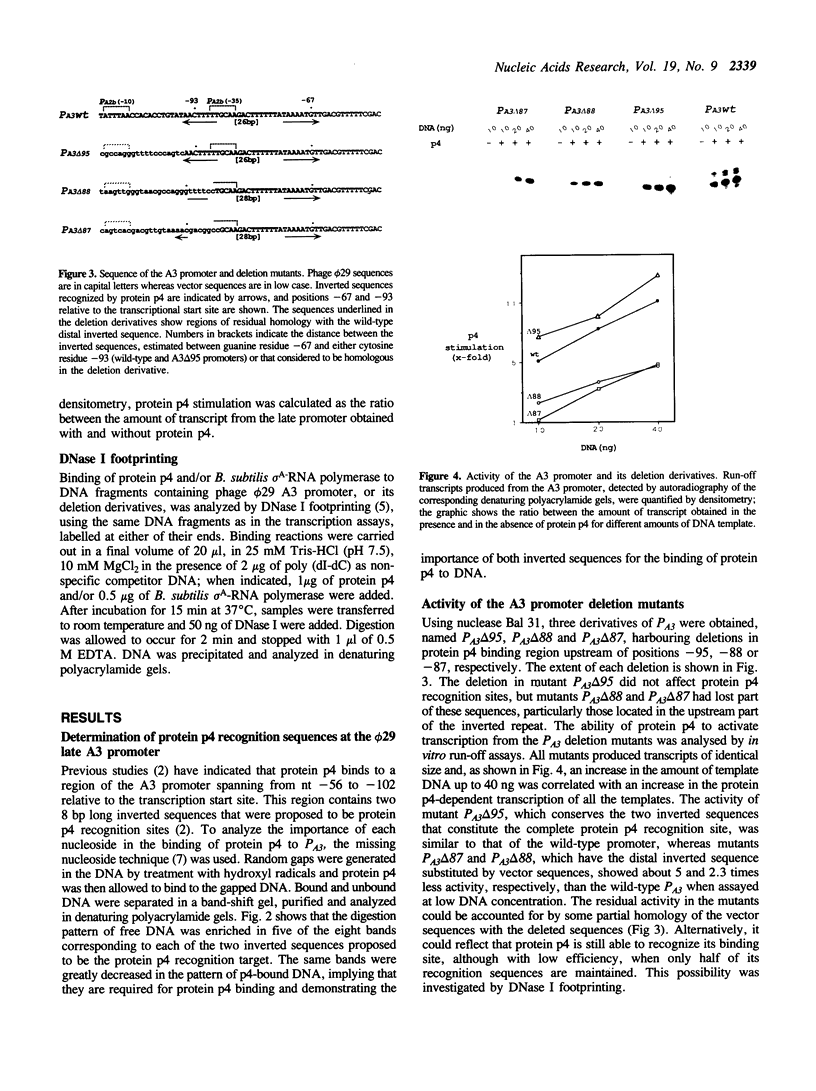
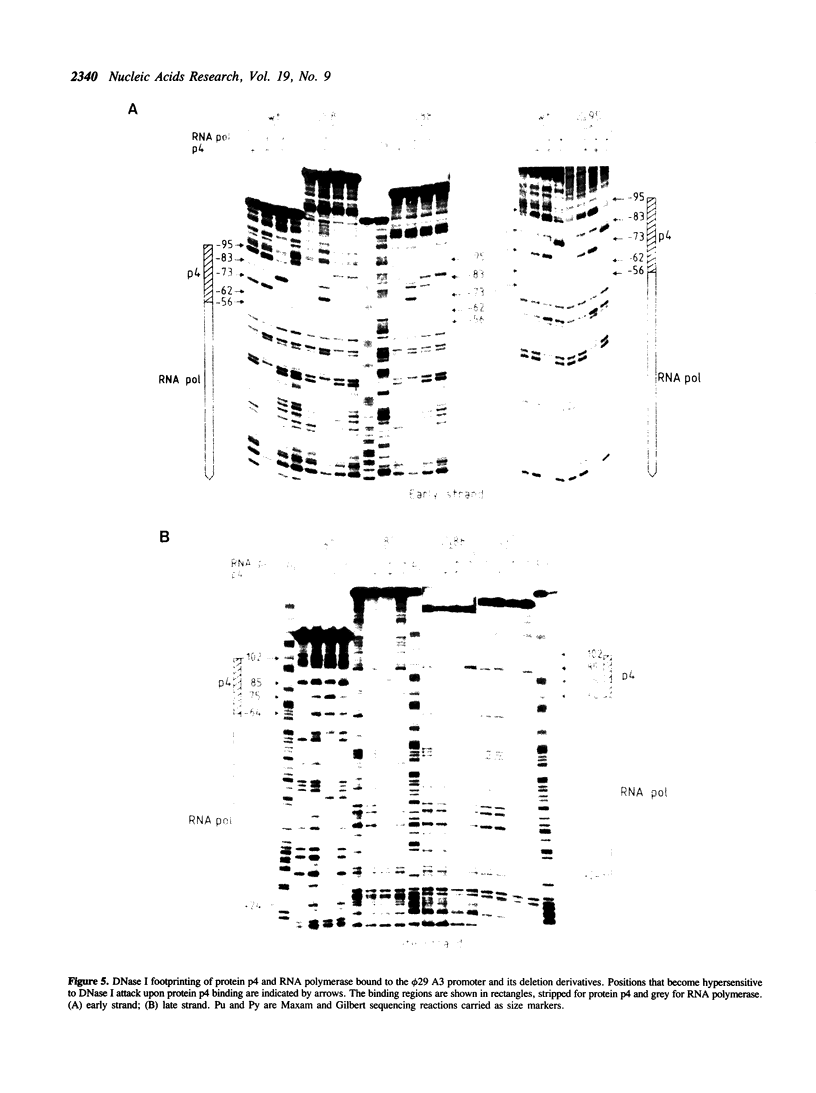
Expression of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29 late genes requires the transcriptional activator protein p4. This activator binds to a region of the late A3 promoter spanning nucleotides -56 to -102 relative to the transcription start site, generating a strong bending Tin the DNA. In this work the target sequences recognized by protein p4 in the phage phi 29 late A3 promoter have been characterized. The binding of protein p4 to derivatives of the late A3 promoter harbouring deletions in the protein p4 binding site has been studied. When protein p4 recognition sequences were altered, the activator could only bind to the promoter in the presence of RNA polymerase. This strong cooperativity in the binding of protein p4 and RNA polymerase to the promoter suggests the presence of direct protein-protein contacts between them.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Garges S. Positive control. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10797–10800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthelemy I., Salas M. Characterization of a new prokaryotic transcriptional activator and its DNA recognition site. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 20;208(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracco L., Kotlarz D., Kolb A., Diekmann S., Buc H. Synthetic curved DNA sequences can act as transcriptional activators in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4289–4296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Ptashne M. Activation of transcription by the bacteriophage 434 repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9353–9357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston K., Bell A., Kolb A., Buc H., Busby S. Stringent spacing requirements for transcription activation by CRP. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. J., Tullius T. D. The missing nucleoside experiment: a new technique to study recognition of DNA by protein. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9521–9527. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inciarte M. R., Lázaro J. M., Salas M., Vińuela E. Physical map of bacteriophage phi29 DNA. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):314–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado R. P., Barthelemy I., Salas M. In vitro transcription of bacteriophage phi 29 DNA. Correlation between in vitro and in vivo promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4731–4741. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhill J., Brown N. L. Site-specific insertion and deletion mutants in the mer promoter-operator region of Tn501; the nineteen base-pair spacer is essential for normal induction of the promoter by MerR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5157–5162. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren Y. L., Garges S., Adhya S., Krakow J. S. Cooperative DNA binding of heterologous proteins: evidence for contact between the cyclic AMP receptor protein and RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4138–4142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo F., Zaballos A., Salas M. Bend induced by the phage phi 29 transcriptional activator in the viral late promoter is required for activation. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):713–725. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90072-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. DNA binding by proteins. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1182–1187. doi: 10.1126/science.2842864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogo J. M., Inciarte M. R., Corral J., Viñuela E., Salas M. RNA polymerase binding sites and transcription map of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 5;127(4):411–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney D. C., Straney S. B., Crothers D. M. Synergy between Escherichia coli CAP protein and RNA polymerase in the lac promoter open complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):41–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90522-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Porter S., Kustu S., Echols H. DNA-looping and enhancer activity: association between DNA-bound NtrC activator and RNA polymerase at the bacterial glnA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. DNA conformation and protein binding. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:427–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedel A., Weiss D. S., Popham D., Dröge P., Kustu S. A bacterial enhancer functions to tether a transcriptional activator near a promoter. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):486–490. doi: 10.1126/science.1970441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Ito J. Nucleotide sequence of the major early region of bacteriophage phi 29. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]