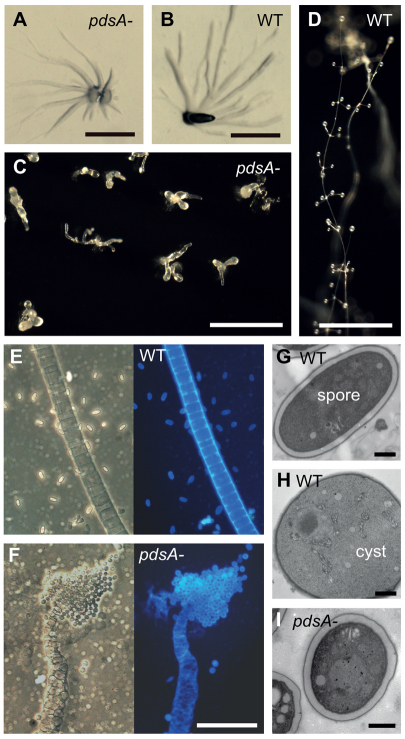
Fig. 5.
Phenotype of the P. pallidum pdsA– mutant. (A-D) Multicellular structures. Wild-type (WT) and pdsA– cells were harvested from bacterial growth plates, plated on water agar or charcoal agar, and incubated at 22°C until aggregates (A,B) had formed at 12 hours, or mature fruiting bodies (C,D) at 38 hours. Scale bars: 0.5 mm. (E,F) Terminal cell differentiation. Fruiting bodies of wild-type (E) and pdsA– (F) Ppal cells were transferred to a droplet of 0.001% Calcofluor on a slide glass and photographed under phase contrast (left) and UV illumination (right). Scale bar: 50 μm. (G-I) Fruiting structures were prepared for transmission electron microscopy as described previously (Kawabe et al., 2009) and sectioned. The images show an elliptical wild-type spore (G) and spherical wild-type cyst (H), and a spherical pdsA– spore (I). Scale bars: 1 μm.