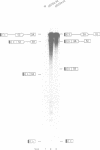
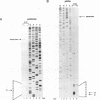
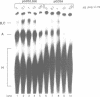
Abstract
During an adenovirus infection the expression of mRNA from late region L1 is temporally regulated at the level of alternative 3' splice site selection to produce two major mRNAs encoding the 52,55K and IIIa polypeptides. The proximal 3' splice site (52,55K) is used at all times of the infectious cycle whereas the distal site (IIIa) is used exclusively late after infection. We show that a single A branch nucleotide located at position -23 is used in 52,55K splicing and that two A's located at positions -21 and -22 are used in IIIa splicing. Both 3' splice sites were active in vitro in nuclear extracts prepared from uninfected HeLa cells. However, the efficiency of IIIa splicing was only approximately 10% of 52,55K splicing. This difference in splice site activity correlated with a reduced affinity of the IIIa, relative to the 52,55K, 3' splice site for polypyrimidine tract binding proteins. Reversing the order of 3' splice sites on a tandem pre-mRNA resulted in an almost exclusive IIIa splicing indicating that the order of 3' splice site presentation is important for the outcome of alternative L1 splicing. Based on our results we suggest a cis competition model where the two 3' splice sites compete for a common RNA splicing factor(s). This may represent an important mechanism by which L1 alternative splicing is regulated.
Full text
PDF
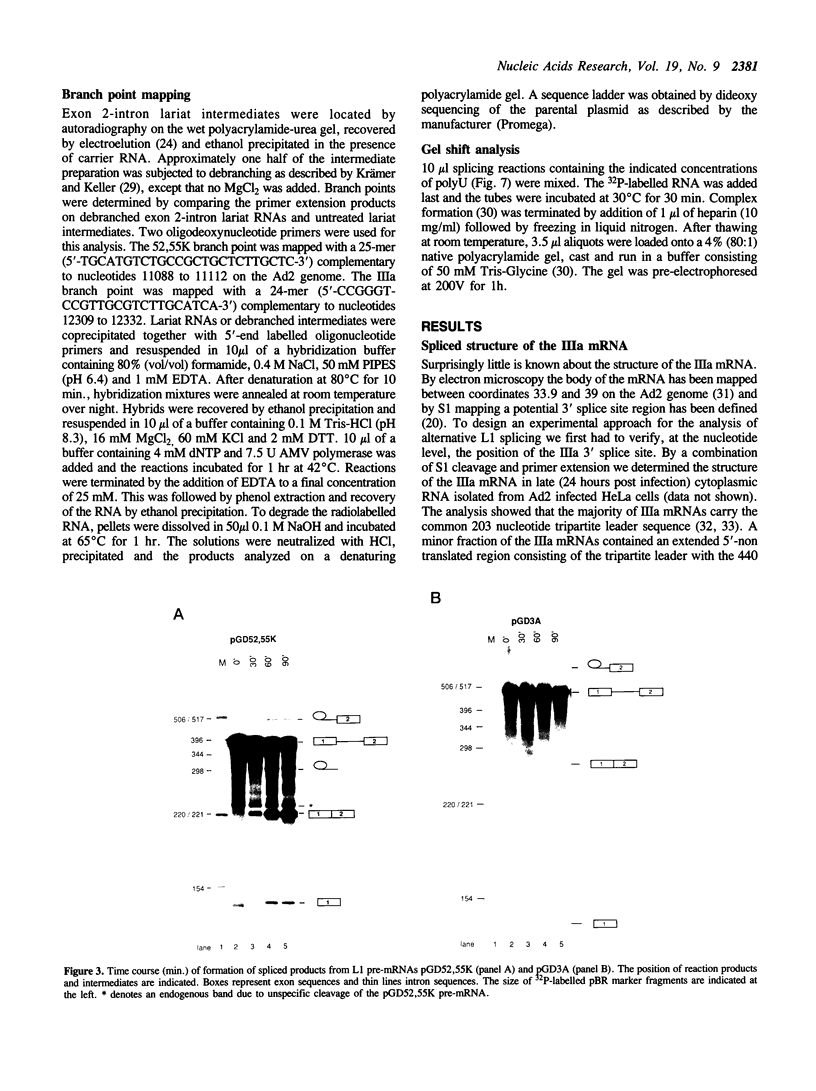


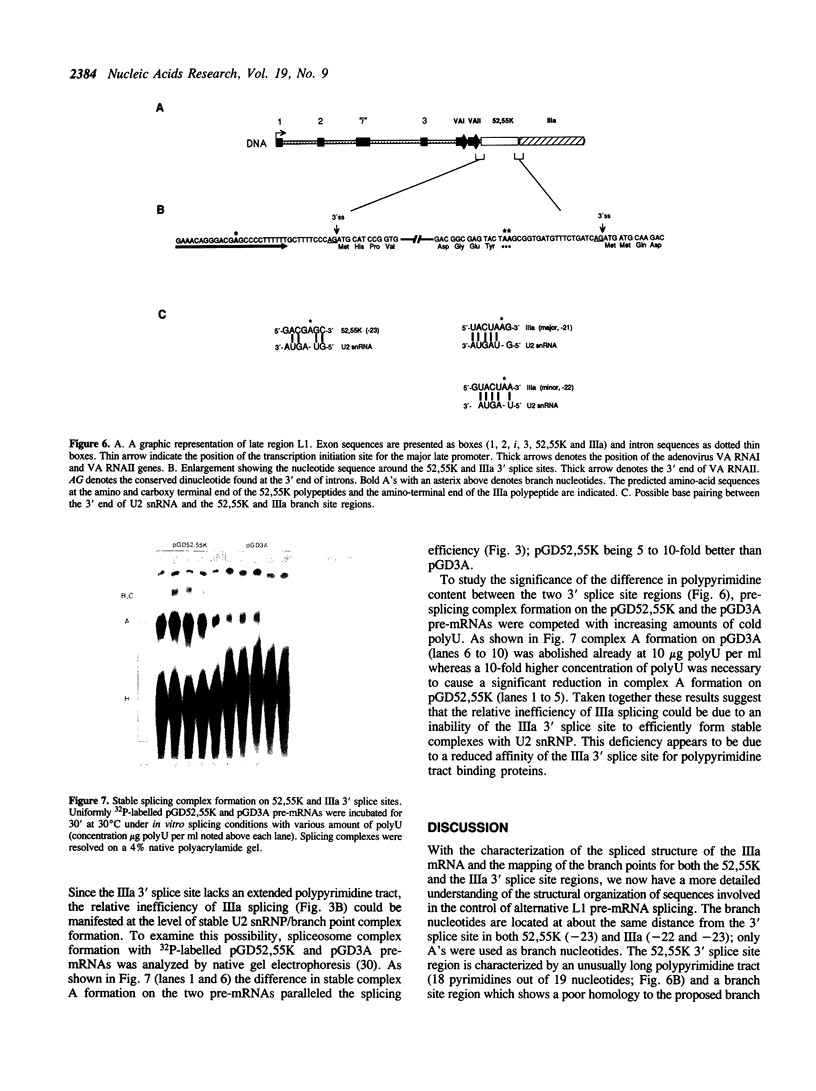


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akusjärvi G., Mathews M. B., Andersson P., Vennström B., Pettersson U. Structure of genes for virus-associated RNAI and RNAII of adenovirus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akusjärvi G., Persson H. Controls of RNA splicing and termination in the major late adenovirus transcription unit. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):420–426. doi: 10.1038/292420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akusjärvi G., Pettersson U. Sequence analysis of adenovirus DNA: complete nucleotide sequence of the spliced 5' noncoding region of adenovirus 2 hexon messenger RNA. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):841–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L. R., Maine E. M., Schedl P., Cline T. W. Sex-lethal, a Drosophila sex determination switch gene, exhibits sex-specific RNA splicing and sequence similarity to RNA binding proteins. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1037–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90248-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M., Sharp P. A. Structure of late adenovirus 2 heterogeneous nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 25;129(4):547–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindereif A., Green M. R. An ordered pathway of snRNP binding during mammalian pre-mRNA splicing complex assembly. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2415–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebli K., Gattoni R., Schmitt P., Hildwein G., Stevenin J. The 216-nucleotide intron of the E1A pre-mRNA contains a hairpin structure that permits utilization of unusually distant branch acceptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4852–4861. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou T. B., Zachar Z., Bingham P. M. Developmental expression of a regulatory gene is programmed at the level of splicing. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4095–4104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02755.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R. The spliced structures of adenovirus 2 fiber message and the other late mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):497–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Frendewey D., Keller W. Two spliceosomes can form simultaneously and independently on synthetic double-intron messenger RNA precursors. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1747–1755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delsert C., Morin N., Klessig D. F. cis-acting elements and a trans-acting factor affecting alternative splicing of adenovirus L1 transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4364–4371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeson R. B., Hedjran F., Yeakley J. M., Guise J. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Alternative production of calcitonin and CGRP mRNA is regulated at the calcitonin-specific splice acceptor. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):76–80. doi: 10.1038/341076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon L. P., Graham I. R., Griffiths A. D., Eperon I. C. Effects of RNA secondary structure on alternative splicing of pre-mRNA: is folding limited to a region behind the transcribing RNA polymerase? Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falvey E., Ziff E. Sequence arrangement and protein coding capacity of the adenovirus type 2 "i" leader. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):185–191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.185-191.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Ge H., Manley J. L. The role of the polypyrimidine stretch at the SV40 early pre-mRNA 3' splice site in alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):809–817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Manley J. L. Factors influencing alternative splice site utilization in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):738–748. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Blanco M. A., Jamison S. F., Sharp P. A. Identification and purification of a 62,000-dalton protein that binds specifically to the polypyrimidine tract of introns. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1874–1886. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Steitz J. A. A protein associated with small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles recognizes the 3' splice site of premessenger RNA. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):973–984. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90812-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Transcription of human histone genes in extracts from synchronized HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2713–2717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. M., Anderson K. P., Klessig D. F. Partial block to transcription of human adenovirus type 2 late genes in abortively infected monkey cells. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):378–385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.378-385.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller E. B., Noon W. A. Intron splicing: a conserved internal signal in introns of animal pre-mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7417–7420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohavong P., Gattoni R., LeMoullec J. M., Jacob M., Stévenin J. The orderly splicing of the first three leaders of the adenovirus-2 major late transcript. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1215–1229. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in formation of spliceosomes. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90614-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 influences 5' splice site selection by activating proximal sites. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W. Purification of a protein required for the splicing of pre-mRNA and its separation from the lariat debranching enzyme. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3571–3581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang K. M., Spritz R. A. RNA splice site selection: evidence for a 5' leads to 3' scanning model. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.6304877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariman E. C., van Beek-Reinders R. J., van Venrooij W. J. Alternative splicing pathways exist in the formation of adenoviral late messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 15;163(2):239–256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Control of adenovirus E1B mRNA synthesis by a shift in the activities of RNA splice sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):966–972. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. K., Green M. R. Mammalian U2 snRNP has a sequence-specific RNA-binding activity. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1562–1571. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. K., Green M. R. Splice site selection and ribonucleoprotein complex assembly during in vitro pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):319–329. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Wilson M. C. Regulation of adenovirus-2 gene expression at the level of transcriptional termination and RNA processing. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):113–118. doi: 10.1038/290113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofverstedt L. G., Hammarström K., Balgobin N., Hjertén S., Pettersson U., Chattopadhyaya J. Rapid and quantitative recovery of DNA fragments from gels by displacement electrophoresis (isotachophoresis). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 16;782(2):120–126. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilder S., Moore M., Logan J., Shenk T. The adenovirus E1B-55K transforming polypeptide modulates transport or cytoplasmic stabilization of viral and host cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):470–476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. The role of the mammalian branchpoint sequence in pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1268–1276. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. An RNA processing activity that debranches RNA lariats. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):135–140. doi: 10.1126/science.2990042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Greene J. M., Green M. R. Cryptic branch point activation allows accurate in vitro splicing of human beta-globin intron mutants. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):833–844. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Zamore P. D., Green M. R. A factor, U2AF, is required for U2 snRNP binding and splicing complex assembly. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90509-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing in the control of gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:527–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D., Lee S. I. Amount of RNA secondary structure required to induce an alternative splice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3194–3198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Adenovirus VA RNAI mediates a translational stimulation which is not restricted to the viral mRNAs. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):957–964. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Defective RNA splicing in the absence of adenovirus-associated RNAI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4690–4694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA binding specificity of hnRNP proteins: a subset bind to the 3' end of introns. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3519–3529. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund H., Pettersson U., Vennström B., Philipson L., Mathews M. B. A new species of virus-coded low molecular weight RNA from cells infected with adenovirus type 2. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Alibert C., Temsamani J., Reveillaud I., Cathala G., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. A protein that specifically recognizes the 3' splice site of mammalian pre-mRNA introns is associated with a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):755–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90518-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen A., Aleström P., Persson H., Katze M. G., Pettersson U. An adenovirus agnogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2539–2548. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Pederson T. A 62,000 molecular weight spliceosome protein crosslinks to the intron polypyrimidine tract. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):5995–6001. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.5995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Control of messenger RNA concentration by differential cytoplasmic half-life. Adenovirus messenger RNAs from transcription units 1A and 1B. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):231–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Manley J. L. Mammalian pre-mRNA branch site selection by U2 snRNP involves base pairing. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1553–1561. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Chou T. B., Bingham P. M. Evidence that a regulatory gene autoregulates splicing of its transcript. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4105–4111. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain S., Sambrook J., Roberts R. J., Keller W., Fried M., Dunn A. R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the leader segments in a cloned copy of adenovirus 2 fiber mRNA. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):851–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamore P. D., Green M. R. Identification, purification, and biochemical characterization of U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein auxiliary factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9243–9247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Leung H., Weiner A. M. The natural 5' splice site of simian virus 40 large T antigen can be improved by increasing the base complementarity to U1 RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):3018–3020. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.3018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in human U2 snRNA can suppress a branch site mutation. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1545–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]