Abstract
The cochlear nucleus, the first central auditory structure, performs initial stimulus processing and segregation of information into parallel ascending pathways. It also receives nonauditory inputs. Here we show in vivo that responses of dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN) principal neurons to sounds can change significantly depending on the presence or absence of inputs from the somatosensory dorsal column nucleus occurring before the onset of auditory stimuli. The effects range from short-term suppression of spikes lasting a few milliseconds at the onset of the stimulus to long-term increases or decreases in spike rate that last throughout the duration of an acoustic stimulus (up to several hundred milliseconds). The long-term effect requires only a single electrical stimulus pulse to initiate and seems to be similar to persistent activity reported in other parts of the brain. Among the DCN inhibitory interneurons, only the cartwheel cells show a long-term rate decrease that could account for the rate increases (but not the decreases) of DCN principal cells. Thus even at the earliest stages of auditory processing, the represented information is dependent on nonauditory context, in this case somatosensory events.
Keywords: auditory-evoked discharge, somatosensory events, dorsal column nuclei
the cochlear nucleus is the entry site of auditory information into the brain (Osen 1969). In addition to primary auditory afferents from the inner ear, its dorsal division (DCN) receives nonauditory inputs from a variety of sources (reviewed by Dehmel et al. 2008); prominent among these are somatosensory inputs from the dorsal column nuclei (DCoN; Itoh et al. 1987; Weinberg and Rustioni 1987; Wright and Ryugo 1996) and the spinal trigeminal nuclei (Haenggeli et al. 2005; Shore and Zhou 2006). The somatosensory input can influence the output neurons of the DCN, the pyramidal cells, with a mix of excitatory and inhibitory effects (Shore 2005; Young et al. 1995). The inhibitory effects predominate for inputs from the DCoN and seem to be transferred through cartwheel cells in the superficial DCN (Davis and Young 1997). The functional role of this multimodal interaction early in the auditory pathway is unclear. In the cat, the somatosensory inputs seem to be related to sound localization (Kanold and Young 2001; May 2000; Sutherland et al. 1998; Young and Davis 2002), but the diversity of pinna types and sources of nonauditory inputs across species suggest that sound localization may be only one aspect of a more general DCN function (Oertel and Young 2004). Interactions between auditory inputs and somatosensory ones from the trigeminal nuclei have been studied (Shore 2005; Shore and Zhou 2006), but the interactions with those from the DCoN have not.
Pyramidal cells show distinct integrative properties; in vitro studies (Kanold and Manis 1999; Manis 1990) have shown that these neurons can change their discharge patterns in response to a previous hyperpolarization due to the expression of an A-type K+ current (IKIF;). Thus somatosensory activation of inhibitory inputs to DCN principal neurons should modify their discharge patterns to auditory inputs (Kanold and Manis 2005). We therefore examined in vivo how activation of the somatosensory DCoN projections to the DCN affects the pattern of the sound-evoked responses. Because the strongest inputs from DCoN to DCN are from the portion of the DCoN representing the pinna (Young et al. 1995), we focused on that projection. We show two effects, a short-term direct inhibition lasting only slightly beyond the stimulus-evoked inhibitory postsynaptic potential and a long-term excitation or inhibition that can last for over 100 ms. These results indicate that the history of somatosensory activity can alter the responses to subsequent auditory stimuli. Preliminary results from this work were presented in abstract form (Kanold and Young 1999).
METHODS
Experiments were done in 22 adult cats weighing ∼3–4 kg; the cats had clean ears and clear tympanic membranes. Animals were used for other experiments at the same time. The experiments were done as described previously (Kanold and Young 2001), using a protocol approved by the Johns Hopkins Animal Care and Use Committee. Cats were decerebrated under ketamine (40 mg/kg im) plus xylazine (2 mg im) anesthesia; following decerebration, anesthesia was discontinued. Body temperature was maintained at 38.5°. Cats were paralyzed (gallamine triethiodide, 10 mg/h iv) and end-tidal CO2 was maintained at 4% with respiration. A platinum-iridium recording microelectrode was used to isolate single neurons in DCN, and a tungsten stimulating electrode was placed in a region of DCoN where neurons responded to touch or manipulation of the pinna.
Most of the data are from neurons with type IV response properties (Spirou and Young 1991), typical of DCN principal neurons in unanesthetized cats (Young 1980). All of the examples shown in results (see Figs. 1–4) are from principal neurons. Best frequencies (BFs) ranged between 1 and 50 kHz (mean of 16 ± 10 kHz). Responses were also recorded from neurons with properties associated with DCN inhibitory interneurons, namely type II neurons (from vertical cells; Rhode 1999) and complex-spiking neurons (presumed cartwheel cells; Davis and Young 1997).
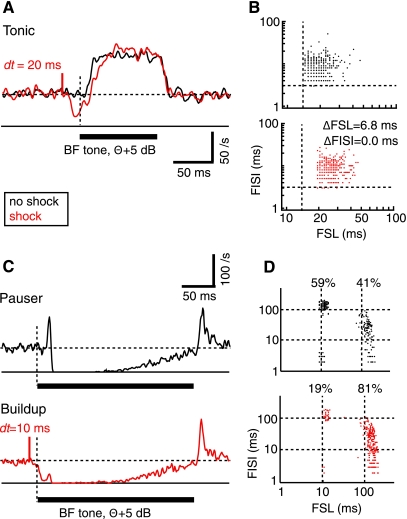
Fig. 1.
Stimulation of dorsal column nuclei (DCoN) suppresses the first spike in response to a best frequency (BF) tone. A and C: responses to acoustic stimuli alone (black) are compared with responses to the acoustic stimuli preceded (with time interval dt) by a single bipolar electrical stimulus pulse in DCoN (red). A: tonic response. C: pauser response from a different neuron. Acoustic stimulus is marked by the heavy horizontal bar. Horizontal dashed line is the spontaneous discharge rate. Short red vertical solid line shows the time of the electrical stimulus, labeled with dt the time delay between the electrical stimulus pulse and the start of the stimulus tone. First spike is delayed in the tonic response in A, and pauser in C is converted to a buildup response by the DCoN stimulus. B and D: scatter plots of the first spike latency (FSL; abscissa) and first interspike interval (FISI; ordinate) measured from responses to individual stimuli. Dashed lines show the minimum first spike latency and first interspike interval in the absence of DCoN stimulation in B. Cell in B showed an increased first spike latency by 6.8 ms (P < 0.05), while first interspike interval did not change (NS). In D, the fraction of stimulus trials giving pauser (short first spike latency) and buildup (long first spike latency) responses is shown. Dashed lines show 10 and 100 ms to aid in lining up the data points. Peristimulus time histograms (PSTHs) are not smoothed.
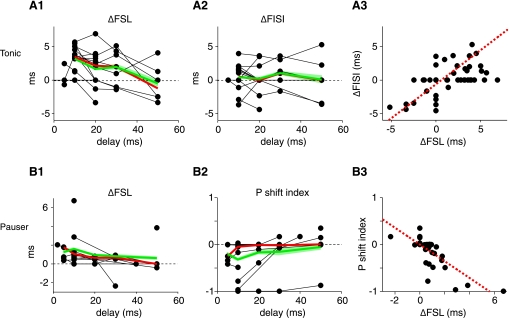
Fig. 2.
Electrical stimulation of the DCoN changes the tone-evoked discharge pattern in tonic (A) and pauser type (B) responses for delays (dt) up to 50 ms. A: changes in first spike latency (A1) and first interspike interval (A2) in tonic cases. Each point is the difference in latency or interspike interval between cases with and without electrical stimulation, plotted vs. dt; only significant (P < 0.05) cases are plotted as non-zero ΔFSL or ΔFISI. Heavy red and green lines show medians and means computed at dt values with 3 or more observations. Green shading indicates the ±1 SE. Note that not all neurons were tested with all latencies. A3: changes in first spike latency and first interspike interval are correlated (dashed red line) (ΔFISI = −0.6076 + 0.4881 * ΔFSL; r2 = 0.338). B: pauser responses. B1: first spike latency increases with electrical stimulation in pauser trials for which the onset spike is not suppressed. B2. Firing mode of pauser responses changes for short dt values. Plotted is the relative change in the number of pauser trials P as defined in the text. P of −1 indicates that all “pauser” trials have converted to “buildup” trials. A P shift index of 0 indicates no change. A3: changes in first spike latency and P are correlated (dashed red line; P index = 0.0009 − 0.1781 * ΔFSL; r2 = 0.611).
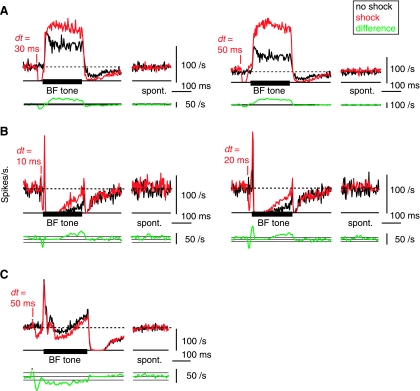
Fig. 3.
Long-term changes in the tone-evoked firing rate after DCoN stimulation. Examples from 3 neurons in which the effects of a DCoN stimulus pulse lasted for the duration of the 200 ms acoustic stimulus. A: DCoN stimulation at 2 dt values increased the tone-evoked firing rate of a tonic neuron by 41.9 and 108.1%, respectively (top traces); compare the black control PSTHs with the red with-shock PSTHs. Small or no differences occurred in the spontaneous rates (“spont”). To quantify the significance of rate changes, the rate differences (with-shock minus no-shock) are plotted below (bottom green traces, smoothed with 5-bin triangular filter) together with horizontal lines showing ±1 SD of the spontaneous rate from the PSTHs. In A, this SD is too small to see on this scale. Significant rate changes are present where the rate differences are outside the ±1 SD area. Note that large rate differences persist for the duration of the stimulus. B: same for a pauser neuron in which DCoN stimulation also increased the tone-evoked firing rate by 125 and 146.5%, respectively. Also note the increase in the onset peak at dt = 20 ms. Again, no change occurred in the spontaneous rate. C: pauser response in which the long-term effect was a decrease in discharge rate. For this case, the shock and no-shock trials were interleaved on alternating trials, as opposed to A and B where they were interleaved with other stimuli in 100-repetition sets. PSTHs (except rate differences) were not smoothed.
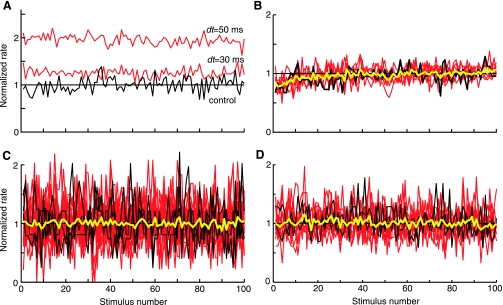
Fig. 4.
Long-term rate changes occur on the first trial of a stimulus set and do not build up over time. A: average discharge rate over the duration of the 100 acoustic stimuli of a stimulus block for the control (black, no shock) and with-shock (red) stimuli at 2 values of dt. Rates are normalized by the average rate during the control stimuli (horizontal line). Same data as Fig. 3A. B: same plot for a similar neuron in which all rates are normalized by the average rate during the last 50 presentations. Yellow line is the average of all the other plots. Rate transients at the start of these stimulus blocks are identical for shock and no-shock cases and presumably are rate adaptation. Despite the adaptation, no trend in rate differences is seen in these data. C and D: same plot for 25 cases in 3 neurons with the largest rate increases (C) and 13 cases in 2 neurons with the largest rate decreases (D). No trend in rate differences are seen across these neurons.
The acoustic stimulus was a 100- to 400-ms tone burst at the BF of the neuron, presented once per second usually at a sound level 5–15 dB above threshold, with repetitions at higher sound levels when possible. The electrical stimulus was a single bipolar pulse 200 μs/phase in the DCoN; the current level was adjusted to produce an inhibitory effect in DCN and was typically 10–50 μA. The electrical stimulus preceded the onset of sound by a time period dt, usually 10–50 ms. When possible, data were taken over a range of sound levels and dt values. Trials with and without the electrical stimulus were presented in groups of 100 repetitions. Usually, the 100-stimulus sets were repeated 2–4 times for a total of several hundred trials of each type. In some cases, the sets of 100 alternated (100 no-shock, 100 with shock, etc.), but in other cases only one no-shock block of trials was presented as the first block. In later experiments, shock and no-shock trials were interleaved on alternate stimulus presentations.
Peristimulus time histograms (PSTHs) were made from 100–400 trials and binned in 3-ms bins; for analysis of long-term changes (see Figs. 3 and 5), rate changes were evaluated by subtracting the control PSTH bin by bin from the PSTH in the presence of electrical stimulation. For plotting, the rate differences were smoothed with a five-point triangular filter.
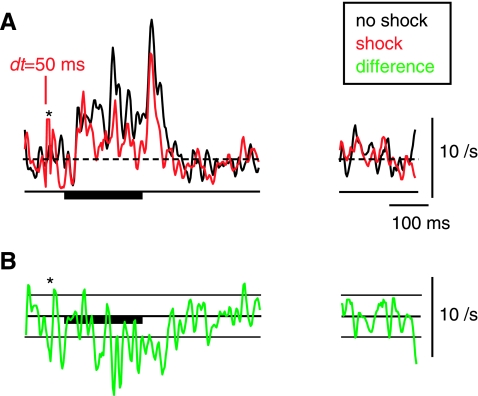
Fig. 5.
Long-term rate changes in a cartwheel-cell inhibitory interneuron. A: rates in response to a BF tone following somatosensory electrical stimulation, plotted as in Fig. 3. B: point-by-point rate difference between the shock (red) and no-shock (black) histograms, with horizontal lines at ±1 SD of the spontaneous activity in the (unsmoothed) PSTHs. Asterisks show where a large stimulus artifact was eliminated. Plotted PSTHs and the difference plot were smoothed with a 5-bin triangular filter.
As sound level changed, the neurons showed various responses to BF tones, classed here as tonic (meaning a steady “through” response with regular interspike intervals), pauser, and buildup (Godfrey et al. 1975b; Young and Brownell 1976). These patterns can be defined by the first spike latency and first interspike interval. The tonic pattern has a short first spike latency and a first interspike interval of comparable size. The pauser pattern shows a short first spike latency to the onset spike, followed by a long first interspike interval during the pause; after the onset spike, the neuron's response may be inhibited for as long as 100–200 ms. The buildup pattern is like the pauser, except that it shows no onset spike, so it has long first spike latency and (usually) a short first interspike interval. Note that all three response types can be observed in one neuron, depending on the stimulus frequency and sound level (Godfrey et al. 1975b). Typically, pauser responses show either the pauser or buildup patterns in individual trials, the difference being the presence or absence of the onset spike. The average firing pattern of the neuron in the PSTH is determined by the ratio of occurrence of these two distinct firing patterns in individual trials. If the majority of trials evoked pauser responses, the response was classified as a pauser. With the sound levels used here neurons showed the buildup pattern only in the presence of DCoN stimulation.
RESULTS
Short-term effects of stimulation in DCoN.
As expected from the inhibitory nature of the DCoN input to DCN principal cells, electrical stimulation in DCoN produced a direct short-latency suppression of spontaneous spiking with a latency of a few milliseconds; this inhibition has been characterized in previous work (Davis et al. 1996) and is evident (see Figs. 1 and 3) by the rate decrease preceding the tone onset. In addition, the initial spike(s) in response to the acoustic stimulus was suppressed or delayed, an effect most clearly seen in tonic responses (Fig. 1A; n = 15/15 cases). The suppression caused an extension of the first spike latency (by 6.8 ms in Fig. 1A; see Fig. 1B) and little change in first interspike interval. The change in first spike latency varied across neurons (Fig. 2, A1) but was observed for delays (dt) between the electrical pulse and the onset of the sound of up to 50 ms. In some units, an effect was seen only for the first spike in the train, as in Fig. 1A where first spike latency changed but first interspike interval did not. However, most neurons (12/15) showed significant increases or decreases of the first interspike interval by several milliseconds (Fig. 2A2). Significant effects on first interspike interval were observed for dt values up to 50 ms. The changes in first spike latency were correlated with the changes in first interspike interval (Fig. 2A3).
The electrical stimulation could suppress the onset spike in pauser responses (n = 14/15), so that the neuron fired fewer short first spike latency trials (Fig. 1C). In such cases, the average response converted to a buildup pattern as in the red histogram in Fig. 1C, bottom. For this case, the neuron fired in the pauser pattern on 59% of trials without a DCoN stimulus (Fig. 1D, black dots) but only on 19% of trials in the presence of DCoN stimulus (Fig. 1D, red dots). In the population of pauser responses, the average first spike latency of the remaining pauser trials increased by up to 3 ms (Fig. 2B1, all changes; P < 0.05; n = 11/15), while the first spike latency and first interspike interval of the buildup trials was unchanged (not shown). The extent of conversion of pauser to buildup responses was measured with the P index, defined as the relative change in the fraction of pauser trials (denoted P) and given by P = (Nelect_stim − Ncontrol)/Ncontrol, where Nx is the number of trials with pauser responses to stimulus x. Neurons varied in the extent of conversion (Fig. 2B2), and conversion was observed only for short interstimulus delays. The changes in first spike latency and P were correlated (Fig. 2B3).
Overall, electrical stimulation increased the first spike latency dramatically in the two ways described above by extending the latency of the first spike in tonic responses and by delaying or eliminating the first spike in pauser responses. These effects were visible at intervals of up to 50 ms between DCoN stimulation and tone onset but were progressively weaker as delay dt increased (Fig. 2).
Long-term effects of stimulation in DCoN.
While most neurons showed the short-term (<5 ms) changes described above, ∼30% of the neurons (18/55) also exhibited a persistent change in the auditory-evoked discharge pattern through the duration of a tone burst (Fig. 3). In 13/18 neurons, the change was to higher rate (Fig. 3, A and B) and in 5/18 neurons the change was to lower firing rate (Fig. 3C). In tonic cases (Fig. 3A), 10/33 neurons showed long-term changes, rate increases in 7 cases (up to 108%) and rate decreases in 3 cases (up to −73%). The changes in firing rate were visible from the onset of the tone-evoked response and persisted until the offset of the tone (tested up to 250 ms). Similar effects were observed in 8/22 pauser responses (Fig. 3, B and C) in that the discharge rate during the buildup phase was increased in 6 cases (up to 217%, as in Fig. 3B) and decreased in 2 cases (up to −61%, as in Fig. 3C).
The spontaneous firing rate of the neurons immediately after tone offset was sometimes changed slightly (as in Fig. 3A) but did not change in steady state; the rates marked “spont” in Fig. 3 are from the last 200 ms of the 800-ms interstimulus interval.
The long-term change in tone-evoked discharge rate was present even when the neuron's direct response to the electrical stimulus pulse had returned to spontaneous firing rate before tone onset, as in the dt = 50-ms cases in Fig. 3, A and C.
The presence or strength of the long-term change might be affected by the pairing conditions. For example, the strength of the effect might be increased by a larger number of pairing episodes or might depend on repetitive pairing episodes. We thus tested the temporal evolution of the rate changes. When no-shock control and with-shock stimulation trials were interleaved, we found that the effects were still observed (Fig. 3C), suggesting that the effect did not depend on repetitive pairing. Plotting the rates as a function of shock number in a series of shocks (100; Fig. 4) did not show either an increase or a decrease in the rate difference with time. In Fig. 4A, the with-shock rates for a unit showing an increase in rate under shock conditions are normalized by the average control rate. In Fig. 4, B–D, each shock rate series is normalized by its own average rate during the last half of the data, thus allowing direct comparison of the temporal evolution of the rates. Because all the rate series superimpose in these normalized plots, there was no buildup of the rate change over successive stimulus shocks, whether the effect was an increase (Fig. 4, B and C) or decrease in the rate (Fig. 4D). Together these results suggest that effects require only a single episode of pairing and that one pairing episode is sufficient to produce the full effect that can be seen with the particular stimulus used.
Long-term rate changes in inhibitory neurons.
Neurons associated with inhibitory response types in DCN were tested to evaluate the possibility that the long-term effects can be traced to inhibitory inputs. Type II neurons are recorded from vertical cells (Rhode 1999) and are the strongest source of sound-evoked inhibition in DCN principal cells (Spirou et al. 1999; Voigt and Young 1990). We tested the tone-evoked responses of type II neurons following DCoN stimulation and did not observe firing rate changes in the majority of them (20/24), although some neurons showed slight firing rate increases (n = 3, up to 12%) or decreases (n = 1, up to −14%). These rate changes were transient, lasting ∼50 ms.
Long-term rate changes were observed in cartwheel cells (Fig. 5). These neurons are inhibitory and terminate on DCN principal cells (Berrebi and Mugnaini 1991). They show responses to sound that may be strong or weak and are often complex and highly variable from stimulus to stimulus (Davis and Young 1997; Portfors and Roberts 2007). Cartwheel cells showed long-lasting decreases in sound-evoked responses after DCoN stimulation (n = 6/11 up to 30% decrease), which could explain a rate increase in principal cells.
DISCUSSION
We find that a brief single-pulse electrical stimulation of the somatosensory inputs to the DCN affects the firing rate of DCN pyramidal cells well after the direct hyperpolarization produced by the stimulus has abated. This is in contrast to other multimodal interactions such as in the superior colliculus where a coincidence between the inputs of different modalities is required (Meredith et al. 1987; Meredith and Stein 1986). Interactions between responses to sounds and electrical stimulation in the spinal trigeminal nucleus have been reported previously for multiunit and multiple-single unit responses (Shore 2005); these effects include both short- and long-term excitation and inhibition.
There are two distinct effects of somatosensory stimulation: short term and long term. The short-term effects include increases in the first spike latency and first interspike interval after the inhibition, as well as a loss of the first spike (Figs. 1 and 2). These changes in vivo are consistent with the recruitment of a transient potassium current (IKIF) by deinactivation during the inhibition, previously studied in vitro (Kanold and Manis 2005). The potassium channels produce a transient outward current when the membrane is depolarized by the acoustic stimulus, thus prolonging the inhibitory effect sufficiently to act on the first spike produced by the sound (Kanold and Manis 1999; Manis 1990). Modeling the effects of IKIF shows that the latency of responses to injected current, the first interval in the same circumstance, and the existence of the first pauser spike can be produced by activation of this current (Kanold and Manis 2001). Those effects are induced by a hyperpolarization followed by depolarization, similar to the presumed synaptic sequence studied here. Although there are some quantitative differences in the first interspike interval behavior between the in vitro and model data on the one hand and the present in vivo data, the results are in qualitative agreement. Thus a parsimonious explanation for the short-term effects is the activation of IKIF. This hypothesis is supported by the correlated changes in first spike latency and first interspike interval (Fig. 2A3) and between first spike latency and suppression of the first spike in pauser neurons (Fig. 2B3), as is expected for a single-element mechanism.
The second effect is a more long-lasting change in firing rate for the duration of a succeeding sound stimulus (Figs. 3 and 5). The change may be either an increase or a decrease and is observed as long as the sound is left on (a few hundred milliseconds); however, there is little or no effect on the spontaneous activity following the sound. Although the recovery of the rate change was not tracked here (stimuli were 100–400 ms in duration), the demonstration of the phenomenon with interleaved stimuli (Fig. 3C) and the fact that the rate change does not cumulate over multiple stimulus presentations (Fig. 4) suggest that it recovers within a time period of <1 s.
This long-term effect is clearly different from the suppression or delay of the first spike in response to the sound. The existing data are not sufficient to answer questions about potential links between the short and long-term effects. For example, the cases used as examples of the long-term effect in Fig. 3 do not reliably show the expected short-term effects. This lack of connection is consistent with the suggestion that the short-term effect is caused by deinactivation of the KIF current, because that current does not have time constants nearly long enough to cause the long-term effect (Kanold and Manis 1999).
The long-term effects reported previously by Shore (2005) for inputs from the spinal trigeminal nucleus are generally similar to those reported here. However, inhibition was more commonly seen than excitation in the data reported by Shore and some of the responses appear to differ in that longer latencies were sometimes seen and the duration of the effect varied. It is not clear whether these differences are due to the species (rat vs. cat), the source of the inputs being stimulated (spinal trigeminal vs. dorsal column), or differences in technique.
Possible mechanisms for the long-term effect.
Potential mechanisms for the long-term effects must account for four aspects of the data: 1) the rate changes are evoked by a single stimulus to the somatosensory inputs; 2) the rate changes are observed for responses to acoustic stimuli (plasticity at the somatosensory synaptic inputs was not tested) and not in spontaneous activity; 3) the rate changes must last for a time duration of a few hundred milliseconds or must be switched off by the termination of an acoustic stimulus; and 4) the rate changes can be either positive or negative. Note that the long-term effect occurs after the termination of the direct effect of the stimulus pulse, the sharp drops in rate occurring just after the stimulus pulse and lasting <10 ms in Fig. 3.
The long-term rate changes resemble persistent activity observed in various parts of the brain following a single stimulus (reviewed by Major and Tank 2004). Sometimes the persistent activity depends on reverberation in the networks associated with the neuron under study (e.g., Mann et al. 2009; Wang 2001) in that it can be modulated or terminated by synaptic agonists and antagonists. In other cases, persistent activity is generated by intrinsic cellular mechanisms and does not depend on the network (e.g., Egorov et al. 2002; Yoshida and Hasselmo 2009).
Intrinsic cellular mechanisms for persistent activity often involve activation of noninactivating ion channels to produce maintained activity (Major and Tank 2004). Although such channels are present in some neurons in DCN (Kim and Trussell 2009), this form of persistence produces maintained firing that would show up as a change in spontaneous activity that is not observed here.
The commonly studied forms of neural plasticity and long-term potentiation (LTP) and depression (LTD), including endocannabenoid-mediated effects, are observed in DCN neurons including DCN principal cells (Fujino and Oertel 2003; Tzounopoulos et al. 2004). However, the reported forms of LTP and LTD in the DCN affect the strength of parallel fibers inputs and do not seem to change the strength of auditory synapses on DCN principal neurons, as would be required by our data. It remains to be shown that forms of LTP or LTD exist on the auditory nerve synapse on DCN principal neurons.
In the vestibular nucleus, so-called “firing rate potentiation” increases the excitability of the cells by downmodulating potassium channels, thus increasing the response gain for stimuli without necessarily changing spontaneous activity, as observed here (Nelson et al. 2003; Smith et al. 2002). Firing rate potentiation, like LTP and LTD, has been induced by tetanic stimulation, on the order of tens of stimuli, as opposed to the single stimulus required here. Nevertheless firing rate potentiation is a possible mechanism, if it would produce short-term changes when stimulated by only one pulse.
Our data can also be explained by a network mechanism. There are several possibilities for network effects in the DCN. The axons of pyramidal cells form recurrent excitatory projections that could support persistent activity (Smith and Rhode 1985). However, it is likely that both spontaneous and sound-driven responses would be affected, making recurrent circuits a less attractive explanation. Another possibility is a modulation of the inhibitory inputs to the principal neuron under study. Such a mechanism is attractive because the known inhibitory interneurons in DCN have little or no spontaneous activity themselves [cartwheel cells (Davis and Young 1997; Portfors and Roberts 2007); onset-C neurons (Smith and Rhode 1989); and type II neurons or vertical cells (Spirou et al. 1999)], thus explaining the lack of a significant effect on the spontaneous activity of principal cells. Of the interneurons targeting DCN principal cells, the properties of type II neurons do not seem consistent with the effects needed to produce long-term changes, because the minority of type II neurons that did show rate changes did not show long-lasting changes of the type required to explain persistence in principal cells. Onset-C neurons were not studied here, but they have been reported previously to show only weak responses to somatosensory stimuli, similar to type II neurons (Young et al. 1995).
A possible locus for generation of the long-lasting changes are cartwheel cells (Berrebi and Mugnaini 1991). These inhibitory neurons mediate somatosensory inputs to principal cells (Davis and Young 1997; Kanold and Young 2001) and show variable degrees of response to sound (Davis and Young 1997; Portfors and Roberts 2007). Here they were shown to display long-term rate decreases in their responses to sound following a somatosensory stimulus (Fig. 5). Cartwheel cells participate in a recurrent network of interconnections with other cartwheel cells (Berrebi and Mugnaini 1991; Golding and Oertel 1997), and the receptor channels in the synapses have been reported to be conditionally excitatory or inhibitory, depending on the membrane potential of the cell relative to the chloride equilibrium potential (Golding and Oertel 1996; Kim and Trussell 2009). Thus the cartwheel network could conceivably maintain a slightly elevated or a slightly depressed discharge rate in response to a pulse of spikes from a somatosensory input, depending on the preexisting membrane potentials of the cells. This rate change could produce long-term rate modification in principal cells like that seen here. However, this possibility still requires a mechanism to terminate the altered cartwheel rate at the end of a tone burst. This might be provided by events associated with the termination of the acoustic stimulus, such as a loss of the acoustically driven inputs or an off response. These or similar effects could change the state of the postulated cartwheel network. These multiple possibilities require further study to work out the mechanism for persistence in DCN neurons.
Conclusions and Implications
These results show that the auditory-evoked discharge pattern relayed to higher centers is modulated by nonauditory inputs occurring immediately before the acoustic stimulus. Thus the auditory-evoked firing pattern is dependent on nonauditory context. These contextual effects could be important in signaling auditory-relevant somatosensory events, such as sound-producing movements of the ears, sounds produced by touching or moving the vibrissae or other parts of the body, or shifts in the positions of the ears that are important in localization of sounds. The changes reported here could be an expression in vivo of forms of plasticity in the synaptic circuitry of the DCN usually studied under more artificial conditions in vitro (e.g., Nelson et al. 2003). It is important to determine whether the long-term effects are a relatively fixed system that provides signals to the auditory system about nonauditory events or a plastic system that learns associations between auditory and nonauditory events, as in the fish electrosensory system (Bell et al. 1999). An exact theory of the usefulness of this plasticity cannot be specified at present, but future studies of auditory processing above brain stem level have to take the nonauditory context into account.
GRANTS
This work was supported by National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders DC-00979 and DC-00115.
DISCLOSURES
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We appreciated comments on the manuscript by Sean Slee and Paul Nelson.
REFERENCES
- Bell CC, Han VZ, Sugawara Y, Grant K. Synaptic plasticity in the mormyrid electrosensory lobe. J Exp Biol 202: 1339–1347, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrebi AS, Mugnaini E. Distribution and targets of the cartwheel cell axon in the dorsal cochlear nucleus of the guinea pig. Anat Embryol 183: 427–454, 1991 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis KA, Miller RL, Young ED. Effects of somatosensory and parallel-fiber stimulation on neurons in dorsal cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 76: 3012–3024, 1996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis KA, Young ED. Granule cell activation of complex-spiking neurons in dorsal cochlear nucleus. J Neurosci 17: 6798–6806, 1997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehmel S, Cui YL, Shore SE. Cross-modal interactions of auditory and somatic inputs in the brainstem and midbrain and their imbalance in tinnitus and deafness. Am J Audiol 17: S193–S209, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egorov AV, Hamam BN, Fransen E, Hasselmo ME, Alonso AA. Graded persistent activity in entorhinal cortex neurons. Nature 420: 173–178, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujino K, Oertel D. Bidirectional synaptic plasticity in the cerebellum-like mammalian dorsal cochlear nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 265–270, 2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey DA, Kiang NYS, Norris BE. Single unit activity in the dorsal cochlear nucleus of the cat. J Comp Neurol 162: 269–284, 1975b [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding NL, Oertel D. Context-dependent synaptic action of glycinergic and GABAergic inputs in the dorsal cochlear nucleus. J Neurosci 16: 2208–2219, 1996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding NL, Oertel D. Physiological identification of the targets of cartwheel cells in the dorsal cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 78: 248–260, 1997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenggeli CA, Pongstaporn T, Doucet JR, Ryugo DK. Projections from the spinal trigeminal nucleus to the cochlear nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 484: 191–205, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K, Kamiya H, Mitani A, Yasui Y, Takada M, Mizuno N. Direct projection from the dorsal column nuclei and the spinal trigeminal nuclei to the cochlear nuclei in the cat. Brain Res 400: 145–150, 1987 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanold PO, Manis PB. A physiologically based model of discharge pattern regulation by transient K+ currents in cochlear nucleus pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol 85: 523–538, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanold PO, Manis PB. Encoding the timing of inhibitory inputs. J Neurophysiol 93: 2887–2897, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanold PO, Manis PB. Transient potassium currents regulate the discharge patterns of dorsal cochlear nucleus pyramidal cells. J Neurosci 19: 2195–2208, 1999 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanold PO, Young ED. Proprioceptive information from the pinna provides somatosensory input to cat dorsal cochlear nucleus. J Neurosci 21: 7848–7858, 2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanold PO, Young ED. Somatosensory inputs modify the acoustic evoked discharge pattern of dorsal cochlear nucleus principal cells. In: Abstracts of the Association of Research in Otolaryngology. St. Petersburg, FL: Association of Research in Otolaryngology, 1999 [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y, Trussell LO. Negative shift in the glycine reversal potential mediated by a Ca2+ and pH-dependent mechanism in interneurons. J Neurosci 29: 11495–11510, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major G, Tank D. Persistent neural activity: prevalence and mechanisms. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14: 675–684, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manis PB. Membrane properties and discharge characteristics of guinea pig dorsal cochlear nucleus neurons studied in vitro. J Neurosci 10: 2338–2351, 1990 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann EO, Kohl MM, Paulsen O. Distinct roles of GABAA and GABAB receptors in balancing and terminating persistent cortical activity. J Neurosci 29: 7513–7518, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May BJ. Role of the dorsal cochlear nucleus in the sound localization behavior of cats. Hear Res 148: 74–87, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith MA, Nemitz JW, Stein BE. Determinants of multisensory integration in superior colliculus neurons. I. Temporal factors. J Neurosci 7: 3215–3229, 1987 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith MA, Stein BE. Visual, auditory, and somatosensory convergence on cells in superior colliculus results in multisensory integration. J Neurophysiol 56: 640–662, 1986 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson AB, Krispel CM, Sekirnjak C, du Lac S. Long-lasting increases in intrinsic excitability triggered by inhibition. Neuron 40: 609–620, 2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertel D, Young ED. What's a cerebellar circuit doing in the auditory system? Trends Neurosci 27: 104–110, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osen KK. Cytoarchitecture of the cochlear nuclei in the cat. J Comp Neurol 136: 453–482, 1969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portfors CV, Roberts PD. Temporal and frequency characteristics of cartwheel cells in the dorwal cochlear nucleus of the awake mouse. J Neurophysiol 98: 744–756, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode WS. Vertical cell responses to sound in cat dorsal cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 82: 1019–1032, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore SE. Multisensory integration in the dorsal cochlear nucleus: unit responses to acoustic and trigeminal ganglion stimulation. Eur J Neurosci 21: 3334–3348, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore SE, Zhou J. Somatosensory influence on the cochlear nucleus and beyond. Hear Res 216–217: 90–99, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith MR, Nelson AB, Du Lac S. Regulation of firing response gain by calcium-dependent mechanisms in vestibular nucleus neurons. J Neurophysiol 87: 2031–2042, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith PH, Rhode WS. Electron microscopic features of physiologically characterized, HRP-labeled fusiform cells in the cat dorsal cochlear nucleus. J Comp Neurol 237: 127–143, 1985 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith PH, Rhode WS. Structural and functional properties distinguish two types of multipolar cells in the ventral cochlear nucleus. J Comp Neurol 282: 595–616, 1989 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirou GA, Davis KA, Nelken I, Young ED. Spectral integration by type II interneurons in dorsal cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 82: 648–663, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirou GA, Young ED. Organization of dorsal cochlear nucleus type IV unit response maps and their relationship to activation by bandlimited noise. J Neurophysiol 65: 1750–1768, 1991 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland DP, Masterton RB, Glendenning KK. Role of acoustic striae in hearing: reflexive responses to elevated sound-sources. Behav Brain Res 97: 1–12, 1998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzounopoulos T, Kim Y, Oertel D, Trussell LO. Cell-specific, spike timing-dependent plasticities in the dorsal cochlear nucleus. Nat Neurosci 7: 719–725, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt HF, Young ED. Cross-correlation analysis of inhibitory interactions in dorsal cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 64: 1590–1610, 1990 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang XJ. Synaptic reverberation underlying mnemonic persistent activity. Trends Neurosci 24: 455–463, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg RJ, Rustioni A. A cuneocochlear pathway in the rat. Neuroscience 20: 209–219, 1987 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright DD, Ryugo DK. Mossy fiber projections from the cuneate nucleus to the dorsal cochlear nucleus of rat. J Comp Neurol 365: 159–172, 1996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M, Hasselmo ME. Persistent firing supported by an intrinsic cellular mechanism in a component of the head direction system. J Neurosci 29: 4945–4952, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young ED. Identification of response properties of ascending axons from dorsal cochlear nucleus. Brain Res 200: 23–38, 1980 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young ED, Brownell WE. Responses to tones and noise of single cells in dorsal cochlear nucleus of unanesthetized cats. J Neurophysiol 39: 282–300, 1976 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young ED, Davis KA. Circuitry and function of the dorsal cochlear nucleus. In: Integrative Functions in the Mammalian Auditory Pathway, edited by Oertel D, Popper AN, Fay RR. New York: Springer Verlag, 2002, p. 160–206 [Google Scholar]
- Young ED, Nelken I, Conley RA. Somatosensory effects on neurons in dorsal cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 73: 743–765, 1995 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]