Abstract
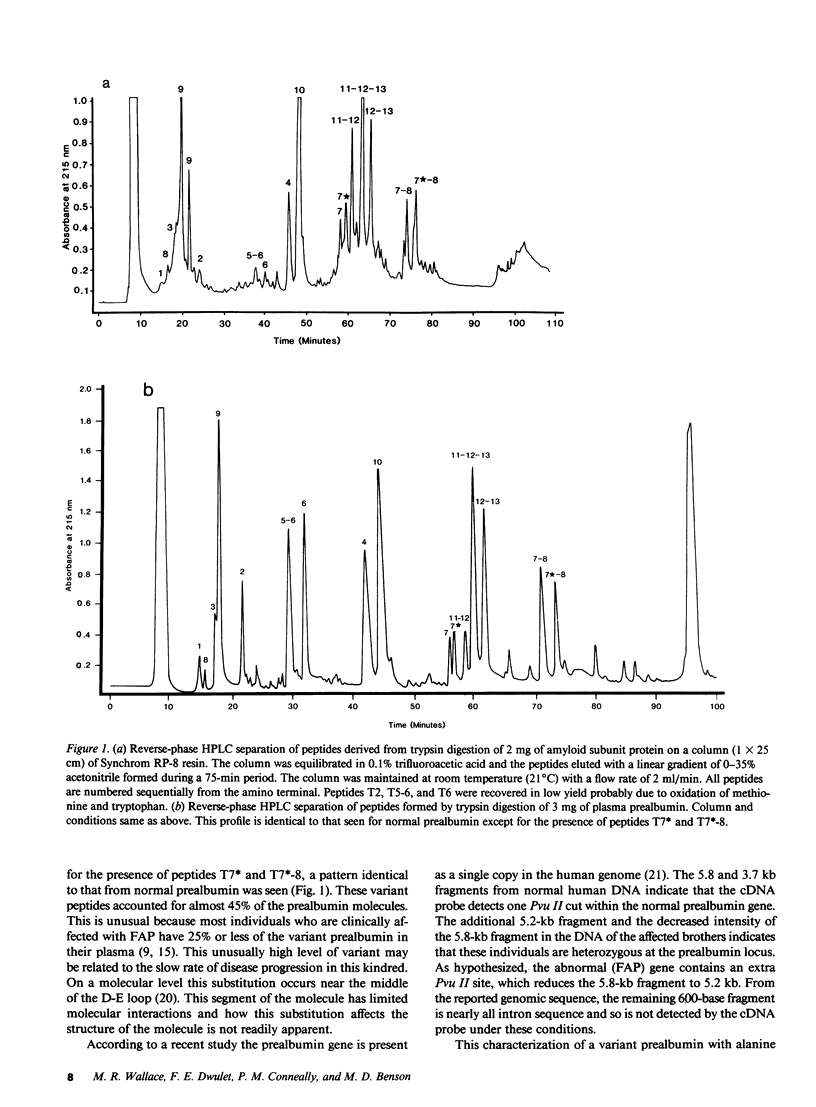
Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP) is an autosomal dominant late-onset disorder characterized by the extracellular deposition of amyloid fibrils. In all cases studied these fibrils have been found to be composed of plasma prealbumin (transthyretin) containing a single amino acid substitution. Biochemical studies were conducted on amyloid from one patient and plasma prealbumin from his affected brother, both part of a large kindred from the Appalachian region of the United States. Sequence analysis of the amyloid subunit protein showed it to be prealbumin with about two-thirds of the molecules containing a substitution of alanine for threonine at position 60. Studies of the plasma prealbumin showed that the same substitution was present in 40-45% of the protein. Based on this substitution and the prealbumin cDNA sequence, a Pvu II restriction fragment length DNA polymorphism (RFLP) was predicted and demonstrated in DNA of both patients as well as other family members. This RFLP confirms the predicted DNA mutation responsible for the protein variant, and represents an accurate method for detection of this gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRADE C. A peculiar form of peripheral neuropathy; familiar atypical generalized amyloidosis with special involvement of the peripheral nerves. Brain. 1952 Sep;75(3):408–427. doi: 10.1093/brain/75.3.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson R. Hereditary amyloidosis with polyneuropathy. Acta Med Scand. 1970 Jul-Aug;1-2(1):85–94. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1970.tb08009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade C., Araki S., Block W. D., Cohen A. S., Jackson C. E., Kuroiwa Y., Nissim J., Sohar E., McKusick V. A., Van Allen M. W. Hereditary amyloidosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):902–915. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D., Cohen A. S. Generalized amyloid in a family of Swedish origin. A study of 426 family members in seven generations of a new kinship with neuropathy, nephropathy, and central nervous system involvement. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Apr;86(4):419–424. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-4-419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D., Dwulet F. E. Prealbumin and retinol binding protein serum concentrations in the Indiana type hereditary amyloidosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Dec;26(12):1493–1498. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D. Partial amino acid sequence homology between an heredofamilial amyloid protein and human plasma prealbumin. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1035–1041. doi: 10.1172/JCI110114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Geisow M. J., Oatley S. J., Rérat B., Rérat C. Structure of prealbumin: secondary, tertiary and quaternary interactions determined by Fourier refinement at 1.8 A. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):339–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90368-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwulet F. E., Benson M. D. Polymorphism of human plasma thyroxine binding prealbumin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):657–662. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90831-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwulet F. E., Benson M. D. Primary structure of an amyloid prealbumin and its plasma precursor in a heredofamilial polyneuropathy of Swedish origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):694–698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J., Vital C., Vallat J. M., Lagueny A., Ferrer X. Neuropathies amyloides familiales dans trois familles d'origine française. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1983;139(4):259–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kametani F., Tonoike H., Hoshi A., Shinoda T., Kito S. A variant prealbumin-related low molecular weight amyloid fibril protein in familial amyloid polyneuropathy of Japanese origin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):622–628. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen A. H., Mitzen E. J., Hans M. B., Peng S. K., Bailey R. O. Familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 1985 Nov-Dec;8(9):733–749. doi: 10.1002/mus.880080902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahloudji M., Teasdall R. D., Adamkiewicz J. J., Hartmann W. H., Lambird P. A., McKusick V. A. The genetic amyloidoses with particular reference to hereditary neuropathic amyloidosis, type II (Indiana or Rukavina type). Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 Jan;48(1):1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazato M., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Tawara S., Matsuo H., Araki S. Revised analysis of amino acid replacement in a prealbumin variant (SKO-III) associated with familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy of Jewish origin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 28;123(3):921–928. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Franklin E. C., Prelli F., Frangione B. A variant of prealbumin from amyloid fibrils in familial polyneuropathy of Jewish origin. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):989–993. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Prelli F., Franklin E. C., Frangione B. Primary structure of an amyloid prealbumin variant in familial polyneuropathy of Jewish origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):539–542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraiva M. J., Birken S., Costa P. P., Goodman D. S. Amyloid fibril protein in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy, Portuguese type. Definition of molecular abnormality in transthyretin (prealbumin). J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):104–119. doi: 10.1172/JCI111390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Sakaki Y., Matsuo H., Goto I., Kuroiwa Y., Sahashi I., Takahashi A., Shinoda T., Isobe T., Takagi Y. Diagnosis of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy by recombinant DNA techniques. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):636–642. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90586-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Cohen A. S. The prealbumin nature of the amyloid protein in familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP)-swedish variety. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1326–1332. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90764-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawara S., Nakazato M., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Araki S. Identification of amyloid prealbumin variant in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (Japanese type). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):880–888. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Allen M. W., Frohlich J. A., Davis J. R. Inherited predisposition to generalized amyloidosis. Clinical and pathological study of a family with neuropathy, nephropathy, and peptic ulcer. Neurology. 1969 Jan;19(1):10–25. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.1.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Naylor S. L., Kluve-Beckerman B., Long G. L., McDonald L., Shows T. B., Benson M. D. Localization of the human prealbumin gene to chromosome 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):753–758. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91956-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




