Abstract
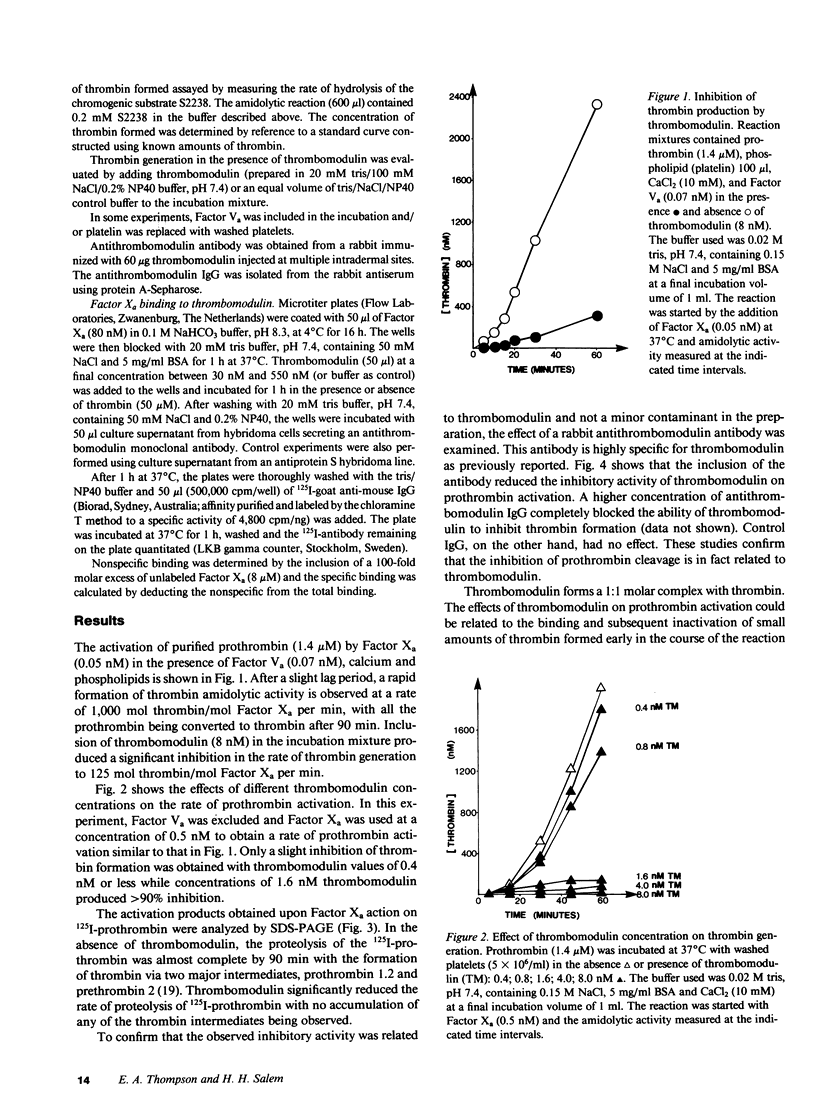
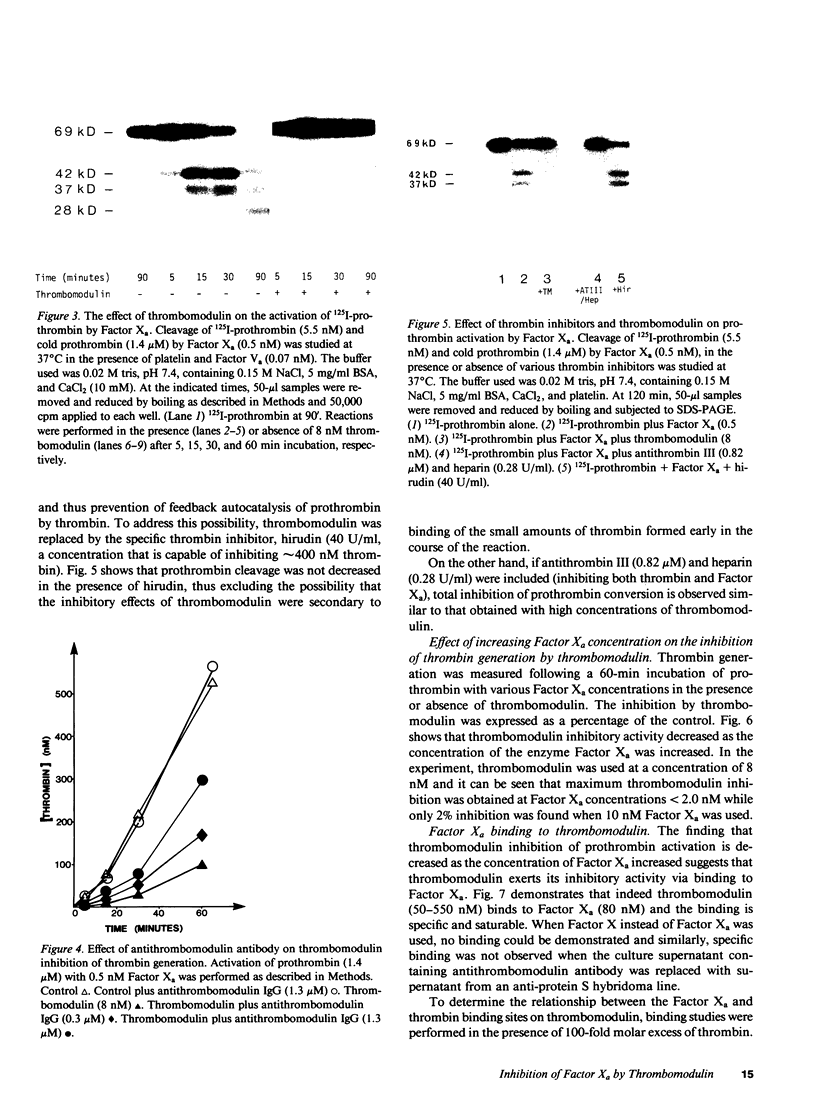
Human thrombomodulin significantly inhibited the rate of prothrombin conversion to thrombin by Factor Xa in the presence of phospholipid or platelets, calcium, and Factor Va. Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of 125I-prothrombin activation revealed that thrombomodulin reduced the rate of prothrombin activation but did not alter the cleavage pattern. The inhibition was reversed by the inclusion of a highly specific rabbit antithrombomodulin antibody. If thrombomodulin was replaced by hirudin, the rate of thrombin generation was not decreased excluding the possibility that the inhibition by thrombomodulin was secondary to the binding of small amounts of thrombin formed early in the reaction and the prevention of feedback breakdown of prothrombin by thrombin. The inhibitory activity of thrombomodulin was overcome by increasing the concentration of Factor Xa and specific, saturable binding of thrombomodulin to Factor Xa was demonstrated. These results indicate that thrombomodulin binds to Factor Xa and thereby inhibits the activity of the prothrombinase complex.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Esmon C. T., Esmon N. L., Harris K. W. Complex formation between thrombin and thrombomodulin inhibits both thrombin-catalyzed fibrin formation and factor V activation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7944–7947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Jackson C. M. The conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. III. The factor Xa-catalyzed activation of prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7782–7790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G. Identification of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2249–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G., Jackson C. M. A plausible mechanism for prothrombin activation by factor Xa, factor Va, phospholipid, and calcium ions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8045–8047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Carroll R. C., Esmon C. T. Thrombomodulin blocks the ability of thrombin to activate platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12238–12242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Gardiner J. E., Griffin J. H., Zimmerman T. S. Proteolytic inactivation of human factor VIII procoagulant protein by activated human protein C and its analogy with factor V. Blood. 1984 Feb;63(2):486–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Majerus P. W. Purification and characterization of human coagulation factor V. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1002–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I., Salem H. H., Ishii H., Majerus P. W. Human thrombomodulin is not an efficient inhibitor of the procoagulant activity of thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):987–991. doi: 10.1172/JCI111800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr, Majerus P. W. The synthesis of sulfated dextran beads for isolation of human plasma coagulation factors II, IX, and X. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):304–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Properties of the factor Xa binding site on human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6908–6916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Functional properties of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5532–5535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G. Evidence for the formation of an ester between thrombin and heparin cofactor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 20;405(2):380–387. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M., Greenberg C. S., Shuman M. A. Characterization of the effects of cultured vascular cells on the activation of blood coagulation. Blood. 1983 Jun;61(6):1155–1162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M., Shuman M. A. Prothrombin is activated on vascular endothelial cells by factor Xa and calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):7001–7005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.7001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem H. H., Maruyama I., Ishii H., Majerus P. W. Isolation and characterization of thrombomodulin from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12246–12251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Stenflo J., Dahlbäck B., Teodorsson B. Inactivation of human coagulation factor V by activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1914–1920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Davie E. W. Preparation and properties of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):401–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J., Sexton P. W., Esmon C. T. The inhibition of blood coagulation by activated Protein C through the selective inactivation of activated Factor V. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 7;571(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]