Abstract
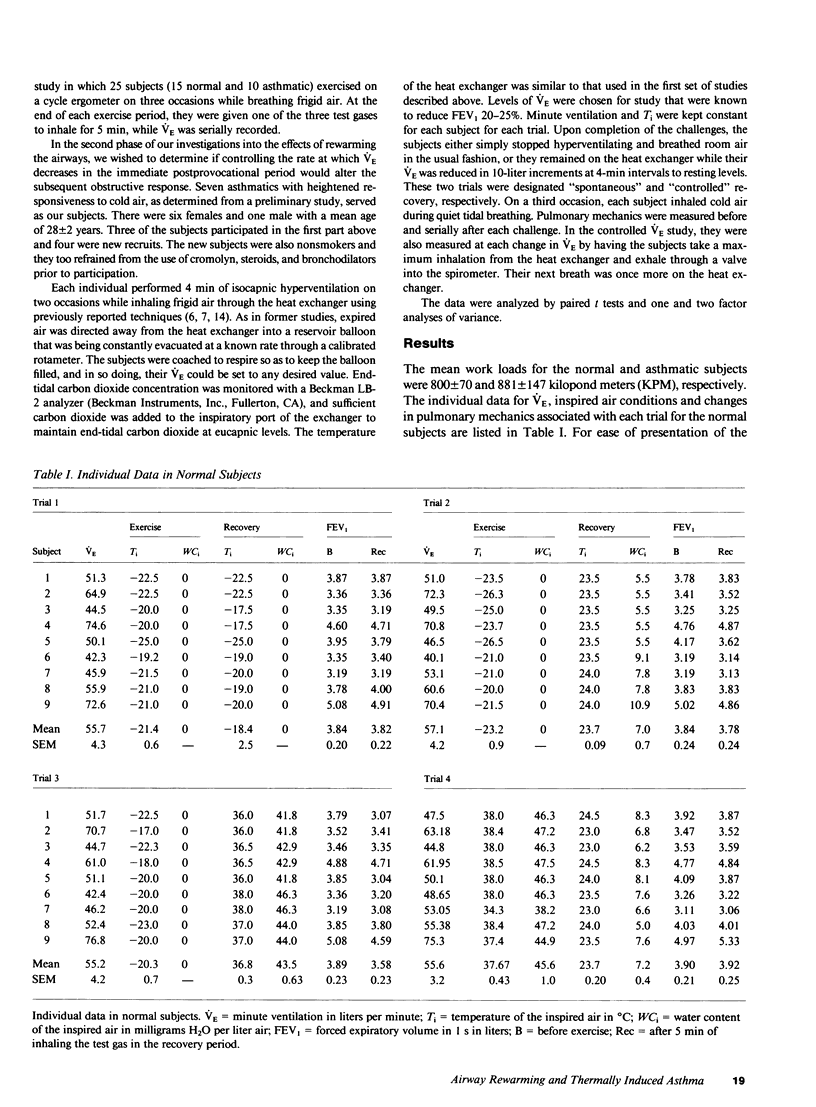
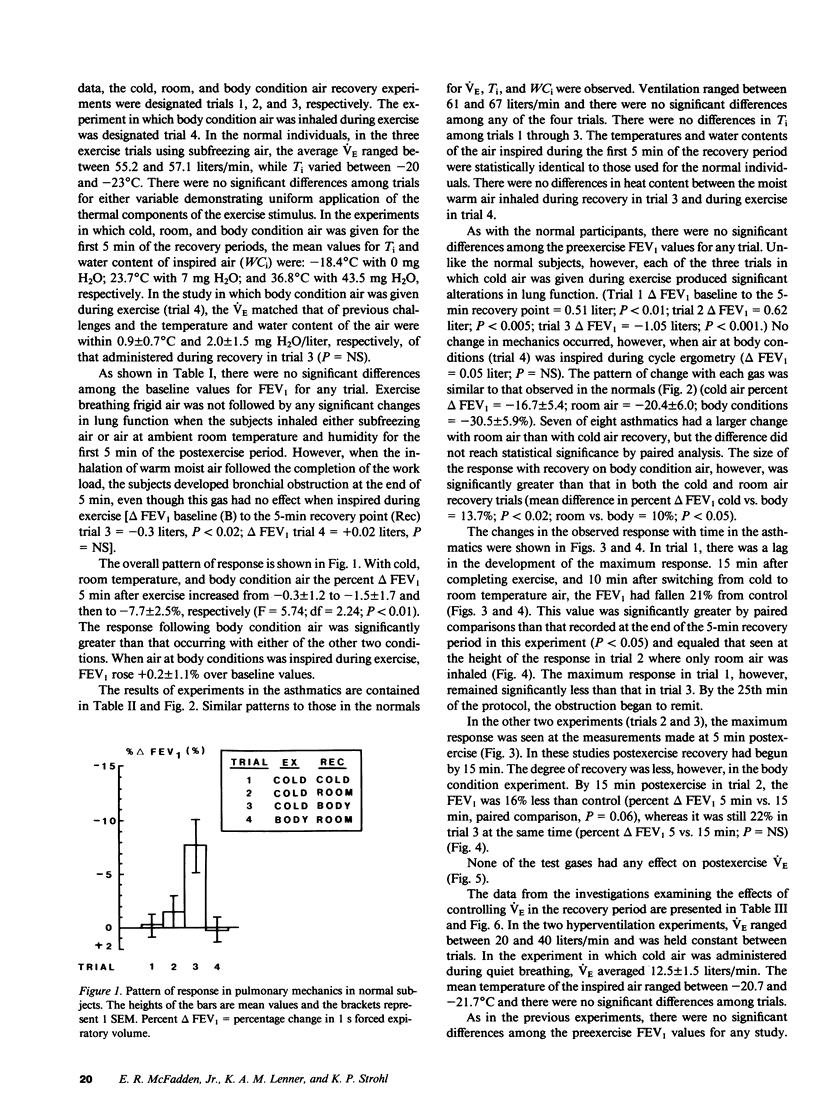
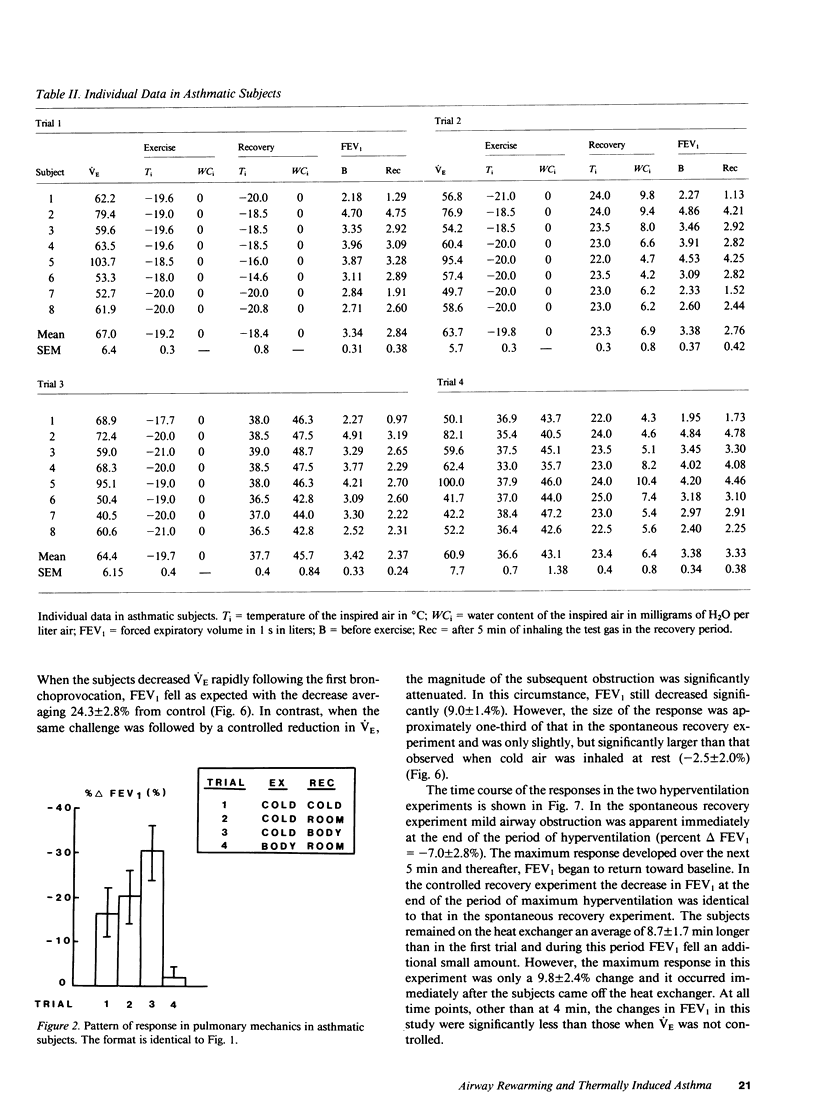
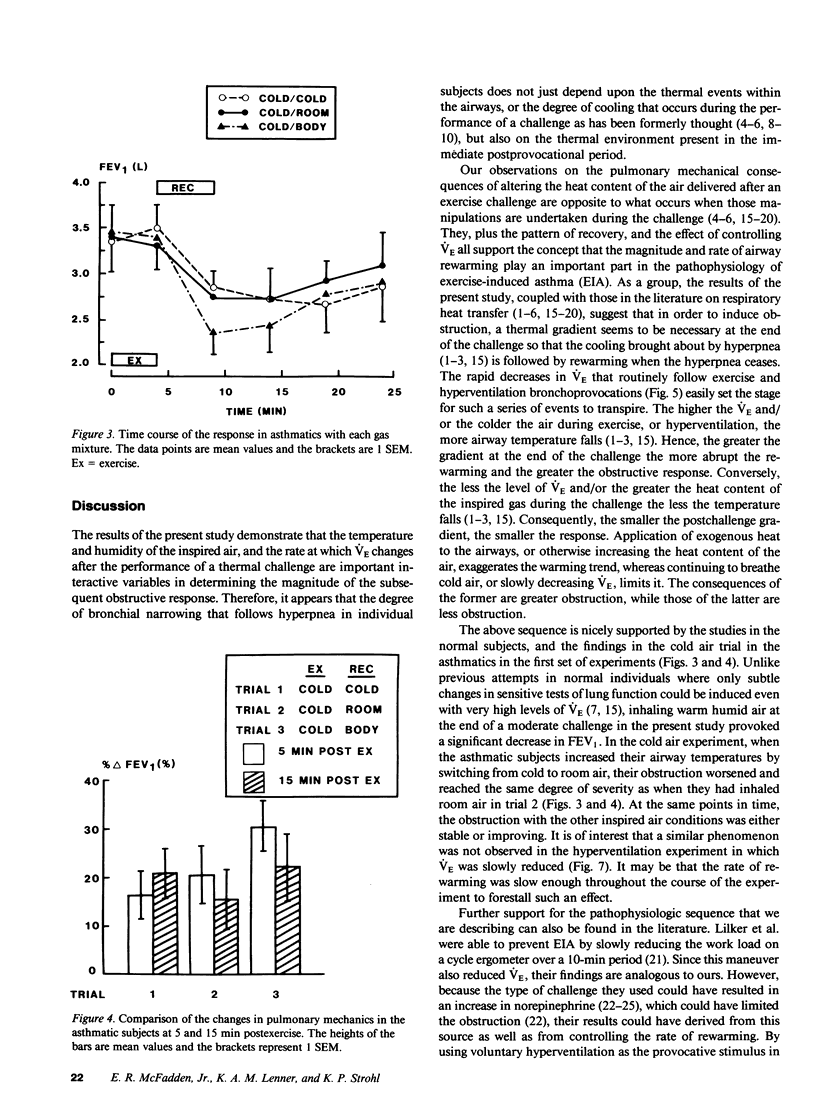
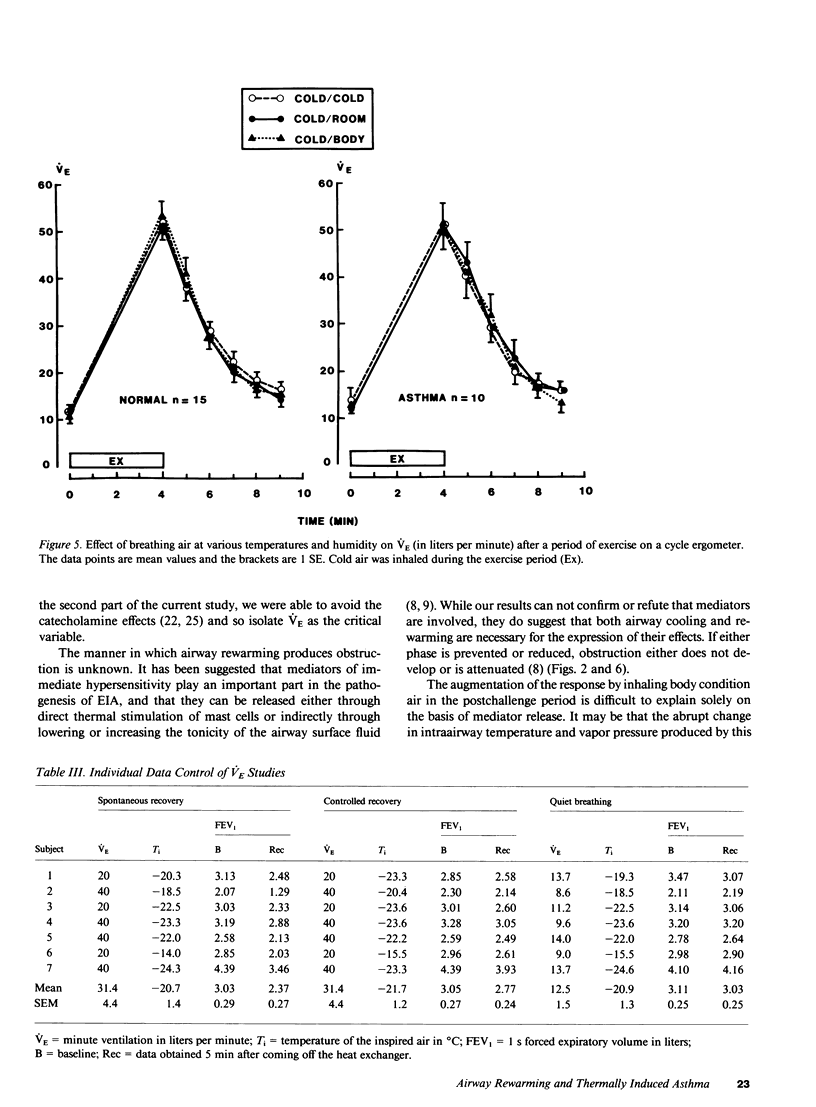
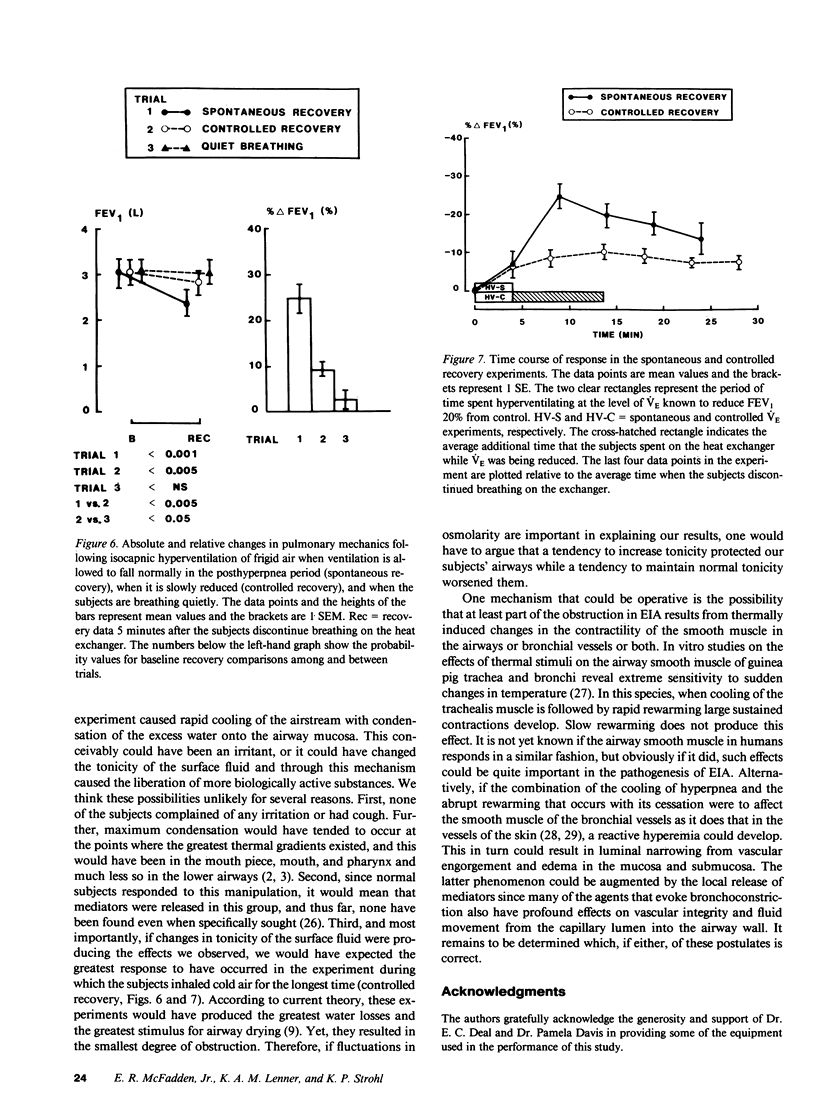
To determine if postexercise thermal events play a role in exercise-induced asthma (EIA), nine normal and eight asthmatic subjects on three occasions exercised while they inhaled frigid air. During the recovery period, either cold air, air at room temperature and humidity, or air at body conditions was administered in a random fashion. On a fourth occasion, body-condition air was given during exercise. Pulmonary mechanics were measured before and after each challenge. No changes in mechanics developed when air at body conditions was inhaled during exercise, however, increasing the heat content of the air during recovery produced progressively greater obstruction in both groups. On a separate occasion, seven asthmatics hyperventilated frigid air and either recovered spontaneously or had their ventilation slowly reduced. Controlling ventilation markedly attenuated the obstructive response. These data demonstrate that the severity of EIA is dependent not only on airway cooling but also upon the rapidity and magnitude of airway rewarming postchallenge.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. D., Daviskas E., Schoeffel R. E., Unger S. F. Prevention of severe exercise-induced asthma with hot humid air. Lancet. 1979 Sep 22;2(8143):629–629. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91681-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. D. Is there a unifying hypothesis for exercise-induced asthma? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 May;73(5 Pt 2):660–665. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Or O., Neuman I., Dotan R. Effects of dry and humid climates on exercise-induced asthma in children and preadolescents. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1977 Sep;60(3):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(77)90119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J., Brown M. J., Silverman M., Dollery C. T. Circulating catecholamines in exercise and hyperventilation induced asthma. Thorax. 1981 Jun;36(6):435–440. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.6.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleecker E. R., Chahal K. S., Mason P., Permutt S. The effect of alpha adrenergic blockade on non-specific airways reactivity and exercise induced asthma. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1983;128(Pt 1):258–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundgaard A., Ingemann-Hansen T., Schmidt A., Halkjaer-Kristensen J. Influence of temperature and relative humidity of inhaled gas on exercise-induced asthma. Eur J Respir Dis. 1982 May;63(3):239–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. Y., Horton D. J. Heat and water loss from the airways and exercise-induced asthma. Respiration. 1977;34(6):305–313. doi: 10.1159/000193842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal E. C., Jr, McFadden E. R., Jr, Ingram R. H., Jr, Breslin F. J., Jaeger J. J. Airway responsiveness to cold air and hyperpnea in normal subjects and in those with hay fever and asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Apr;121(4):621–628. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.4.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal E. C., Jr, McFadden E. R., Jr, Ingram R. H., Jr, Jaeger J. J. Esophageal temperature during exercise in asthmatic and nonasthmatic subjects. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Mar;46(3):484–490. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal E. C., Jr, McFadden E. R., Jr, Ingram R. H., Jr, Jaeger J. J. Hyperpnea and heat flux: initial reaction sequence in exercise-induced asthma. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Mar;46(3):476–483. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.3.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal E. C., Jr, McFadden E. R., Jr, Ingram R. H., Jr, Strauss R. H., Jaeger J. J. Role of respiratory heat exchange in production of exercise-induced asthma. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Mar;46(3):467–475. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.3.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley L. H., Mason J. W., Hogan R. P., Jones L. G., Kotchen T. A., Mougey E. H., Wherry F. E., Pennington L. L., Ricketts P. T. Multiple hormonal responses to graded exercise in relation to physical training. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Nov;33(5):602–606. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.33.5.602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Assoufi B. K., Kay A. B. The link between exercise, respiratory heat exchange, and the mast cell in bronchial asthma. Lancet. 1983 Mar 5;1(8323):520–522. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92204-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Brown M. J., Nagy L., Causon R., Walport M. J., Kay A. B. Exercise-induced release of histamine and neutrophil chemotactic factor in atopic asthmatics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Aug;70(2):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden E. R., Jr, Denison D. M., Waller J. F., Assoufi B., Peacock A., Sopwith T. Direct recordings of the temperatures in the tracheobronchial tree in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):700–705. doi: 10.1172/JCI110498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden E. R., Jr, Pichurko B. M., Bowman H. F., Ingenito E., Burns S., Dowling N., Solway J. Thermal mapping of the airways in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Feb;58(2):564–570. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.58.2.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden E. R., Jr, Pichurko B. M. Intraairway thermal profiles during exercise and hyperventilation in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1007–1010. doi: 10.1172/JCI112052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin F. J., Dozor A. J. Cold air inhalation challenge in the diagnosis of asthma in children. Pediatrics. 1983 Oct;72(4):503–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Cain C. F., Dowling N. B., Slutsky A. S., Hensley M. J., Strohl K. P., McFadden E. R., Jr, Ingram R. H., Jr Airway effects of respiratory heat loss in normal subjects. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Nov;49(5):875–880. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.5.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichurko B. M., Sullivan B., Porcelli R. J., McFadden E. R., Jr Endogenous adrenergic modification of exercise-induced asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Jun;77(6):796–801. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savard G. K., Cooper K. E., Veale W. L., Malkinson T. J. Peripheral blood flow during rewarming from mild hypothermia in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Jan;58(1):4–13. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.58.1.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shephard R. J. Exercise-induced bronchospasm-a review. Med Sci Sports. 1977 Spring;9(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souhrada J. F., Presley D., Souhrada M. Mechanisms of the temperature effect on airway smooth muscle. Respir Physiol. 1983 Aug;53(2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(83)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss R. H., McFadden E. R., Jr, Ingram R. H., Jr, Deal E. C., Jr, Jaeger J. J. Influence of heat and humidity on the airway obstruction induced by exercise in asthma. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):433–440. doi: 10.1172/JCI108954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss R. H., McFadden E. R., Jr, Ingram R. H., Jr, Jaeger J. J. Enhancement of exercise-induced asthma by cold air. N Engl J Med. 1977 Oct 6;297(14):743–747. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197710062971402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I. Mediators of immediate hypersensitivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Aug;72(2):101–119. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90512-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. D., Hamilton C. A., Jones D. H., Reid J. L., Stallard T. J., Littler W. A. Sequential changes in plasma noradrenaline during bicycle exercise. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Jan;58(1):37–43. doi: 10.1042/cs0580037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


