Abstract
In the title compound, C24H15Cl2N3O3, the C=C double bond is E configured. The 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole moiety is roughly planar (r.m.s. deviation of all fitted non-H atoms = 0.0780 Å), but the mean planes of the two components are inclined at an angle of 9.95 (7)°. The mean plane defined by the non-H atoms of the 1H-pyrazole ring encloses angles of 9.95 (7), 24.54 (6) and 43.02 (6)° with the mean planes of the different benzene rings. In the crystal, C—H⋯O contacts are present and result in the formation of a double-layer two-dimensional network lying parallel to (110). The shortest intercentroid distance between two aromatic systems is 3.5455 (7) Å and is apparent between two pyrazole systems. Further π–π interactions are manifest between a pair of 4-nitrophenyl rings [centroid-to-centroid distance = 3.6443 (7) Å] and a pair of 2,4-dichlorophenyl rings [centroid-to-centroid distance = 3.7797 (7) Å].
Related literature
For general background on the pharmaceutical and biological activity of pyrazole compounds, see: Isloor et al. (2009 ▶); Vijesh et al. (2010 ▶); Sharma et al. (2010 ▶); Rostom et al. (2003 ▶); Ghorab et al. (2010 ▶); Amnekar & Bhusari (2010 ▶). For graph-set analysis of hydrogen bonds, see: Etter et al. (1990 ▶); Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).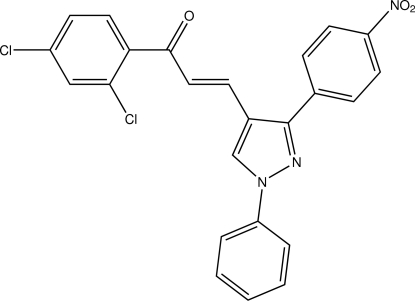
Experimental
Crystal data
C24H15Cl2N3O3
M r = 464.29
Triclinic,
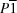
a = 8.3343 (3) Å
b = 9.3115 (4) Å
c = 13.8699 (6) Å
α = 92.896 (2)°
β = 104.669 (2)°
γ = 96.060 (2)°
V = 1032.12 (7) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.35 mm−1
T = 200 K
0.53 × 0.30 × 0.13 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▶) T min = 0.931, T max = 1.000
18344 measured reflections
5116 independent reflections
4588 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.013
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.030
wR(F 2) = 0.086
S = 1.02
5116 reflections
304 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.36 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2010 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003960/su2371sup1.cif
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003960/su2371Isup2.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003960/su2371Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003960/su2371Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5—H5⋯O1i | 0.95 | 2.39 | 3.3421 (14) | 176 |
| C36—H36⋯O3ii | 0.95 | 2.41 | 3.3139 (15) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii) 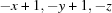 .
.
Acknowledgments
AMI is grateful to the Department of Atomic Energy, Board for Research in Nuclear Sciences, Government of India, for a Young Scientist award.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The pyrazole ring is an important structural motif found in several pharmaceutically active compounds. Because of its easy preparation and rich biological activity, the pyrazole skeleton plays an important role in biologically active compounds such as antibacterial (Isloor et al., 2009; Vijesh et al., 2010), anti-inflammatory (Sharma et al., 2010), analgesic (Rostom et al., 2003), anticancer, radioprotective (Ghorab et al., 2010) and anti-convulsant agents (Amnekar & Bhusari, 2010). Prompted by the diverse activities of pyrazole derivatives, we have synthesized the title compound to study its crystal structure.
In the title compound the C═C double bond in the Michael system adopts (E)-configuration (Fig. 1). The 1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole moiety is essentially planar (r.m.s. deviation of all fitted non-hydrogen atoms = 0.0780 Å). However, the mean planes of the two components are inclined at an angle of 9.95 (7)°.
The N-bonded phenyl ring B (C21–C26), the 4-nitrophenyl ring C (C11–C16), and the 2,4-dichlorophenyl ring D (C31–C36) are inclined to the mean plane of the central heterocyclic five-membered ring A (N1,N2,C4–C6) by 9.95 (7), 24.54 (6) and 43.06 (6) °, respectively. The mean planes defined the phenyl rings (B, C and D) are inclined to one another by angles of B/C = 16.28 (6)°, C/D = 28.40 (6)° and B/D = 40.14 (6)°.
In the crystal, C—H···O contacts whose range falls by more than 0.3 Å below the sum of van der Waals radii of the corresponding atoms are present. They are supported by one of the H atoms of the pyrazole system on the one hand and one of the H atoms on the dichlorophenyl moiety on the other hand. While the former of these contacts applies exclusively to one of the O atoms (O1) on the nitro group as acceptor, the latter ones are apparent in conjunction with the O atom (O3) on the Michael system (Table 1 and Fig. 2). In terms of graph-set analysis (Etter et al., 1990; Bernstein et al., 1995), the descriptor for the C—H···O contacts is C11(11)R22(10) on the unitary level.
The shortest intercentroid distance between two aromatic systems is 3.5455 (7) Å involving inversion related pyrazole systems [CgA···CgAi]. Further π–π interactions are manifest between inversion related 4-nitrophenyl rings (CgC···CgCii = 3.6443 (7) Å) and inversion related 2,4-dichlorophenyl rings (CgD···CgDiii = 3.7797 (7) Å) [symmetry codes: (i) -x + 2, -y + 1, -z + 1; (ii) -x + 2, -y + 2, -z + 1; (iii) -x + 1, -y, -z].
In total, the molecules are connected into a double layer two-dimensional network lying parallel to plane (110) [Fig. 3].
Experimental
To a cold, stirred mixture of methanol (20 ml) and sodium hydroxide (12.09 mmol) was added 2,4-dichloroacetophenone (4.03 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred for 10 min. To this was added 3-(4-nitrophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbaldehyde (4.03 mmol) followed by tetrahydrofuran (30 ml). The solution was further stirred at 0°C for 2 h and then at room temperature for 5 h. It was then poured into ice cold water. The resulting solution was neutralized with diluted hydrochloric acid. The solid that separated was filtered, washed with water, dried and crystallized from ethanol. Yield: 1.48 g, 79.39% (m.p. 478–480 K).
Refinement
Carbon-bound H atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H 0.95 Å) and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with U(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labels and displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A partial view along the a axis of the crystal packing of the title compound, showing the C—H···O intermolecular contacts [Symmetry operators: (i) x - 1, y - 1, z; (ii) x + 1, y + 1, z; (iii) -x + 1, -y + 1, -z].
Fig. 3.
A view along the a axis of the crystal packing of the title compound (displacement ellipsoids are drawn at 50% probability level).
Crystal data
| C24H15Cl2N3O3 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 464.29 | F(000) = 476 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.494 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Melting point = 478–480 K |
| a = 8.3343 (3) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 9.3115 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 9938 reflections |
| c = 13.8699 (6) Å | θ = 2.6–28.3° |
| α = 92.896 (2)° | µ = 0.35 mm−1 |
| β = 104.669 (2)° | T = 200 K |
| γ = 96.060 (2)° | Plate, yellow |
| V = 1032.12 (7) Å3 | 0.53 × 0.30 × 0.13 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 5116 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4588 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.013 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.4°, θmin = 1.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.931, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −11→12 |
| 18344 measured reflections | l = −18→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.030 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.086 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.046P)2 + 0.3579P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 5116 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 304 parameters | Δρmax = 0.36 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.61554 (4) | 0.04973 (3) | 0.23425 (2) | 0.03315 (9) | |
| Cl2 | 0.09111 (4) | −0.11303 (4) | −0.07809 (2) | 0.03888 (9) | |
| O1 | 1.42080 (12) | 1.17926 (10) | 0.43746 (8) | 0.0407 (2) | |
| O2 | 1.27245 (13) | 1.14934 (11) | 0.28397 (7) | 0.0398 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.69233 (12) | 0.43425 (10) | 0.10434 (6) | 0.0350 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.78730 (12) | 0.53362 (9) | 0.57632 (7) | 0.02186 (18) | |
| N2 | 0.89358 (12) | 0.65279 (10) | 0.57207 (7) | 0.02233 (18) | |
| N3 | 1.30319 (13) | 1.11802 (11) | 0.37064 (8) | 0.0286 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.61545 (15) | 0.35986 (12) | 0.15177 (8) | 0.0248 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.63269 (15) | 0.39188 (12) | 0.25920 (8) | 0.0256 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.5617 | 0.3378 | 0.2917 | 0.029 (4)* | |
| C3 | 0.74872 (14) | 0.49747 (12) | 0.31106 (8) | 0.0238 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.8177 | 0.5483 | 0.2758 | 0.030 (4)* | |
| C4 | 0.77783 (13) | 0.54064 (11) | 0.41643 (8) | 0.0219 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.71502 (14) | 0.46538 (11) | 0.48506 (8) | 0.0233 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.6355 | 0.3811 | 0.4706 | 0.034 (4)* | |
| C6 | 0.88826 (13) | 0.65830 (11) | 0.47531 (8) | 0.0205 (2) | |
| C11 | 0.99209 (13) | 0.77692 (11) | 0.44612 (8) | 0.0206 (2) | |
| C12 | 0.95250 (15) | 0.82678 (12) | 0.35047 (8) | 0.0261 (2) | |
| H12 | 0.8545 | 0.7837 | 0.3022 | 0.035 (4)* | |
| C13 | 1.05435 (15) | 0.93829 (12) | 0.32506 (8) | 0.0271 (2) | |
| H13 | 1.0283 | 0.9710 | 0.2597 | 0.039 (4)* | |
| C14 | 1.19461 (13) | 1.00064 (11) | 0.39712 (8) | 0.0236 (2) | |
| C15 | 1.23561 (14) | 0.95718 (12) | 0.49328 (8) | 0.0252 (2) | |
| H15 | 1.3312 | 1.0037 | 0.5419 | 0.038 (4)* | |
| C16 | 1.13429 (14) | 0.84452 (12) | 0.51712 (8) | 0.0239 (2) | |
| H16 | 1.1616 | 0.8126 | 0.5826 | 0.030 (4)* | |
| C21 | 0.77030 (14) | 0.49032 (12) | 0.67088 (8) | 0.0240 (2) | |
| C22 | 0.87694 (18) | 0.55949 (14) | 0.75788 (9) | 0.0331 (3) | |
| H22 | 0.9608 | 0.6352 | 0.7548 | 0.043 (4)* | |
| C23 | 0.8601 (2) | 0.51708 (15) | 0.84967 (10) | 0.0414 (3) | |
| H23 | 0.9330 | 0.5642 | 0.9096 | 0.054 (5)* | |
| C24 | 0.7381 (2) | 0.40681 (15) | 0.85476 (10) | 0.0414 (3) | |
| H24 | 0.7266 | 0.3784 | 0.9177 | 0.054 (5)* | |
| C25 | 0.63317 (19) | 0.33854 (16) | 0.76723 (11) | 0.0403 (3) | |
| H25 | 0.5493 | 0.2629 | 0.7705 | 0.056 (5)* | |
| C26 | 0.64836 (16) | 0.37876 (14) | 0.67454 (9) | 0.0322 (3) | |
| H26 | 0.5764 | 0.3307 | 0.6147 | 0.046 (5)* | |
| C31 | 0.48885 (14) | 0.23647 (12) | 0.09753 (8) | 0.0237 (2) | |
| C32 | 0.47465 (14) | 0.09718 (12) | 0.12861 (8) | 0.0240 (2) | |
| C33 | 0.35401 (15) | −0.01128 (12) | 0.07491 (8) | 0.0271 (2) | |
| H33 | 0.3472 | −0.1063 | 0.0968 | 0.040 (4)* | |
| C34 | 0.24377 (15) | 0.02196 (13) | −0.01124 (8) | 0.0277 (2) | |
| C35 | 0.25331 (16) | 0.15887 (14) | −0.04498 (9) | 0.0315 (3) | |
| H35 | 0.1762 | 0.1799 | −0.1043 | 0.045 (4)* | |
| C36 | 0.37677 (16) | 0.26473 (13) | 0.00889 (8) | 0.0292 (2) | |
| H36 | 0.3857 | 0.3585 | −0.0147 | 0.034 (4)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.04021 (17) | 0.02982 (15) | 0.02282 (14) | 0.00229 (11) | −0.00347 (11) | 0.00416 (10) |
| Cl2 | 0.03790 (17) | 0.03595 (17) | 0.03315 (16) | −0.01017 (13) | −0.00076 (12) | −0.00578 (12) |
| O1 | 0.0281 (4) | 0.0329 (5) | 0.0548 (6) | −0.0099 (4) | 0.0046 (4) | 0.0044 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0452 (5) | 0.0380 (5) | 0.0402 (5) | −0.0023 (4) | 0.0201 (4) | 0.0115 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0458 (5) | 0.0326 (4) | 0.0242 (4) | −0.0089 (4) | 0.0100 (4) | 0.0028 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0256 (4) | 0.0183 (4) | 0.0212 (4) | −0.0012 (3) | 0.0069 (3) | 0.0010 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0257 (4) | 0.0182 (4) | 0.0214 (4) | −0.0023 (3) | 0.0052 (3) | 0.0006 (3) |
| N3 | 0.0259 (5) | 0.0227 (4) | 0.0393 (6) | 0.0001 (4) | 0.0131 (4) | 0.0039 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0310 (5) | 0.0209 (5) | 0.0199 (5) | −0.0009 (4) | 0.0040 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0306 (5) | 0.0241 (5) | 0.0205 (5) | −0.0032 (4) | 0.0067 (4) | −0.0015 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0284 (5) | 0.0207 (5) | 0.0211 (5) | −0.0016 (4) | 0.0064 (4) | −0.0006 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0232 (5) | 0.0192 (5) | 0.0215 (5) | −0.0013 (4) | 0.0045 (4) | −0.0009 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0254 (5) | 0.0195 (5) | 0.0232 (5) | −0.0020 (4) | 0.0055 (4) | −0.0010 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0219 (5) | 0.0183 (4) | 0.0198 (5) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0040 (4) | 0.0000 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0225 (5) | 0.0175 (4) | 0.0205 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | 0.0044 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0281 (5) | 0.0246 (5) | 0.0204 (5) | −0.0048 (4) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0010 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0322 (6) | 0.0259 (5) | 0.0207 (5) | −0.0029 (4) | 0.0046 (4) | 0.0039 (4) |
| C14 | 0.0232 (5) | 0.0191 (5) | 0.0288 (5) | −0.0010 (4) | 0.0091 (4) | 0.0016 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0231 (5) | 0.0222 (5) | 0.0263 (5) | −0.0016 (4) | 0.0010 (4) | −0.0004 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0260 (5) | 0.0223 (5) | 0.0201 (5) | −0.0004 (4) | 0.0012 (4) | 0.0008 (4) |
| C21 | 0.0295 (5) | 0.0216 (5) | 0.0222 (5) | 0.0038 (4) | 0.0087 (4) | 0.0041 (4) |
| C22 | 0.0443 (7) | 0.0281 (6) | 0.0249 (6) | −0.0043 (5) | 0.0092 (5) | 0.0008 (4) |
| C23 | 0.0618 (9) | 0.0359 (7) | 0.0228 (6) | −0.0046 (6) | 0.0087 (6) | 0.0018 (5) |
| C24 | 0.0604 (9) | 0.0387 (7) | 0.0279 (6) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0167 (6) | 0.0108 (5) |
| C25 | 0.0454 (8) | 0.0393 (7) | 0.0369 (7) | −0.0044 (6) | 0.0135 (6) | 0.0149 (6) |
| C26 | 0.0349 (6) | 0.0311 (6) | 0.0283 (6) | −0.0030 (5) | 0.0062 (5) | 0.0073 (5) |
| C31 | 0.0304 (5) | 0.0217 (5) | 0.0169 (5) | −0.0009 (4) | 0.0048 (4) | −0.0010 (4) |
| C32 | 0.0290 (5) | 0.0245 (5) | 0.0165 (4) | 0.0015 (4) | 0.0030 (4) | 0.0011 (4) |
| C33 | 0.0332 (6) | 0.0223 (5) | 0.0233 (5) | −0.0012 (4) | 0.0050 (4) | 0.0012 (4) |
| C34 | 0.0291 (5) | 0.0274 (5) | 0.0225 (5) | −0.0026 (4) | 0.0032 (4) | −0.0042 (4) |
| C35 | 0.0361 (6) | 0.0319 (6) | 0.0205 (5) | 0.0018 (5) | −0.0023 (4) | 0.0009 (4) |
| C36 | 0.0398 (6) | 0.0233 (5) | 0.0209 (5) | 0.0013 (5) | 0.0022 (5) | 0.0030 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C32 | 1.7391 (11) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| Cl2—C34 | 1.7336 (11) | C14—C15 | 1.3829 (16) |
| O1—N3 | 1.2302 (14) | C15—C16 | 1.3829 (15) |
| O2—N3 | 1.2210 (14) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| O3—C1 | 1.2203 (14) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C5 | 1.3493 (14) | C21—C22 | 1.3850 (16) |
| N1—N2 | 1.3582 (12) | C21—C26 | 1.3868 (16) |
| N1—C21 | 1.4277 (13) | C22—C23 | 1.3878 (17) |
| N2—C6 | 1.3354 (14) | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C14 | 1.4657 (14) | C23—C24 | 1.384 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.4722 (15) | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C31 | 1.5014 (15) | C24—C25 | 1.382 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.3397 (15) | C24—H24 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C25—C26 | 1.3892 (17) |
| C3—C4 | 1.4481 (14) | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C26—H26 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3832 (15) | C31—C32 | 1.3899 (15) |
| C4—C6 | 1.4248 (14) | C31—C36 | 1.3986 (16) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C32—C33 | 1.3842 (15) |
| C6—C11 | 1.4675 (14) | C33—C34 | 1.3817 (16) |
| C11—C12 | 1.3990 (15) | C33—H33 | 0.9500 |
| C11—C16 | 1.3998 (14) | C34—C35 | 1.3815 (17) |
| C12—C13 | 1.3875 (15) | C35—C36 | 1.3823 (16) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9500 | C35—H35 | 0.9500 |
| C13—C14 | 1.3815 (16) | C36—H36 | 0.9500 |
| C5—N1—N2 | 112.12 (9) | C15—C16—C11 | 120.93 (10) |
| C5—N1—C21 | 127.88 (9) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.5 |
| N2—N1—C21 | 119.91 (9) | C11—C16—H16 | 119.5 |
| C6—N2—N1 | 105.11 (8) | C22—C21—C26 | 120.80 (11) |
| O2—N3—O1 | 123.73 (10) | C22—C21—N1 | 119.53 (10) |
| O2—N3—C14 | 118.48 (10) | C26—C21—N1 | 119.66 (10) |
| O1—N3—C14 | 117.79 (10) | C21—C22—C23 | 119.37 (12) |
| O3—C1—C2 | 122.78 (10) | C21—C22—H22 | 120.3 |
| O3—C1—C31 | 118.98 (10) | C23—C22—H22 | 120.3 |
| C2—C1—C31 | 118.10 (10) | C24—C23—C22 | 120.62 (13) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.88 (10) | C24—C23—H23 | 119.7 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.1 | C22—C23—H23 | 119.7 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.1 | C25—C24—C23 | 119.27 (12) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 125.46 (10) | C25—C24—H24 | 120.4 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 117.3 | C23—C24—H24 | 120.4 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 117.3 | C24—C25—C26 | 121.08 (12) |
| C5—C4—C6 | 104.13 (9) | C24—C25—H25 | 119.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 126.45 (10) | C26—C25—H25 | 119.5 |
| C6—C4—C3 | 129.11 (10) | C21—C26—C25 | 118.86 (12) |
| N1—C5—C4 | 107.48 (9) | C21—C26—H26 | 120.6 |
| N1—C5—H5 | 126.3 | C25—C26—H26 | 120.6 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 126.3 | C32—C31—C36 | 117.80 (10) |
| N2—C6—C4 | 111.14 (9) | C32—C31—C1 | 125.11 (10) |
| N2—C6—C11 | 118.25 (9) | C36—C31—C1 | 117.09 (10) |
| C4—C6—C11 | 130.60 (9) | C33—C32—C31 | 121.95 (10) |
| C12—C11—C16 | 118.75 (10) | C33—C32—Cl1 | 117.05 (9) |
| C12—C11—C6 | 122.43 (9) | C31—C32—Cl1 | 120.93 (8) |
| C16—C11—C6 | 118.82 (9) | C34—C33—C32 | 118.38 (10) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 120.93 (10) | C34—C33—H33 | 120.8 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.5 | C32—C33—H33 | 120.8 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.5 | C35—C34—C33 | 121.64 (11) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 118.35 (10) | C35—C34—Cl2 | 119.80 (9) |
| C14—C13—H13 | 120.8 | C33—C34—Cl2 | 118.57 (9) |
| C12—C13—H13 | 120.8 | C34—C35—C36 | 118.94 (11) |
| C13—C14—C15 | 122.50 (10) | C34—C35—H35 | 120.5 |
| C13—C14—N3 | 118.63 (10) | C36—C35—H35 | 120.5 |
| C15—C14—N3 | 118.87 (10) | C35—C36—C31 | 121.26 (11) |
| C14—C15—C16 | 118.51 (10) | C35—C36—H36 | 119.4 |
| C14—C15—H15 | 120.7 | C31—C36—H36 | 119.4 |
| C16—C15—H15 | 120.7 | ||
| C5—N1—N2—C6 | −0.46 (12) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.82 (17) |
| C21—N1—N2—C6 | 176.30 (9) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.90 (17) |
| O3—C1—C2—C3 | −6.97 (19) | C6—C11—C16—C15 | −179.72 (10) |
| C31—C1—C2—C3 | 177.41 (11) | C5—N1—C21—C22 | 168.36 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 179.47 (11) | N2—N1—C21—C22 | −7.84 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 12.94 (19) | C5—N1—C21—C26 | −11.06 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4—C6 | −174.38 (12) | N2—N1—C21—C26 | 172.74 (10) |
| N2—N1—C5—C4 | 1.10 (13) | C26—C21—C22—C23 | −0.6 (2) |
| C21—N1—C5—C4 | −175.35 (10) | N1—C21—C22—C23 | −179.98 (12) |
| C6—C4—C5—N1 | −1.21 (12) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | 0.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 172.94 (10) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | 0.3 (2) |
| N1—N2—C6—C4 | −0.35 (12) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | 0.0 (2) |
| N1—N2—C6—C11 | −179.79 (9) | C22—C21—C26—C25 | 0.87 (19) |
| C5—C4—C6—N2 | 0.98 (12) | N1—C21—C26—C25 | −179.71 (12) |
| C3—C4—C6—N2 | −172.95 (11) | C24—C25—C26—C21 | −0.6 (2) |
| C5—C4—C6—C11 | −179.66 (11) | O3—C1—C31—C32 | 133.57 (13) |
| C3—C4—C6—C11 | 6.41 (19) | C2—C1—C31—C32 | −50.63 (16) |
| N2—C6—C11—C12 | −154.77 (11) | O3—C1—C31—C36 | −46.48 (16) |
| C4—C6—C11—C12 | 25.91 (18) | C2—C1—C31—C36 | 129.32 (12) |
| N2—C6—C11—C16 | 24.00 (15) | C36—C31—C32—C33 | −0.28 (17) |
| C4—C6—C11—C16 | −155.32 (11) | C1—C31—C32—C33 | 179.67 (11) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | 1.85 (17) | C36—C31—C32—Cl1 | 176.56 (9) |
| C6—C11—C12—C13 | −179.37 (11) | C1—C31—C32—Cl1 | −3.49 (16) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.05 (18) | C31—C32—C33—C34 | −0.93 (18) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.76 (18) | Cl1—C32—C33—C34 | −177.88 (9) |
| C12—C13—C14—N3 | 179.71 (10) | C32—C33—C34—C35 | 0.97 (18) |
| O2—N3—C14—C13 | −5.21 (16) | C32—C33—C34—Cl2 | −179.36 (9) |
| O1—N3—C14—C13 | 174.93 (11) | C33—C34—C35—C36 | 0.21 (19) |
| O2—N3—C14—C15 | 175.23 (11) | Cl2—C34—C35—C36 | −179.46 (10) |
| O1—N3—C14—C15 | −4.62 (16) | C34—C35—C36—C31 | −1.5 (2) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | 1.68 (17) | C32—C31—C36—C35 | 1.50 (18) |
| N3—C14—C15—C16 | −178.78 (10) | C1—C31—C36—C35 | −178.46 (11) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C5—H5···O1i | 0.95 | 2.39 | 3.3421 (14) | 176 |
| C36—H36···O3ii | 0.95 | 2.41 | 3.3139 (15) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y−1, z; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SU2371).
References
- Amnekar, N. D. & Bhusari, K. P. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 149–159. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2008). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2010). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, USA.
- Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C. & Bernstein, J. (1990). Acta Cryst. B46, 256–262. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Ghorab, M. M., Ragab, F. A., Alqasoumi, S. I., Alafeefy, A. M. & Aboulmagd, S. A. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 171–178. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Isloor, A. M., Kalluraya, B. & Shetty, P. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 3784–3787. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Rostom, S. A. F., Shalaby, M. A. & El-Demellawy, M. A. (2003). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 38, 959–974. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P. K., Kumar, S., Kumar, P., Kaushik, P., Kaushik, D., Dhingra, Y. & Aneja, K. R. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 2650–2655. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Vijesh, A. M., Isloor, A. M., Prabhu, V., Ahmad, S. & Malladi, S. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 5460–5464. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003960/su2371sup1.cif
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003960/su2371Isup2.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003960/su2371Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003960/su2371Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





