Abstract
In the title quinazolin-4-one derivative, C24H20N2O3, both the 4-methylbenzoate [dihedral angle = 83.90 (9)°] and 2-tolyl [87.88 (9)°] groups are almost orthogonal to the central fused ring system. These aryl groups are oriented towards the quinazolin-4-one-bound methyl group. In the crystal, molecules are connected into a three-dimensional architecture by C—H⋯O, C—H⋯π and π–π [ring centroid-to-centroid separation = 3.6458 (13) Å] interactions.
Related literature
For the pharmacological activity of substituted quinazoline-4(3H)-ones, see: El-Azab & ElTahir (2012 ▶); El-Azab et al. (2011 ▶); Al-Omary et al. (2010 ▶); Al-Obaid et al. (2009 ▶); Aziza et al. (1996 ▶). For the synthesis and evaluation of the anticonvulsant activity of the title compound, see: El-Azab et al. (2010 ▶). For the structure of the benzoate derivative, see: El-Azab et al. (2012 ▶).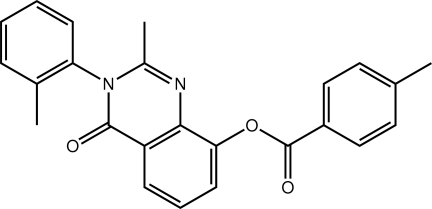
Experimental
Crystal data
C24H20N2O3
M r = 384.42
Monoclinic,
a = 18.8216 (5) Å
b = 7.6332 (2) Å
c = 13.3092 (3) Å
β = 97.286 (2)°
V = 1896.68 (8) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 0.72 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.25 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Agilent SuperNova Dual diffractometer with an Atlas detector
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2011 ▶) T min = 0.755, T max = 1.000
7966 measured reflections
3883 independent reflections
3478 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.027
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.067
wR(F 2) = 0.186
S = 1.06
3883 reflections
265 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 1.09 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2011 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812006265/hb6636sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812006265/hb6636Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812006265/hb6636Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C18–C23 benzene ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C17—H17C⋯O2i | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.434 (3) | 150 |
| C21—H21⋯O3ii | 0.95 | 2.47 | 3.299 (3) | 146 |
| C12—H12⋯Cg1iii | 0.95 | 2.79 | 3.658 (2) | 153 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 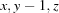 ; (ii)
; (ii) 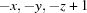 ; (iii)
; (iii) 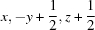 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Center of Pharmacy, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. We also thank the Ministry of Higher Education (Malaysia) for funding structural studies through the High-Impact Research Scheme (grant No. UM.C/HIR/MOHE/SC/12).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound, (I), a methaqualone analogue, was recently synthesized and evaluated for its anti-convulsant activity (El-Azab et al., 2010). Herein, the crystal structure determination of 3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-3-(2-methylphenyl)-4-oxoquinazolin-8-yl 4-methylbenzoate (I) is reported. These studies were motivated by the observation that substituted quinazoline-4(3H)-ones are known to display various biological activities (El-Azab & ElTahir, 2012; El-Azab et al., 2011; El-Azab et al., 2010; Al-Omary et al., 2010; Al-Obaid et al., 2009; Aziza et al., 1996).
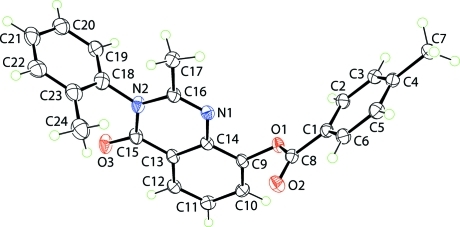
In (I), Fig. 1, the carboxylate residue is co-planar to the benzene ring to which it is connected as seen in the value of the C2—C1—C8—O1 torsion angle -3.8 (3)°. With respect to the central quinazolin-4-one fused ring system [r.m.s. deviation = 0.045 Å for the 10 atoms], both the 4-methylbenzoate and 2-tolyl groups are orthogonal: the dihedral angles between the central plane and six-membered rings being 83.90 (9) and 87.88 (9)°, respectively. Both aryl substituents are orientated towards the methyl group bound to the quinazolin-4-one system and the dihedral angle between the two six-membered rings is 77.04 (11)°. The molecular structure resembles closely that of the benzoate derivative (El-Azab et al., 2012).
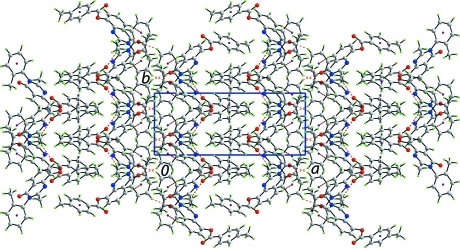
In the crystal packing, C—H···O [involving both carbonyl-O atoms] and C—H···π [involving the (C18···C23) benzene ring] interactions, Table 1, lead to the formation of layers in the bc plane. These interdigitate to allow for the formation of π–π interactions between the 4-methylbenzoate rings [ring centroid···centroid separation = 3.6458 (13) Å between centrosymmetrically related (C1–C6) rings; symmetry operation: 1 - x, 2 - y, 1 - z]. The combination of intermolecular interactions leads to a three-dimensional architecture, Fig. 2.
Experimental
A mixture of 8-hydroxymethaqualone (532 mg, 0.002 M) and 4-methylbenzoyl chloride (325 mg, 0.0021 mmol) in 15 ml pyridine was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and the residue was triturated with water and filtered. The solid obtained was dried and recrystallized from EtOH to yield colourless prisms. m.p. 465–467 K. Yield: 95%. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 8.25–8.22 (m, 3H), 7.64 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz), 7.52 (t, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz), 7.43–7.28 (m, 5H), 7.15 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz), 2.49 (s, 3H), 2.15 (s, 3H), 2.11 (s, 3H) p.p.m.. 13C NMR (CDCl3): δ = 17.4, 21.8, 24.3, 120.7, 124.9, 126.4, 126.7, 127.4, 127.6, 127.9, 129.3, 129.6, 130.5, 131.5, 135.4, 136.8, 141.0, 144.5, 146.3, 154.7, 161.2, 165.3 p.p.m.. MS (70 eV): m/z = 384.
Refinement
Carbon-bound H atoms were placed in calculated positions [C—H = 0.95 to 0.98 Å, Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C)] and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation. The maximum and minimum residual electron density peaks of 1.09 and 0.33 e Å-3, respectively, were located 0.92 Å and 0.56 Å from the C18 and C23 atoms, respectively.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing displacement ellipsoids at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A view in projection down the c axis of the unit-cell contents for (I). The C—H···O, C—H···π and π–π interactions are shown as orange, brown and purple dashed lines, respectively.
Crystal data
| C24H20N2O3 | F(000) = 808 |
| Mr = 384.42 | Dx = 1.346 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.5418 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 3857 reflections |
| a = 18.8216 (5) Å | θ = 3.4–76.5° |
| b = 7.6332 (2) Å | µ = 0.72 mm−1 |
| c = 13.3092 (3) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 97.286 (2)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 1896.68 (8) Å3 | 0.25 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova Dual diffractometer with an Atlas detector | 3883 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Cu) X-ray Source | 3478 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.027 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4041 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 76.7°, θmin = 4.7° |
| ω scans | h = −23→23 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2011) | k = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.755, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −16→8 |
| 7966 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.067 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.186 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0962P)2 + 2.188P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3883 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 265 parameters | Δρmax = 1.09 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.37531 (7) | 0.7195 (2) | 0.60223 (11) | 0.0223 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.31966 (8) | 0.9210 (2) | 0.49638 (12) | 0.0279 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.10542 (9) | 0.3305 (2) | 0.65096 (12) | 0.0339 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.27420 (9) | 0.4903 (2) | 0.50849 (12) | 0.0211 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.17341 (10) | 0.3084 (3) | 0.52035 (13) | 0.0267 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.43599 (11) | 0.8207 (3) | 0.46864 (15) | 0.0212 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.49532 (11) | 0.7190 (3) | 0.50441 (16) | 0.0238 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.4958 | 0.6552 | 0.5658 | 0.029* | |
| C3 | 0.55359 (11) | 0.7105 (3) | 0.45073 (16) | 0.0246 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.5939 | 0.6414 | 0.4760 | 0.030* | |
| C4 | 0.55385 (11) | 0.8024 (3) | 0.35973 (16) | 0.0237 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.49471 (12) | 0.9054 (3) | 0.32543 (16) | 0.0254 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.4943 | 0.9695 | 0.2642 | 0.030* | |
| C6 | 0.43625 (11) | 0.9158 (3) | 0.37932 (16) | 0.0235 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.3965 | 0.9877 | 0.3553 | 0.028* | |
| C7 | 0.61739 (12) | 0.7901 (3) | 0.30194 (17) | 0.0277 (5) | |
| H7A | 0.6324 | 0.6674 | 0.2988 | 0.041* | |
| H7B | 0.6569 | 0.8599 | 0.3363 | 0.041* | |
| H7C | 0.6042 | 0.8348 | 0.2331 | 0.041* | |
| C8 | 0.37095 (11) | 0.8299 (3) | 0.52067 (15) | 0.0209 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.31180 (11) | 0.6918 (3) | 0.64461 (15) | 0.0210 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.30198 (11) | 0.7733 (3) | 0.73413 (15) | 0.0233 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.3360 | 0.8566 | 0.7634 | 0.028* | |
| C11 | 0.24158 (12) | 0.7332 (3) | 0.78214 (15) | 0.0255 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.2340 | 0.7921 | 0.8428 | 0.031* | |
| C12 | 0.19361 (11) | 0.6093 (3) | 0.74151 (15) | 0.0236 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.1533 | 0.5808 | 0.7746 | 0.028* | |
| C13 | 0.20422 (11) | 0.5243 (3) | 0.65079 (15) | 0.0214 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.26278 (10) | 0.5673 (3) | 0.59976 (14) | 0.0195 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.15613 (11) | 0.3839 (3) | 0.61094 (15) | 0.0252 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.23027 (11) | 0.3681 (3) | 0.47275 (15) | 0.0228 (4) | |
| C17 | 0.24100 (12) | 0.2818 (3) | 0.37470 (16) | 0.0270 (5) | |
| H17A | 0.2801 | 0.3402 | 0.3458 | 0.040* | |
| H17B | 0.1968 | 0.2906 | 0.3273 | 0.040* | |
| H17C | 0.2531 | 0.1581 | 0.3869 | 0.040* | |
| C18 | 0.12952 (13) | 0.1602 (3) | 0.47919 (16) | 0.0311 (5) | |
| C19 | 0.15047 (12) | −0.0095 (3) | 0.50999 (18) | 0.0316 (5) | |
| H19 | 0.1922 | −0.0288 | 0.5567 | 0.038* | |
| C20 | 0.10838 (14) | −0.1495 (3) | 0.47021 (19) | 0.0348 (5) | |
| H20 | 0.1219 | −0.2665 | 0.4880 | 0.042* | |
| C21 | 0.04685 (13) | −0.1168 (4) | 0.40471 (19) | 0.0362 (6) | |
| H21 | 0.0177 | −0.2127 | 0.3794 | 0.043* | |
| C22 | 0.02648 (14) | 0.0491 (4) | 0.37508 (18) | 0.0350 (6) | |
| H22 | −0.0158 | 0.0669 | 0.3291 | 0.042* | |
| C23 | 0.06853 (13) | 0.1950 (4) | 0.41299 (18) | 0.0333 (5) | |
| C24 | 0.04695 (14) | 0.3739 (4) | 0.3848 (2) | 0.0406 (6) | |
| H24A | 0.0457 | 0.4443 | 0.4461 | 0.061* | |
| H24B | −0.0008 | 0.3725 | 0.3455 | 0.061* | |
| H24C | 0.0814 | 0.4250 | 0.3437 | 0.061* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0183 (7) | 0.0267 (8) | 0.0224 (7) | −0.0018 (6) | 0.0046 (5) | 0.0041 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0240 (7) | 0.0329 (9) | 0.0279 (8) | 0.0037 (6) | 0.0072 (6) | 0.0059 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0299 (8) | 0.0486 (11) | 0.0258 (8) | −0.0159 (7) | 0.0138 (6) | −0.0061 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0214 (8) | 0.0249 (9) | 0.0181 (8) | −0.0008 (7) | 0.0062 (6) | 0.0012 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0267 (9) | 0.0356 (11) | 0.0194 (8) | −0.0107 (8) | 0.0094 (7) | −0.0046 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0214 (10) | 0.0221 (10) | 0.0205 (9) | −0.0031 (8) | 0.0043 (7) | −0.0025 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0239 (10) | 0.0247 (11) | 0.0233 (10) | −0.0016 (8) | 0.0044 (8) | 0.0014 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0232 (10) | 0.0225 (11) | 0.0286 (11) | 0.0005 (8) | 0.0054 (8) | 0.0004 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0246 (10) | 0.0235 (10) | 0.0243 (10) | −0.0048 (8) | 0.0083 (8) | −0.0056 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0290 (11) | 0.0271 (11) | 0.0209 (10) | −0.0024 (9) | 0.0065 (8) | 0.0012 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0230 (10) | 0.0247 (10) | 0.0227 (10) | −0.0004 (8) | 0.0032 (8) | 0.0008 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0283 (11) | 0.0281 (11) | 0.0286 (11) | −0.0006 (9) | 0.0113 (9) | −0.0020 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0212 (9) | 0.0223 (10) | 0.0193 (9) | −0.0029 (8) | 0.0030 (7) | −0.0009 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0189 (9) | 0.0239 (10) | 0.0209 (9) | 0.0005 (8) | 0.0057 (7) | 0.0044 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0269 (10) | 0.0209 (10) | 0.0218 (10) | −0.0011 (8) | 0.0015 (8) | 0.0013 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0321 (11) | 0.0273 (11) | 0.0183 (9) | 0.0010 (9) | 0.0080 (8) | −0.0001 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0238 (10) | 0.0286 (11) | 0.0195 (9) | 0.0006 (8) | 0.0075 (8) | 0.0018 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0205 (9) | 0.0266 (10) | 0.0178 (9) | −0.0003 (8) | 0.0054 (7) | 0.0024 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0201 (9) | 0.0231 (10) | 0.0159 (9) | 0.0013 (8) | 0.0040 (7) | 0.0022 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0237 (10) | 0.0344 (12) | 0.0188 (9) | −0.0042 (9) | 0.0074 (8) | −0.0003 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0241 (10) | 0.0273 (11) | 0.0183 (9) | −0.0028 (8) | 0.0078 (8) | 0.0016 (8) |
| C17 | 0.0309 (11) | 0.0317 (12) | 0.0203 (10) | −0.0060 (9) | 0.0108 (8) | −0.0036 (8) |
| C18 | 0.0319 (12) | 0.0415 (14) | 0.0218 (10) | −0.0080 (10) | 0.0102 (9) | −0.0064 (9) |
| C19 | 0.0276 (11) | 0.0339 (13) | 0.0347 (12) | −0.0023 (9) | 0.0096 (9) | −0.0011 (10) |
| C20 | 0.0356 (12) | 0.0355 (13) | 0.0355 (12) | −0.0007 (10) | 0.0131 (10) | 0.0001 (10) |
| C21 | 0.0293 (12) | 0.0482 (15) | 0.0334 (12) | −0.0061 (11) | 0.0128 (9) | −0.0019 (11) |
| C22 | 0.0357 (12) | 0.0456 (14) | 0.0254 (11) | 0.0019 (11) | 0.0106 (9) | −0.0053 (10) |
| C23 | 0.0307 (12) | 0.0432 (14) | 0.0276 (11) | −0.0010 (10) | 0.0106 (9) | −0.0032 (10) |
| C24 | 0.0332 (13) | 0.0548 (17) | 0.0332 (13) | 0.0001 (12) | 0.0013 (10) | −0.0041 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C8 | 1.368 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.407 (3) |
| O1—C9 | 1.401 (2) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C8 | 1.201 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.370 (3) |
| O3—C15 | 1.220 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C16 | 1.296 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.407 (3) |
| N1—C14 | 1.390 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C16 | 1.388 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.405 (3) |
| N2—C15 | 1.411 (3) | C13—C15 | 1.459 (3) |
| N2—C18 | 1.465 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.498 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.393 (3) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.394 (3) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C8 | 1.483 (3) | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.384 (3) | C18—C23 | 1.381 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C18—C19 | 1.400 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.400 (3) | C19—C20 | 1.394 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.391 (3) | C20—C21 | 1.381 (4) |
| C4—C7 | 1.505 (3) | C20—H20 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.390 (3) | C21—C22 | 1.367 (4) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C21—H21 | 0.9500 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C22—C23 | 1.421 (4) |
| C7—H7A | 0.9800 | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| C7—H7B | 0.9800 | C23—C24 | 1.460 (4) |
| C7—H7C | 0.9800 | C24—H24A | 0.9800 |
| C9—C10 | 1.377 (3) | C24—H24B | 0.9800 |
| C9—C14 | 1.404 (3) | C24—H24C | 0.9800 |
| C8—O1—C9 | 116.36 (15) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.0 |
| C16—N1—C14 | 117.56 (17) | C14—C13—C12 | 120.85 (19) |
| C16—N2—C15 | 122.04 (18) | C14—C13—C15 | 118.97 (18) |
| C16—N2—C18 | 120.91 (17) | C12—C13—C15 | 120.12 (18) |
| C15—N2—C18 | 117.04 (17) | N1—C14—C9 | 119.44 (17) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 119.51 (19) | N1—C14—C13 | 122.78 (18) |
| C6—C1—C8 | 117.80 (19) | C9—C14—C13 | 117.77 (18) |
| C2—C1—C8 | 122.68 (19) | O3—C15—N2 | 121.0 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.2 (2) | O3—C15—C13 | 124.76 (19) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.9 | N2—C15—C13 | 114.28 (17) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.9 | N1—C16—N2 | 124.17 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.9 (2) | N1—C16—C17 | 119.07 (18) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.6 | N2—C16—C17 | 116.75 (18) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C16—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.45 (19) | C16—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C7 | 121.5 (2) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C7 | 120.1 (2) | C16—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.1 (2) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C23—C18—C19 | 123.1 (2) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.9 (2) | C23—C18—N2 | 118.2 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.0 | C19—C18—N2 | 118.7 (2) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.0 | C20—C19—C18 | 118.2 (2) |
| C4—C7—H7A | 109.5 | C20—C19—H19 | 120.9 |
| C4—C7—H7B | 109.5 | C18—C19—H19 | 120.9 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 | C21—C20—C19 | 119.4 (2) |
| C4—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C21—C20—H20 | 120.3 |
| H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C19—C20—H20 | 120.3 |
| H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C22—C21—C20 | 122.1 (3) |
| O2—C8—O1 | 122.40 (18) | C22—C21—H21 | 118.9 |
| O2—C8—C1 | 125.79 (19) | C20—C21—H21 | 118.9 |
| O1—C8—C1 | 111.81 (17) | C21—C22—C23 | 120.0 (2) |
| C10—C9—O1 | 119.68 (18) | C21—C22—H22 | 120.0 |
| C10—C9—C14 | 121.38 (18) | C23—C22—H22 | 120.0 |
| O1—C9—C14 | 118.63 (18) | C18—C23—C22 | 117.1 (2) |
| C9—C10—C11 | 120.0 (2) | C18—C23—C24 | 121.7 (2) |
| C9—C10—H10 | 120.0 | C22—C23—C24 | 121.2 (2) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.0 | C23—C24—H24A | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 120.06 (19) | C23—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 120.0 | H24A—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 120.0 | C23—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.92 (19) | H24A—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 120.0 | H24B—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.0 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | 2.7 (3) |
| C8—C1—C2—C3 | 177.69 (19) | C15—C13—C14—C9 | −174.38 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.4 (3) | C16—N2—C15—O3 | 179.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.2 (3) | C18—N2—C15—O3 | −2.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C7 | −179.4 (2) | C16—N2—C15—C13 | −1.9 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.7 (3) | C18—N2—C15—C13 | 176.80 (19) |
| C7—C4—C5—C6 | 180.0 (2) | C14—C13—C15—O3 | 176.9 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.7 (3) | C12—C13—C15—O3 | −0.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.5 (3) | C14—C13—C15—N2 | −2.0 (3) |
| C8—C1—C6—C5 | −177.18 (19) | C12—C13—C15—N2 | −179.15 (19) |
| C9—O1—C8—O2 | 12.0 (3) | C14—N1—C16—N2 | −0.8 (3) |
| C9—O1—C8—C1 | −167.83 (17) | C14—N1—C16—C17 | −179.84 (18) |
| C6—C1—C8—O2 | −5.0 (3) | C15—N2—C16—N1 | 3.5 (3) |
| C2—C1—C8—O2 | 176.3 (2) | C18—N2—C16—N1 | −175.1 (2) |
| C6—C1—C8—O1 | 174.84 (17) | C15—N2—C16—C17 | −177.4 (2) |
| C2—C1—C8—O1 | −3.8 (3) | C18—N2—C16—C17 | 4.0 (3) |
| C8—O1—C9—C10 | −103.9 (2) | C16—N2—C18—C23 | −92.2 (3) |
| C8—O1—C9—C14 | 82.5 (2) | C15—N2—C18—C23 | 89.1 (3) |
| O1—C9—C10—C11 | −173.89 (18) | C16—N2—C18—C19 | 88.9 (3) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | −0.4 (3) | C15—N2—C18—C19 | −89.7 (3) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.9 (3) | C23—C18—C19—C20 | 1.3 (3) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | −1.1 (3) | N2—C18—C19—C20 | −179.9 (2) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.3 (3) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | −1.9 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13—C15 | 175.8 (2) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | 1.8 (4) |
| C16—N1—C14—C9 | 175.77 (19) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | −0.9 (4) |
| C16—N1—C14—C13 | −3.4 (3) | C19—C18—C23—C22 | −0.5 (3) |
| C10—C9—C14—N1 | 178.96 (19) | N2—C18—C23—C22 | −179.30 (19) |
| O1—C9—C14—N1 | −7.5 (3) | C19—C18—C23—C24 | 178.1 (2) |
| C10—C9—C14—C13 | −1.9 (3) | N2—C18—C23—C24 | −0.7 (3) |
| O1—C9—C14—C13 | 171.66 (17) | C21—C22—C23—C18 | 0.3 (3) |
| C12—C13—C14—N1 | −178.11 (18) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | −178.3 (2) |
| C15—C13—C14—N1 | 4.8 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the C18–C23 benzene ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C17—H17C···O2i | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.434 (3) | 150 |
| C21—H21···O3ii | 0.95 | 2.47 | 3.299 (3) | 146 |
| C12—H12···Cg1iii | 0.95 | 2.79 | 3.658 (2) | 153 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y−1, z; (ii) −x, −y, −z+1; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB6636).
References
- Agilent (2011). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England.
- Al-Obaid, A. M., Abdel-Hamide, S. G., El-Kashef, H. A., Abdel-Aziz, A. A.-M., El-Azab, A. S., Al-Khamees, H. A. & El-Subbagh, H. I. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 2379–2391. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Al-Omary, F. A., Abou-Zeid, L. A., Nagi, M. N., Habib, S. E., Abdel-Aziz, A. A.-M., Hamide, S. G., Al-Omar, M. A., Al-Obaid, A. M. & El-Subbagh, H. I. (2010). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18, 2849–2863. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Aziza, M. A., Nassar, M. W. I., Abdel Hamid, S. G., El-Hakim, A. E. & El-Azab, A. S. (1996). Indian J. Heterocycl. Chem, 6, 25–30.
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- El-Azab, A. S., Abdel-Aziz, A. A.-M., Ng, S. W. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o732–o733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Azab, A. S., Al-Omar, M. A., Abdel-Aziz, A. A.-M., Abdel-Aziz, N. I., El-Sayed, M. A.-A., Aleisa, A. M., Sayed-Ahmed, M. M. & Abdel-Hamide, S. G. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 4188–4198. [DOI] [PubMed]
- El-Azab, A. S. & ElTahir, K. H. (2012). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 22, 327–333. [DOI] [PubMed]
- El-Azab, A. S., ElTahir, K. H. & Attia, S. M. (2011). Monatsh. Chem. 142, 837–848.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812006265/hb6636sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812006265/hb6636Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812006265/hb6636Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report