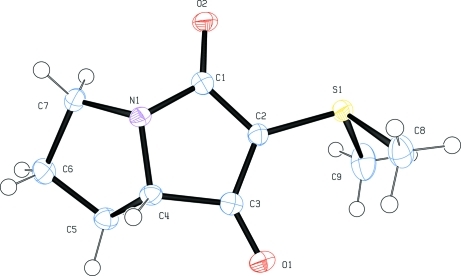
Abstract
In the zwitterionic title compound, C9H13NO2S, the pyrrolidine heterocycle adopts an envelope conformation (with the C atom in the 7-position as the flap). The negative charge is delocalized over the two carbonyl groups and the C atom connecting them. The positive charge is located on the S atom. Two intermolecular C—H⋯O interactions are observed. The molecular geometry at the S atom is trigonal pyramidal.
Related literature
For background to the synthesis of chiral non-racemic zwitterionic compounds, see: Zang et al. (2008 ▶); Kappe et al. (1983 ▶); Palillero et al. (2009 ▶). For the biological activity of related structures, see: Basco et al. (1994 ▶); Koruznjak et al. (2003 ▶). For puckering parameters, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶).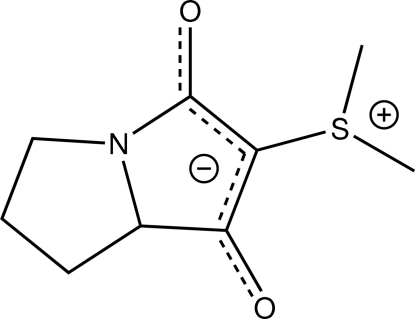
Experimental
Crystal data
C9H13NO2S
M r = 199.26
Orthorhombic,
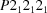
a = 5.8761 (3) Å
b = 9.0858 (5) Å
c = 17.7107 (9) Å
V = 945.56 (9) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.31 mm−1
T = 130 K
0.46 × 0.33 × 0.07 mm
Data collection
Oxford Xcalibur Atlas Gemini diffractometer
Absorption correction: analytical (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.895, T max = 0.976
6356 measured reflections
1873 independent reflections
1736 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.037
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.027
wR(F 2) = 0.065
S = 1.04
1873 reflections
120 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), with 758 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: −0.07 (7)
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2002 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003601/bt5793sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003601/bt5793Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003601/bt5793Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4⋯O2i | 1.00 | 2.55 | 3.4145 (19) | 145 |
| C7—H7B⋯O1ii | 0.99 | 2.59 | 3.570 (2) | 173 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 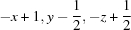 ; (ii)
; (ii) 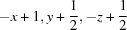 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to BUAP (Project VIEP 2011) for financial support. LGL thanks VIEP for a scholarship.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The synthesis of chiral non racemic zwitterionic compounds is an original area of interest in organic chemistry (Zang et al., 2008; Kappe et al., 1983) because they are useful intermediates for the synthesis of diverse interesting nitrogen heterocyclic compounds (Palillero et al., 2009) with interesting biological properties (Basco et al., 1994; Koruznjak et al., 2003).
In the title zwitterionic compound, C19H13NO2S, the chiral centre shows an S configuration, and the five membered pyrrolidine heterocycle shows an envelope conformations on C5 with puckering parameters (Cremer & Pople, 1975) φ2 = 258.4 (3)° and q2 = 0.4038 (19) Å. The five membered ring N1/C1/C2/C3/C4 shows a twist conformation on N1—C1 with puckering parameters φ2 = 0.0903 (18)° and q2 = 22.4 (12) Å. The bond distances of C1—O2 [1.235 (2) Å] and C3—O1 [1.238 (2) Å] are similar as in related systems which were previously reported. The C2—C3 bond distance [1.406 (2) Å] has the same length as an aromatic bond and C2—C1 [1.435 (2) Å] is shorter than a typical sp3—sp3 bond distance. This suggests, that the negative charge is delocalized on the O1/C3/C2/C2/O2 system. Two intermolecular weak interactions C4—H4···O2 (3.412 (2) Å) and C7—H7B···O1 (3.570 (2) Å) are observed.
Experimental
The title compound, was obtained by an intramolecular cyclization reaction of (S)-(-)-[2-(2-Methoxycarbonyl-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-2-oxo-ethyl]-dimethyl-sulfonium; bromide (1 mmol), which was dissolved in CH3CN (10 ml), treated with KOH (1.2 mmol) and stirred for 2 h at room temperature. The resulting mixture was concentrated in vacuum and dissolved in ethyl acetate, filtered and concentrated giving the desired compound in 98%. Crystals were obtained from an ethyl acetate/diethyl ether solution; m.p. 110–112 °C, [α]D= -13.4 (c 1.0, CH2Cl2). IR (KBr) 3447, 1655, 1591, 1372 cm-1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) d(p.p.m., JHz): 1.51 (m, 1H), 2.05 (m, 3H), 2.99 (s, 3H), 3.01 (s, 3H), 3.12 (m, 1H), 3.57 (td, J = 7.8, 11.0 Hz, 1H), 3.85 (dd, J = 7.24, 9.28 Hz, 1H). HRMS (FAB+): Calcd for C9H13NO2S: 199.0667. Found: 199.0665.
Refinement
H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and refined as riding on their parent atoms, with C—H distances fixed to 0.960 (methyl CH3) and 0.980 Å (methine CH) and with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(methyl C) or 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of title compound, with atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms.
Crystal data
| C9H13NO2S | Dx = 1.406 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 199.26 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Cell parameters from 4129 reflections |
| a = 5.8761 (3) Å | θ = 3.5–26.0° |
| b = 9.0858 (5) Å | µ = 0.31 mm−1 |
| c = 17.7107 (9) Å | T = 130 K |
| V = 945.56 (9) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.46 × 0.33 × 0.07 mm |
| F(000) = 424 |
Data collection
| Oxford Xcalibur Atlas Gemini diffractometer | 1873 independent reflections |
| Graphite monochromator | 1736 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.4685 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.037 |
| ω scans | θmax = 26.1°, θmin = 3.7° |
| Absorption correction: analytical (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2002) | h = −7→7 |
| Tmin = 0.895, Tmax = 0.976 | k = −10→11 |
| 6356 measured reflections | l = −18→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.027 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.065 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0385P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1873 reflections | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 120 parameters | Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), with 758 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: −0.07 (7) |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.72287 (7) | 0.59085 (4) | 0.01093 (2) | 0.01852 (12) | |
| O1 | 0.6977 (3) | 0.26576 (13) | 0.09183 (7) | 0.0293 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.4048 (2) | 0.74463 (12) | 0.13031 (6) | 0.0229 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.4198 (2) | 0.53624 (15) | 0.20467 (8) | 0.0172 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.4721 (3) | 0.61719 (18) | 0.14100 (9) | 0.0172 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.6056 (3) | 0.52340 (19) | 0.09255 (9) | 0.0188 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.6092 (3) | 0.37738 (18) | 0.11921 (10) | 0.0193 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.4806 (3) | 0.38002 (17) | 0.19391 (9) | 0.0173 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.5823 | 0.3464 | 0.2358 | 0.021* | |
| C5 | 0.2519 (3) | 0.30179 (17) | 0.19885 (10) | 0.0216 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.2702 | 0.1975 | 0.2138 | 0.026* | |
| H5B | 0.1682 | 0.3069 | 0.1504 | 0.026* | |
| C6 | 0.1329 (3) | 0.3908 (2) | 0.26032 (10) | 0.0228 (4) | |
| H6A | 0.1871 | 0.3614 | 0.3111 | 0.027* | |
| H6B | −0.0341 | 0.3772 | 0.2579 | 0.027* | |
| C7 | 0.1984 (3) | 0.55113 (19) | 0.24287 (10) | 0.0222 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.0847 | 0.5982 | 0.2094 | 0.027* | |
| H7B | 0.2125 | 0.6096 | 0.2898 | 0.027* | |
| C8 | 1.0123 (3) | 0.5311 (2) | 0.01195 (12) | 0.0296 (4) | |
| H8A | 1.0832 | 0.5535 | −0.0368 | 0.044* | |
| H8B | 1.0179 | 0.4248 | 0.0209 | 0.044* | |
| H8C | 1.0946 | 0.5823 | 0.0523 | 0.044* | |
| C9 | 0.6187 (4) | 0.4744 (3) | −0.06291 (11) | 0.0370 (5) | |
| H9A | 0.6929 | 0.5007 | −0.1106 | 0.056* | |
| H9B | 0.4538 | 0.4873 | −0.0679 | 0.056* | |
| H9C | 0.6523 | 0.3715 | −0.0507 | 0.056* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0209 (2) | 0.0186 (2) | 0.0160 (2) | 0.00209 (17) | 0.00126 (16) | 0.00138 (16) |
| O1 | 0.0388 (8) | 0.0202 (6) | 0.0290 (7) | 0.0101 (6) | 0.0091 (6) | 0.0018 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0311 (7) | 0.0156 (6) | 0.0220 (6) | 0.0036 (5) | 0.0008 (6) | −0.0003 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0200 (8) | 0.0147 (7) | 0.0170 (7) | −0.0002 (6) | 0.0002 (6) | −0.0023 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0173 (9) | 0.0194 (9) | 0.0150 (8) | −0.0035 (7) | −0.0038 (7) | −0.0014 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0205 (9) | 0.0190 (8) | 0.0169 (9) | 0.0022 (8) | 0.0023 (8) | 0.0016 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0178 (9) | 0.0193 (9) | 0.0209 (9) | −0.0004 (7) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0003 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0176 (8) | 0.0165 (8) | 0.0179 (9) | 0.0031 (7) | −0.0021 (7) | 0.0013 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0213 (10) | 0.0186 (8) | 0.0250 (9) | −0.0018 (8) | −0.0005 (8) | −0.0005 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0166 (9) | 0.0247 (10) | 0.0272 (9) | −0.0060 (8) | 0.0030 (7) | −0.0001 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0236 (10) | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0221 (9) | −0.0006 (8) | 0.0067 (8) | −0.0029 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0191 (9) | 0.0384 (10) | 0.0314 (10) | 0.0013 (8) | 0.0018 (8) | 0.0086 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0366 (13) | 0.0563 (13) | 0.0181 (10) | −0.0149 (11) | −0.0006 (9) | −0.0074 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C2 | 1.7146 (17) | C5—H5A | 0.99 |
| S1—C8 | 1.7851 (18) | C5—H5B | 0.99 |
| S1—C9 | 1.7900 (19) | C6—C7 | 1.538 (3) |
| O1—C3 | 1.238 (2) | C6—H6A | 0.99 |
| O2—C1 | 1.238 (2) | C6—H6B | 0.99 |
| N1—C1 | 1.381 (2) | C7—H7A | 0.99 |
| N1—C7 | 1.473 (2) | C7—H7B | 0.99 |
| N1—C4 | 1.476 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.98 |
| C1—C2 | 1.442 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.98 |
| C2—C3 | 1.408 (2) | C8—H8C | 0.98 |
| C3—C4 | 1.524 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.98 |
| C4—C5 | 1.523 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.98 |
| C4—H4 | 1 | C9—H9C | 0.98 |
| C5—C6 | 1.526 (2) | ||
| C2—S1—C8 | 105.40 (9) | H5A—C5—H5B | 109.3 |
| C2—S1—C9 | 105.50 (9) | C5—C6—C7 | 104.11 (14) |
| C8—S1—C9 | 98.84 (11) | C5—C6—H6A | 110.9 |
| C1—N1—C7 | 121.50 (14) | C7—C6—H6A | 110.9 |
| C1—N1—C4 | 110.68 (13) | C5—C6—H6B | 110.9 |
| C7—N1—C4 | 111.17 (13) | C7—C6—H6B | 110.9 |
| O2—C1—N1 | 123.51 (15) | H6A—C6—H6B | 109 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 129.47 (15) | N1—C7—C6 | 103.08 (13) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 106.99 (14) | N1—C7—H7A | 111.1 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 111.43 (15) | C6—C7—H7A | 111.1 |
| C3—C2—S1 | 127.84 (13) | N1—C7—H7B | 111.1 |
| C1—C2—S1 | 120.61 (13) | C6—C7—H7B | 111.1 |
| O1—C3—C2 | 130.27 (16) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.1 |
| O1—C3—C4 | 124.12 (15) | S1—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 105.60 (14) | S1—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| N1—C4—C5 | 103.19 (13) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| N1—C4—C3 | 104.31 (13) | S1—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.71 (14) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| N1—C4—H4 | 110 | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 110 | S1—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 110 | S1—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 101.43 (13) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 111.5 | S1—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 111.5 | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5B | 111.5 | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5B | 111.5 | ||
| C7—N1—C1—O2 | 34.5 (2) | S1—C2—C3—C4 | 179.92 (13) |
| C4—N1—C1—O2 | 167.62 (15) | C1—N1—C4—C5 | −116.83 (15) |
| C7—N1—C1—C2 | −143.55 (15) | C7—N1—C4—C5 | 21.34 (17) |
| C4—N1—C1—C2 | −10.39 (18) | C1—N1—C4—C3 | 7.84 (18) |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | −168.74 (17) | C7—N1—C4—C3 | 146.01 (13) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 9.1 (2) | O1—C3—C4—N1 | 176.79 (16) |
| O2—C1—C2—S1 | 7.6 (3) | C2—C3—C4—N1 | −2.07 (18) |
| N1—C1—C2—S1 | −174.58 (12) | O1—C3—C4—C5 | −69.1 (2) |
| C8—S1—C2—C3 | −52.18 (19) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 112.01 (16) |
| C9—S1—C2—C3 | 51.81 (19) | N1—C4—C5—C6 | −37.44 (16) |
| C8—S1—C2—C1 | 132.16 (15) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −152.13 (15) |
| C9—S1—C2—C1 | −123.85 (16) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 40.51 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—O1 | 177.13 (18) | C1—N1—C7—C6 | 136.85 (15) |
| S1—C2—C3—O1 | 1.1 (3) | C4—N1—C7—C6 | 3.89 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −4.1 (2) | C5—C6—C7—N1 | −27.69 (17) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4···O2i | 1.00 | 2.55 | 3.4145 (19) | 145 |
| C7—H7B···O1ii | 0.99 | 2.59 | 3.570 (2) | 173 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5793).
References
- Basco, L. K., Mitaku, S., Skaltsounis, A. L., Ravelomanantsoa, N., Tillequin, F., Koch, M. & Le Bras, J. (1994). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 38, 1169–1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Kappe, T., Korbuuly, G. & Pongratz, E. (1983). Monatsh. Chem. 114, 303–315.
- Koruznjak, J. D., Grdisa, M., Slade, N., Zamola, B., Pavelic, K. & Karminski-Zamola, G. (2003). J. Med. Chem. 46, 4516–4524. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Oxford Diffraction (2009). CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, England.
- Palillero, A., Teran, J. L., Gnecco, D., Juárez, J. R., Orea, M. L. & Castro, A. (2009). Tetrahedron Lett. 50, 4208–4211.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zang, S. L., Huang, Z. S., Li, Y. M., Chan, A. S. C. & Gu, L. Q. (2008). Tetrahedron, 64, 4403–4407.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003601/bt5793sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003601/bt5793Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003601/bt5793Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report