Abstract
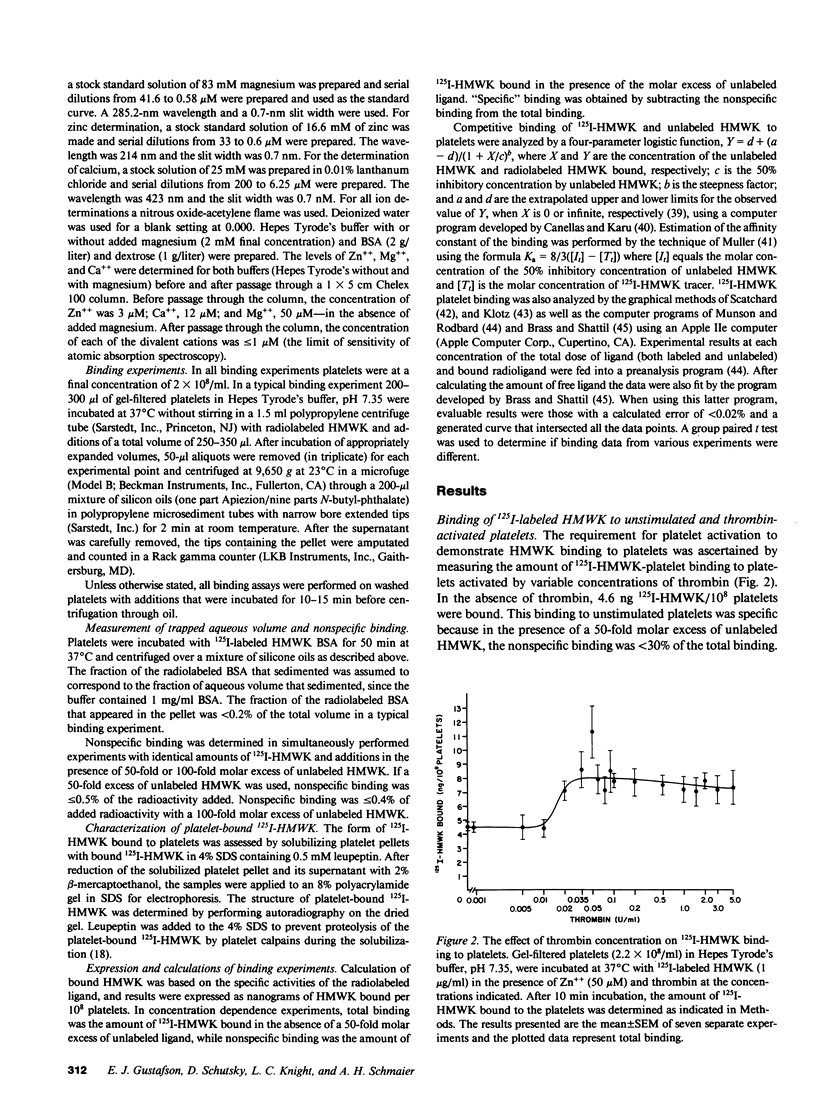
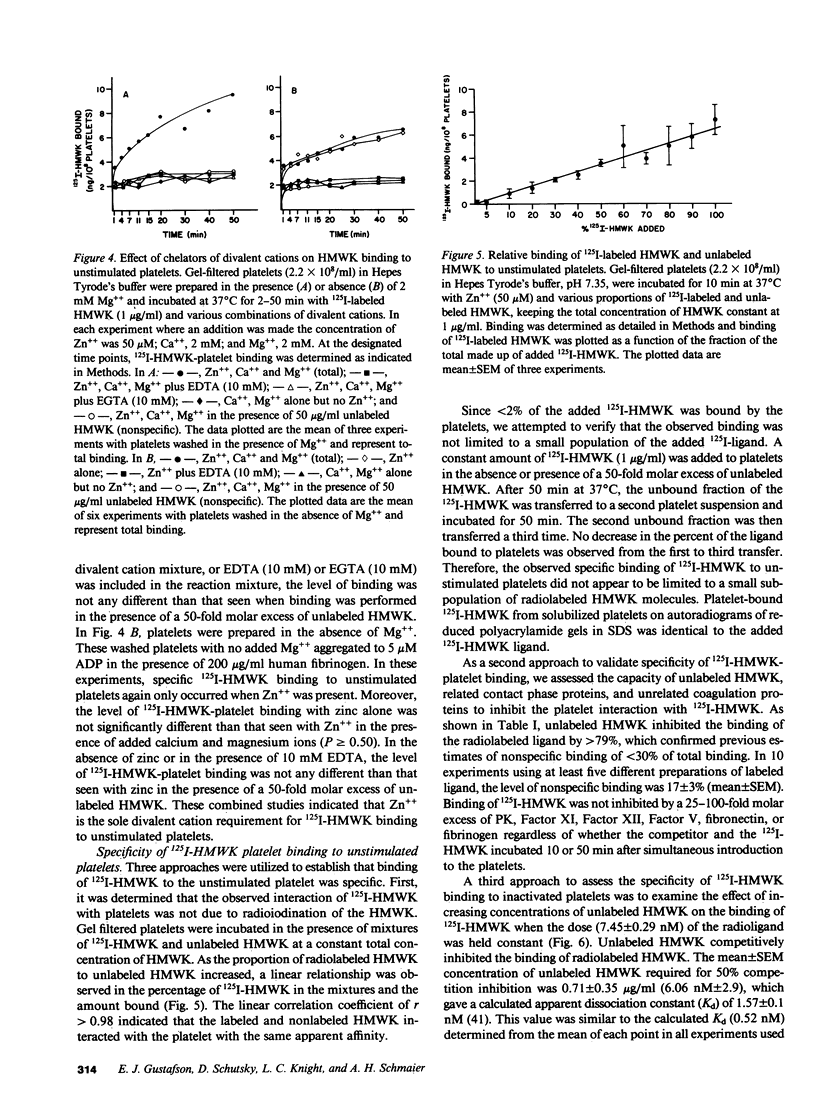
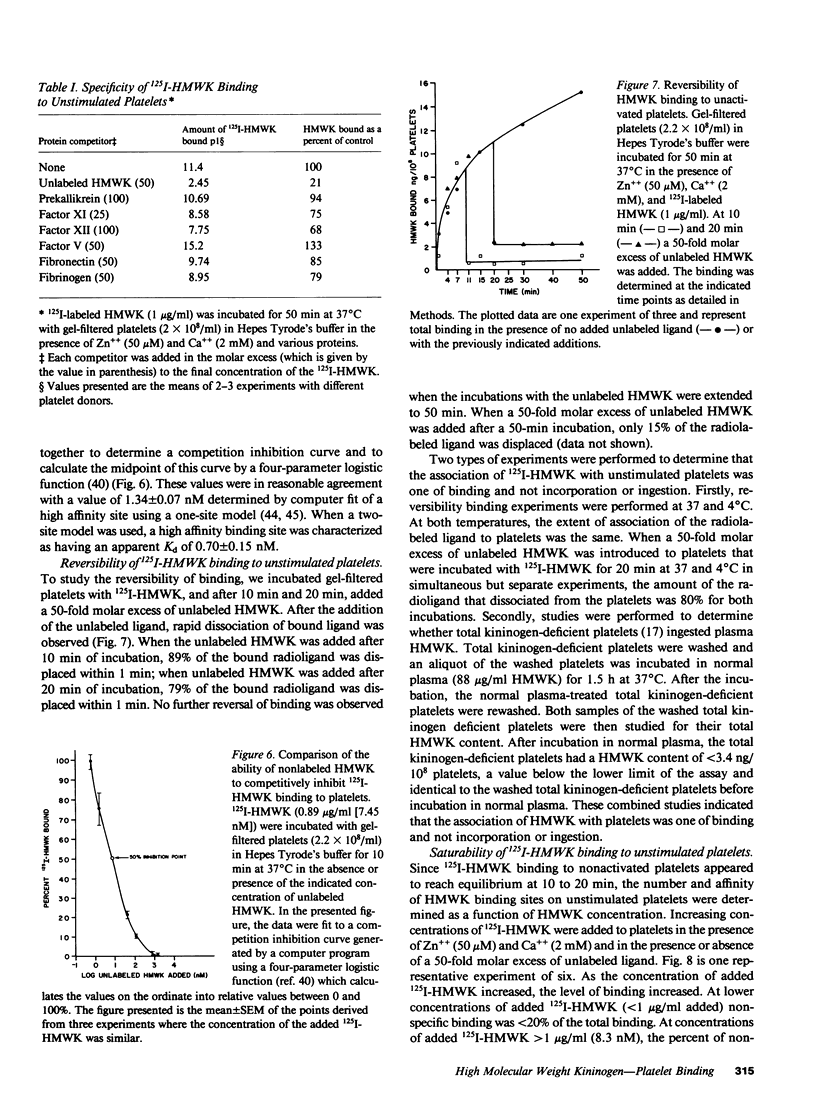
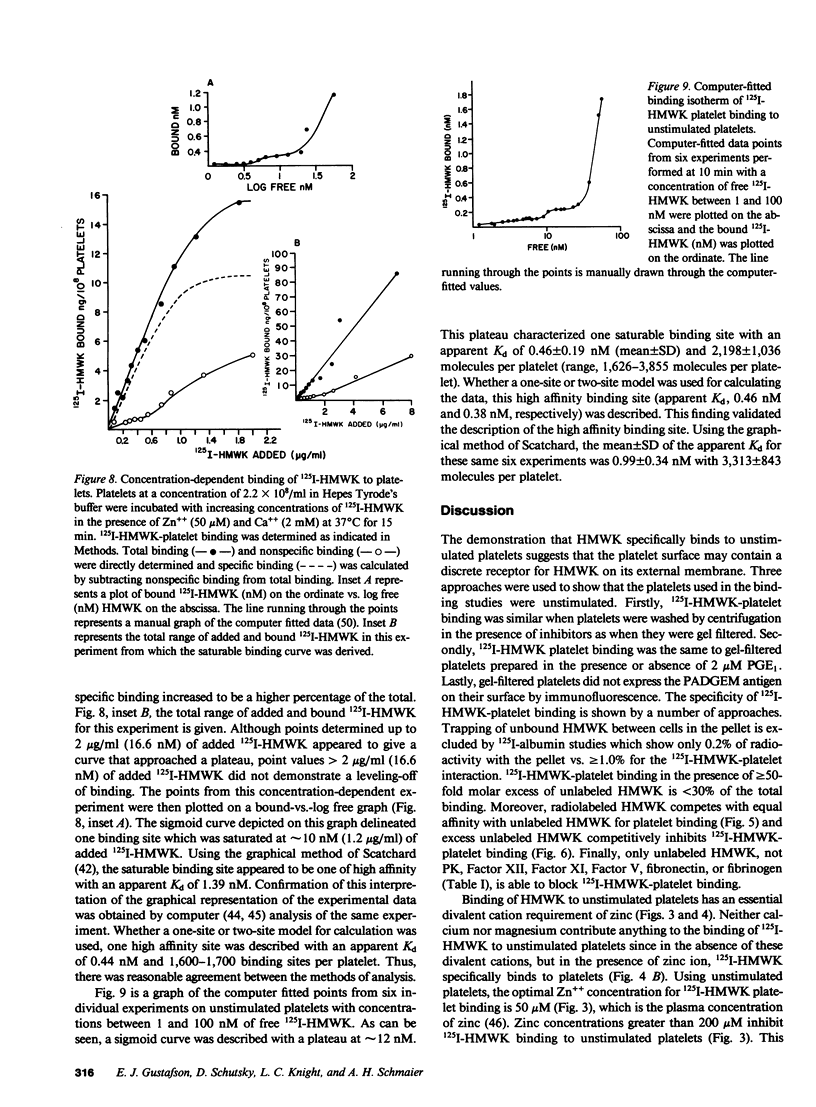
Studies were performed to determine if the unstimulated platelet membrane has a site for high molecular weight kininogen (HMWK) binding. 125I-HMWK bound to unstimulated platelets. Zn++ was required for 125I-HMWK binding to unstimulated platelets and binding was maximal at 50 microM Zn++. Neither Mg++ nor Ca++ substituted for Zn++ in supporting 125I-HMWK binding to unstimulated platelets, and neither ion potentiated binding in the presence of 50 microM zinc. 125I-HMWK competed with equal affinity with HMWK for binding, and excess HMWK inhibited 125I-HMWK-platelet binding. Only HMWK, not prekallikrein, Factor XII, Factor XI, Factor V, fibrinogen, or fibronectin inhibited 125I-HMWK-platelet binding. 125I-HMWK binding to unstimulated platelets was 89% reversible within 10 min with a 50-fold molar excess of HMWK. Unstimulated platelets contained a single set of saturable, high affinity binding sites for 125I-HMWK with an apparent dissociation constant of 0.99 nM +/- 0.35 and 3,313 molecules/platelet +/- 843. These studies indicate that the unstimulated external platelet membrane has a binding site for HMWK that could serve as a surface to modulate contact phase activation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdasarian A., Lahiri B., Talamo R. C., Wong P., Colman R. W. Immunochemical studies of plasma kallikrein. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1444–1454. doi: 10.1172/JCI107892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Shattil S. J. Changes in surface-bound and exchangeable calcium during platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14000–14005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canellas P. F., Karu A. E. Statistical package for analysis of competition ELISA results. J Immunol Methods. 1981;47(3):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Revak S. D., Wuepper K. D. Activation of Hageman factor in solid and fluid phases. A critical role of kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1564–1583. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Bagdasarian A., Talamo R. C., Scott C. F., Seavey M., Guimaraes J. A., Pierce J. V., Kaplan A. P. Williams trait. Human kininogen deficiency with diminished levels of plasminogen proactivator and prekallikrein associated with abnormalities of the Hageman factor-dependent pathways. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1650–1662. doi: 10.1172/JCI108247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Hancock A. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Validation and statistical analysis of a computer modeling method for quantitative analysis of radioligand binding data for mixtures of pharmacological receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;21(1):5–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. A., Schmaier A. H., Addonizio V. P., Colman R. W. Assay of prekallikrein in human plasma: comparison of amidolytic, esterolytic, coagulation, and immunochemical assays. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):963–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley B., Johnson S. A., Hackley B., Smith J. C., Jr, Halsted J. A. Zinc content of human platelets. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 May;128(1):265–269. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-32993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Heimark R. L., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Activation of bovine factor XII (Hageman factor) by plasma kallikrein. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1322–1330. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard J. S., Griffin J. H. Receptors for high molecular weight kininogen on stimulated washed human platelets. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6863–6869. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H. Role of surface in surface-dependent activation of Hageman factor (blood coagulation factor XII). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1998–2002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harfenist E. J., Guccione M. A., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. The use of the synthetic peptide, Gly-Pro-Arg-Pro, in the preparation of thrombin-degranulated rabbit platelets. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):952–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Studies on the interaction between collagen and a plasma kallikrein-like activity. Evidence for a surface-active enzyme system. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1813–1822. doi: 10.1172/JCI106983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hojima Y., Cochrane C. G., Wiggins R. C., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. In vitro activation of the contact (Hageman factor) system of plasma by heparin and chondroitin sulfate E. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1453–1459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu-Lin S., Berman C. L., Furie B. C., August D., Furie B. A platelet membrane protein expressed during platelet activation and secretion. Studies using a monoclonal antibody specific for thrombin-activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9121–9126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbiriou D. M., Griffin J. H. Human high molecular weight kininogen. Studies of structure-function relationships and of proteolysis of the molecule occurring during contact activation of plasma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12020–12027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby E. P., McDevitt P. J. The binding of bovine factor XII to kaolin. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):652–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz I. M. Numbers of receptor sites from Scatchard graphs: facts and fantasies. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1247–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.6287580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLNAR J., LORAND L. Studies on apyrases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:353–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90278-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur E. M., Hoffman R., Chasis J., Marchesi S., Bruno E. Immunofluorescent identification of human megakaryocyte colonies using an antiplatelet glycoprotein antiserum. Blood. 1981 Feb;57(2):277–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillin C. R., Saito H., Ratnoff O. D., Walton A. G. The secondary structure of human Hageman factor (factor XII) and its alteration by activating agents. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1312–1322. doi: 10.1172/JCI107877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Silverberg M., Kaplan A. P. Autoactivatability of human Hageman factor (factor XII). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 12;92(3):803–810. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90774-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Perry D. W., Ardlie N. G., Packham M. A. Preparation of suspensions of washed platelets from humans. Br J Haematol. 1972 Feb;22(2):193–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R. Determination of affinity and specificity of anti-hapten antibodies by competitive radioimmunoassay. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:589–601. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., ROSENBLUM J. M. Role of Hageman factor in the initiation of clotting by glass; evidence that glass frees Hageman factor from inhibition. Am J Med. 1958 Aug;25(2):160–168. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Saito H. Amidolytic properties of single-chain activated Hageman factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1461–1463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G., Griffin J. H. The binding and cleavage characteristics of human Hageman factor during contact activation. A comparison of normal plasma with plasmas deficient in factor XI, prekallikrein, or high molecular weight kininogen. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1167–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI108741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Claypool W., Colman R. W. Crotalocytin: recognition and purification of a timber rattlesnake platelet aggregating protein. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):1013–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Colman R. W. Crotalocytin: characterization of the timber rattlesnake platelet activating protein. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):1020–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Smith P. M., Purdon A. D., White J. G., Colman R. W. High molecular weight kininogen: localization in the unstimulated and activated platelet and activation by a platelet calpain(s). Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):119–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Zuckerberg A., Silverman C., Kuchibhotla J., Tuszynski G. P., Colman R. W. High-molecular weight kininogen. A secreted platelet protein. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1477–1489. doi: 10.1172/JCI110901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. F., Liu C. Y., Colman R. W. Human plasma prekallikrein: a rapid high-yield method for purification. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):77–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. F., Silver L. D., Schapira M., Colman R. W. Cleavage of human high molecular weight kininogen markedly enhances its coagulant activity. Evidence that this molecule exists as a procofactor. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):954–962. doi: 10.1172/JCI111319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg M., Dunn J. T., Garen L., Kaplan A. P. Autoactivation of human Hageman factor. Demonstration utilizing a synthetic substrate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7281–7286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg M., Nicoll J. E., Kaplan A. P. The mechanism by which the light chain of cleaved HMW-kininogen augments the activation of prekallikrein, factor XI and Hageman factor. Thromb Res. 1980 Oct 15;20(2):173–189. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90383-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha D., Seaman F. S., Koshy A., Knight L. C., Walsh P. N. Blood coagulation factor XIa binds specifically to a site on activated human platelets distinct from that for factor XI. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jun;73(6):1550–1556. doi: 10.1172/JCI111361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tankersley D. L., Finlayson J. S. Kinetics of activation and autoactivation of human factor XII. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):273–279. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tans G., Rosing J., Griffin J. H. Sulfatide-dependent autoactivation of human blood coagulation Factor XII (Hageman Factor). J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8215–8222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. E., Mandle R., Jr, Kaplan A. P. Association of factor XI and high molecular weight kininogen in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1977 Dec;60(6):1376–1380. doi: 10.1172/JCI108898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmons S., Hawiger J. Separation of human platelets from plasma proteins including factor VIII VWF by a combined albumin gradient-gel filtration method using HEPES buffer. Thromb Res. 1978 Feb;12(2):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90300-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wencel-Drake J. D., Plow E. F., Zimmerman T. S., Painter R. G., Ginsberg M. H. Immunofluorescent localization of adhesive glycoproteins in resting and thrombin-stimulated platelets. Am J Pathol. 1984 May;115(2):156–164. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins R. C., Cochrane C. C. The autoactivation of rabbit Hageman factor. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1122–1133. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




