Abstract
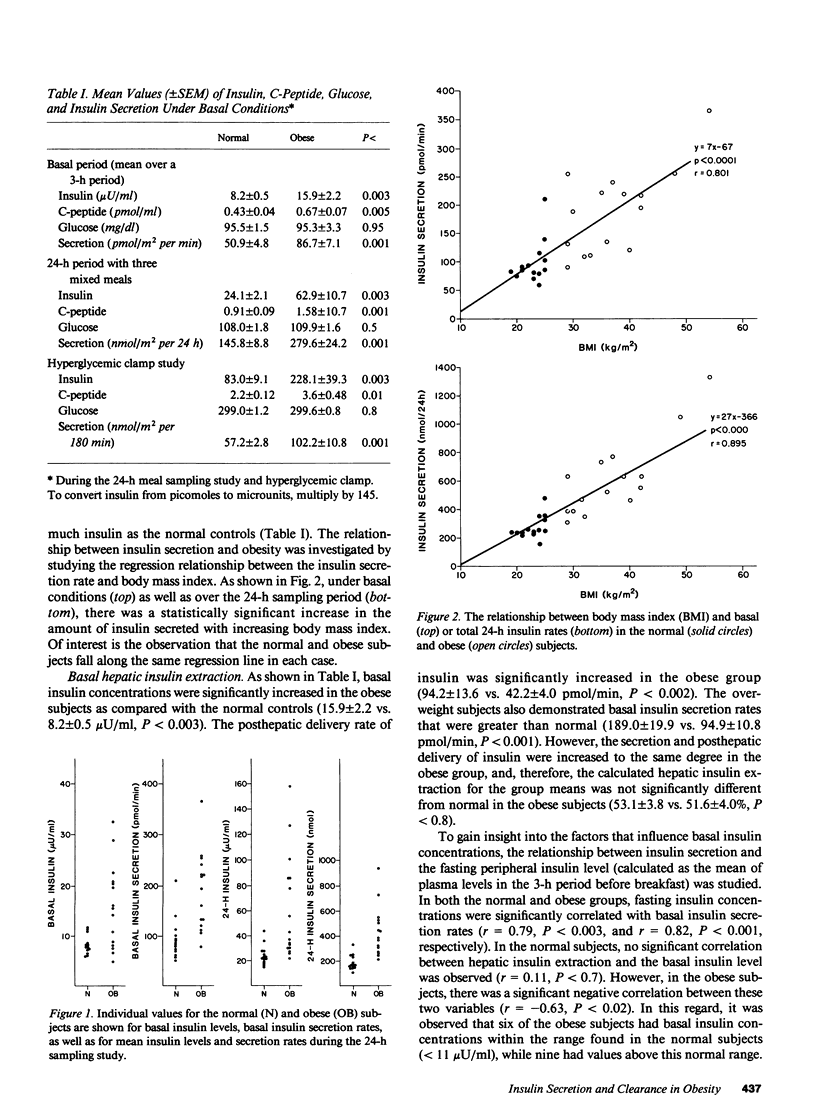
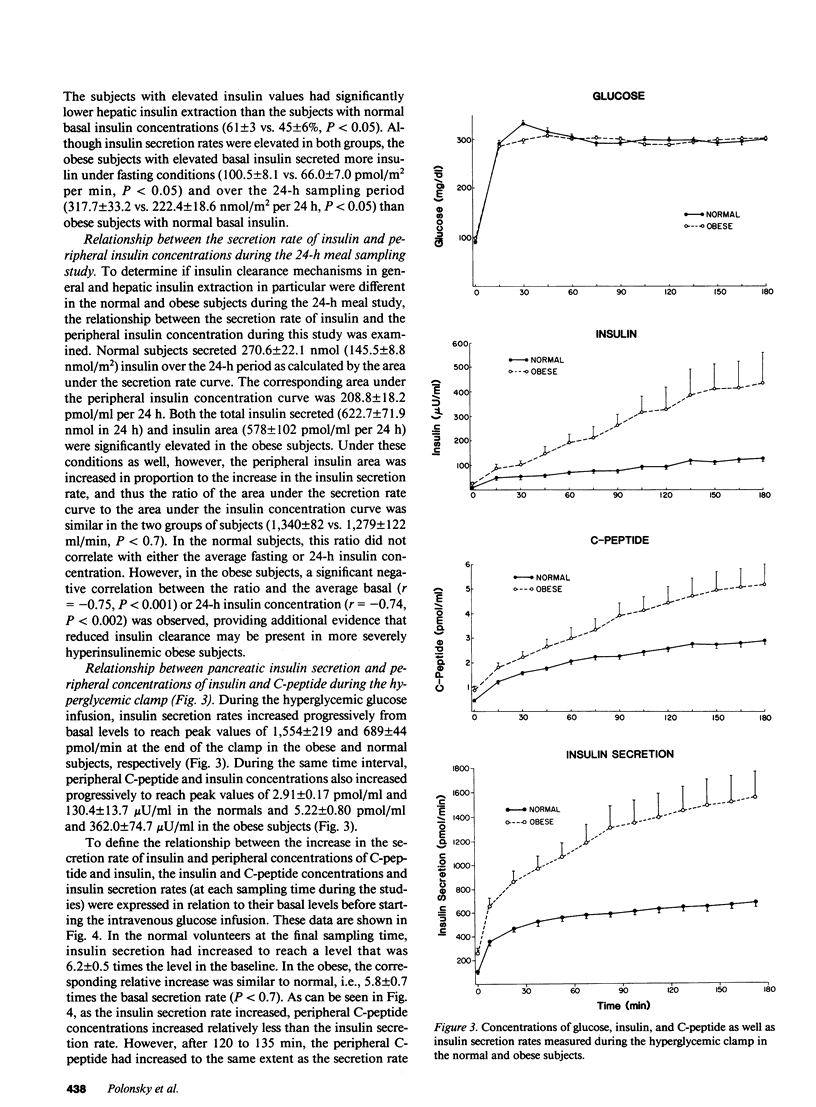
The secretion and hepatic extraction of insulin were compared in 14 normal volunteers and 15 obese subjects using a previously validated mathematical model of insulin secretion and rate constants for C-peptide derived from analysis of individual decay curves after intravenous bolus injections of biosynthetic human C-peptide. Insulin secretion rates were substantially higher than normal in the obese subjects after an overnight fast (86.7 +/- 7.1 vs. 50.9 +/- 4.8 pmol/m2 per min, P less than 0.001, mean +/- SEM), over a 24-h period on a mixed diet (279.6 +/- 24.2 vs. 145.8 +/- 8.8 nmol/m2 per 24 h, P less than 0.001), and during a hyperglycemic intravenous glucose infusion (102.2 +/- 10.8 vs. 57.2 +/- 2.8 nmol/m2 per 180 min, P less than 0.001). Linear regression analysis revealed a highly significant relationship between insulin secretion and body mass index. Basal hepatic insulin extraction was not significantly different in the normal and obese subjects (53.1 +/- 3.8 vs. 51.6 +/- 4.0%). In the normal subjects, fasting insulin did not correlate with basal hepatic insulin extraction, but a significant negative correlation between fasting insulin and hepatic insulin extraction was seen in obesity (r = -0.63, P less than 0.02). This finding reflected a higher extraction in the six obese subjects with fasting insulin levels within the range of the normal subjects than in the nine subjects with elevated fasting insulin concentrations (61 +/- 3 vs. 45 +/- 6%, P less than 0.05). During the hyperglycemic clamp, the insulin secretion rate increased to an average maximum of 6.2-fold over baseline in the normal subjects and 5.8-fold in the obese subjects. Over the same time, the peripheral insulin concentration increased 14.1-fold over baseline in the normals and 16.6-fold over baseline in the obese, indicating a reduction in the clearance of endogenously secreted insulin. Although the fall in insulin clearance tended to be greater in the obese subjects, the differences between the two groups were not statistically significant. Thus, under basal, fasting conditions and during ingestion of a mixed diet, the hyperinsulinemia of obesity results predominantly from increased insulin secretion. In patients with more marked basal hyperinsulinemia and during intense stimulation of insulin secretion, a reduction in insulin clearance may contribute to the greater increase in peripheral insulin concentrations that are characteristic of the obese state.+
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonora E., Zavaroni I., Coscelli C., Butturini U. Decreased hepatic insulin extraction in subjects with mild glucose intolerance. Metabolism. 1983 May;32(5):438–446. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M. B., Harris M. D., Rosenberg C. S. Inverse relationship of metabolic clearance rate of insulin to body mass index. Metabolism. 1987 Mar;36(3):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. P., Allen R. C., Schade D. S., Erickson K. M., Standefer J. Prehepatic insulin production in man: kinetic analysis using peripheral connecting peptide behavior. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Sep;51(3):520–528. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-3-520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. P., Allen R. C., Schade D. S. Hepatic removal of insulin in normal man: dose response to endogenous insulin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jun;56(6):1294–1300. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-6-1294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber O. K., Binder C., Markussen J., Heding L. G., Naithani V. K., Kuzuya H., Blix P., Horwitz D. L., Rubenstein A. H. Characterization of seven C-peptide antisera. Diabetes. 1978;27 (Suppl 1):170–177. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.s170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber O. K., Christensen K., Kehlet H., Madsbad S., Binder C. Decreased insulin removal contributes to hyperinsulinemia in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Sep;53(3):618–621. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-3-618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Wahren J., Faber O. K., Felig P., Binder C., DeFronzo R. A. Splanchnic and renal metabolism of insulin in human subjects: a dose-response study. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):E517–E527. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.6.E517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida T., Chap Z., Chou J., Lewis R., Hartley C., Entman M., Field J. B. Differential effects of oral, peripheral intravenous, and intraportal glucose on hepatic glucose uptake and insulin and glucagon extraction in conscious dogs. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):590–601. doi: 10.1172/JCI111007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaden M., Harding P., Field J. B. Effect of intraduodenal glucose administration on hepatic extraction of insulin in the anesthetized dog. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):2016–2028. doi: 10.1172/JCI107386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissebah A. H., Vydelingum N., Murray R., Evans D. J., Hartz A. J., Kalkhoff R. K., Adams P. W. Relation of body fat distribution to metabolic complications of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):254–260. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. R., Olefsky J. M. Retroendocytosis of insulin in rat adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1986 Aug;119(2):572–579. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-2-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsbad S., Kehlet H., Hilsted J., Tronier B. Discrepancy between plasma C-peptide and insulin response to oral and intravenous glucose. Diabetes. 1983 May;32(5):436–438. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.5.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistas M. T., Rendell M., Margolis S., Kowarski A. A. Estimation of the secretion rate of insulin from the urinary excretion rate of C-peptide. Study in obese and diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1982 May;31(5 Pt 1):449–453. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.5.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistas M. T., Zadik Z., Margolis S., Kowarski A. A. Correlation of urinary excretion of C-peptide with the integrated concentration and secretion rate of insulin. Diabetes. 1981 Aug;30(8):639–643. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.8.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishima T., Bradshaw C., Radziuk J. Measurement using tracers of steady-state turnover and metabolic clearance of insulin in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 1):E203–E208. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.2.E203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peiris A. N., Mueller R. A., Smith G. A., Struve M. F., Kissebah A. H. Splanchnic insulin metabolism in obesity. Influence of body fat distribution. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1648–1657. doi: 10.1172/JCI112758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K. S., Given B. D., Pugh W., Licinio-Paixao J., Thompson J. E., Karrison T., Rubenstein A. H. Calculation of the systemic delivery rate of insulin in normal man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jul;63(1):113–118. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K. S., Licinio-Paixao J., Given B. D., Pugh W., Rue P., Galloway J., Karrison T., Frank B. Use of biosynthetic human C-peptide in the measurement of insulin secretion rates in normal volunteers and type I diabetic patients. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):98–105. doi: 10.1172/JCI112308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K. S., Rubenstein A. H. C-peptide as a measure of the secretion and hepatic extraction of insulin. Pitfalls and limitations. Diabetes. 1984 May;33(5):486–494. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.5.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K., Frank B., Pugh W., Addis A., Karrison T., Meier P., Tager H., Rubenstein A. The limitations to and valid use of C-peptide as a marker of the secretion of insulin. Diabetes. 1986 Apr;35(4):379–386. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.4.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossell R., Gomis R., Casamitjana R., Segura R., Vilardell E., Rivera F. Reduced hepatic insulin extraction in obesity: relationship with plasma insulin levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Mar;56(3):608–611. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-3-608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage P. J., Flock E. V., Mako M. E., Blix P. M., Rubenstein A. H., Bennett P. H. C-Peptide and insulin secretion in Pima Indians and Caucasians: constant fractional hepatic extraction over a wide range of insulin concentrations and in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Apr;48(4):594–598. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-4-594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönksen P. H., Tompkins C. V., Srivastava M. C., Nabarro J. D. A comparative study on the metabolism of human insulin and porcine proinsulin in man. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Nov;45(5):633–654. doi: 10.1042/cs0450633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldhäusl W., Bratusch-Marrain P., Gasic S., Korn A., Nowotny P. Insulin production rate following glucose ingestion estimated by splanchnic C-peptide output in normal man. Diabetologia. 1979 Oct;17(4):221–227. doi: 10.1007/BF01235858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



