Abstract
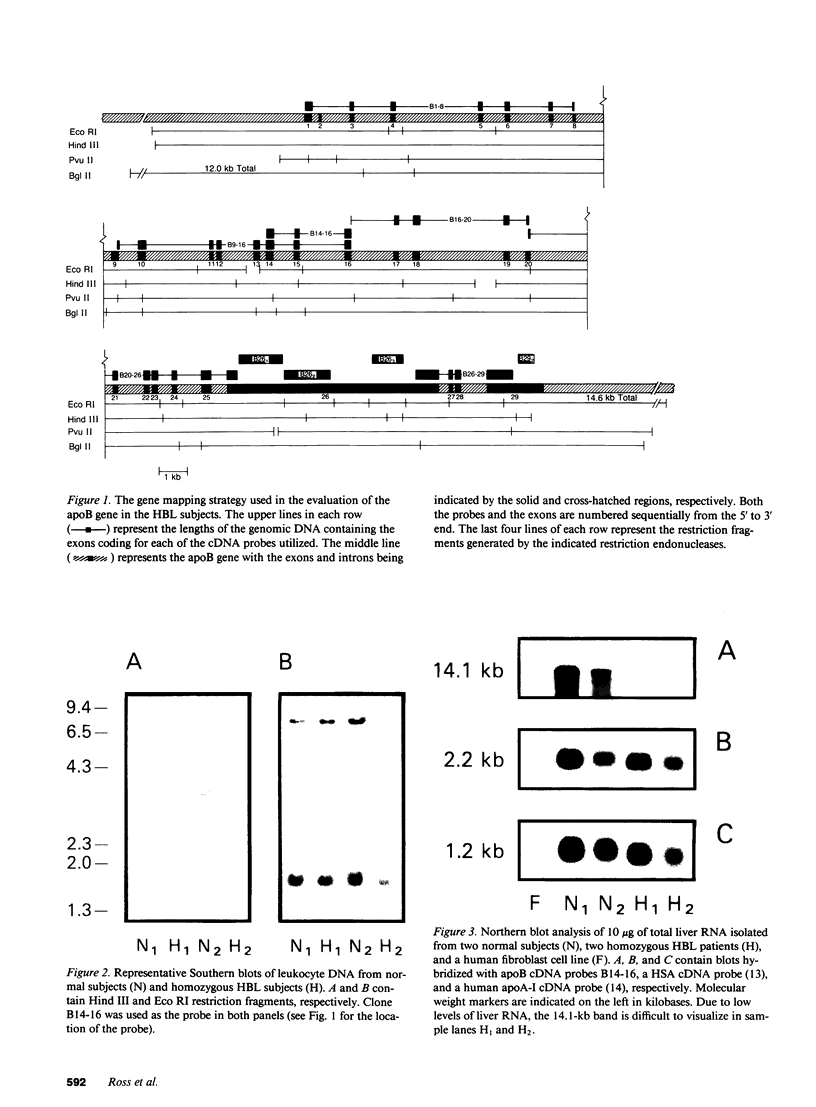
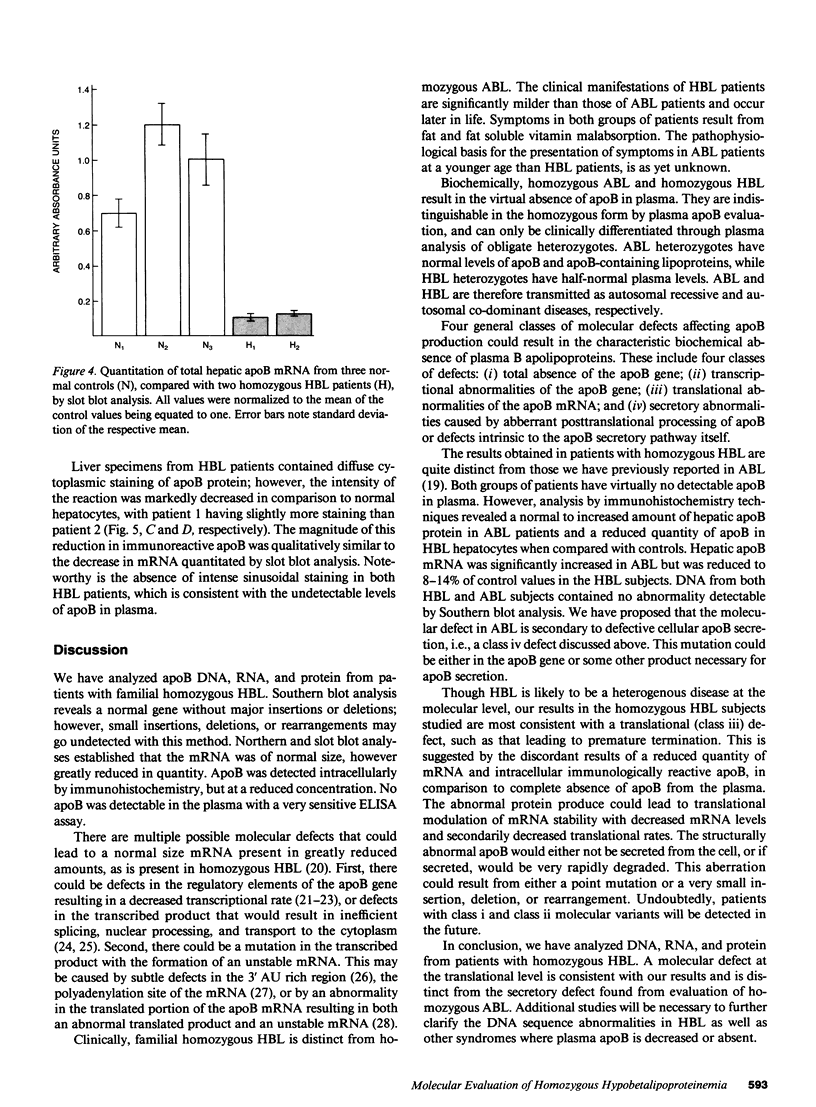
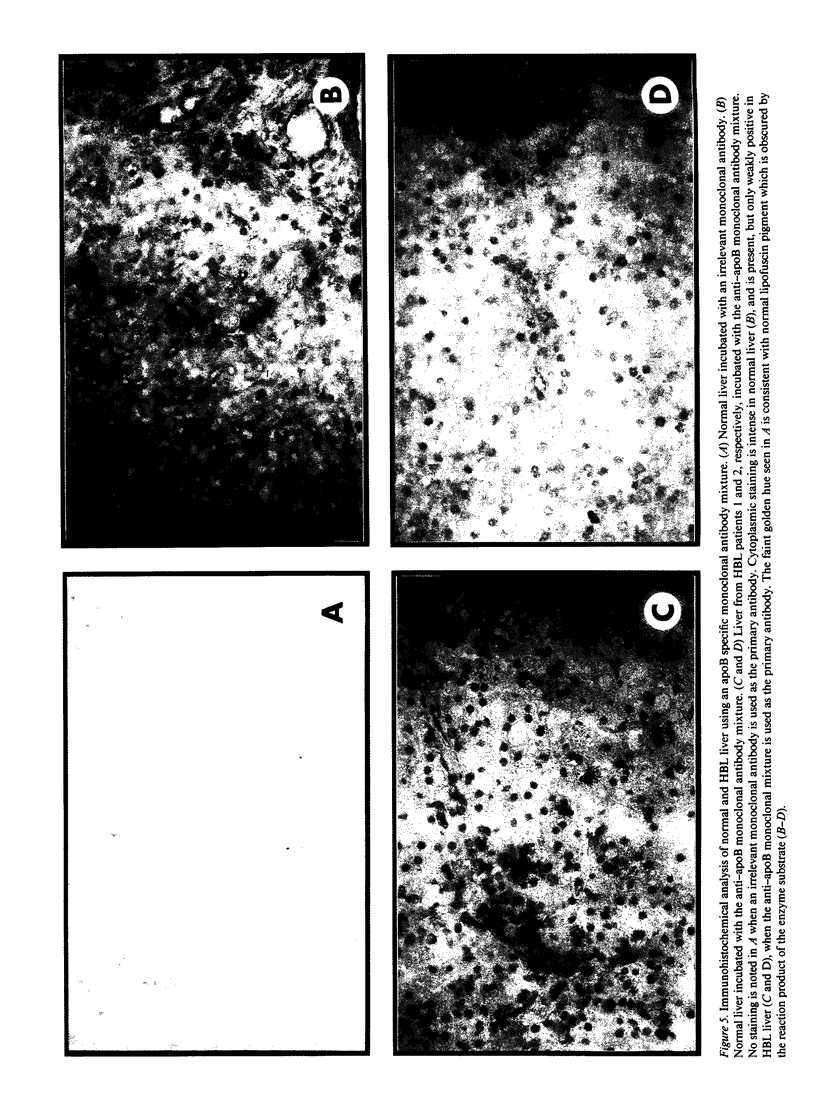
apoB DNA, RNA, and protein from two patients with homozygous hypobetalipoproteinemia (HBL) were evaluated and compared with normal individuals. Southern blot analysis with 10 different cDNA probes revealed a normal gene without major insertions, deletions, or rearrangements. Northern and slot blot analyses of total liver mRNA from HBL patients documented a normal size apoB mRNA that was present in greatly reduced quantities. ApoB protein was detected within HBL hepatocytes utilizing immunohistochemical techniques; however, it was markedly reduced in quantity when compared with control samples. No apoB was detectable in the plasma of HBL individuals with an ELISA assay. These data are most consistent with a mutation in the coding portion of the apoB gene in HBL patients, leading to an abnormal apoB protein and apoB mRNA instability. These results are distinct from those previously noted in abetalipoproteinemia, which was characterized by an elevated level of hepatic apoB mRNA and accumulation of intracellular hepatic apoB protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E., Irkin S. H., Cheng T. C., Scott A. F., Sexton J. P., Trusko S. P., Charache S., Kazazian H. H., Jr beta-Thalassemia in American Blacks: novel mutations in the "TATA" box and an acceptor splice site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1154–1158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avioli L. V. Absorption and metabolism of vitamin D3 in man. Am J Clin Nutr. 1969 Apr;22(4):437–446. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/22.4.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biemer J. J., McCammon R. E. The genetic relationship of abetalipoproteinemia and hypobetalipoproteinemia: a report of the occurence of both diseases within the same family. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Apr;85(4):556–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackhart B. D., Ludwig E. M., Pierotti V. R., Caiati L., Onasch M. A., Wallis S. C., Powell L., Pease R., Knott T. J., Chu M. L. Structure of the human apolipoprotein B gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15364–15367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Goodbourn S. E., Lamb J., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Proudfoot N. J. Alpha-thalassaemia caused by a polyadenylation signal mutation. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):398–400. doi: 10.1038/306398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner K. J., Law S. W., Brewer H. B., Jr The human apolipoprotein A-II gene: complete nucleic acid sequence and genomic organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4597–4608. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner K. J., Monge J. C., Gregg R. E., Hoeg J. M., Triche T. J., Law S. W., Brewer H. B., Jr Analysis of the apolipoprotein B gene and messenger ribonucleic acid in abetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1707–1712. doi: 10.1172/JCI112766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Brewer H. B., Jr Nucleotide sequence and the encoded amino acids of human apolipoprotein A-I mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):66–70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Grant S. M., Higuchi K., Hospattankar A., Lackner K., Lee N., Brewer H. B., Jr Human liver apolipoprotein B-100 cDNA: complete nucleic acid and derived amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8142–8146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Gray G., Brewer H. B., Jr cDNA cloning of human apoA-I: amino acid sequence of preproapoA-I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 15;112(1):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91824-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley T. J., Anagnou N. P., Pepe G., Nienhuis A. W. RNA processing errors in patients with beta-thalassemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4775–4779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D. P., Lloyd J. K. Effect of large oral doses of vitamin E on the neurological sequelae of patients with abetalipoproteinemia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;393:133–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb31239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Antonarakis S. E., Kazazian H. H., Jr Base substitution at position -88 in a beta-thalassemic globin gene. Further evidence for the role of distal promoter element ACACCC. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8679–8681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Goff S. C. Nonsense and frameshift mutations in beta 0-thalassemia detected in cloned beta-globin genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9782–9784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr The mutation and polymorphism of the human beta-globin gene and its surrounding DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:131–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Sexton J. P., Cheng T. C., Goff S. C., Giardina P. J., Lee J. I., Kazazian H. H., Jr ATA box transcription mutation in beta-thalassemia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4727–4734. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protter A. A., Hardman D. A., Schilling J. W., Miller J., Appleby V., Chen G. C., Kirsher S. W., McEnroe G., Kane J. P. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding the amino-terminal region of human apolipoprotein B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1467–1471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOBREVILLA L. A., GOODMAN M. L., KANE C. A. DEMYELINATING CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM DISEASE, MACULAR ATROPHY AND ACANTHOCYTOSIS (BASSEN-KORNZWEIG SYNDROME). Am J Med. 1964 Nov;37:821–828. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Heaton W. H., Wetzel M. G., Brewer H. B., Jr Plasma apolipoprotein A-1 absence associated with a marked reduction of high density lipoproteins and premature coronary artery disease. Arteriosclerosis. 1982 Jan-Feb;2(1):16–26. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.2.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Orkin S. H., Maniatis T. Specific transcription and RNA splicing defects in five cloned beta-thalassaemia genes. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):591–596. doi: 10.1038/302591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]