Abstract
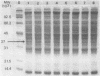
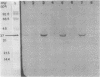
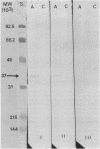
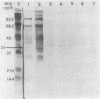
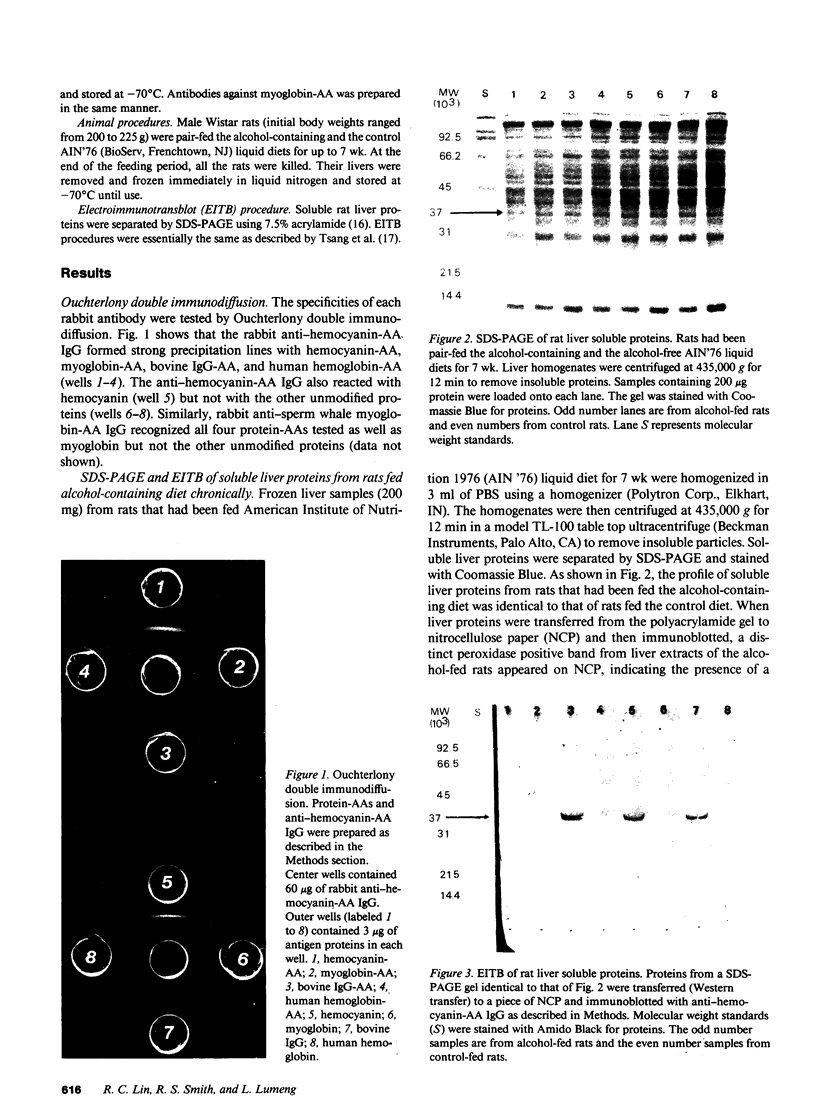
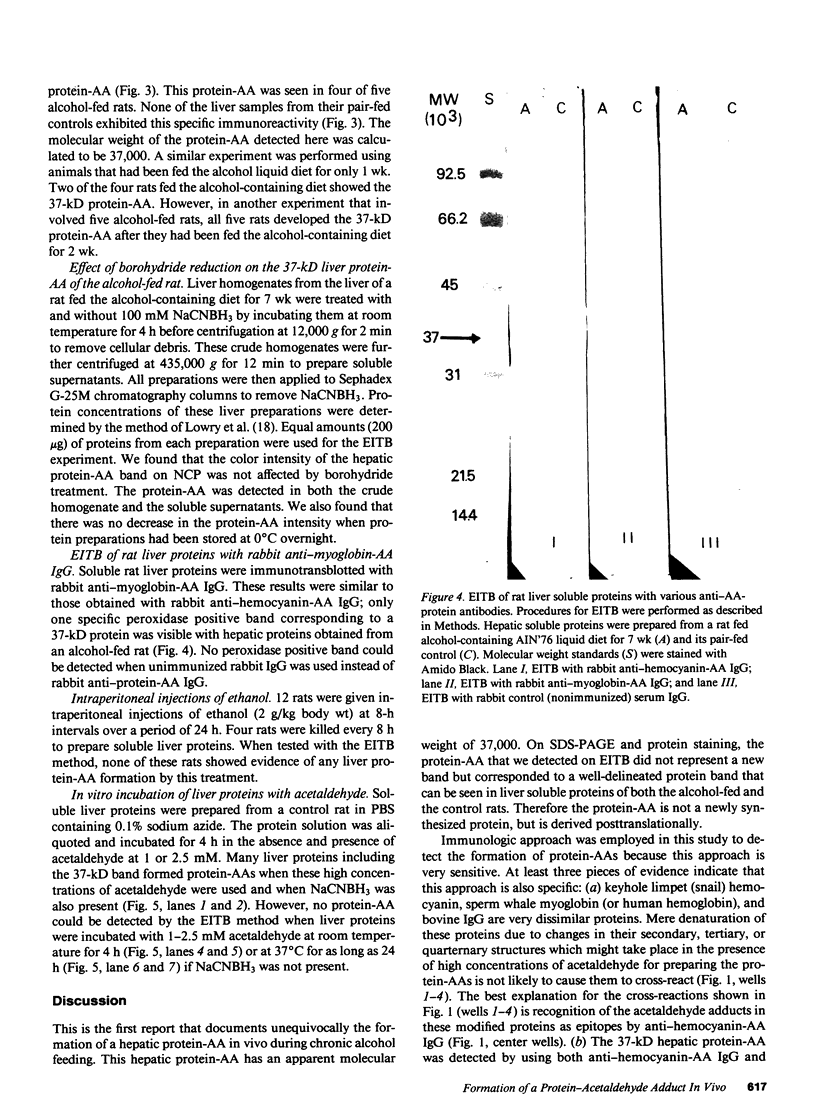
We report here the formation in vivo of a protein-acetaldehyde adduct (protein-AA) in liver when rats were fed alcohol chronically. This chemically modified protein was demonstrated by electroimmunotransblot technique and with rabbit polyclonal antibodies that recognize acetaldehyde adduct as an epitope (i.e., both anti-hemocyanin-AA IgG and anti-myoglobin-AA IgG). It has a molecular weight of 37,000. It can be detected in the liver of rats fed the alcohol-containing American Institute of Nutrition 1976 liquid diet for only 1 wk. Since the protein profiles of soluble hepatic proteins from alcohol-fed and control rats were identical on SDS-PAGE, the peroxidase-positive band demonstrated by electroimmunotransblot was most likely not a new protein synthesized de novo. Borohydride reduction was not necessary to stabilize this protein-AA. Intraperitoneal injections of ethanol (2 g/kg body wt) at 8-h intervals to rats over a 24-h period did not produce any detectable protein-AA in the liver. Incubation of the liver homogenate from a control liver with acetaldehyde without sodium cyanoborohydride for 4 h also failed to generate any protein-AA. Therefore, the formation of the 37-kD protein-AA in vivo reported here is dependent on chronic alcohol consumption.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Donohue T. M., Jr, Tuma D. J., Sorrell M. F. Acetaldehyde adducts with proteins: binding of [14C]acetaldehyde to serum albumin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jan;220(1):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90406-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines K. C., Salhany J. M., Tuma D. J., Sorrell M. F. Reaction of acetaldehyde with human erythrocyte membrane proteins. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoerner M., Behrens U. J., Worner T., Lieber C. S. Humoral immune response to acetaldehyde adducts in alcoholic patients. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;54(1):3–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel Y., Hurwitz E., Niemelä O., Arnon R. Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies against acetaldehyde-containing epitopes in acetaldehyde-protein adducts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7923–7927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennett R. B., Tuma D. J., Sorrell M. F. Effect of ethanol and its metabolites on microtubule formation. Pharmacology. 1980;21(5):363–368. doi: 10.1159/000137453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber C. S., DeCarli L. M. The feeding of alcohol in liquid diets: two decades of applications and 1982 update. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1982 Fall;6(4):523–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1982.tb05017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. C. Quantification of apolipoproteins in rat serum and in cultured rat hepatocytes by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):316–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumeng L., Li T. K. The development of metabolic tolerance in the alcohol-preferring P rats: comparison of forced and free-choice drinking of ethanol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1986 Nov;25(5):1013–1020. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(86)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina V. A., Donohue T. M., Jr, Sorrell M. F., Tuma D. J. Covalent binding of acetaldehyde to hepatic proteins during ethanol oxidation. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Jan;105(1):5–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura F., Lieber C. S. Binding of acetaldehyde to rat liver microsomes: enhancement after chronic alcohol consumption. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 15;100(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San George R. C., Hoberman H. D. Reaction of acetaldehyde with hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6811–6821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrell M. F., Tuma D. J. Hypothesis: alcoholic liver injury and the covalent binding of acetaldehyde. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1985 Jul-Aug;9(4):306–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1985.tb05549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens V. J., Fantl W. J., Newman C. B., Sims R. V., Cerami A., Peterson C. M. Acetaldehyde adducts with hemoglobin. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):361–369. doi: 10.1172/JCI110043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Peralta J. M., Simons A. R. Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques (EITB) for studying the specificities of antigens and antibodies separated by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:377–391. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuma D. J., Donohue T. M., Jr, Medina V. A., Sorrell M. F. Enhancement of acetaldehyde-protein adduct formation by L-ascorbate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Nov 1;234(2):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90283-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]