Abstract
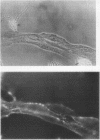
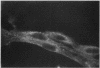
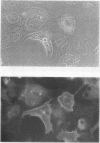
Studies of bone marrow transplant patients have suggested that the stromal cells of the in vitro hematopoietic microenvironment are transplantable into conditioned recipients. Moreover, in patients with myeloproliferative disorders, all of the stromal cells, which include presumptive endothelial cells, appear to be derived from hematopoietic precursors. To confirm these findings, we have constructed two chimeric mouse models: (a) traditional radiation chimeras, and (b) fetal chimeras, produced by placental injection of bone marrow into genetically anemic Wx/Wv fetuses, a technique that essentially precludes engraftment of nonhematopoietic cells. Using two-color indirect immunofluorescence, the stromal cells in long-term bone marrow culture derived from these chimeras were analyzed for donor or host origin by strain-specific H-2 antigens, and for cell lineage by a variety of other specific markers. 75-95% of the stromal cells were shown to be hematopoietic cells of the monocyte-macrophage lineage, based upon donor origin, phagocytosis, and expression of specific hematopoietic surface antigens. The remaining 5-25% of the stromal cells were exclusively host in origin. Apart from occasional fat cells, these cells uniformly expressed collagen type IV, laminin, and a surface antigen associated with endothelial cells. Since these endothelial-like cells are not transplantable into radiation or fetal chimeras, they are not derived from hematopoietic stem cells. The contrast between our findings and human studies suggests either unexpected species differences in the origin of stromal lineages or limitations in the previous methodology used to detect nonhematopoietic stromal cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austyn J. M., Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Oct;11(10):805–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley S. A., Alabaster O., Foidart J. M. Collagen heterogeneity in normal human bone marrow. Br J Haematol. 1981 Jun;48(2):287–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley S. A., Knutsen T., Whang-Peng J. The origin of the hematopoietic microenvironment in continuous bone marrow culture. Exp Hematol. 1982 Apr;10(4):367–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley S. A., Tralka T. S. Characterization of marrow-derived adherent cells. Evidence against an endothelial subpopulation. Scand J Haematol. 1982 May;28(5):381–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1982.tb00543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Allen T. D., Lajtha L. G. Conditions controlling the proliferation of haemopoietic stem cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):335–344. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Moore M. A. In vitro duplication and "cure" of haemopoietic defects in genetically anaemic mice. Nature. 1977 Sep 29;269(5627):412–414. doi: 10.1038/269412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duijvestijn A. M., Schreiber A. B., Butcher E. C. Interferon-gamma regulates an antigen specific for endothelial cells involved in lymphocyte traffic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9114–9118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge P. W., Dewey M. J. Genotype-limited changes in platelet and erythroid kinetics in Friend-virus-infected allophenic mice. Exp Hematol. 1986 Jun;14(5):380–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman R. A., Mintz B. Development of adult bone marrow stem cells in H-2-compatible and -incompatible mouse fetuses. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):731–745. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman R. A., Mintz B. Prevention of genetic anemias in mice by microinjection of normal hematopoietic stem cells into the fetal placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5736–5740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francescutti L. H., Gambel P., Wegmann T. G. Characterization of hemopoietic stem cell chimerism in antibody-facilitated bone marrow chimeras. Transplantation. 1985 Jul;40(1):7–11. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198507000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating A., Singer J. W., Killen P. D., Striker G. E., Salo A. C., Sanders J., Thomas E. D., Thorning D., Fialkow P. J. Donor origin of the in vitro haematopoietic microenvironment after marrow transplantation in man. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):280–283. doi: 10.1038/298280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon J. E., Micklem H. S. Stromal cells in long-term murine bone marrow culture: FACS studies and origin of stromal cells in radiation chimeras. Exp Hematol. 1986 May;14(4):287–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. J., Nisbet N. W., Evans S. Donor origin of the in vitro hematopoietic microenvironment after marrow transplantation in mice. Experientia. 1984 Apr 15;40(4):385–386. doi: 10.1007/BF01952566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Anthony K., Mintz B. Abnormal development of genetically normal fetal hematopoietic stem cells in steel mutant mouse fetuses. Dev Biol. 1985 May;109(1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90366-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piersma A. H., Ploemacher R. E., Brockbank K. G. Transplantation of bone marrow fibroblastoid stromal cells in mice via the intravenous route. Br J Haematol. 1983 Jun;54(2):285–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Reiss C. S., Burakoff S. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A. Ia expression by vascular endothelium is inducible by activated T cells and by human gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1983 Apr 1;157(4):1339–1353. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons P. J., Przepiorka D., Thomas E. D., Torok-Storb B. Host origin of marrow stromal cells following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):429–432. doi: 10.1038/328429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J. W., Keating A., Cuttner J., Gown A. M., Jacobson R., Killen P. D., Moohr J. W., Najfeld V., Powell J., Sanders J. Evidence for a stem cell common to hematopoiesis and its in vitro microenvironment: studies of patients with clonal hematopoietic neoplasia. Leuk Res. 1984;8(4):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(84)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfré G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Mac-1: a macrophage differentiation antigen identified by monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Apr;9(4):301–306. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Alvarez O. M., Bere E. W., Jr, Eaglstein W. H., Katz S. I. Detection of basement membrane zone antigens during epidermal wound healing in pigs. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Aug;77(2):240–243. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12480082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TILL J. E., McCULLOCH E. A. A direct measurement of the radiation sensitivity of normal mouse bone marrow cells. Radiat Res. 1961 Feb;14:213–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte P. L., Robinson M., Henley A., Low M. G., Stiers D. L., Perkins S., Fleischman R. A., Kincade P. W. Relationships between B-lineage lymphocytes and stromal cells in long-term bone marrow cultures. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1473–1484. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman K. S., Wicha M. S. Extracellular matrix production by the adherent cells of long-term murine bone marrow cultures. Blood. 1983 Mar;61(3):540–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]