Abstract
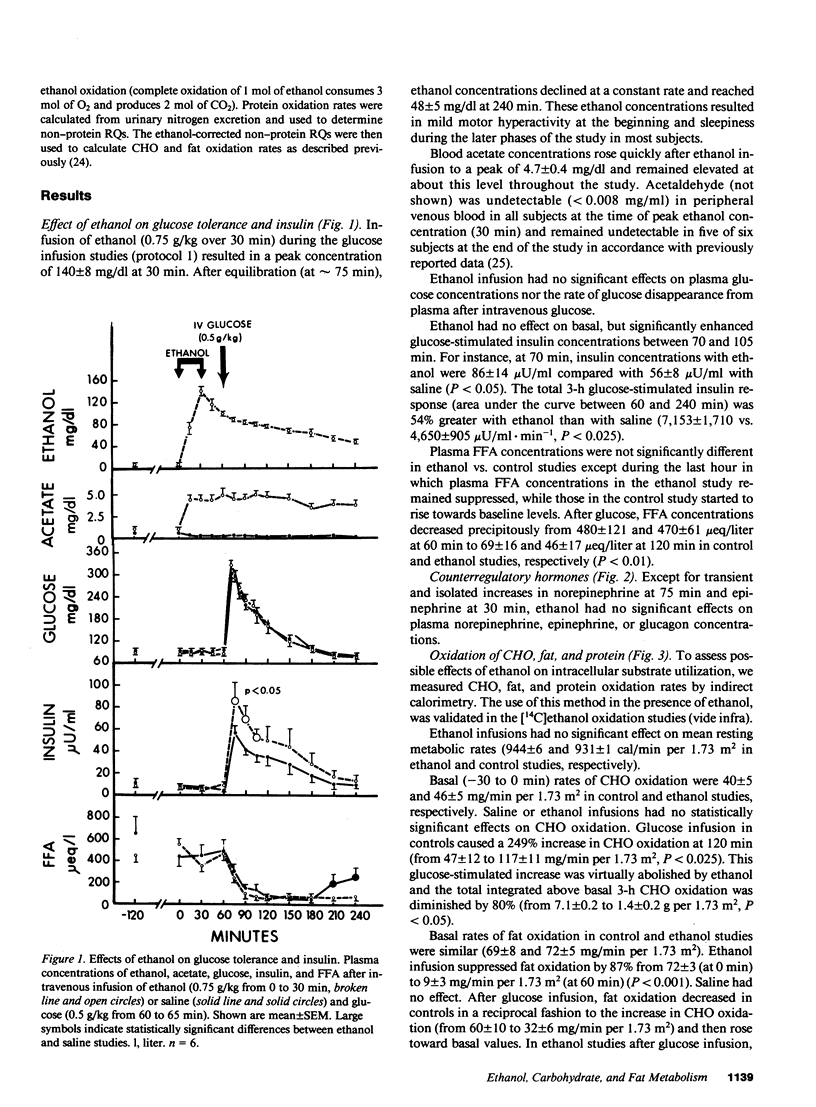
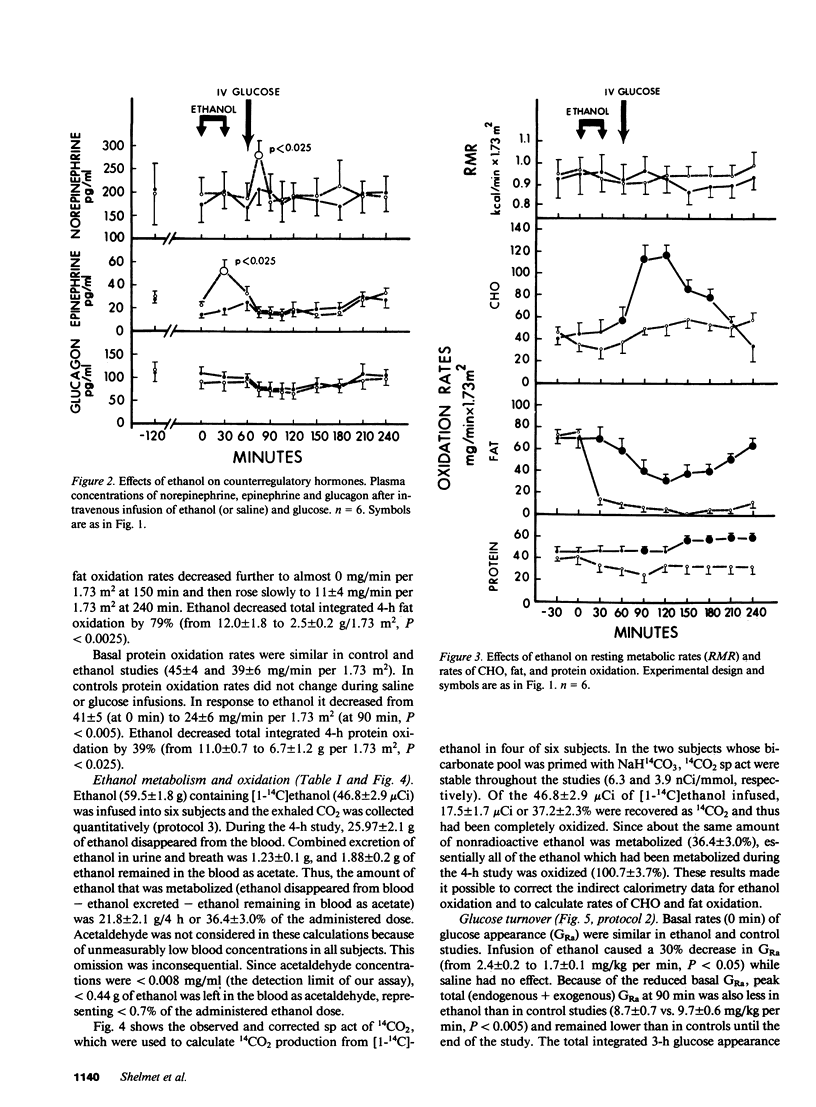
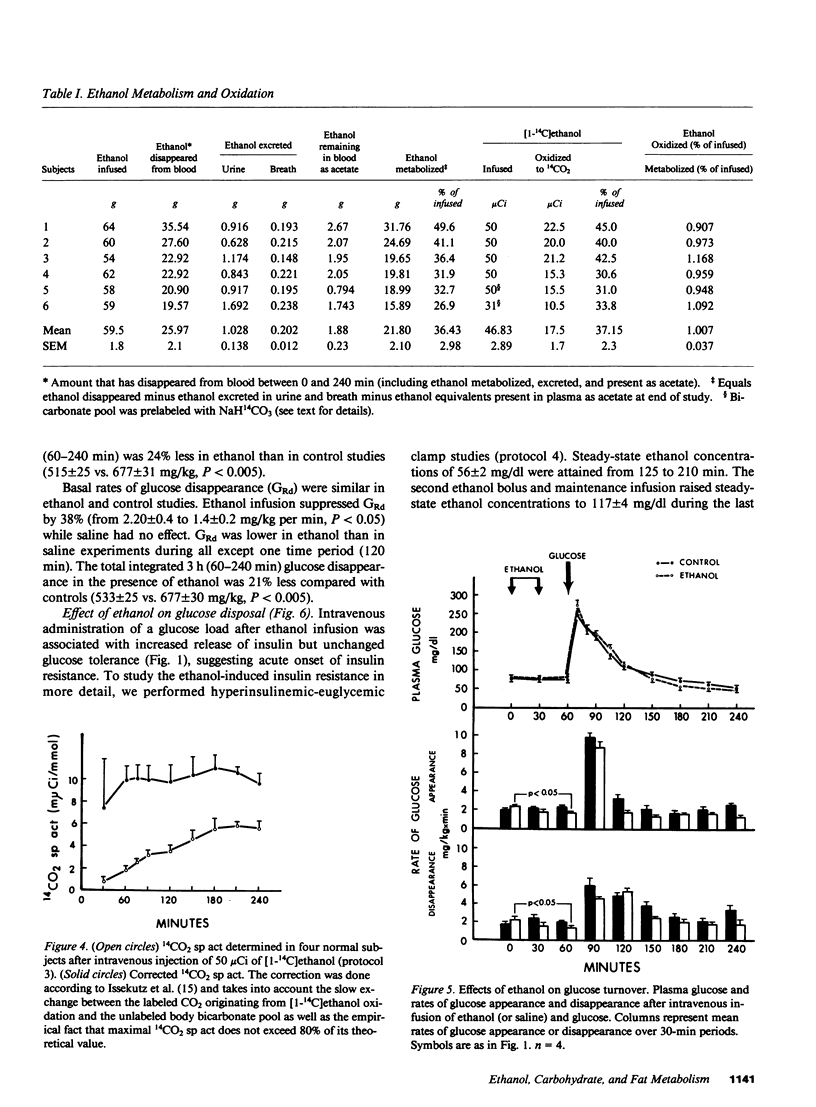
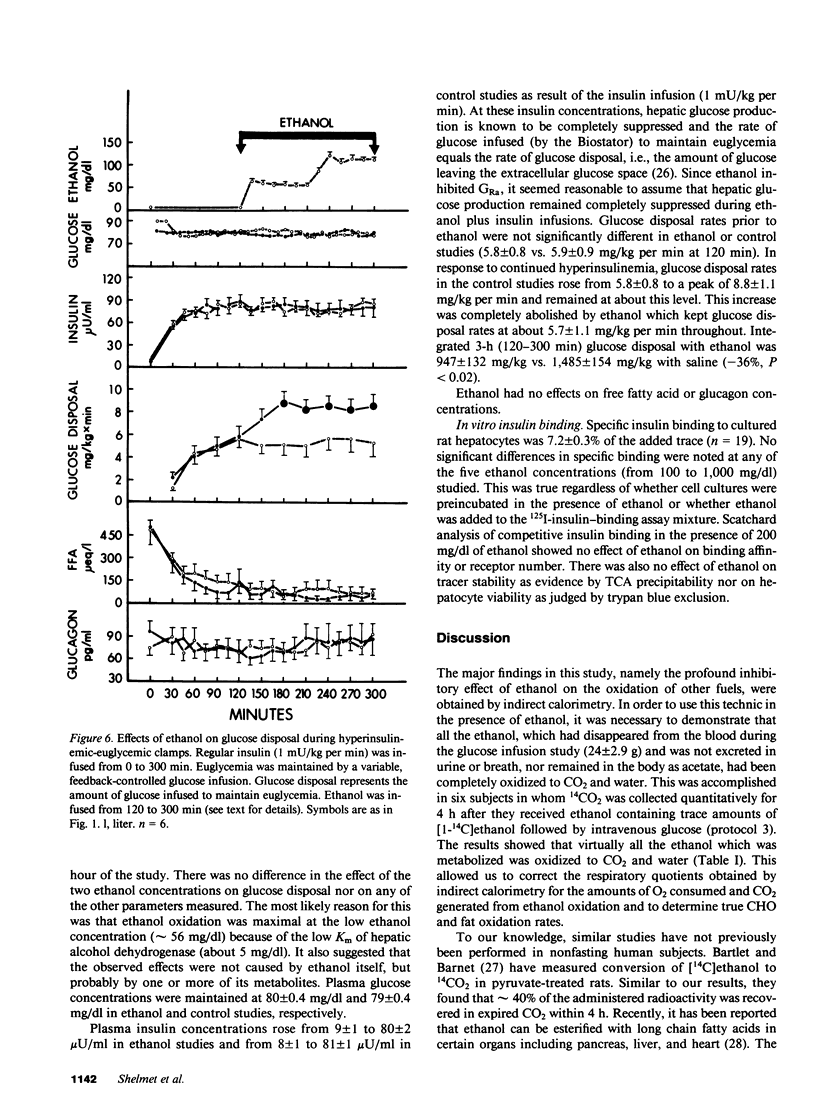
To study the mechanism of the diabetogenic action of ethanol, ethanol (0.75 g/kg over 30 min) and then glucose (0.5 g/kg over 5 min) were infused intravenously into six normal males. During the 4-h study, 21.8 +/- 2.1 g of ethanol was metabolized and oxidized to CO2 and H2O. Ethanol decreased total body fat oxidation by 79% and protein oxidation by 39%, and almost completely abolished the 249% rise in carbohydrate (CHO) oxidation seen in controls after glucose infusion. Ethanol decreased the basal rate of glucose appearance (GRa) by 30% and the basal rate of glucose disappearance (GRd) by 38%, potentiated glucose-stimulated insulin release by 54%, and had no effect on glucose tolerance. In hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp studies, ethanol caused a 36% decrease in glucose disposal. We conclude that ethanol was a preferred fuel preventing fat, and to lesser degrees, CHO and protein, from being oxidized. It also caused acute insulin resistance which was compensated for by hypersecretion of insulin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R., BARNET H. N. Some observations on alcohol metabolism with radioactive ethyl alcohol. Q J Stud Alcohol. 1949 Dec;10(3-4):381–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Ray T. K., Smith R. H., Owen O. E. Carbohydrate oxidation and storage in obese non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Effects of improving glycemic control. Diabetes. 1983 Nov;32(11):982–987. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.11.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. W., EVANS R. L. The influence of alcohol upon carbohydrate metabolism in the liver and in isolated diaphragms. Q J Stud Alcohol. 1960 Mar;21:13–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutter W. E., Bier D. M., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Epinephrine plasma metabolic clearance rates and physiologic thresholds for metabolic and hemodynamic actions in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):94–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI109840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Gerich J. E. Relevance of glucose counterregulatory systems to patients with diabetes: critical roles of glucagon and epinephrine. Diabetes Care. 1983 Jan-Feb;6(1):95–99. doi: 10.2337/diacare.6.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P., MEINERTZ H. Microdetermination of long-chain fatty acids in plasma and tissues. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2595–2599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornhorst A., Ouyang A. Effect of alcohol on glucose tolerance. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):957–959. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90273-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD J. B., WILLIAMS H. E., MORTIMORE G. E. Studies on the mechanism of ethanol-induced hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1963 Apr;42:497–506. doi: 10.1172/JCI104738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDRICKSON D. S., ONO K. An improved technique for assay of C14O2 in expired air using the liquid scintillation counter. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Jan;51(1):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREINKEL N., COHEN A. K., ARKY R. A., FOSTER A. E. ALCOHOL HYPOGLYCEMIA. II. A POSTULATED MECHANISM OF ACTION BASED ON EXPERIMENTS WITH RAT LIVER SLICES. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Jan;25:76–94. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-1-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Siperstein M. D. Normalization of fasting blood glucose levels in insulin-requiring diabetes: the role of ethanol abstention. Diabetes Care. 1983 Mar-Apr;6(2):186–188. doi: 10.2337/diacare.6.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N., Singer D. L., Arky R. A., Bleicher S. J., Anderson J. B., Silbert C. K. ALCOHOL HYPOGLYCEMIA. I. CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM OF PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL ALCOHOL HYPOGLYCEMIA AND THE EXPERIMENTAL REPRODUCTION OF THE SYNDROME WITH PURE ETHANOL. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42(7):1112–1133. doi: 10.1172/JCI104797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz B., Jr, Paul P., Miller H. I., Bortz W. M. Oxidation of plasma FFA in lean and obese humans. Metabolism. 1968 Jan;17(1):62–73. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(68)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg R. A., Siegal A. M., Owen W. C. Glucose-lactate interrelationships: effect of ethanol. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):175–185. doi: 10.1172/JCI106471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBER C. S., SCHMID R. The effect of ethanol on fatty acid metabolism; stimulation of hepatic fatty acid synthesis in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1961 Feb;40:394–399. doi: 10.1172/JCI104266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDQUIST F., TYGSTRUP N., WINKLER K., MELLEMGAARD K., MUNCK-PETERSEN S. Ethanol metabolism and production of free acetate in the human liver. J Clin Invest. 1962 May;41:955–961. doi: 10.1172/JCI104574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laposata E. A., Lange L. G. Presence of nonoxidative ethanol metabolism in human organs commonly damaged by ethanol abuse. Science. 1986 Jan 31;231(4737):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.3941913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochner A., Wulff J., Madison L. L. Ethanol-induced hypoglycemia. I. The acute effects of glucose output and peripheral glucose utilization in fasted dogs. Metabolism. 1967 Jan;16(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(67)90154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch E., Gey K. F. Photometric "titration" of free fatty acids with the Technicon AutoAnalyzer. Anal Biochem. 1966 Aug;16(2):244–252. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison L. L., Lochner A., Wulff J. Ethanol-induced hypoglycemia. II. Mechanism of suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Diabetes. 1967 Apr;16(4):252–258. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.4.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMonagle J., Felig P. Effects of ethanol ingestion on glucose tolerance and insulin secretion in normal and diabetic subjects. Metabolism. 1975 May;24(5):625–632. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90142-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz R., Berger S., Mako M. Potentiation of the plasma insulin response to glucose by prior administration of alcohol. An apparent islet-priming effect. Diabetes. 1969 Aug;18(8):517–522. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.8.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikkilä E. A., Taskinen M. R. Ethanol-induced alterations of glucose tolerance, postglucose hypoglycemia, and insulin secretion in normal, obese, and diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1975 Oct;24(10):933–943. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.10.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuutinen H. U., Salaspuro M. P., Valle M., Lindros K. O. Blood acetaldehyde concentration gradient between hepatic and antecubital venous blood in ethanol-intoxicated alcoholics and controls. Eur J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;14(4):306–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1984.tb01186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Trapp V. E., Reichard G. A., Jr, Mozzoli M. A., Smith R., Boden G. Effects of therapy on the nature and quantity of fuels oxidized during diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes. 1980 May;29(5):365–372. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.5.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passon P. G., Peuler J. D. A simplified radiometric assay for plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):618–631. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90517-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. B., Safrit H. F. Alcoholic diabetes. Induction of glucose intolerance with alcohol. JAMA. 1971 Sep 13;217(11):1513–1519. doi: 10.1001/jama.217.11.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REBOUCAS G., ISSELBACHER K. J. Studies on the pathogenesis of the ethanol-induced fatty liver. I. Synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids by the liver. J Clin Invest. 1961 Aug;40:1355–1362. doi: 10.1172/JCI104366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk J., Norwich K. H., Vranic M. Experimental validation of measurements of glucose turnover in nonsteady state. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):E84–E93. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.1.E84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichard G. A., Jr, Haff A. C., Skutches C. L., Paul P., Holroyde C. P., Owen O. E. Plasma acetone metabolism in the fasting human. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):619–626. doi: 10.1172/JCI109344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Dose-response characteristics for effects of insulin on production and utilization of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):E630–E639. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.6.E630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., WALL J. S., DE BODO R. C., ALTSZULER N. Measurement of size and turnover rate of body glucose pool by the isotope dilution method. Am J Physiol. 1956 Sep;187(1):15–24. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauerheber R. D., Esgate J. A., Kuhn C. E. Alcohols inhibit adipocyte basal and insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and increase the membrane lipid fluidity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 24;691(1):115–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoyama R., Ray T. K., Savage C. R., Jr, Owen O. E., Boden G. In vivo and in vitro effects of antiinsulin receptor antibodies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Nov;59(5):916–923. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-5-916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg A. B., Shah S. D., Haymond M. W., Cryer P. E. Norepinephrine: hormone and neurotransmitter in man. Am J Physiol. 1978 Mar;234(3):E252–E256. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.3.E252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skutches C. L., Holroyde C. P., Myers R. N., Paul P., Reichard G. A. Plasma acetate turnover and oxidation. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):708–713. doi: 10.1172/JCI109513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skutches C. L., Sigler M. H., Teehan B. P., Cooper J. H., Reichard G. A. Contribution of dialysate acetate to energy metabolism: metabolic implications. Kidney Int. 1983 Jan;23(1):57–63. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Slone D. Critical variables in the radioimmunoassay of serum insulin using the double antibody technic. Diabetes. 1965 Dec;14(12):771–779. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.12.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. H., O'Sullivan D. J. Effect of moderate alcohol intake on control of diabetes. Diabetes. 1974 May;23(5):440–442. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.5.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Nikkilä E. A. Ethanol decreases glucose utilization in healthy man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Nov;61(5):941–945. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-5-941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



