Abstract
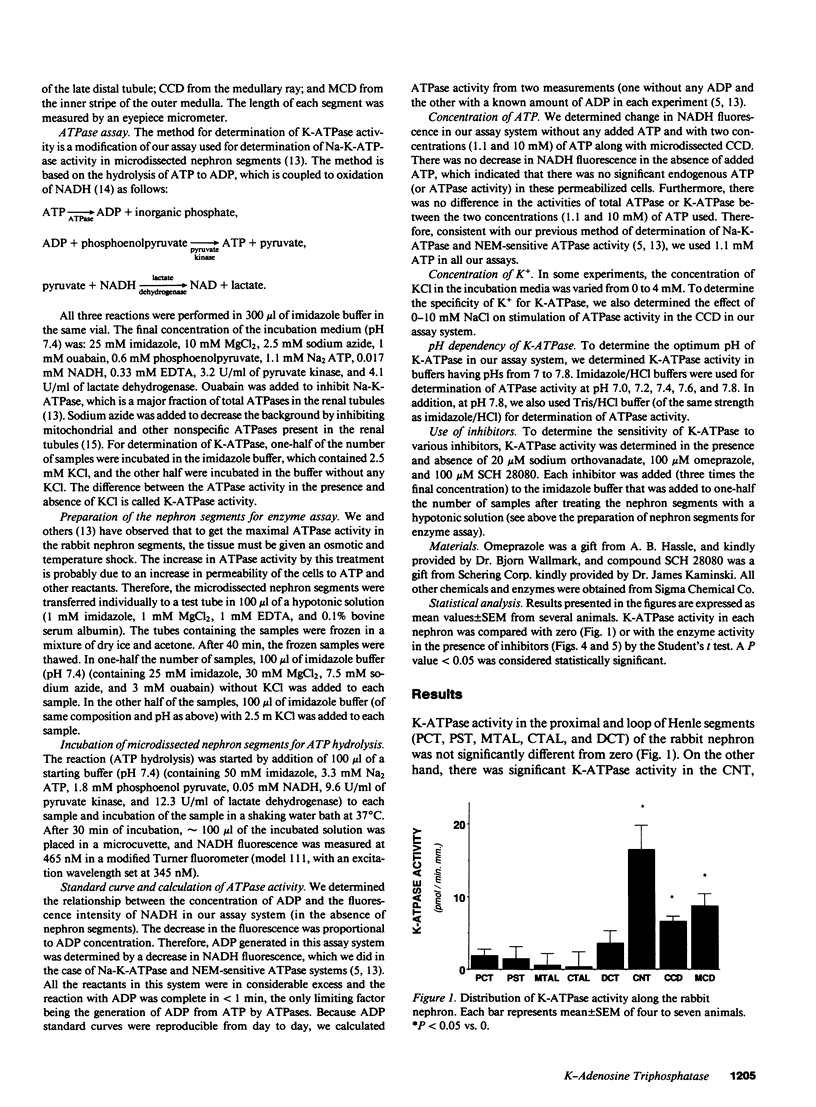
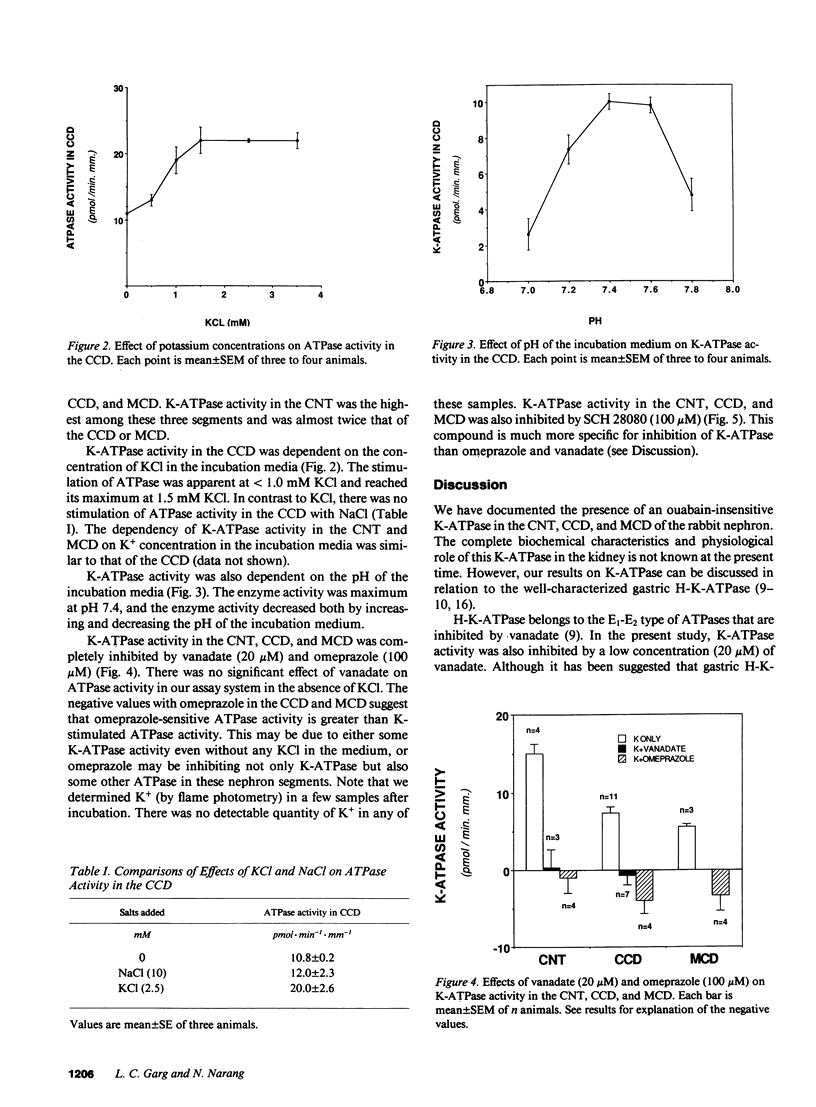
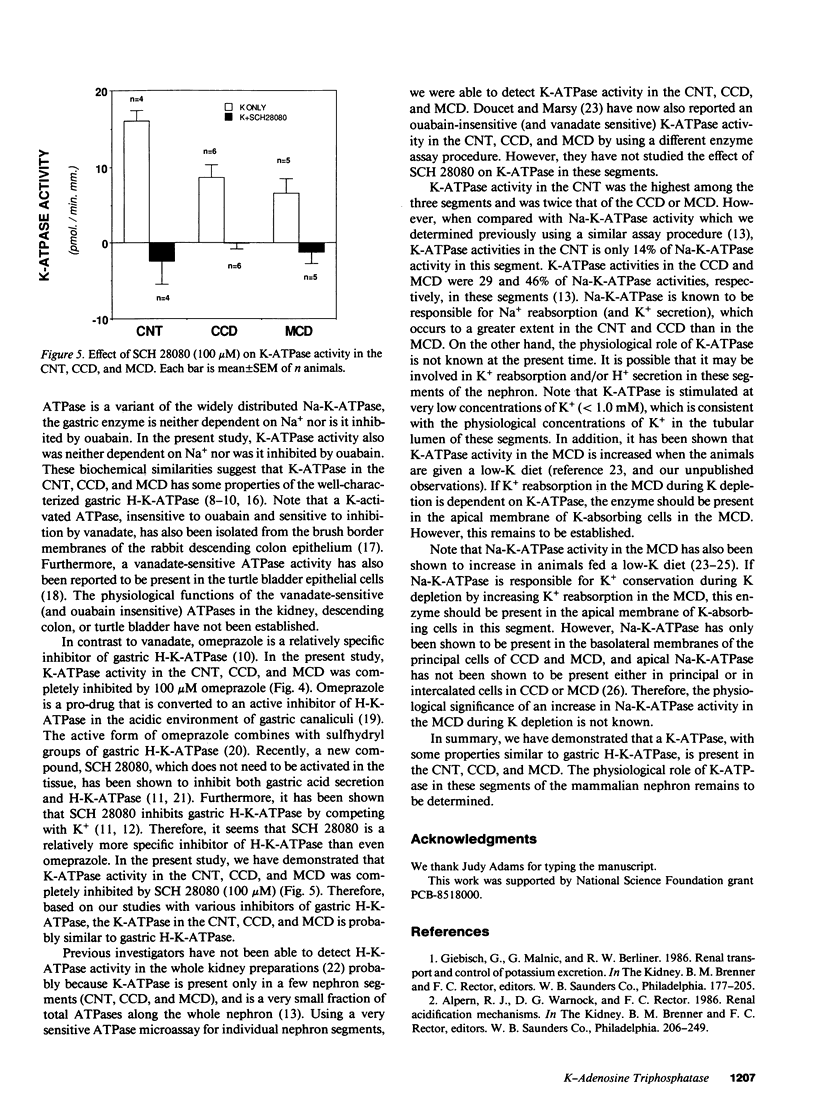
An electrogenic H-ATpase sensitive to inhibition by N-ethyl-maleimide has been reported to be present in renal distal tubules. In contrast to another H-ATPase (gastric H-K-ATPase), the renal enzyme is not stimulated by K+ and is not inhibited by vanadate. However, our preliminary observations indicated that a K-stimulated ATPase (K-ATPase) sensitive to inhibition by vanadate is present in renal medullary collecting duct (MCD). To localize and further characterize this renal tubular K-ATPase, we measured K-ATPase activity in eight specific segments of the rabbit nephron. K-ATPase activity was the difference in ATPase activity in the presence and absence of KCl but in the presence of ouabain (to inhibit Na-K-ATPase). ATPase activity was determined by a fluorometric microassay in which ATP hydrolysis is coupled to the oxidation of NADH. There was a significant K-ATPase activity (expressed as pmol.min-1.mm-1) in the connecting tubule (CNT, 17.0 +/- 3.3), cortical collecting duct (CCD, 6.6 +/- 0.7), and MCD (8.8 +/- 1.7), but not in the proximal segments and the thick ascending limbs. The renal tubular K-ATPase was not only inhibited by vanadate but also by omeprazole and SCH 28080 (relatively specific inhibitors of gastric H-K-ATPase). It is concluded that K-ATPase present in the CNT, CCD, and MCD has some properties in common with gastric H-K-ATPase. However, the physiological role of K-ATPase in the distal nephron segments remains to be elucidated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdelkhalek M. B., Barlet C., Doucet A. Presence of an extramitochondrial anion-stimulated ATPase in the rabbit kidney: localization along the nephron and effect of corticosteroids. J Membr Biol. 1986;89(3):225–240. doi: 10.1007/BF01870666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet A., Marsy S. Characterization of K-ATPase activity in distal nephron: stimulation by potassium depletion. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 2):F418–F423. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.3.F418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faller L., Jackson R., Malinowska D., Mukidjam E., Rabon E., Saccomani G., Sachs G., Smolka A. Mechanistic aspects of gastric (H+ + K+)-ATPase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:146–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellenius E., Berglindh T., Sachs G., Olbe L., Elander B., Sjöstrand S. E., Wallmark B. Substituted benzimidazoles inhibit gastric acid secretion by blocking (H+ + K+)ATPase. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):159–161. doi: 10.1038/290159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Knepper M. A., Burg M. B. Mineralocorticoid effects on Na-K-ATPase in individual nephron segments. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):F536–F544. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.6.F536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Narang N. Stimulation of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive ATPase in the collecting duct segments of the rat nephron by metabolic acidosis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;63(10):1291–1296. doi: 10.1139/y85-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluck S., Al-Awqati Q. An electrogenic proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatase from bovine kidney medulla. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jun;73(6):1704–1710. doi: 10.1172/JCI111378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustin M. C., Goodman D. B. Isolation of brush-border membrane from the rabbit descending colon epithelium. Partial characterization of a unique K+-activated ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10651–10656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Katz A. I. The kidney in potassium depletion. I. Na+-K+-ATPase activity and [3H]ouabain binding in MCT. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 2):F437–F446. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.3.F437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im W. B., Sih J. C., Blakeman D. P., McGrath J. P. Omeprazole, a specific inhibitor of gastric (H+-K+)-ATPase, is a H+-activated oxidizing agent of sulfhydryl groups. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4591–4597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbert-Teboul M., Doucet A., Marsy S., Siaume-Perez S. Alterations of enzymatic activities along rat collecting tubule in potassium depletion. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 2):F408–F417. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.3.F408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashgarian M., Biemesderfer D., Caplan M., Forbush B., 3rd Monoclonal antibody to Na,K-ATPase: immunocytochemical localization along nephron segments. Kidney Int. 1985 Dec;28(6):899–913. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaunitz J. D., Gunther R. D., Sachs G. Characterization of an electrogenic ATP and chloride-dependent proton translocating pump from rat renal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11567–11573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J. F., Chiu P. J., Derelanko M. J., Steinberg M. Gastric antisecretory and cytoprotective activities of SCH 28080. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jul;226(1):114–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner W., von Ilberg C., Kramer R., Seubert W. On the mechanism of Na+- and K+-stimulated hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate. 1. Purification and properties of a Na+-and K+-activated ATPase from ox brain. Eur J Biochem. 1967 May;1(3):334–343. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. K., Sundell E., Castrovilly L. Studies on the mechanism of action of the gastric microsomal (H+ + K+)-ATPase inhibitors SCH 32651 and SCH 28080. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 1;36(1):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone D. K., Seldin D. W., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Anion dependence of rabbit medullary collecting duct acidification. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1505–1508. doi: 10.1172/JCI110905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallmark B., Brändström A., Larsson H. Evidence for acid-induced transformation of omeprazole into an active inhibitor of (H+ + K+)-ATPase within the parietal cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 19;778(3):549–558. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90406-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallmark B., Larsson H., Humble L. The relationship between gastric acid secretion and gastric H+,K+-ATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13681–13684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans S. J., Brodsky W. A. Vanadate inhibition of ATP-dependent H+ transport in membrane vesicles from turtle bladder epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 12;900(1):88–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



