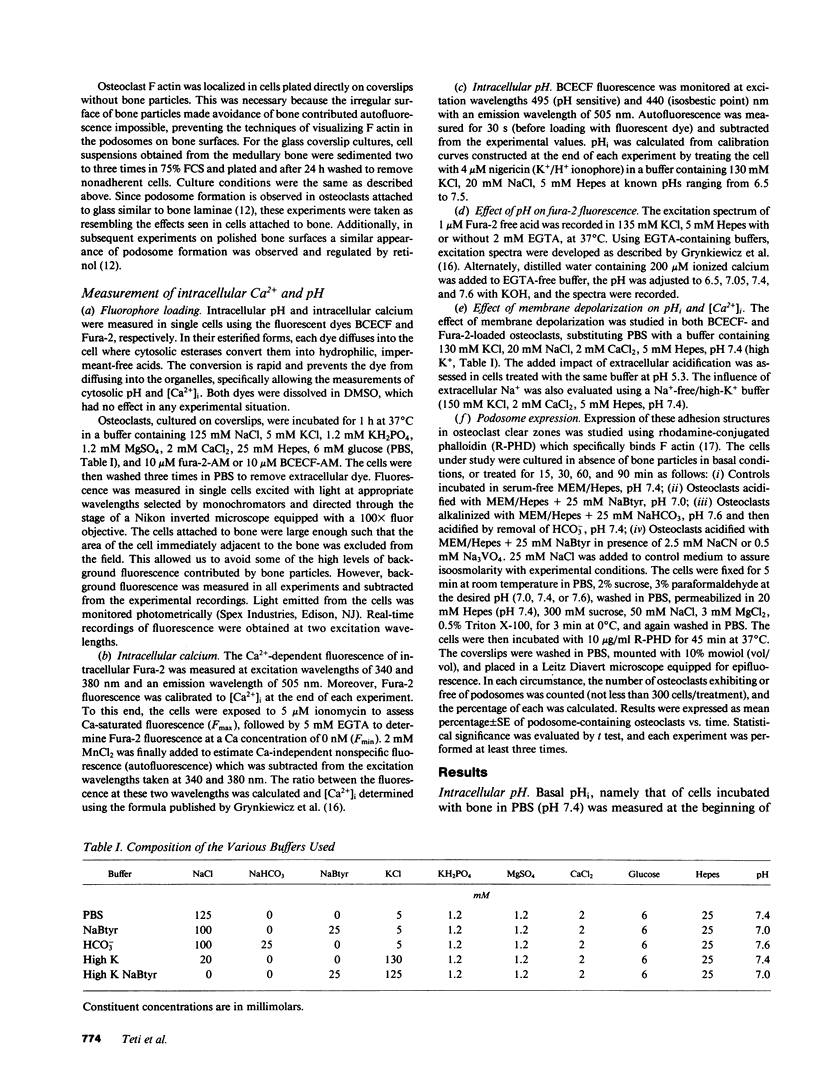
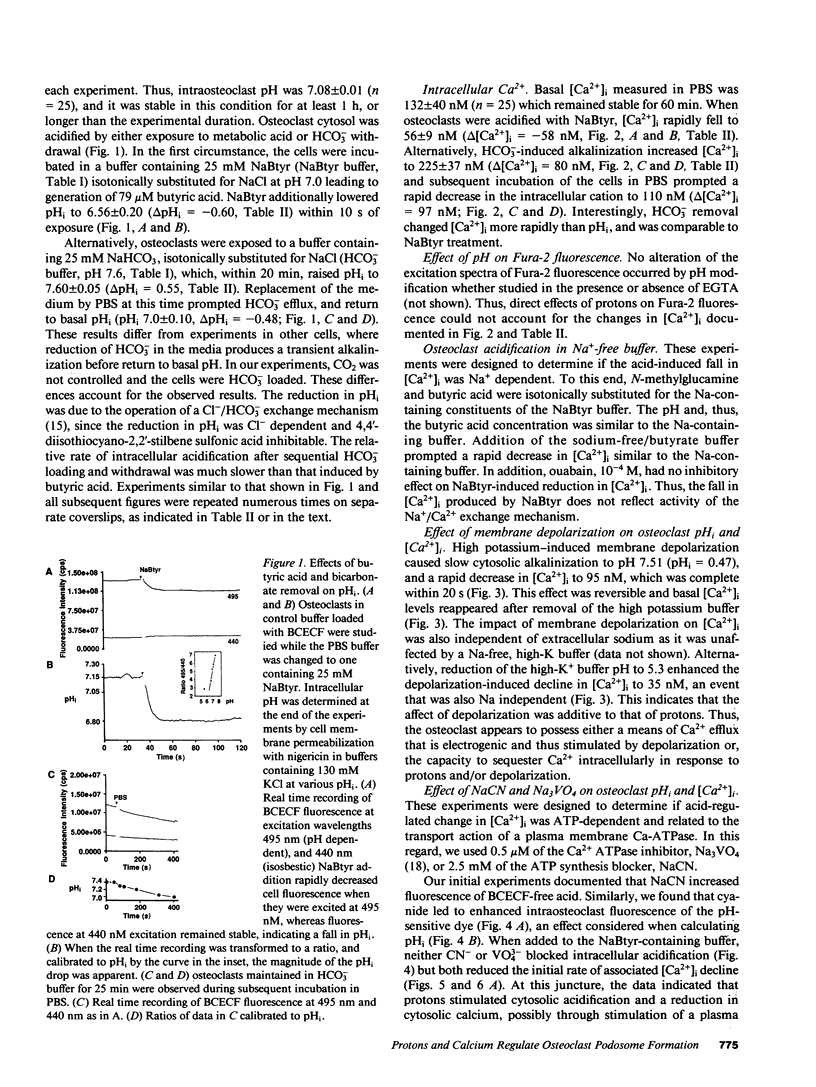
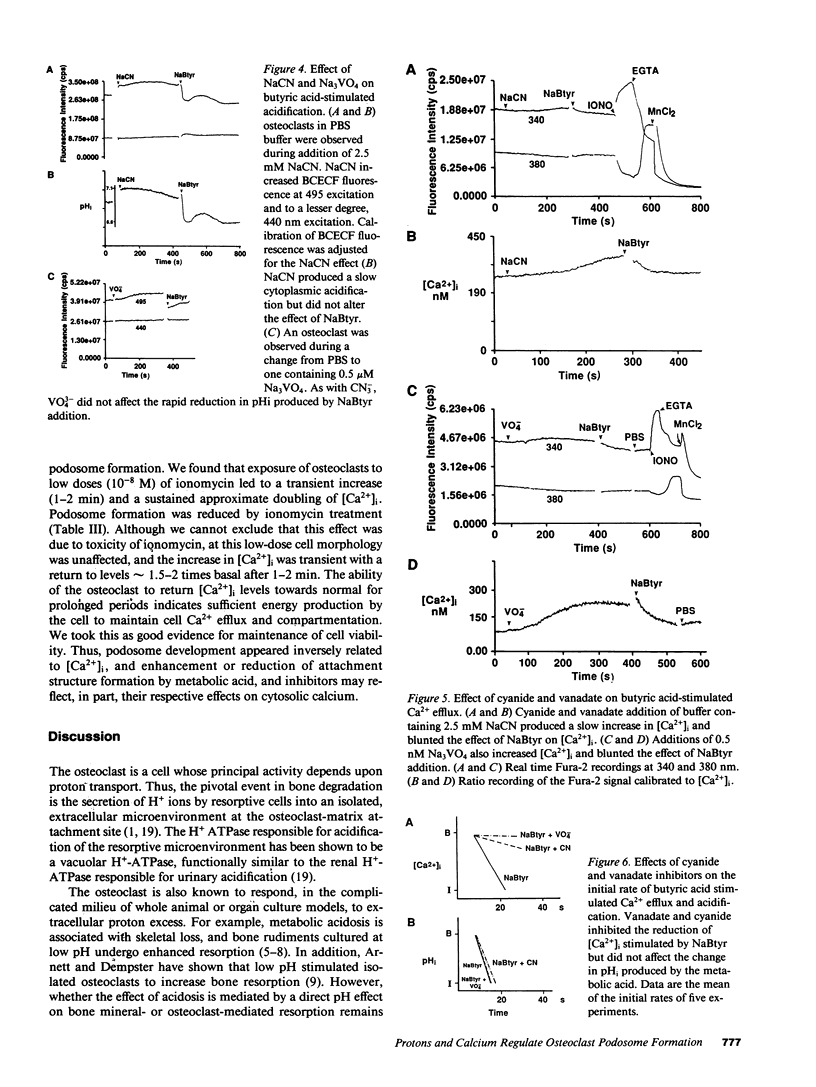
Abstract
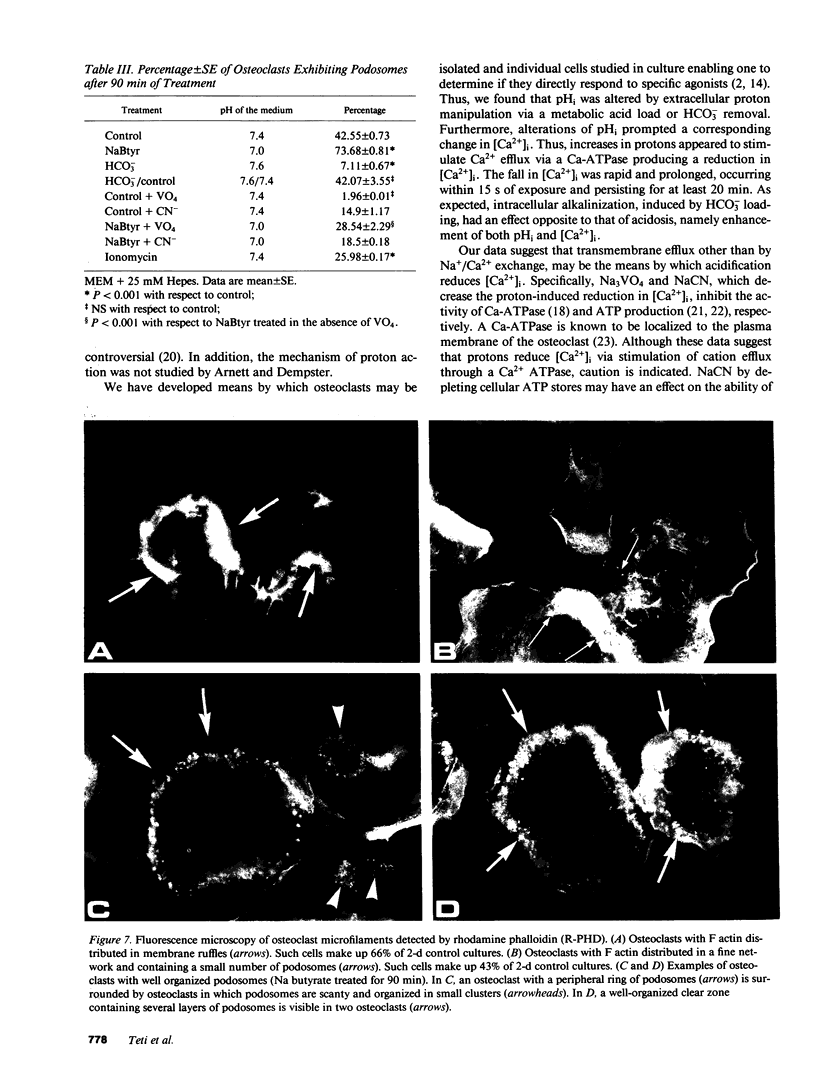
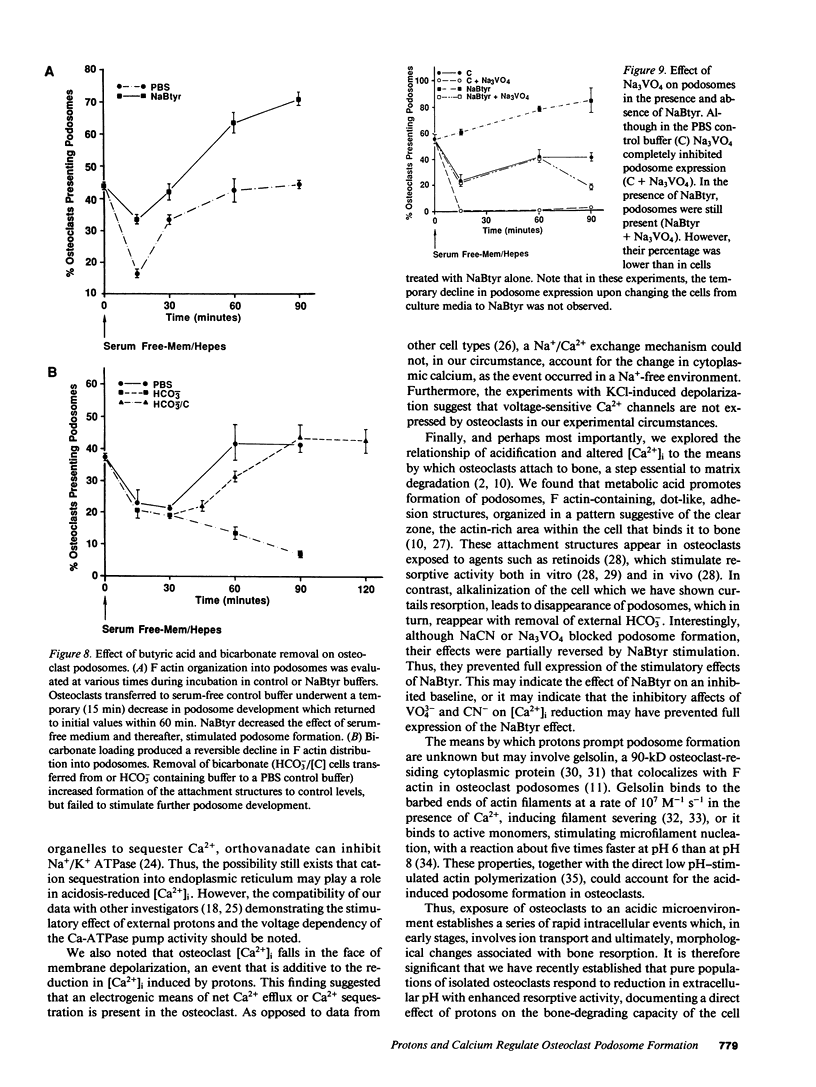
Because metabolic acids stimulate bone resorption in vitro and in vivo, we focused on the cellular events produced by acidosis that might be associated with stimulation of bone remodeling. To this end, we exposed isolated chicken osteoclasts to a metabolic (butyric) acid and observed a fall in both intracellular pH and cytosolic calcium [( Ca2+]i). These phenomena were recapitulated when bone resorptive cells, alkalinized by HCO3 loading, were transferred to a bicarbonate-free environment. The acid-induced decline in osteoclast [Ca2+]i was blocked by either NaCN or Na3VO4, in a Na+-independent fashion, despite the failure of each inhibitor to alter stimulated intracellular acidification. Moreover, K+-induced membrane depolarization also reduced cytosolic calcium in a manner additive to the effect of protons. These findings suggest that osteoclasts adherent to bone lack functional voltage-operated Ca2+ channels, and they reduced [Ca2+]i in response to protons via a membrane residing Ca-ATPase. Most importantly, acidosis enhances formation of podosomes, the contact areas of the osteoclast clear zone, indicating increased adhesion to substrate, an early step in bone resorption. Thus, extracellular acidification of osteoclasts leads to decrements in intracellular pH and calcium, and appears to promote cell-matrix attachment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akisaka T., Yamamoto T., Gay C. V. Ultracytochemical investigation of calcium-activated adenosine triphosphatase (Ca++-ATPase) in chick tibia. J Bone Miner Res. 1988 Feb;3(1):19–25. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650030105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. E., Woodbury D. M., Jee W. S. Humoral and ionic regulation of osteoclast acidity. Calcif Tissue Int. 1986 Oct;39(4):252–258. doi: 10.1007/BF02555214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett T. R., Dempster D. W. Effect of pH on bone resorption by rat osteoclasts in vitro. Endocrinology. 1986 Jul;119(1):119–124. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Knight D. E. Exocytosis: control by calcium and other factors. Br Med Bull. 1986 Oct;42(4):399–404. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron R., Neff L., Louvard D., Courtoy P. J. Cell-mediated extracellular acidification and bone resorption: evidence for a low pH in resorbing lacunae and localization of a 100-kD lysosomal membrane protein at the osteoclast ruffled border. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2210–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair H. C., Kahn A. J., Crouch E. C., Jeffrey J. J., Teitelbaum S. L. Isolated osteoclasts resorb the organic and inorganic components of bone. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1164–1172. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J., Coluccio L. M. Kinetic analysis of F-actin depolymerization in the presence of platelet gelsolin and gelsolin-actin complexes. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1236–1244. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushinsky D. A., Goldring J. M., Coe F. L. Cellular contribution to pH-mediated calcium flux in neonatal mouse calvariae. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 2):F785–F789. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.6.F785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Resh M. D., Guidotti G. Vanadate inhibits the red cell (Na+, K+) ATPase from the cytoplasmic side. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):552–554. doi: 10.1038/272552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Zurini M. The Ca2+-pumping ATPase of plasma membranes. Purification, reconstitution and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 31;683(3-4):279–301. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(82)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., McSheehy P. M., Thomson B. M., Fuller K. The effect of calcium-regulating hormones and prostaglandins on bone resorption by osteoclasts disaggregated from neonatal rabbit bones. Endocrinology. 1985 Jan;116(1):234–239. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-1-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Savdie E., Mason R. S., Posen S. The effect of metabolic acidosis on vitamin D metabolites and bone histology in uremic rats. Calcif Tissue Int. 1985 Mar;37(2):158–164. doi: 10.1007/BF02554835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaponnier C., Janmey P. A., Yin H. L. The actin filament-severing domain of plasma gelsolin. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1473–1481. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez J. H., Raisz L. G. Effects of changing hydrogen ion, carbonic acid, and bicarbonate concentrations on bone resorption in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int. 1979 Nov;29(1):7–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02408049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassner B., Luterbacher S., Schatzmann H. J., Wüthrich A. Dependence of the red blood cell calcium pump on the membrane potential. Cell Calcium. 1988 Apr;9(2):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(88)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldhaber P., Rabadjija L. H+ stimulation of cell-mediated bone resorption in tissue culture. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):E90–E98. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.1.E90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough S., Avioli L. V., Muir H., Gelderblom D., Jenkins G., Kurasi H., Slatopolsky E., Bergfeld M. A., Teitelbaum S. L. Effects of hypervitaminosis A on the bone and mineral metabolism of the rat. Endocrinology. 1988 Jun;122(6):2933–2939. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-6-2933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. J., Schraer H., Gay C. V. Characterization of isolated and cultured chick osteoclasts: the effects of acetazolamide, calcitonin, and parathyroid hormone on acid production. J Bone Miner Res. 1988 Jun;3(3):297–303. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650030308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchisio P. C., Cirillo D., Naldini L., Primavera M. V., Teti A., Zambonin-Zallone A. Cell-substratum interaction of cultured avian osteoclasts is mediated by specific adhesion structures. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1696–1705. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchisio P. C., Cirillo D., Teti A., Zambonin-Zallone A., Tarone G. Rous sarcoma virus-transformed fibroblasts and cells of monocytic origin display a peculiar dot-like organization of cytoskeletal proteins involved in microfilament-membrane interactions. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Mar;169(1):202–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90238-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. C. Osteoclast cell-surface changes during the egg-laying cycle in Japanese quail. J Cell Biol. 1977 Oct;75(1):104–118. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oreffo R. O., Teti A., Triffitt J. T., Francis M. J., Carano A., Zallone A. Z. Effect of vitamin A on bone resorption: evidence for direct stimulation of isolated chicken osteoclasts by retinol and retinoic acid. J Bone Miner Res. 1988 Apr;3(2):203–210. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650030213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selve N., Wegner A. pH-dependent rate of formation of the gelsolin-actin complex from gelsolin and monomeric actin. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 1;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoback D. M., Brown E. M. PTH release stimulated by high extracellular potassium is associated with a decrease in cytosolic calcium in bovine parathyroid cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):684–690. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90283-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teti A., Blair H. C., Teitelbaum S. L., Kahn A. J., Koziol C., Konsek J., Zambonin-Zallone A., Schlesinger P. H. Cytoplasmic pH regulation and chloride/bicarbonate exchange in avian osteoclasts. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):227–233. doi: 10.1172/JCI113863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulf E., Deboben A., Bautz F. A., Faulstich H., Wieland T. Fluorescent phallotoxin, a tool for the visualization of cellular actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4498–4502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Albrecht J. H., Fattoum A. Identification of gelsolin, a Ca2+-dependent regulatory protein of actin gel-sol transformation, and its intracellular distribution in a variety of cells and tissues. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):901–906. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Purification and structural properties of gelsolin, a Ca2+-activated regulatory protein of macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9490–9493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambonin Zallone A., Teti A., Primavera M. V. Isolated osteoclasts in primary culture: first observations on structure and survival in culture media. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1982 Dec;165(3):405–413. doi: 10.1007/BF00305576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
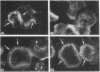
- Zambonin-Zallone A., Teti A., Carano A., Marchisio P. C. The distribution of podosomes in osteoclasts cultured on bone laminae: effect of retinol. J Bone Miner Res. 1988 Oct;3(5):517–523. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650030507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerle C. T., Frieden C. Effect of pH on the mechanism of actin polymerization. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 4;27(20):7766–7772. doi: 10.1021/bi00420a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]