Abstract
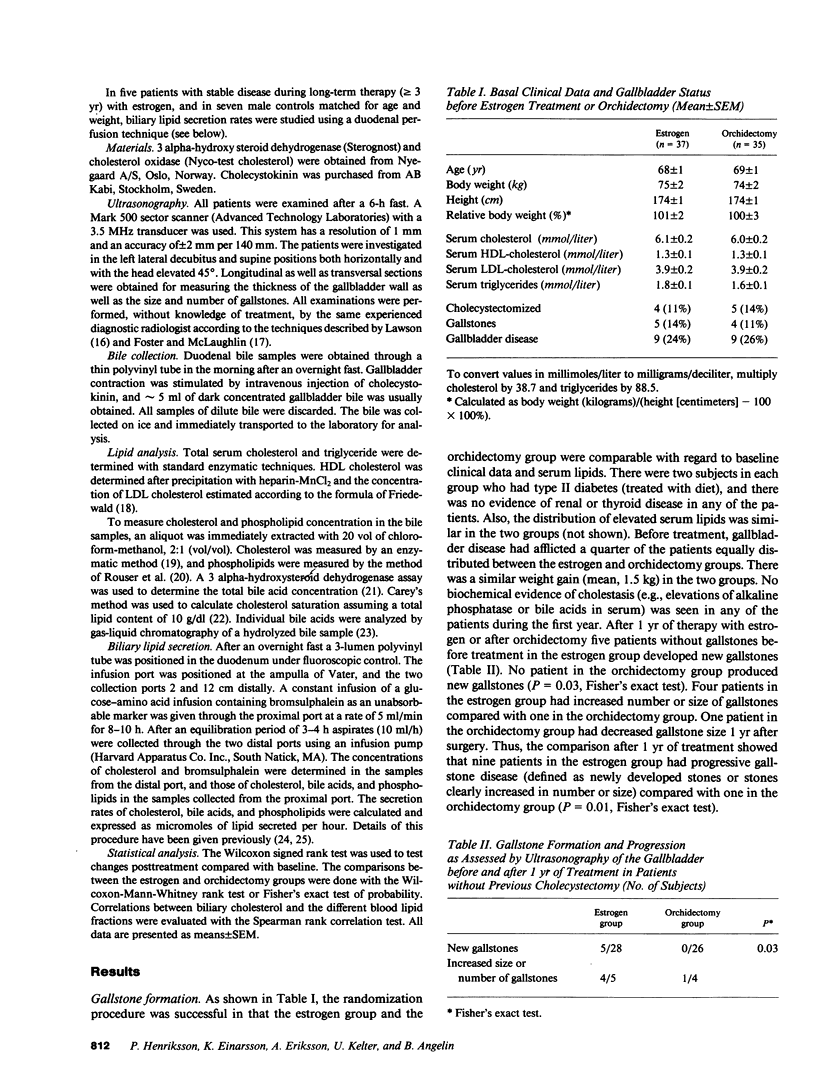
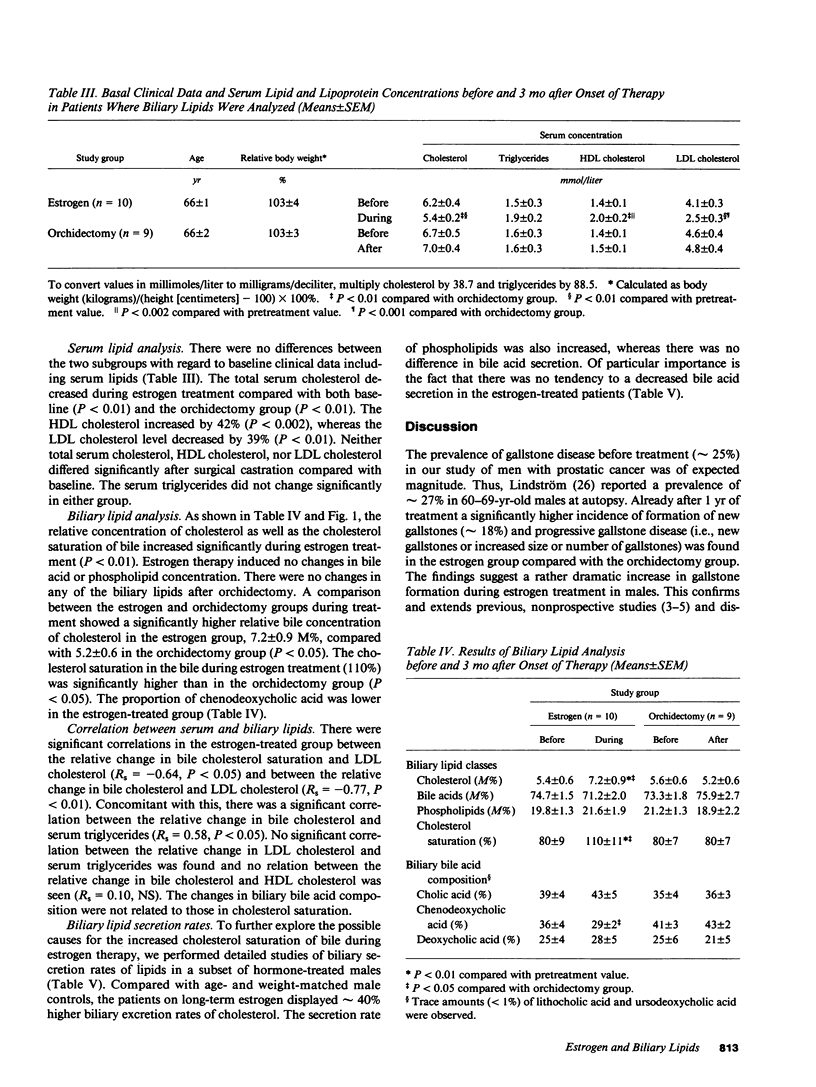
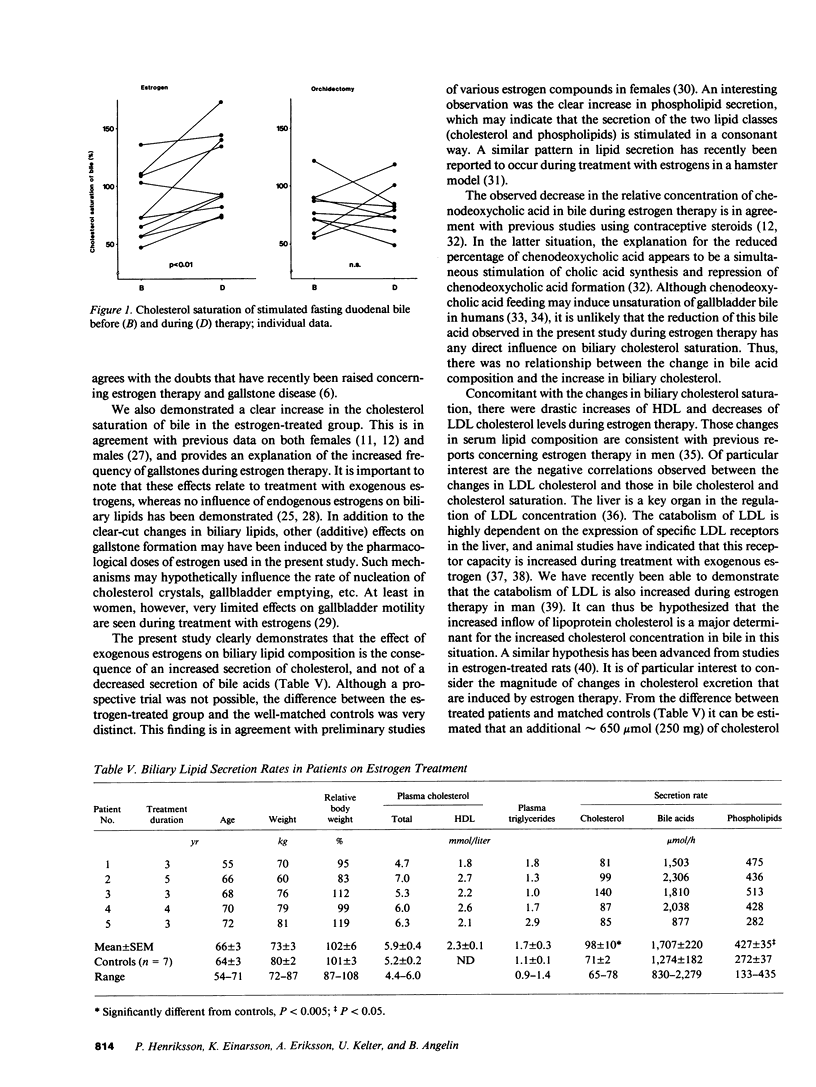
To assess if and by which mechanisms pharmacological estrogen treatment induces gallstone disease, we examined patients with recently diagnosed prostatic cancer randomly allocated to estrogen therapy (n = 37) or orchidectomy (n = 35). According to gallbladder ultrasonography, after 1 yr new gallstones had developed in 5 of 28 estrogen-treated patients, compared with 0 of 26 orchidectomized patients (P = 0.03). Estrogen therapy for 3 mo increased the relative concentration of cholesterol and cholesterol saturation of bile by approximately 30% (n = 10). Serum LDL cholesterol was reduced by approximately 40%, and its relative change related inversely to that of bile cholesterol (Rs = -0.77). There were no changes in biliary or serum lipids after orchidectomy (n = 9). Secretion rates of biliary lipids were measured with a duodenal perfusion technique. Patients on chronic estrogen therapy (n = 5) had approximately 40% higher biliary excretion rates of cholesterol than age-matched controls (n = 7). Phospholipid secretion was also higher, but no difference in bile acid secretion was found. We conclude that an increased hepatic secretion of cholesterol results in increased cholesterol saturation of bile and an enhanced rate of gallstone formation during estrogen treatment. The changes in bile cholesterol seem to be related to the induced changes in serum lipoprotein metabolism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler R. D., Bennion L. J., Duane W. C., Grundy S. M. Effects of low dose chenodeoxycholic acid feeding on biliary lipid metabolism. Gastroenterology. 1975 Feb;68(2):326–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Admirand W. H., Small D. M. The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1043–1052. doi: 10.1172/JCI105794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlberg J., Angelin B., Einarsson K., Hellström K., Leijd B. Biliary lipid composition in normo- and hyperlipoproteinemia. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):90–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlberg J., Angelin B., Einarsson K., Hellström K., Leijd B. Prevalence of gallbladder disease in hyperlipoproteinemia. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Jun;24(6):459–464. doi: 10.1007/BF01299828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson A., James O. F., MacDonald H. S., Snowball S., Taylor W. The effect of ethynyl oestradiol on biliary lipid composition in young men. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;10(1):77–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb00013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelin B., Einarsson K., Leijd B. Biliary lipid composition during treatment with different hypolipidaemic drugs. Eur J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;9(3):185–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1979.tb00921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion L. J., Ginsberg R. L., Gernick M. B., Bennett P. H. Effects of oral contraceptives on the gallbladder bile of normal women. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jan 22;294(4):189–192. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197601222940403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion L. J., Grundy S. M. Risk factors for the development of cholelithiasis in man (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 23;299(21):1161–1167. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811232992104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion L. J., Mott D. M., Howard B. V. Oral contraceptives raise the cholesterol saturation of bile by increasing biliary cholesterol secretion. Metabolism. 1980 Jan;29(1):18–22. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berr F., Stellaard F., Goetz A., Hammer C., Paumgartner G. Ethinylestradiol stimulates a biliary cholesterol-phospholipid cosecretion mechanism in the hamster. Hepatology. 1988 May-Jun;8(3):619–624. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman D. Z., Johnson M. L., Kern F., Jr Effects of pregnancy and contraceptive steroids on gallbladder function. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 14;302(7):362–364. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002143020702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C. Critical tables for calculating the cholesterol saturation of native bile. J Lipid Res. 1978 Nov;19(8):945–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Nilsell K., Leijd B., Angelin B. Influence of age on secretion of cholesterol and synthesis of bile acids by the liver. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 1;313(5):277–282. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508013130501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erfling W. Effect of estrogens on the liver. Case presentation. Gastroenterology. 1978 Sep;75(3):512–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson M., Berglund L., Rudling M., Henriksson P., Angelin B. Effects of estrogen on low density lipoprotein metabolism in males. Short-term and long-term studies during hormonal treatment of prostatic carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):802–810. doi: 10.1172/JCI114239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everson G. T., Fennessey P., Kern F., Jr Contraceptive steroids alter the steady-state kinetics of bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1988 Jan;29(1):68–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fausa O., Skålhegg B. A. Quantitative determination of bile acids and their conjugates using thin-layer chromatography and a purified 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1974;9(3):249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster S. C., McLaughlin S. M. Improvement in the ultrasonic evaluation of the gall bladder by using the left lateral decubitus position. J Clin Ultrasound. 1977 Aug;5(4):253–256. doi: 10.1002/jcu.1870050408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedewald W. T., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972 Jun;18(6):499–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M. Mechanism of cholesterol gallstones formation. Semin Liver Dis. 1983 May;3(2):97–111. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksson P., Edhag O. Orchidectomy versus oestrogen for prostatic cancer: cardiovascular effects. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Aug 16;293(6544):413–415. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6544.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Thistle J. L., Klein P. D., Szczepanik P. A., Yu P. Y. Chenotherapy for gallstone dissolution. II. Induced changes in bile composition and gallstone response. JAMA. 1978 Mar 20;239(12):1138–1144. doi: 10.1001/jama.239.12.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holan K. R., Holzbach R. T., Hermann R. E., Cooperman A. M., Claffey W. J. Nucleation time: a key factor in the pathogenesis of cholesterol gallstone disease. Gastroenterology. 1979 Oct;77(4 Pt 1):611–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto T., Mao S. J., LaRusso N. F. Biliary excretion of apolipoprotein B by the isolated perfused rat liver. Relationship to receptor-mediated uptake of human low-density lipoprotein and biliary lipid secretion. Gastroenterology. 1987 May;92(5 Pt 1):1236–1242. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(87)91083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern F., Jr, Everson G. T., DeMark B., McKinley C., Showalter R., Erfling W., Braverman D. Z., Szczepanik-van Leeuwen P., Klein P. D. Biliary lipids, bile acids, and gallbladder function in the human female. Effects of pregnancy and the ovulatory cycle. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1229–1242. doi: 10.1172/JCI110369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson T. L. Gray scale cholecystosonography. Diagnostic criteria and accuracy. Radiology. 1977 Jan;122(1):247–251. doi: 10.1148/122.1.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindström C. G. Frequency of gallstone disease in a well-defined Swedish population. A prospective necropsy study in Malmö. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(3):341–346. doi: 10.3109/00365527709180938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsell K., Angelin B., Leijd B., Einarsson K. Comparative effects of ursodeoxycholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid on bile acid kinetics and biliary lipid secretion in humans. Evidence for different modes of action on bile acid synthesis. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1248–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertsemlidis D., Panveliwalla D., Ahrens E. H., Jr Effects of clofibrate and of an estrogen-progestin combination on fasting biliary lipids and cholic acid kinetics in man. Gastroenterology. 1974 Apr;66(4):565–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petitti D. B., Friedman G. D., Klatsky A. L. Association of a history of gallbladder disease with a reduced concentration of high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 4;304(23):1396–1398. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106043042305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roda A., Festi D., Sama C., Mazzella G., Alini R., Roda E., Barbara L. Enzymatic determination of cholesterol in bile. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Nov 3;64(3):337–341. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90364-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedaghat A., Grundy S. M. Cholesterol crystals and the formation of cholesterol gallstones. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1274–1277. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolley P. D., Tonascia J. A., Tockman M. S., Sartwell P. E., Rutledge A. H., Jacobs M. P. Thrombosis with low-estrogen oral contraceptives. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Sep;102(3):197–208. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. R., Heaton K. W., Macfarlane D. G. A relation between high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol and bile cholesterol saturation. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Nov 21;283(6303):1352–1354. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6303.1352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti F. M. Hormonal therapy for prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 15;311(20):1313–1314. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411153112010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallentin L., Varenhorst E. Changes of plasma lipid metabolism in males during estrogen treatment for prostatic carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Sep;47(3):596–599. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-3-596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E. E., Kovanen P. T., Chao Y. S., Brown M. S., Havel R. J., Goldstein J. L. The estradiol-stimulated lipoprotein receptor of rat liver. A binding site that membrane mediates the uptake of rat lipoproteins containing apoproteins B and E. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10464–10471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


