Abstract
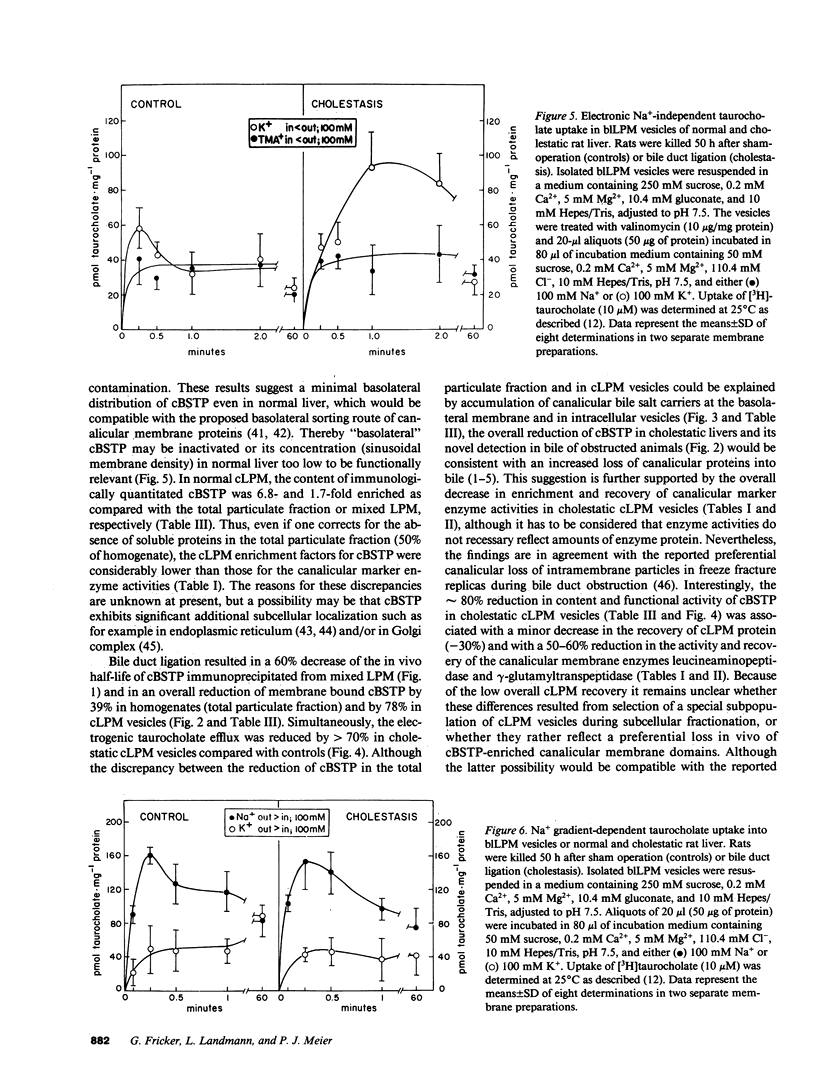
To elucidate the consequences of extrahepatic cholestasis on the structure and function of hepatocytes, we studied the effects of bile duct ligation on the turnover, surface distribution, and functional activity of the canalicular 100-kD bile salt transport protein (cBSTP). Basolateral (blLPM) and canalicular (cLPM) liver plasma membrane vesicles were purified to the same degree from normal and cholestatic rat livers and the membrane bound cBSTP identified and quantitated using polyclonal anti-cBSTP antibodies. Cholestasis of 50 h resulted in an increased release of cBSTP into bile, thereby decreasing its in vivo half-life from 65 to 25 h. Furthermore, a significant portion of cBSTP accumulated at the basolateral surface and in intracellular vesicles of cholestatic hepatocytes. This redistribution of cBSTP was functionally paralleled by decreased and increased electrogenic taurocholate anion transport in cLPM and blLPM vesicles, respectively. These results demonstrate that biliary obstruction causes a reversal of the bile salt secretory polarity of rat hepatocytes. The resulting increase in basolateral (sinusoidal) bile salt efflux might protect hepatocytes from too high an accumulation of toxic bile salts within the cell interior.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Accatino L., Contreras A., Fernańdez S., Quintana C. The effect of complete biliary obstruction on bile flow and bile acid excretion: postcholestatic choleresis in the rat. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 May;93(5):706–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartles J. R., Feracci H. M., Stieger B., Hubbard A. L. Biogenesis of the rat hepatocyte plasma membrane in vivo: comparison of the pathways taken by apical and basolateral proteins using subcellular fractionation. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1241–1251. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartles J. R., Hubbard A. L. Plasma membrane protein sorting in epithelial cells: do secretory pathways hold the key? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 May;13(5):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk P. D., Potter B. J., Stremmel W. Role of plasma membrane ligand-binding proteins in the hepatocellular uptake of albumin-bound organic anions. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):165–176. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer B. L., Boyer J. L. Cytochemical localization of Na+, K+-ATPase in the rat hepatocyte. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1104–1108. doi: 10.1172/JCI109216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer B. L., Donovan C. B. A new method for the rapid isolation of basolateral plasma membrane vesicles from rat liver. Characterization, validation, and bile acid transport studies. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9295–9301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Allen R. M., Ng O. C. Biochemical separation of Na+,K+-ATPase from a "purified" light density, "canalicular"-enriched plasma membrane fraction from rat liver. Hepatology. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):18–28. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busachi C., Mebis J., Broeckaert L., Desmet V. Histochemistry of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in human liver biopsies. Pathol Res Pract. 1981 Jul;172(1-2):99–108. doi: 10.1016/s0344-0338(81)80126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos R., Desmet V. J. Morphologic changes of the junctional complex of the hepatocytes in rat liver after bile duct ligation. Br J Exp Pathol. 1978 Apr;59(2):220–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmet V. J. Current problems in diagnosis of biliary disease and cholestasis. Semin Liver Dis. 1986 Aug;6(3):233–245. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmet V. J. Morphologic and histochemical aspects of cholestasis. Prog Liver Dis. 1972;4:97–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand-Schneider A. M., Maurice M., Dumont M., Feldmann G. Effect of colchicine and phalloidin on the distribution of three plasma membrane antigens in rat hepatocytes: comparison with bile duct ligation. Hepatology. 1987 Nov-Dec;7(6):1239–1248. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G. Progress in unraveling pathways of Golgi traffic. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:447–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felker T. E., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Secretion of lipoprotein-X by perfused livers of rats with cholestasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3459–3463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Smigel M. Solubilization and properties of galactosyltransferase and sulfotransferase activities of Golgi membranes in Triton X-100. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1632–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker G., Schneider S., Gerok W., Kurz G. Identification of different transport systems for bile salts in sinusoidal and canalicular membranes of hepatocytes. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Sep;368(9):1143–1150. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBARG J. A., RUTENBURG A. M. The colorimetric determination of leucine aminopeptidase in urine and serum of normal subjects and patients with cancer and other diseases. Cancer. 1958 Mar-Apr;11(2):283–291. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195803/04)11:2<283::aid-cncr2820110209>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kinne R., Tran T., Arias I. M. Taurocholate transport by rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles. Evidence for the presence of an Na+-independent transport system. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):659–663. doi: 10.1172/JCI111257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kinne R., Tran T., Arias I. M. Taurocholate transport by rat liver sinusoidal membrane vesicles: evidence of sodium cotransport. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):572–579. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Hradek G. T., Schmucker D. L., Underdown B. J. The fate of polymeric and secretory immunoglobulin A after retrograde infusion into the common bile duct in rats. Hepatology. 1984 Nov-Dec;4(6):1173–1183. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Schmucker D. L., Mooney J. S., Adler R. D., Ockner R. K. Morphometric analysis of rat hepatocytes after total billary obstruction. Gastroenterology. 1976 Dec;71(6):1050–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M., Ohkubo A., Quaroni E. G., Sze-Tu D. Increased synthesis of rat liver alkaline phosphatase by bile duct ligation. Hepatology. 1983 May-Jun;3(3):368–376. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keefee E. B., Scharschmidt B. F., Blankenship N. M., Ockner R. K. Studies of relationship among bile flow, liver plasma membrane NaK-ATPase, and membrane microviscosity in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1590–1598. doi: 10.1172/JCI109620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kountouras J., McKavanagh S., Burmicky M., Billing B. H. The effect of secretin on bile flow and bile acid and bilirubin excretion following relief of prolonged bile duct obstruction in the rat. J Hepatol. 1987 Apr;4(2):198–205. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamri Y., Roda A., Dumont M., Feldmann G., Erlinger S. Immunoperoxidase localization of bile salts in rat liver cells. Evidence for a role of the Golgi apparatus in bile salt transport. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1173–1182. doi: 10.1172/JCI113714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham P. S., Kashgarian M. The ultrastructural localization of transport ATPase in the rat liver at non-bile canalicular plasma membranes. Gastroenterology. 1979 May;76(5 Pt 1):988–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., Meier-Abt A. S., Boyer J. L. Properties of the canalicular bile acid transport system in rat liver. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):465–469. doi: 10.1042/bj2420465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., St Meier-Abt A., Barrett C., Boyer J. L. Mechanisms of taurocholate transport in canalicular and basolateral rat liver plasma membrane vesicles. Evidence for an electrogenic canalicular organic anion carrier. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10614–10622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., Sztul E. S., Reuben A., Boyer J. L. Structural and functional polarity of canalicular and basolateral plasma membrane vesicles isolated in high yield from rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):991–1000. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Dunau M. L., Goldman D. A rapid sensitive silver stain for polypeptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz J., Aoki A., Merlo M., Forssmann W. G. Morphological alterations and functional changes of interhepatocellular junctions induced by bile duct ligation. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Aug 26;182(3):299–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00219766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi Y., Tashiro K., Hattori M., Sakaki Y., Ikehara Y. Primary structure of rat liver alkaline phosphatase deduced from its cDNA. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):661–668. doi: 10.1042/bj2490661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOWSKI M., MEISTER A. GAMMA-GLUTAMYL-P-NITROANILIDE: A NEW CONVENIENT SUBSTRATE FOR DETERMINATION AND STUDY OF L- AND D-GAMMA-GLUTAMYLTRANSPEPTIDASE ACTIVITIES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 6;73:679–681. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. J., Poucell S., Oda M. Mechanisms of cholestasis. Lab Invest. 1986 Jun;54(6):593–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett C. B., Jeter R. L., Morin J., Lu A. Y. Electroimmunochemical quantitation of cytochrome P-450, cytochrome P-448, and epoxide hydrolase in rat liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8815–8820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robenek H., Grosser V., Kolde G., Themann H. Gefrierätzuntersuchungen zur Morphologie der Zellmembranen von Hepatocyten bei extrahepatischer Cholestase. Pathol Res Pract. 1980;167(2-4):322–334. doi: 10.1016/s0344-0338(80)80062-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robenek H., Herwig J., Themann H. The morphologic characteristics of intercellular junctions between normal human liver cells and cells from patients with extrahepatic cholestasis. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jul;100(1):93–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein T. L., Blum J. J. Lysosomal physiology in Tetrahymena. I. Effect of glucose, acetate, pyruvate, and carmine on intracellular content and extracellular release of three acid hydrolases. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jun;57(3):630–641. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.3.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruetz S., Fricker G., Hugentobler G., Winterhalter K., Kurz G., Meier P. J. Isolation and characterization of the putative canalicular bile salt transport system of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11324–11330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruetz S., Hugentobler G., Meier P. J. Functional reconstitution of the canalicular bile salt transport system of rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt B. F., Keeffe E. B., Blankenship N. M., Ockner R. K. Validation of a recording spectrophotometric method for measurement of membrane-associated Mg- and NaK-ATPase activity. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 May;93(5):790–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seetharam S., Sussman N. L., Komoda T., Alpers D. H. The mechanism of elevated alkaline phosphatase activity after bile duct ligation in the rat. Hepatology. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):374–380. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simion F. A., Fleischer B., Fleischer S. Two distinct mechanisms for taurocholate uptake in subcellular fractions from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10814–10822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottocasa G. L., Kuylenstierna B., Ernster L., Bergstrand A. An electron-transport system associated with the outer membrane of liver mitochondria. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):415–438. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck G., Leuthard P., Bürk R. R. Detection of basic proteins and low molecular weight peptides in polyacrylamide gels by formaldehyde fixation. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90486-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztul E. S., Biemesderfer D., Caplan M. J., Kashgarian M., Boyer J. L. Localization of Na+,K+-ATPase alpha-subunit to the sinusoidal and lateral but not canalicular membranes of rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1239–1248. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda G., Kako M., Oka H., Oda T., Ikeda Y. Uneven distribution of enzymatic alterations on the liver cell surface in experimental extrahepatic cholestasis of rat. Exp Mol Pathol. 1978 Feb;28(1):10–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(78)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]