Abstract
The crystal structure of nilutamide [systematic name: 5,5-dimethyl-3-[4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]imidazolidine-2,4-dione], C12H10F3N3O4, was determined at 150 K. The dihedral angle between the mean planes through the imidazoline [maximum deviation = 0.0396 (14) Å] and benzene rings is 51.49 (5)°. The molecule exhibits intermolecular hydrogen bonding via N—H⋯O interactions, resulting in the formation of chains parallel to the c axis.
Related literature
For the structure of a related compound, see: Cense et al. (1994 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H10F3N3O4
M r = 317.23
Monoclinic,

a = 12.3304 (9) Å
b = 9.8875 (2) Å
c = 12.2118 (3) Å
β = 117.322 (8)°
V = 1322.74 (14) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 1.31 mm−1
T = 150 K
0.20 × 0.12 × 0.05 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Rapid II diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2001 ▶) T min = 0.733, T max = 0.937
13145 measured reflections
2324 independent reflections
2019 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.028
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.032
wR(F 2) = 0.085
S = 1.12
2324 reflections
206 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR2004 (Burla et al., 2005 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶) and a local program based on the method of Prince & Nicholson (1983 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEPII (Johnson, 1976 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and local programs.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003728/rz2702sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003728/rz2702Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003728/rz2702Isup3.mol
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003728/rz2702Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N14—H14⋯O12i | 0.84 (2) | 2.06 (2) | 2.894 (2) | 172.3 (15) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Science Foundation Engineering Research Center for Structured Organic Particulate Systems for financial support (NSF ERCSOPS; EEC-0540855).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound is a potent antiandrogen used primarily in the treatment of advanced stage prostrate cancer. While no single-crystal structure has been reported for this compound before, there have been reported structures for structurally related compounds like flutamide by Cense et al. (1994). However, the molecular arrangement of nilutamide is different from flutamide since flutamide does not exhibit any hydrogen bonding between the NH and the CO.
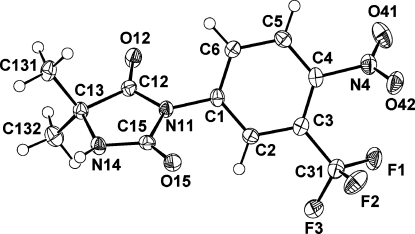
The imidazoline ring of the title compound (Fig. 1) is roughly planar [maximum deviation 0.0396 (14) Å for atom C15] and forms a dihedral angle of 51.49 (5)° with the benzene ring. The nitro group is tilted by 56.35 (7)° with respect to the benzene ring. In the crystal, molecules are linked by intermolecular N—H···O hydrogen interactions (Table 1) forming chains parallel to the c axis.
Experimental
Nilutamide powder was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich Company and used without further purification.A solution of the compound (20 mg ml-1) was prepared in acetonitrile in a 3 ml glass vial. The solution was allowed to evaporate slowly by sealing the vial with parafilm and making a few small holes in the parafilm using a fine needle.
Refinement
The imidazoline H atom was located in a difference Fourier map and refined freely [N–H = 0.841 (19) Å]. All other H atoms were positioned geometrically [C–H = 0.95–0.98 Å] and refined using a riding model, with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C) or 1.5 Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms. A rotating group model was applied to the methyl groups. Seven outliers (-2 0 2, -8 7 8, -8 2 13, -6 2 13, -9 1 14, -7 1 14, -6 1 14), were removed from the final refinement using a local program based on the method of Prince & Nicholson (1983).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound indicating the 50% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atomic numbering for the non-H atoms.
Crystal data
| C12H10F3N3O4 | F(000) = 648 |
| Mr = 317.23 | Dx = 1.593 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 13145 reflections |
| a = 12.3304 (9) Å | θ = 4–66° |
| b = 9.8875 (2) Å | µ = 1.31 mm−1 |
| c = 12.2118 (3) Å | T = 150 K |
| β = 117.322 (8)° | Needle, colorless |
| V = 1322.74 (14) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.12 × 0.05 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Rigaku Rapid II diffractometer | 2019 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Confocal optics monochromator | Rint = 0.028 |
| ω scans | θmax = 66.6°, θmin = 4.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2001) | h = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.733, Tmax = 0.937 | k = −11→11 |
| 13145 measured reflections | l = −13→14 |
| 2324 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Least-squares matrix: full | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0389P)2 + 0.5381P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| wR(F2) = 0.085 | Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3 |
| S = 1.12 | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| 2324 reflections | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick 2008) |
| 206 parameters | Extinction coefficient: 0.72E-02 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Outlier data were removed using a local program based on the method of Prince and Nicholson.Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except for 0 with very negative F2 or flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R_factor_obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| F1 | 0.23075 (8) | 0.18106 (10) | 0.90252 (9) | 0.0335 (3) | |
| F2 | 0.15392 (8) | 0.06052 (10) | 0.99582 (10) | 0.0362 (3) | |
| F3 | 0.26813 (8) | 0.22939 (11) | 1.08854 (9) | 0.0414 (3) | |
| O12 | −0.39601 (9) | 0.28832 (12) | 0.72787 (9) | 0.0254 (3) | |
| O15 | −0.12113 (9) | 0.25489 (11) | 1.13651 (9) | 0.0236 (3) | |
| O41 | 0.14267 (12) | 0.47236 (14) | 0.74335 (12) | 0.0419 (3) | |
| O42 | 0.26114 (10) | 0.46290 (12) | 0.94084 (12) | 0.0350 (3) | |
| N4 | 0.16293 (12) | 0.44744 (13) | 0.84896 (13) | 0.0264 (3) | |
| N11 | −0.23339 (10) | 0.27413 (13) | 0.92377 (11) | 0.0189 (3) | |
| N14 | −0.32753 (11) | 0.20473 (13) | 1.03076 (12) | 0.0212 (3) | |
| C1 | −0.13395 (12) | 0.31698 (15) | 0.90267 (13) | 0.0189 (3) | |
| C2 | −0.03031 (13) | 0.23688 (15) | 0.94671 (13) | 0.0196 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.06962 (13) | 0.27696 (15) | 0.93109 (13) | 0.0199 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.06014 (13) | 0.39789 (15) | 0.86842 (13) | 0.0208 (3) | |
| C5 | −0.04267 (13) | 0.47766 (16) | 0.82365 (13) | 0.0214 (3) | |
| C6 | −0.14103 (13) | 0.43759 (15) | 0.84249 (13) | 0.0198 (3) | |
| C12 | −0.35389 (13) | 0.26571 (15) | 0.83743 (13) | 0.0187 (3) | |
| C13 | −0.42547 (13) | 0.22238 (15) | 0.90554 (13) | 0.0197 (3) | |
| C15 | −0.21768 (13) | 0.24400 (14) | 1.04444 (13) | 0.0187 (3) | |
| C31 | 0.18088 (13) | 0.18783 (16) | 0.98009 (15) | 0.0261 (4) | |
| C131 | −0.51338 (13) | 0.33459 (17) | 0.89947 (15) | 0.0259 (4) | |
| C132 | −0.49281 (15) | 0.08983 (17) | 0.85113 (15) | 0.0289 (4) | |
| H2 | −0.0276 | 0.1543 | 0.9877 | 0.023* | |
| H5 | −0.0465 | 0.5589 | 0.7805 | 0.026* | |
| H6 | −0.2121 | 0.4924 | 0.8144 | 0.024* | |
| H14 | −0.3407 (15) | 0.2040 (18) | 1.0925 (17) | 0.025 (5)* | |
| H13A | −0.5518 | 0.3103 | 0.9514 | 0.039* | |
| H13B | −0.5765 | 0.3459 | 0.8141 | 0.039* | |
| H13C | −0.4682 | 0.4195 | 0.9290 | 0.039* | |
| H13D | −0.4334 | 0.0188 | 0.8615 | 0.043* | |
| H13E | −0.5479 | 0.1023 | 0.7632 | 0.043* | |
| H13F | −0.5402 | 0.0635 | 0.8938 | 0.043* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| F1 | 0.0288 (5) | 0.0330 (6) | 0.0494 (6) | 0.0026 (4) | 0.0270 (5) | −0.0030 (4) |
| F2 | 0.0316 (5) | 0.0277 (5) | 0.0541 (7) | 0.0076 (4) | 0.0239 (5) | 0.0092 (5) |
| F3 | 0.0242 (5) | 0.0495 (7) | 0.0348 (6) | 0.0072 (4) | 0.0000 (4) | −0.0041 (5) |
| O12 | 0.0208 (5) | 0.0387 (7) | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0017 (5) | 0.0096 (5) | 0.0017 (5) |
| O15 | 0.0213 (5) | 0.0300 (6) | 0.0169 (6) | 0.0000 (4) | 0.0065 (5) | 0.0026 (4) |
| O41 | 0.0498 (8) | 0.0485 (8) | 0.0436 (8) | −0.0091 (6) | 0.0354 (7) | −0.0007 (6) |
| O42 | 0.0190 (6) | 0.0307 (7) | 0.0522 (8) | −0.0037 (5) | 0.0138 (6) | −0.0056 (6) |
| N4 | 0.0255 (7) | 0.0240 (7) | 0.0356 (8) | −0.0028 (5) | 0.0190 (6) | −0.0046 (6) |
| N11 | 0.0165 (6) | 0.0242 (7) | 0.0173 (6) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0088 (5) | 0.0011 (5) |
| N14 | 0.0209 (6) | 0.0295 (7) | 0.0163 (6) | −0.0012 (5) | 0.0111 (5) | 0.0011 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0176 (7) | 0.0244 (8) | 0.0165 (7) | −0.0024 (6) | 0.0093 (6) | −0.0028 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0214 (7) | 0.0198 (8) | 0.0180 (7) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0095 (6) | 0.0001 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0177 (7) | 0.0238 (8) | 0.0172 (7) | 0.0000 (6) | 0.0072 (6) | −0.0041 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0184 (7) | 0.0261 (8) | 0.0198 (7) | −0.0050 (6) | 0.0104 (6) | −0.0053 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0240 (7) | 0.0217 (8) | 0.0186 (7) | −0.0026 (6) | 0.0098 (6) | −0.0003 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0186 (7) | 0.0230 (8) | 0.0177 (7) | 0.0014 (6) | 0.0081 (6) | −0.0009 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0197 (7) | 0.0196 (8) | 0.0182 (7) | 0.0016 (6) | 0.0099 (6) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0187 (7) | 0.0254 (8) | 0.0166 (7) | −0.0011 (6) | 0.0093 (6) | −0.0002 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0225 (8) | 0.0169 (7) | 0.0187 (7) | 0.0021 (6) | 0.0112 (6) | 0.0013 (6) |
| C31 | 0.0211 (8) | 0.0273 (9) | 0.0298 (9) | −0.0004 (6) | 0.0118 (7) | −0.0022 (7) |
| C131 | 0.0213 (8) | 0.0336 (9) | 0.0264 (8) | 0.0016 (7) | 0.0142 (7) | −0.0022 (7) |
| C132 | 0.0291 (8) | 0.0289 (9) | 0.0289 (9) | −0.0069 (7) | 0.0135 (7) | −0.0027 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| F1—C31 | 1.3470 (18) | C2—H2 | 0.9500 |
| F2—C31 | 1.3381 (19) | C3—C4 | 1.395 (2) |
| F3—C31 | 1.3313 (19) | C3—C31 | 1.504 (2) |
| O12—C12 | 1.2133 (18) | C4—C5 | 1.375 (2) |
| O15—C15 | 1.2101 (18) | C5—C6 | 1.392 (2) |
| O41—N4 | 1.2210 (18) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| O42—N4 | 1.2254 (18) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| N4—C4 | 1.4762 (18) | C12—C13 | 1.5258 (19) |
| N11—C12 | 1.3740 (18) | C13—C131 | 1.529 (2) |
| N11—C15 | 1.4268 (18) | C13—C132 | 1.530 (2) |
| N11—C1 | 1.4281 (17) | C131—H13A | 0.9800 |
| N14—C15 | 1.3437 (18) | C131—H13B | 0.9800 |
| N14—C13 | 1.4602 (19) | C131—H13C | 0.9800 |
| N14—H14 | 0.841 (19) | C132—H13D | 0.9800 |
| C1—C6 | 1.382 (2) | C132—H13E | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.385 (2) | C132—H13F | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.388 (2) | ||
| O41—N4—O42 | 125.39 (13) | N11—C12—C13 | 106.92 (12) |
| O41—N4—C4 | 117.55 (13) | N14—C13—C12 | 101.37 (11) |
| O42—N4—C4 | 117.04 (13) | N14—C13—C131 | 111.39 (12) |
| C12—N11—C15 | 111.48 (11) | C12—C13—C131 | 110.15 (12) |
| C12—N11—C1 | 126.52 (12) | N14—C13—C132 | 112.05 (13) |
| C15—N11—C1 | 121.83 (12) | C12—C13—C132 | 109.76 (12) |
| C15—N14—C13 | 113.43 (12) | C131—C13—C132 | 111.66 (12) |
| C15—N14—H14 | 119.3 (12) | O15—C15—N14 | 130.31 (14) |
| C13—N14—H14 | 122.2 (12) | O15—C15—N11 | 123.39 (13) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 121.44 (13) | N14—C15—N11 | 106.30 (12) |
| C6—C1—N11 | 120.12 (13) | F3—C31—F2 | 106.75 (13) |
| C2—C1—N11 | 118.41 (13) | F3—C31—F1 | 107.08 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.15 (14) | F2—C31—F1 | 106.13 (12) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.90 | F3—C31—C3 | 112.82 (13) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.90 | F2—C31—C3 | 111.52 (12) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 117.63 (13) | F1—C31—C3 | 112.13 (13) |
| C2—C3—C31 | 118.88 (14) | C13—C131—H13A | 109.50 |
| C4—C3—C31 | 123.48 (13) | C13—C131—H13B | 109.50 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 122.64 (13) | H13A—C131—H13B | 109.50 |
| C5—C4—N4 | 116.64 (13) | C13—C131—H13C | 109.50 |
| C3—C4—N4 | 120.71 (13) | H13A—C131—H13C | 109.50 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.02 (14) | H13B—C131—H13C | 109.50 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.50 | C13—C132—H13D | 109.50 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.50 | C13—C132—H13E | 109.50 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.09 (13) | H13D—C132—H13E | 109.50 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.50 | C13—C132—H13F | 109.50 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.50 | H13D—C132—H13F | 109.50 |
| O12—C12—N11 | 126.85 (13) | H13E—C132—H13F | 109.50 |
| O12—C12—C13 | 126.22 (13) | ||
| C12—N11—C1—C6 | 51.1 (2) | C15—N11—C12—C13 | −1.60 (16) |
| C15—N11—C1—C6 | −123.91 (15) | C1—N11—C12—C13 | −177.03 (13) |
| C12—N11—C1—C2 | −130.60 (15) | C15—N14—C13—C12 | 6.36 (16) |
| C15—N11—C1—C2 | 54.39 (19) | C15—N14—C13—C131 | −110.78 (14) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.1 (2) | C15—N14—C13—C132 | 123.33 (14) |
| N11—C1—C2—C3 | −178.20 (13) | O12—C12—C13—N14 | 177.45 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.1 (2) | N11—C12—C13—N14 | −2.59 (15) |
| C1—C2—C3—C31 | 179.93 (13) | O12—C12—C13—C131 | −64.52 (19) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.7 (2) | N11—C12—C13—C131 | 115.44 (13) |
| C31—C3—C4—C5 | 179.61 (14) | O12—C12—C13—C132 | 58.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—N4 | 179.62 (13) | N11—C12—C13—C132 | −121.22 (13) |
| C31—C3—C4—N4 | −1.4 (2) | C13—N14—C15—O15 | 172.23 (15) |
| O41—N4—C4—C5 | −55.63 (19) | C13—N14—C15—N11 | −7.49 (16) |
| O42—N4—C4—C5 | 122.84 (15) | C12—N11—C15—O15 | −174.20 (14) |
| O41—N4—C4—C3 | 125.35 (16) | C1—N11—C15—O15 | 1.5 (2) |
| O42—N4—C4—C3 | −56.18 (19) | C12—N11—C15—N14 | 5.55 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.8 (2) | C1—N11—C15—N14 | −178.77 (13) |
| N4—C4—C5—C6 | −178.24 (13) | C2—C3—C31—F3 | −99.05 (16) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.4 (2) | C4—C3—C31—F3 | 82.01 (18) |
| N11—C1—C6—C5 | 179.61 (13) | C2—C3—C31—F2 | 21.1 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.8 (2) | C4—C3—C31—F2 | −157.86 (14) |
| C15—N11—C12—O12 | 178.37 (15) | C2—C3—C31—F1 | 139.95 (14) |
| C1—N11—C12—O12 | 2.9 (2) | C4—C3—C31—F1 | −39.0 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N14—H14···O12i | 0.84 (2) | 2.06 (2) | 2.894 (2) | 172.3 (15) |
Symmetry code: (i) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: RZ2702).
References
- Burla, M. C., Caliandro, R., Camalli, M., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., De Caro, L., Giacovazzo, C., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (2005). J. Appl. Cryst. 38, 381–388.
- Cense, J. M., Agafanov, V., Ceolin, R., Ladure, P. & Rodier, N. (1994). Struct. Chem. 5, 79–84.
- Johnson, C. K. (1976). ORTEPII Report ORNL-5138. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee, USA.
- Prince, E. & Nicholson, W. L. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 407–410.
- Rigaku (2001). CrystalClear. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003728/rz2702sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003728/rz2702Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003728/rz2702Isup3.mol
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003728/rz2702Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report