Abstract
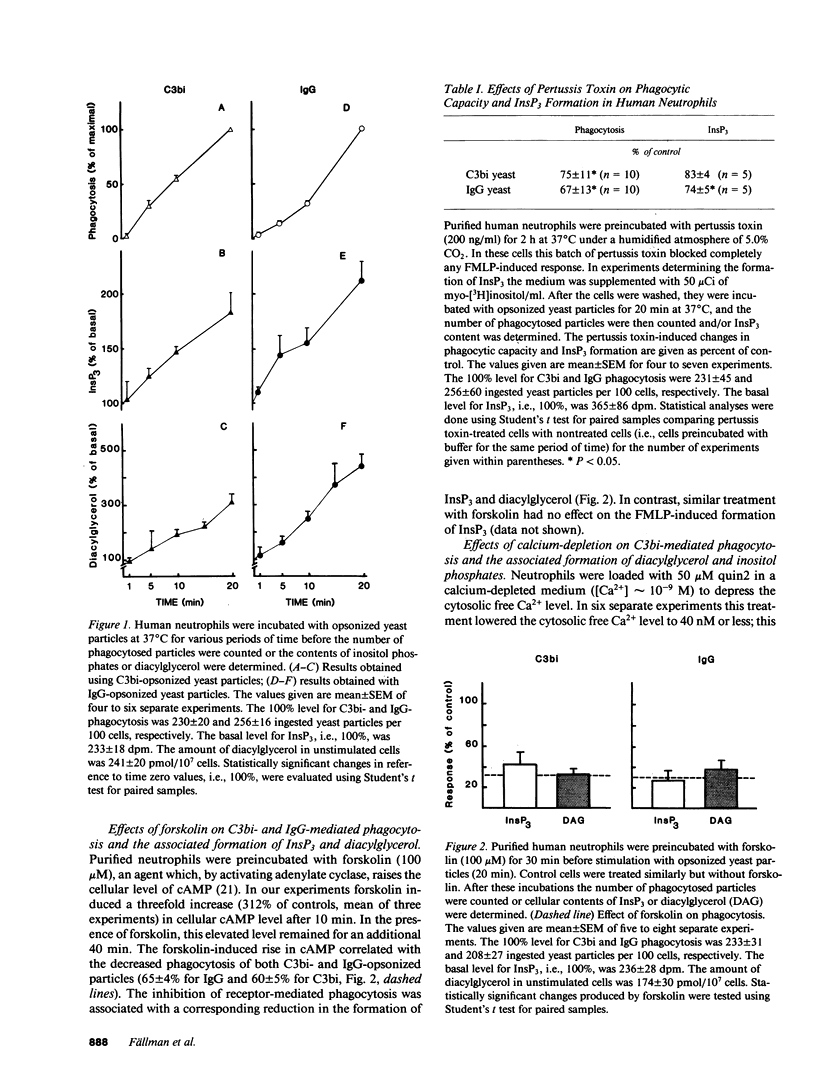
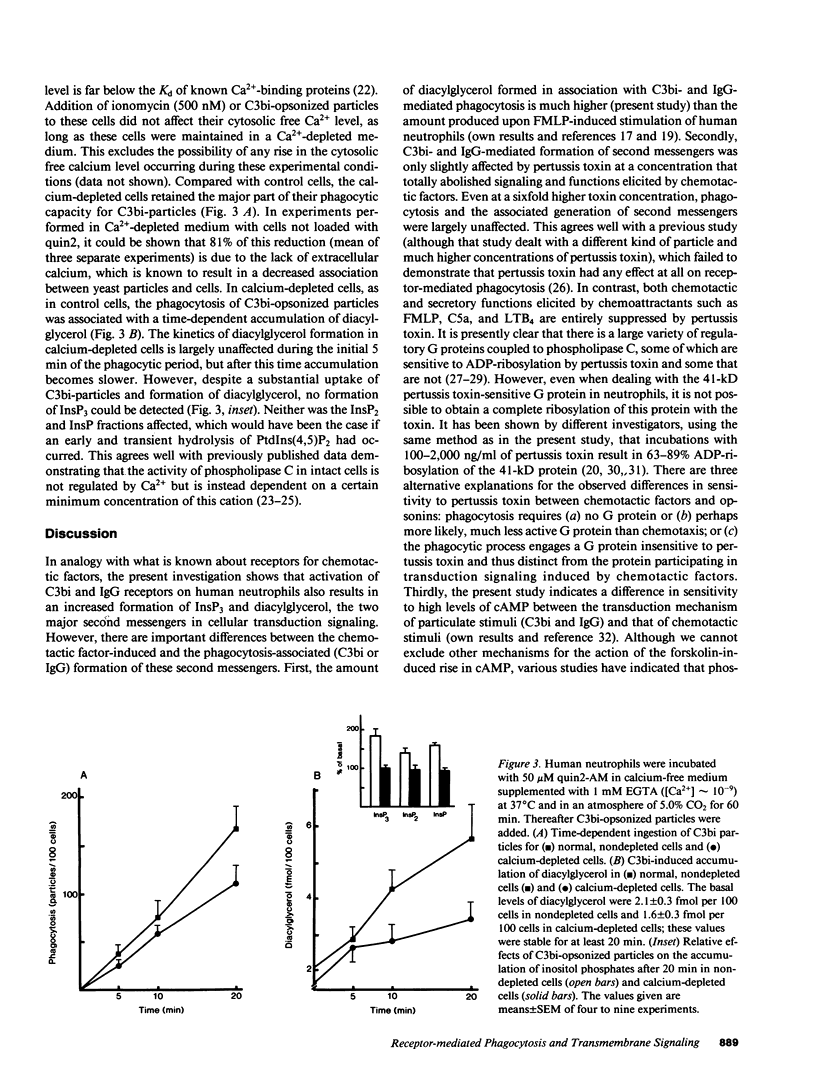
Phagocytosis of C3bi- or IgG-opsonized yeast particles in human neutrophils was found to be associated with an increased formation of inositol phosphates and diacylglycerol. Pertussis toxin only marginally affected phagocytosis of IgG- and C3bi-opsonized particles and the associated formation of second messengers. Forskolin, which induced a threefold rise of cellular cAMP, however, markedly inhibited both C3bi- and IgG-mediated phagocytosis as well as the particle-induced formation of inositol phosphates and diacylglycerol. These observations are in contrast to what was found to occur with chemotactic factors and indicate that chemotactic and phagocytic signaling can be regulated independently in human neutrophils. Since C3bi-mediated phagocytosis has been shown to occur at vanishingly low cytosolic free calcium levels, calcium-depleted cells were used to study the importance of the inositol cycle for the engulfment of C3bi-opsonized particles. Despite a total lack of receptor-induced formation of inositol phosphates, a significantly increased accumulation of diacylglycerol accompanied the ingestion of C3bi-opsonized particles. These data show that the engulfment of C3bi-opsonized particles can occur independently of both a calcium transient and an increased inositol phosphate production. However, the observed accumulation of diacylglycerol, not derived from phosphoinositides, suggests that this second messenger play a role in the control of the engulfment process.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson T., Fällman M., Lew D. P., Stendahl O. Does protein kinase C control receptor-mediated phagocytosis in human neutrophils? FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 7;239(2):371–375. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80954-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson T., Schlegel W., Monod A., Krause K. H., Stendahl O., Lew D. P. Leukotriene B4 stimulation of phagocytes results in the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. A second messenger for Ca2+ mobilization. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):333–340. doi: 10.1042/bj2400333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson T., Rundquist I., Stendahl O., Wymann M. P., Andersson T. Increased breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate is not an initiating factor for actin assembly in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17385–17389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson T., Stendahl O., Andersson T. The role of the cytosolic free Ca2+ transient for fMet-Leu-Phe induced actin polymerization in human neutrophils. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;42(2):338–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besterman J. M., Duronio V., Cuatrecasas P. Rapid formation of diacylglycerol from phosphatidylcholine: a pathway for generation of a second messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6785–6789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford P. G., Rubin R. P. Pertussis toxin inhibits chemotactic factor-induced phospholipase C stimulation and lysosomal enzyme secretion in rabbit neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 22;183(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80801-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S. The dependence on Ca2+ of the guanine-nucleotide-activated polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in neutrophil plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):503–507. doi: 10.1042/bj2400503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel L. W., Waite M., Wykle R. L. A novel mechanism of diglyceride formation. 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate stimulates the cyclic breakdown and resynthesis of phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9128–9132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Bianca V., De Togni P., Grzeskowiak M., Vicentini L. M., Di Virgilio F. Cyclic AMP inhibition of phosphoinositide turnover in human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 29;886(3):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Lew D. P., Pozzan T. Protein kinase C activation of physiological processes in human neutrophils at vanishingly small cytosolic Ca2+ levels. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):691–693. doi: 10.1038/310691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Meyer B. C., Greenberg S., Silverstein S. C. Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis occurs in macrophages at exceedingly low cytosolic Ca2+ levels. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):657–666. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feister A. J., Browder B., Willis H. E., Mohanakumar T., Ruddy S. Pertussis toxin inhibits human neutrophil responses mediated by the 42-kilodalton IgG Fc receptor. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):228–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fällman M., Stendahl O., Andersson T. Phorbol ester-induced activation of protein kinase C leads to increased formation of diacylglycerol in human neutrophils. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Mar;181(1):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatz J. A., Muir J. G., Murray A. W. Direct evidence for phorbol ester-stimulated accumulation of diacylglycerol derived from phosphatidylcholine. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Dec;8(12):1943–1945. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.12.1943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hed J., Stendahl O. Differences in the ingestion mechanisms of IgG and C3b particles in phagocytosis by neutrophils. Immunology. 1982 Apr;45(4):727–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeycutt P. J., Niedel J. E. Cytochalasin B enhancement of the diacylglycerol response in formyl peptide-stimulated neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):15900–15905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Stossel T. P. Modulation of gelsolin function by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):362–364. doi: 10.1038/325362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause K. H., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B., Andersson T., Waldvogel F. A., Lew P. D. Chemotactic peptide activation of human neutrophils and HL-60 cells. Pertussis toxin reveals correlation between inositol trisphosphate generation, calcium ion transients, and cellular activation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1348–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Olson C. V., Grewal I. S. A step sensitive to pertussis toxin and phorbol ester in human neutrophils regulates chemotaxis and capping but not phagocytosis. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 5;200(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80517-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassing I., Lindberg U. Specific interaction between phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and profilactin. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):472–474. doi: 10.1038/314472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. P., Andersson T., Hed J., Di Virgilio F., Pozzan T., Stendahl O. Ca2+-dependent and Ca2+-independent phagocytosis in human neutrophils. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):509–511. doi: 10.1038/315509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew P. D., Monod A., Waldvogel F. A., Dewald B., Baggiolini M., Pozzan T. Quantitative analysis of the cytosolic free calcium dependency of exocytosis from three subcellular compartments in intact human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2197–2204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscat J., Herrero C., Garcia-Barreno P., Municio A. M. Zymosan-induced release of inositol phosphates at resting cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations in macrophages. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):441–445. doi: 10.1042/bj2420441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Roles of G protein subunits in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):129–134. doi: 10.1038/333129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Katada T., Ui M. Coupling of the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein to chemotactic peptide receptors in neutrophil membranes and its uncoupling by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible role of the toxin substrate in Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6761–6768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Loomis C. R., Bishop W. R., Stein R., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8597–8600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Padgett W., Daly J. W. Forskolin: unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and in intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3363–3367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheterline P., Rickard J. E., Richards R. C. Fc receptor-directed phagocytic stimuli induce transient actin assembly at an early stage of phagocytosis in neutrophil leukocytes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1984 May;34(1):80–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Omann G. M., Painter R. G. Relationship of actin polymerization and depolymerization to light scattering in human neutrophils: dependence on receptor occupancy and intracellular Ca++. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1161–1166. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Quantitative studies of phagocytosis. Kinetic effects of cations and heat-labile opsonin. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):346–356. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Marks J. S., Coll K. E., Williamson J. R. Quantitation and early kinetics of inositol lipid changes induced by vasopressin in isolated and cultured hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5716–5725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett A. P., 3rd, Verghese M. W., Dillon S. B., Snyderman R. Calcium influx stimulates a second pathway for sustained diacylglycerol production in leukocytes activated by chemoattractants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1549–1553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhing R. J., Prpic V., Jiang H., Exton J. H. Hormone-stimulated polyphosphoinositide breakdown in rat liver plasma membranes. Roles of guanine nucleotides and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2140–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., McConnell R. T., Lapetina E. G. The rapid formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets by thrombin is inhibited by prostacyclin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13199–13203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Ko S. S., Cohn Z. A. The increase in intracellular free calcium associated with IgG gamma 2b/gamma 1 Fc receptor-ligand interactions: role in phagocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5430–5434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


