Abstract
In the title compound, C17H14N2O2, the hydroxyethanimine group adopts an antiperiplanar conformation. In the crystal, molecules are linked by O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming zigzag chains running along the c axis.
Related literature
For the structures of other acrylate derivatives, see: Zhang et al. (2009 ▶); Wang et al. (2011 ▶); SakthiMurugesan et al. (2011 ▶); Govindan et al. (2011 ▶). For the use of oxime ligands in coordination chemistry, see: Chaudhuri (2003 ▶). For the biological activity of caffeic acids, see: Hwang et al. (2001 ▶); Altug et al. (2008 ▶); Ates et al. (2006 ▶); Atik et al. (2006 ▶); Padinchare et al. (2001 ▶).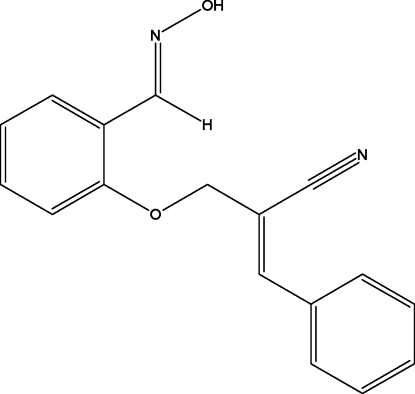
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H14N2O2
M r = 278.30
Monoclinic,

a = 15.8867 (5) Å
b = 6.2381 (2) Å
c = 15.1874 (4) Å
β = 107.199 (2)°
V = 1437.81 (7) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.2 × 0.2 × 0.2 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur-S diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.980, T max = 0.990
19516 measured reflections
4490 independent reflections
2774 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.031
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.049
wR(F 2) = 0.131
S = 0.99
4490 reflections
191 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003923/bt5765sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003923/bt5765Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003923/bt5765Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1A⋯N2i | 0.82 | 2.10 | 2.9187 (17) | 178 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
AS thanks the UGC, India, for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Recently, 2-cyanoacrylates have been extensively used as agrochemicals because of their unique mechanism of action and good environmental profiles (Zhang et al., 2009). Oximes are a classical type of chelating ligands which are widely used in coordination and analytical chemistry (Chaudhuri, 2003). Some naturally occurring caffeic acids and their esters attract much attention in biology and medicine (Hwang et al., 2001; Altug et al., 2008). These compounds show antiviral, antibacterial, vasoactive, antiatherogenic, antiproliferative, antioxidant and antiinflammatory properties (Atik et al., 2006; Padinchare et al., 2001; Ates et al., 2006). Against this background, and in order to obtain detailed information on molecular conformations in the solid state, an X-ray study of the title compound was carried out and the results are presented here. X-Ray analysis confirms the molecular structure and atom connectivity as illustrated in Fig. 1. The oxime group has the C=N bond in an E configuration. The hydroxy ethanimine group is essentially coplanar with the ring to which it is attached. The crystal packing is stabilized by an O—H···N hydrogen bond(Fig. 2).
Experimental
To a stirred solution of (E)-2-((2-formylphenoxy)methyl)-3-phenylacrylonitrile (4 mmol) in 10 ml of EtOH/H2O mixture (1:1) was added NH2OH.HCl (6 mmol) in the presence of 50% NaOH at room temperature. Then the reaction mixture was allowed to stir at room temperature for 1.5 h. After completion of the reaction, solvent was removed and the crude mass was diluted with water (15 ml) and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 τimes 15 ml). The combined organic layer was washed with brine (2 τimes 10 ml) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 and then evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain (E)-2-((2-((E)-(Hydroxyimino)methyl)phenoxy)methyl)-3-phenylacrylonitrile as a colourless solid.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned at calculated positions and refined using a riding model with O-H=0.82Å, Caromatic-H = 0.93Å and Cmethylene-H= 0.97Å and U(H) set to 1.2Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(O).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms.
Fig. 2.
A view of the crystal packing. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding (dashed lines) have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C17H14N2O2 | F(000) = 584 |
| Mr = 278.30 | Dx = 1.286 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 8725 reflections |
| a = 15.8867 (5) Å | θ = 2.8–29.1° |
| b = 6.2381 (2) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 15.1874 (4) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 107.199 (2)° | Monoclinic, colourless |
| V = 1437.81 (7) Å3 | 0.2 × 0.2 × 0.2 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur-S diffractometer | 4490 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2774 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.031 |
| Detector resolution: 15.9948 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 31.4°, θmin = 2.7° |
| ω scans | h = −20→23 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009) | k = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.980, Tmax = 0.990 | l = −22→22 |
| 19516 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.131 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.99 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0521P)2 + 0.226P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4490 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 191 parameters | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.30906 (9) | 0.0194 (2) | 0.29768 (9) | 0.0471 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.2662 | 0.0231 | 0.2407 | 0.057* | |
| C2 | 0.37843 (8) | 0.1812 (2) | 0.31995 (8) | 0.0405 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.44575 (9) | 0.1763 (2) | 0.40269 (9) | 0.0500 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.4456 | 0.0697 | 0.4455 | 0.060* | |
| C4 | 0.51256 (9) | 0.3247 (2) | 0.42297 (9) | 0.0525 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.5574 | 0.3176 | 0.4784 | 0.063* | |
| C5 | 0.51234 (9) | 0.4837 (2) | 0.36050 (10) | 0.0542 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.5574 | 0.5849 | 0.3740 | 0.065* | |
| C6 | 0.44610 (9) | 0.4954 (2) | 0.27781 (9) | 0.0488 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.4464 | 0.6041 | 0.2360 | 0.059* | |
| C7 | 0.37943 (8) | 0.3449 (2) | 0.25758 (8) | 0.0399 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.30879 (9) | 0.5024 (2) | 0.11052 (9) | 0.0474 (3) | |
| H8A | 0.3612 | 0.4952 | 0.0904 | 0.057* | |
| H8B | 0.3058 | 0.6435 | 0.1363 | 0.057* | |
| C9 | 0.22813 (8) | 0.4609 (2) | 0.03129 (8) | 0.0411 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.22894 (9) | 0.2607 (2) | −0.01427 (9) | 0.0486 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.16197 (9) | 0.6014 (2) | 0.00727 (8) | 0.0444 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.1718 | 0.7251 | 0.0431 | 0.053* | |
| C12 | 0.07740 (9) | 0.5990 (2) | −0.06398 (8) | 0.0435 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.04331 (10) | 0.4260 (2) | −0.12169 (10) | 0.0577 (4) | |
| H13 | 0.0768 | 0.3021 | −0.1177 | 0.069* | |
| C14 | −0.03912 (10) | 0.4363 (3) | −0.18424 (10) | 0.0629 (4) | |
| H14 | −0.0607 | 0.3196 | −0.2223 | 0.075* | |
| C15 | −0.08983 (10) | 0.6164 (3) | −0.19123 (11) | 0.0633 (4) | |
| H15 | −0.1460 | 0.6212 | −0.2330 | 0.076* | |
| C16 | −0.05728 (11) | 0.7892 (3) | −0.13634 (12) | 0.0694 (5) | |
| H16 | −0.0911 | 0.9128 | −0.1414 | 0.083* | |
| C17 | 0.02527 (10) | 0.7807 (2) | −0.07360 (10) | 0.0577 (4) | |
| H17 | 0.0466 | 0.8996 | −0.0368 | 0.069* | |
| N1 | 0.30657 (8) | −0.12586 (19) | 0.35497 (8) | 0.0527 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.23413 (9) | 0.0992 (2) | −0.04726 (10) | 0.0728 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.23639 (8) | −0.26430 (19) | 0.31926 (8) | 0.0716 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.2369 | −0.3587 | 0.3570 | 0.107* | |
| O2 | 0.31108 (6) | 0.34087 (15) | 0.17729 (6) | 0.0487 (2) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0432 (7) | 0.0502 (8) | 0.0433 (7) | 0.0001 (6) | 0.0055 (6) | 0.0077 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0369 (6) | 0.0437 (7) | 0.0396 (6) | 0.0029 (5) | 0.0093 (5) | 0.0023 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0488 (8) | 0.0581 (8) | 0.0397 (7) | 0.0044 (7) | 0.0079 (6) | 0.0084 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0455 (8) | 0.0654 (9) | 0.0387 (7) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0004 (6) | −0.0043 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0488 (8) | 0.0567 (9) | 0.0514 (8) | −0.0101 (7) | 0.0061 (6) | −0.0076 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0479 (8) | 0.0474 (8) | 0.0470 (7) | −0.0046 (6) | 0.0075 (6) | 0.0040 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0359 (6) | 0.0441 (7) | 0.0372 (6) | 0.0032 (5) | 0.0070 (5) | 0.0013 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0481 (8) | 0.0434 (7) | 0.0456 (7) | −0.0020 (6) | 0.0060 (6) | 0.0092 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0460 (7) | 0.0386 (6) | 0.0367 (6) | −0.0009 (5) | 0.0090 (5) | 0.0048 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0443 (8) | 0.0476 (8) | 0.0497 (7) | 0.0045 (6) | 0.0076 (6) | 0.0034 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0524 (8) | 0.0397 (7) | 0.0387 (6) | 0.0005 (6) | 0.0096 (6) | −0.0009 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0453 (7) | 0.0462 (7) | 0.0377 (6) | 0.0033 (6) | 0.0104 (5) | 0.0028 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0551 (9) | 0.0542 (9) | 0.0547 (8) | 0.0079 (7) | 0.0023 (7) | −0.0070 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0565 (10) | 0.0695 (10) | 0.0541 (9) | −0.0032 (8) | 0.0030 (7) | −0.0095 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0449 (8) | 0.0833 (12) | 0.0551 (9) | 0.0031 (8) | 0.0048 (7) | 0.0054 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0536 (10) | 0.0700 (11) | 0.0773 (11) | 0.0192 (8) | 0.0080 (8) | 0.0012 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0551 (9) | 0.0527 (9) | 0.0602 (9) | 0.0091 (7) | 0.0093 (7) | −0.0048 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0521 (7) | 0.0517 (7) | 0.0522 (7) | −0.0081 (5) | 0.0119 (5) | 0.0032 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0731 (10) | 0.0553 (8) | 0.0837 (10) | 0.0116 (7) | 0.0136 (8) | −0.0131 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0701 (8) | 0.0631 (7) | 0.0727 (7) | −0.0239 (6) | 0.0074 (6) | 0.0106 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0427 (5) | 0.0525 (5) | 0.0421 (5) | −0.0062 (4) | −0.0009 (4) | 0.0133 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—N1 | 1.2649 (16) | C9—C11 | 1.3339 (18) |
| C1—C2 | 1.4583 (18) | C9—C10 | 1.4296 (19) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C10—N2 | 1.1392 (17) |
| C2—C3 | 1.3889 (18) | C11—C12 | 1.4548 (18) |
| C2—C7 | 1.3962 (17) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.373 (2) | C12—C17 | 1.3857 (19) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C12—C13 | 1.3951 (19) |
| C4—C5 | 1.372 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.373 (2) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3814 (19) | C14—C15 | 1.368 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.3804 (18) | C15—C16 | 1.367 (2) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C7—O2 | 1.3725 (14) | C16—C17 | 1.375 (2) |
| C8—O2 | 1.4225 (14) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.4983 (18) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9700 | N1—O1 | 1.3876 (15) |
| C8—H8B | 0.9700 | O1—H1A | 0.8200 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 120.76 (12) | C11—C9—C8 | 121.58 (12) |
| N1—C1—H1 | 119.6 | C10—C9—C8 | 114.31 (11) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.6 | N2—C10—C9 | 176.18 (16) |
| C3—C2—C7 | 118.02 (12) | C9—C11—C12 | 132.56 (12) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.43 (12) | C9—C11—H11 | 113.7 |
| C7—C2—C1 | 120.55 (11) | C12—C11—H11 | 113.7 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.70 (13) | C17—C12—C13 | 117.24 (13) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.2 | C17—C12—C11 | 117.49 (12) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.2 | C13—C12—C11 | 125.23 (12) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.26 (12) | C14—C13—C12 | 120.79 (14) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.4 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.6 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.4 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.6 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.82 (13) | C15—C14—C13 | 120.76 (15) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.6 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.6 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.64 (12) | C16—C15—C14 | 119.48 (14) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.2 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.3 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.2 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.3 |
| O2—C7—C6 | 124.30 (11) | C15—C16—C17 | 120.22 (15) |
| O2—C7—C2 | 115.14 (11) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C6—C7—C2 | 120.56 (11) | C17—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| O2—C8—C9 | 106.60 (10) | C16—C17—C12 | 121.48 (15) |
| O2—C8—H8A | 110.4 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.3 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 110.4 | C12—C17—H17 | 119.3 |
| O2—C8—H8B | 110.4 | C1—N1—O1 | 111.22 (11) |
| C9—C8—H8B | 110.4 | N1—O1—H1A | 109.5 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 108.6 | C7—O2—C8 | 117.86 (9) |
| C11—C9—C10 | 124.11 (12) | ||
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 2.7 (2) | C8—C9—C11—C12 | −178.61 (12) |
| N1—C1—C2—C7 | −178.10 (13) | C9—C11—C12—C17 | −176.32 (13) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −1.05 (19) | C9—C11—C12—C13 | 5.7 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 178.19 (12) | C17—C12—C13—C14 | −0.9 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.8 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 177.09 (14) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.2 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.2 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.2 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 1.1 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—O2 | −179.43 (12) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −1.0 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | 0.0 (2) | C15—C16—C17—C12 | −0.1 (3) |
| C3—C2—C7—O2 | −179.90 (11) | C13—C12—C17—C16 | 1.1 (2) |
| C1—C2—C7—O2 | 0.86 (16) | C11—C12—C17—C16 | −177.09 (14) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | 0.63 (18) | C2—C1—N1—O1 | −178.97 (12) |
| C1—C2—C7—C6 | −178.62 (12) | C6—C7—O2—C8 | 0.00 (18) |
| O2—C8—C9—C11 | 116.39 (13) | C2—C7—O2—C8 | −179.45 (11) |
| O2—C8—C9—C10 | −63.22 (14) | C9—C8—O2—C7 | −179.66 (10) |
| C10—C9—C11—C12 | 1.0 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1A···N2i | 0.82 | 2.10 | 2.9187 (17) | 178 |
Symmetry code: (i) x, −y−1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5765).
References
- Altug, M. E., Serarslan, Y. & Bal, R. (2008). Brain Res. 1201, 135–142. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ates, B., Dogru, M. I. & Gul, M. (2006). Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 20, 283–289. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Atik, E., Goeruer, S. & Kiper, A. N. (2006). Pharmacol. Res. 54, 293–297. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, P. (2003). Coord. Chem. Rev. 243, 143–168.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Govindan, E., SakthiMurugesan, K., Srinivasan, J., Bakthadoss, M. & SubbiahPandi, A. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D. J., Kim, S. N. & Choi, J. H. (2001). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 9, 1429–1437. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Oxford Diffraction (2009). CrysAlis PRO Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England.
- Padinchare, R., Irina, V., Paul, C., Dirk, V. B., Koen, A. & Achiel, H. (2001). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 11, 215–217.
- SakthiMurugesan, K., Govindan, E., Srinivasan, J., Bakthadoss, M. & SubbiahPandi, A. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wang, L., Meng, F.-Y., Lin, C.-W., Chen, H.-Y. & Luo, X. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D., Zhang, X. & Guo, L. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o90.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003923/bt5765sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003923/bt5765Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812003923/bt5765Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




