Abstract
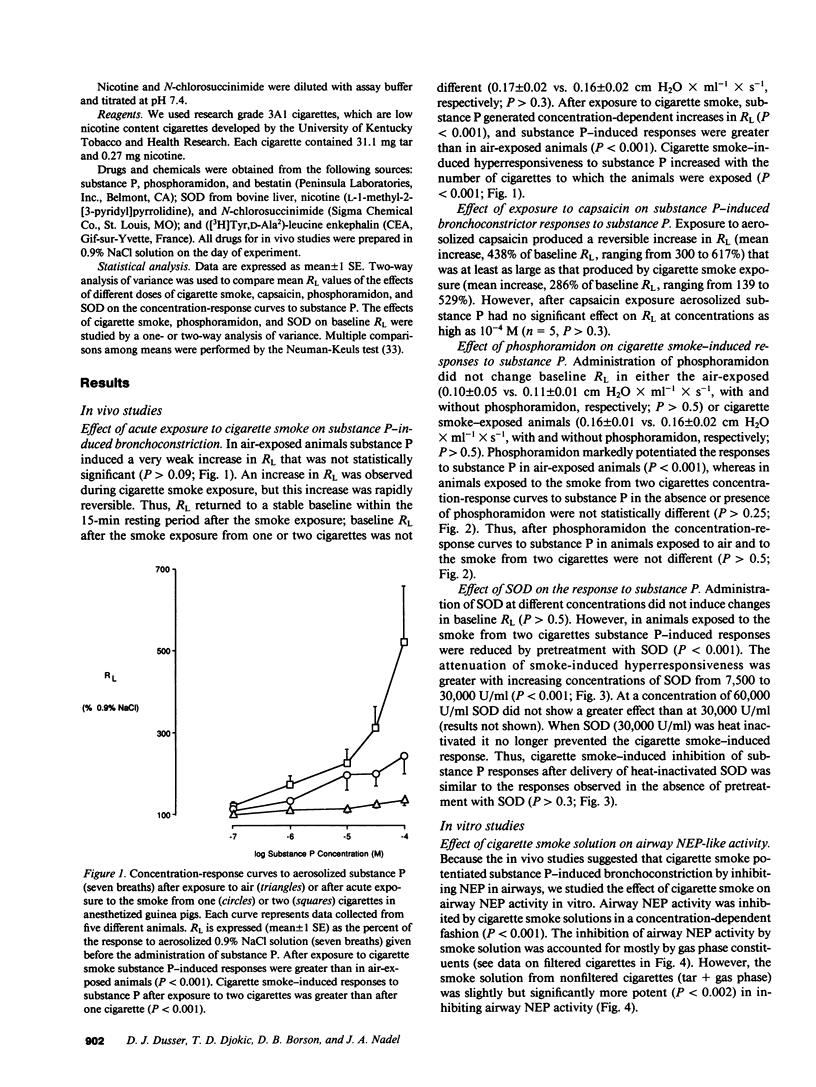
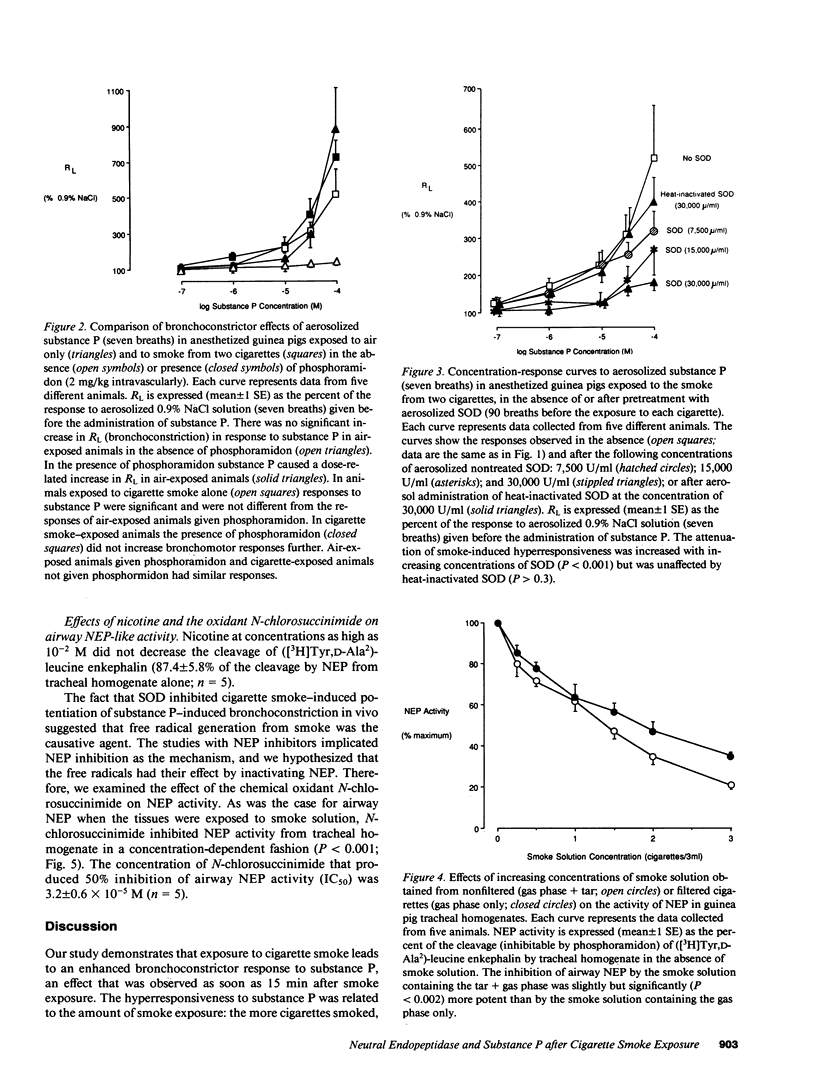
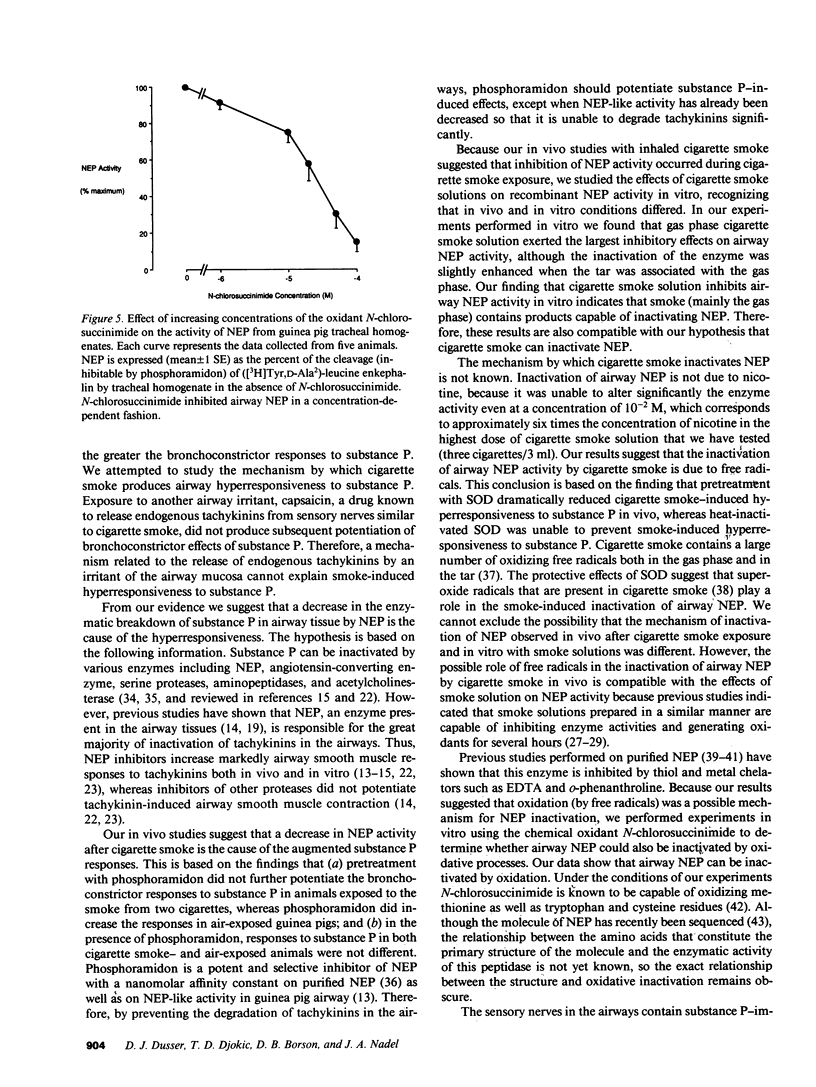
We examined the effects of acute exposure to cigarette smoke on the airway responses to substance P in anesthetized guinea pigs and on the activity of airway neutral endopeptidase (NEP). After exposure to air or to cigarette smoke we measured the change in total pulmonary resistance (RL) induced by increasing concentrations of aerosolized substance P in the absence or presence of the NEP inhibitor phosphoramidon. In the absence of phosphramidon the bronchoconstrictor responses to substance P were greater in cigarette smoke-exposed guinea pigs than in air-exposed animals. Phosphoramidon did not further potentiate the responses to substance P in smoke-exposed guinea pigs, whereas it did so in air-exposed animals. In the presence of phosphoramidon, bronchoconstrictor responses to substance P in animals exposed to air or to cigarette smoke were not different. Aerosols of SOD delivered before cigarette smoke exposures dramatically reduced smoke-induced hyperresponsiveness to substance P, whereas heat-inactivated SOD had no effect on smoke-induced hyper-responsiveness to substance P. Cigarette smoke solution inhibited NEP activity from tracheal homogenate in a concentration-dependent fashion, an inhibitory effect that was mostly due to the gas phase of the smoke, but not to nicotine. The mild chemical oxidant N-chlorosuccinimide mimicked the concentration-dependent inhibitory effect of smoke solution on airway NEP activity. We conclude that cigarette smoke causes enhanced airway responsiveness to substance P in vivo by inactivating airway NEP. We suggest that cigarette smoke-induced inhibition of airway NEP is due to effects of free radicals.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borson D. B., Brokaw J. J., Sekizawa K., McDonald D. M., Nadel J. A. Neutral endopeptidase and neurogenic inflammation in rats with respiratory infections. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Jun;66(6):2653–2658. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.6.2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borson D. B., Corrales R., Varsano S., Gold M., Viro N., Caughey G., Ramachandran J., Nadel J. A. Enkephalinase inhibitors potentiate substance P-induced secretion of 35SO4-macromolecules from ferret trachea. Exp Lung Res. 1987;12(1):21–36. doi: 10.3109/01902148709068812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp H., Janoff A. Potential mediator of inflammation. Phagocyte-derived oxidants suppress the elastase-inhibitory capacity of alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):987–995. doi: 10.1172/JCI109968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLL R., HILL A. B. MORTALITY IN RELATION TO SMOKING: TEN YEARS' OBSERVATIONS OF BRITISH DOCTORS. Br Med J. 1964 May 30;1(5395):1399–1410. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5395.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djokic T. D., Nadel J. A., Dusser D. J., Sekizawa K., Graf P. D., Borson D. B. Inhibitors of neutral endopeptidase potentiate electrically and capsaicin-induced noncholinergic contraction in guinea pig bronchi. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jan;248(1):7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley M. M., Pryor W. A. Free radical pathology: inactivation of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor by products from the reaction of nitrogen dioxide with hydrogen peroxide and the etiology of emphysema. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 15;106(3):981–987. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91807-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusser D. J., Umeno E., Graf P. D., Djokic T., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Airway neutral endopeptidase-like enzyme modulates tachykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in vivo. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Dec;65(6):2585–2591. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.6.2585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvan L., Huang C. H., Prestayko A. W., Stout J. T., Evans J. E., Crooke S. T. Inhibition of bleomycin-induced DNA breakage by superoxide dismutase. Cancer Res. 1981 Dec;41(12 Pt 1):5103–5106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gashi A. A., Borson D. B., Finkbeiner W. E., Nadel J. A., Basbaum C. B. Neuropeptides degranulate serous cells of ferret tracheal glands. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 1):C223–C229. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.2.C223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. W., Cockcroft D. W., Mink J. T., Cotton D. J., Poonawala R., Dosman J. A. Increased nonspecific bronchial reactivity in cigarette smokers with normal lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Oct;122(4):577–581. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.4.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgin R. L., Charleson S. E., Zimmerman M., Mumford R., Wood P. L. Enkephalinase: selective peptide inhibitors. Life Sci. 1981 Dec 21;29(25):2593–2601. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90632-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. R., Ashton J., Schulz W. W., Erdös E. G. Neutral metalloendopeptidase in human lung tissue and cultured cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):564–568. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Kenny A. J. The purification and specificity of a neutral endopeptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):477–488. doi: 10.1042/bj1370477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohrogi H., Graf P. D., Sekizawa K., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Neutral endopeptidase inhibitors potentiate substance P- and capsaicin-induced cough in awake guinea pigs. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2063–2068. doi: 10.1172/JCI113827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llorens C., Malfroy B., Schwartz J. C., Gacel G., Roques B. P., Roy J., Morgat J. L., Javoy-Agid F., Agid Y. Enkephalin dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase (enkephalinase) activity: selective radioassay, properties, and regional distribution in human brain. J Neurochem. 1982 Oct;39(4):1081–1089. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb11500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llorens C., Schwartz J. C. Enkephalinase activity in rat peripheral organs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 5;69(1):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90609-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Saria A., Cuello C. Substance P-immunoreactive sensory nerves in the lower respiratory tract of various mammals including man. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;235(2):251–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00217848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Lundblad L., Saria A., Anggård A. Inhibition of cigarette smoke-induced oedema in the nasal mucosa by capsaicin pretreatment and a substance P antagonist. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;326(2):181–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00517317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Martling C. R., Saria A., Folkers K., Rosell S. Cigarette smoke-induced airway oedema due to activation of capsaicin-sensitive vagal afferents and substance P release. Neuroscience. 1983 Dec;10(4):1361–1368. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A. Capsaicin-induced desensitization of airway mucosa to cigarette smoke, mechanical and chemical irritants. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):251–253. doi: 10.1038/302251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Schofield P. R., Kuang W. J., Seeburg P. H., Mason A. J., Henzel W. J. Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of rat enkephalinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80475-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Swerts J. P., Guyon A., Roques B. P., Schwartz J. C. High-affinity enkephalin-degrading peptidase in brain is increased after morphine. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):523–526. doi: 10.1038/276523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. The hydrolysis of peptides, including enkephalins, tachykinins and their analogues, by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):433–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2230433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald D. M. Respiratory tract infections increase susceptibility to neurogenic inflammation in the rat trachea. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jun;137(6):1432–1440. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.6.1432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. B., Morrison B. J. The effect of cigarette smoke from the mother on bronchial responsiveness and severity of symptoms in children with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Apr;77(4):575–581. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NADEL J. A., COMROE J. H., Jr Acute effects of inhalation of cigarette smoke on airway conductance. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Jul;16:713–716. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.4.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell E. J., Logan G. B. Parental smoking in childhood asthma. Ann Allergy. 1974 Mar;32(3):142–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor G. T., Weiss S. T., Tager I. B., Speizer F. E. The effect of passive smoking on pulmonary function and nonspecific bronchial responsiveness in a population-based sample of children and young adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Apr;135(4):800–804. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.4.800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Wilk S. Purification and specificity of a membrane-bound metalloendopeptidase from bovine pituitaries. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4942–4950. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor W. A., Dooley M. M., Church D. F. Inactivation of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor by gas-phase cigarette smoke. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):676–681. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor W. A., Prier D. G., Church D. F. Electron-spin resonance study of mainstream and sidestream cigarette smoke: nature of the free radicals in gas-phase smoke and in cigarette tar. Environ Health Perspect. 1983 Jan;47:345–355. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8347345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W. J., Fleit H. B., Chung S. I., Janoff A. Characterization of two distinct transglutaminases of murine bone marrow-derived macrophages: effects of exposure of viable cells to cigarette smoke on enzyme activity. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Jul;42(1):9–20. doi: 10.1002/jlb.42.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizawa K., Tamaoki J., Graf P. D., Basbaum C. B., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Enkephalinase inhibitor potentiates mammalian tachykinin-induced contraction in ferret trachea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Dec;243(3):1211–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizawa K., Tamaoki J., Nadel J. A., Borson D. B. Enkephalinase inhibitor potentiates substance P- and electrically induced contraction in ferret trachea. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Oct;63(4):1401–1405. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.4.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y., Burstein Y., Patchornik A. Selective oxidation of methionine residues in proteins. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 7;14(20):4497–4503. doi: 10.1021/bi00691a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. A., Stimler-Gerard N. P., Coats S. R., Drazen J. M. Substance P-induced bronchoconstriction in the guinea pig. Enhancement by inhibitors of neutral metalloendopeptidase and angiotensin-converting enzyme. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Feb;137(2):331–336. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.2.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidgel R. A., Engelbrecht S., Johnson A. R., Erdös E. G. Hydrolysis of substance p and neurotensin by converting enzyme and neutral endopeptidase. Peptides. 1984 Jul-Aug;5(4):769–776. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimler-Gerard N. P. Neutral endopeptidase-like enzyme controls the contractile activity of substance P in guinea pig lung. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1819–1825. doi: 10.1172/JCI113023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka D. T., Grunstein M. M. Mechanisms of substance P-induced contraction of rabbit airway smooth muscle. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Nov;57(5):1551–1557. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.5.1551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu P. H., Boulton A. A. Irreversible inhibition of monoamine oxidase by some components of cigarette smoke. Life Sci. 1987 Aug 10;41(6):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90446-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


