Abstract
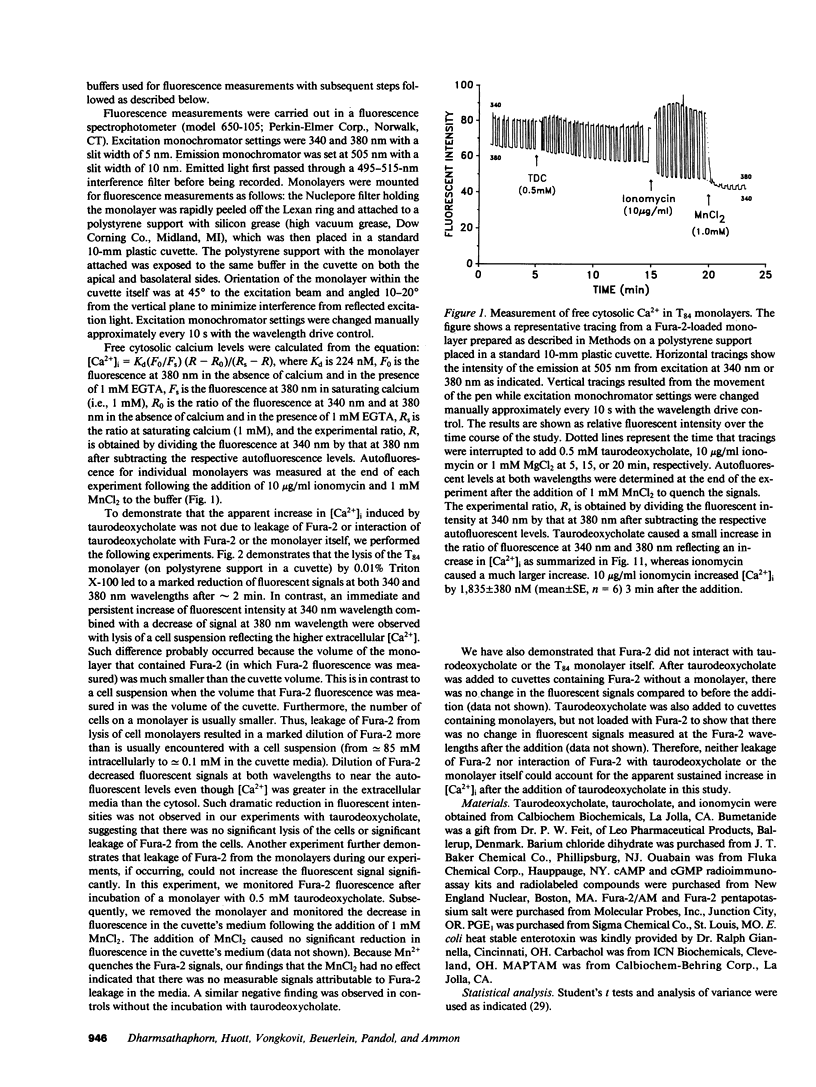
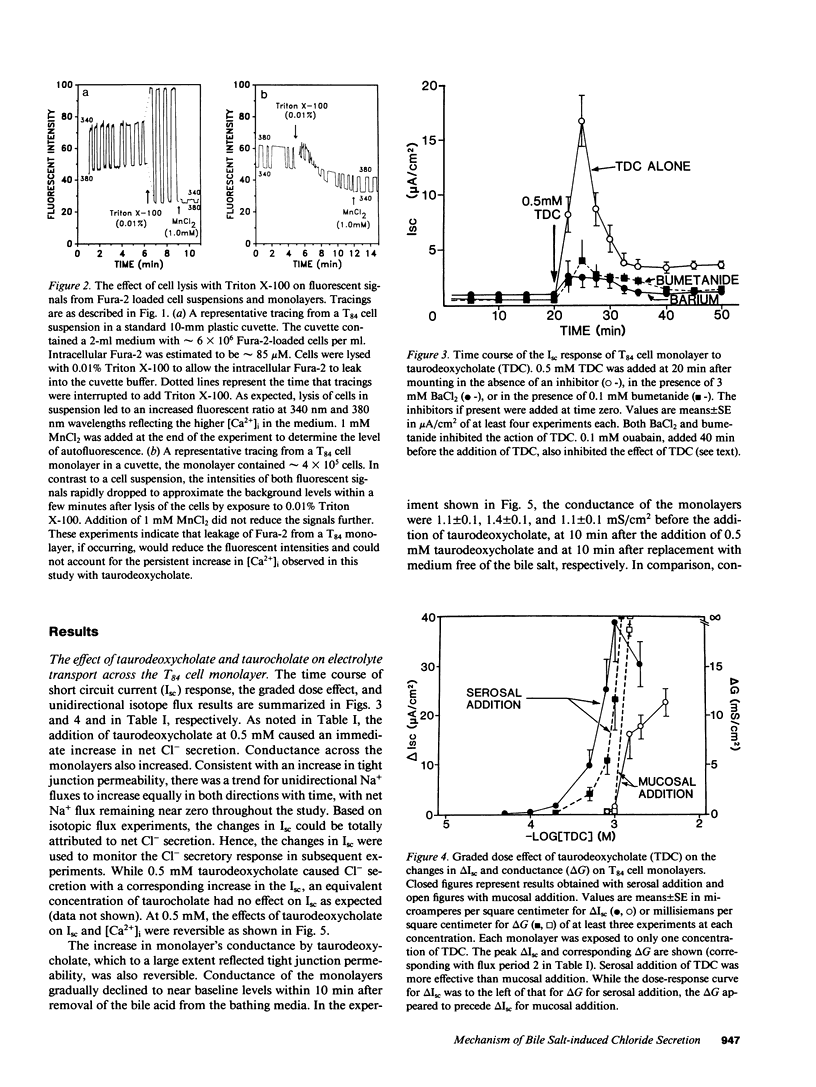
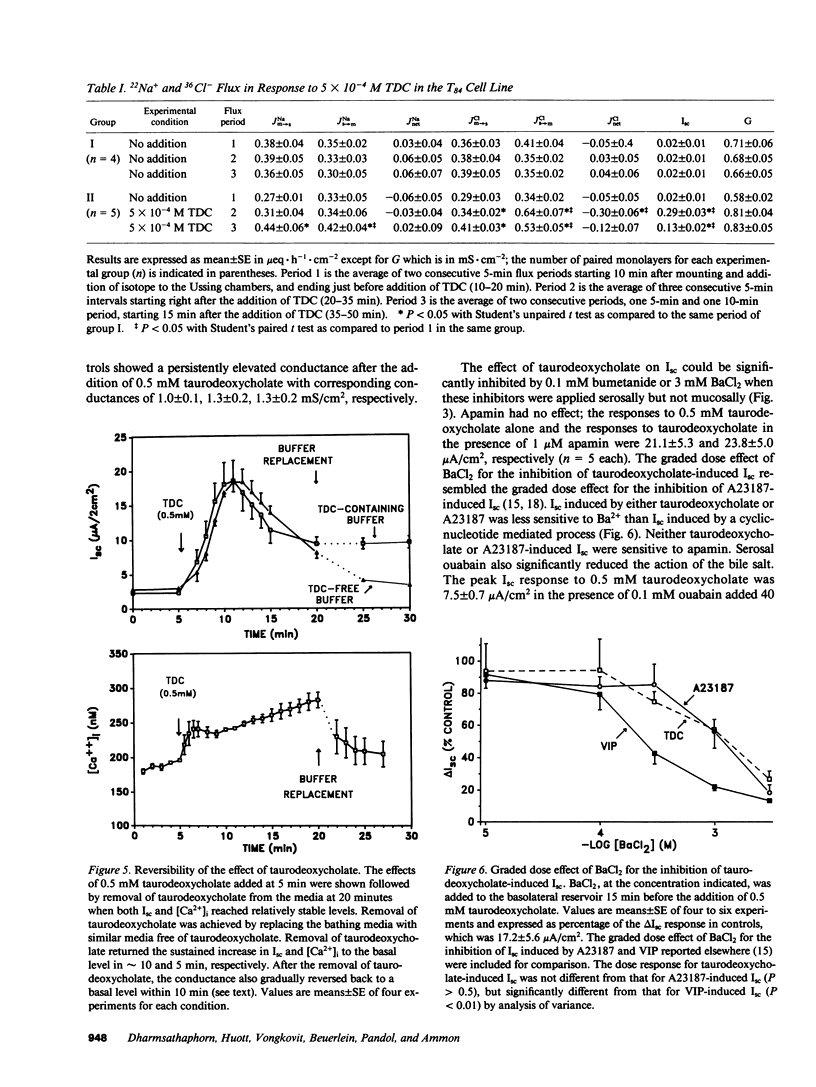
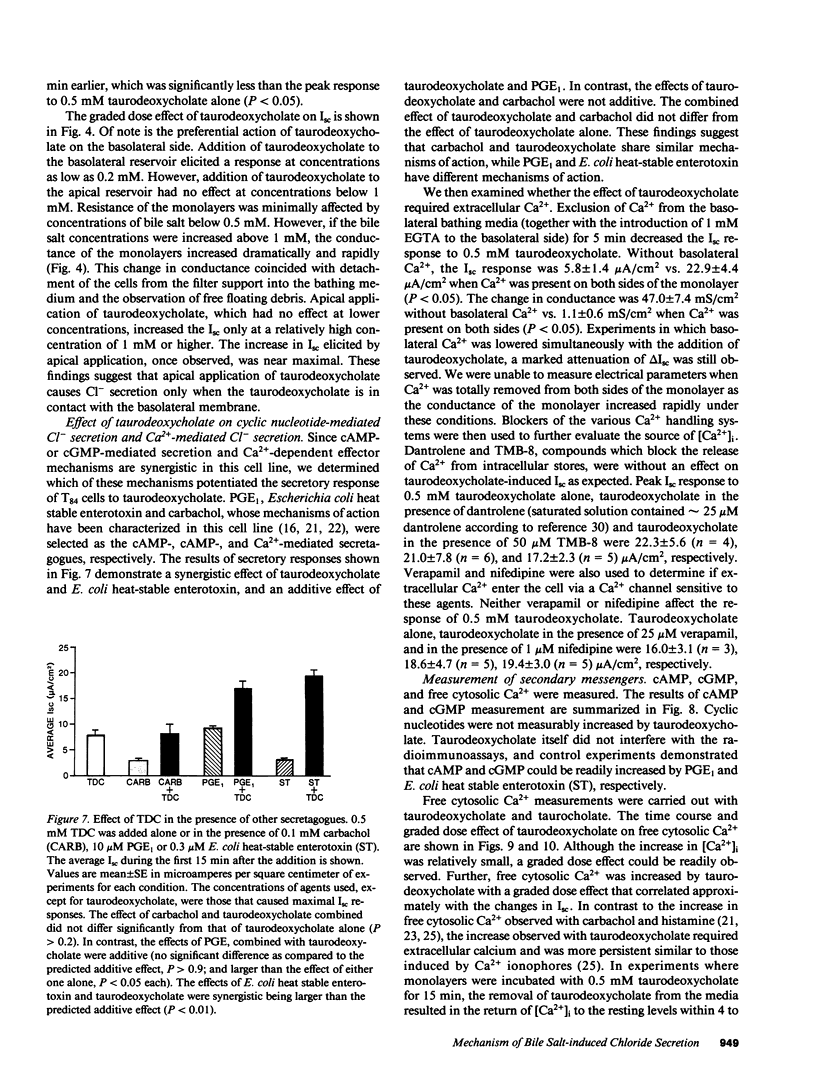
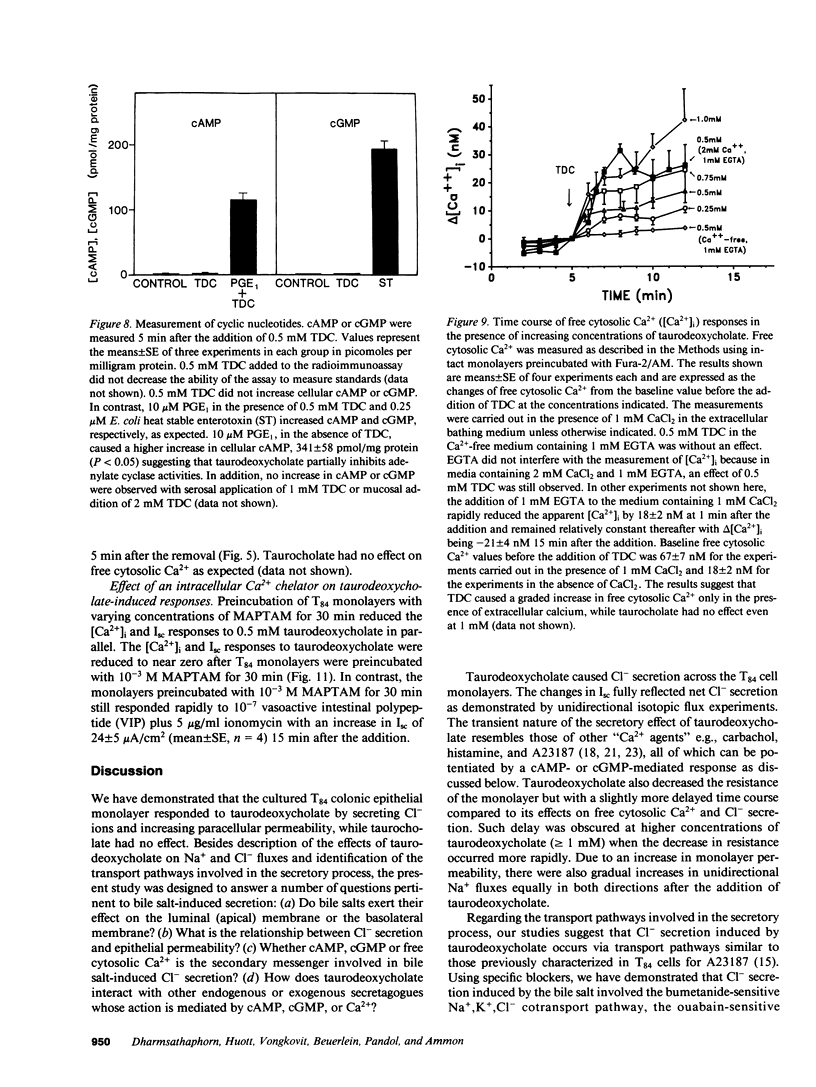
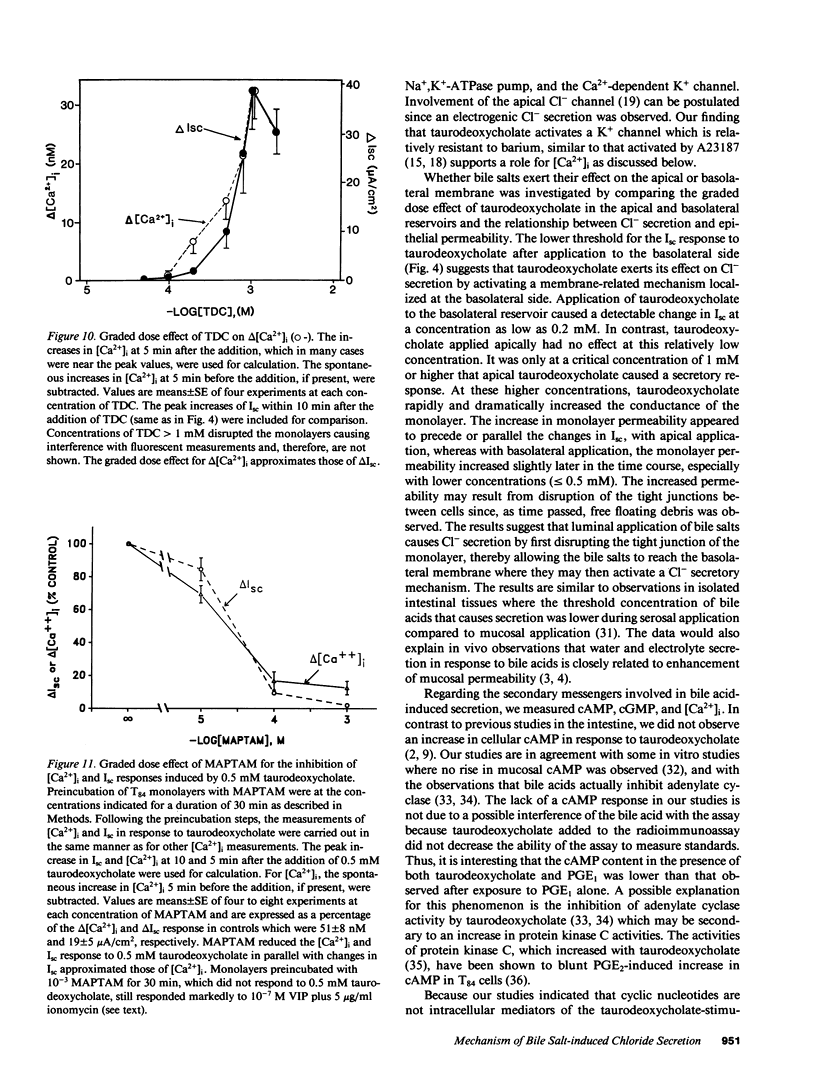
When applied to the basolateral (serosal) side of the T84 colonic epithelial monolayer, taurodeoxycholate caused net Cl- secretion in a dose-dependent manner with a threshold effect observed at 0.2 mM. In contrast, when applied to the apical (luminal) surface, concentrations of taurodeoxycholate below 1 mM had little or no effect. Only when the concentration of taurodeoxycholate present on the apical side was greater than or equal to 1 mM did apical addition results in an electrolyte transport effect. This apical effect on electrolyte transport was associated with an abrupt increase in the permeability of the monolayer. Cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in the T84 monolayers were not increased by the bile salt, but in the presence of extracellular Ca2+, free cytosolic Ca2+ increased with a graded dose effect and time course that corresponded approximately to the changes in short circuit current (Isc). The results suggest that luminal bile salts at a relatively high concentration (greater than or equal to 1 mM) increase tight junction permeability. Once tight junction permeability increases, luminal bile salts could reach the basolateral membrane of the epithelial cells where they act to increase free cytosolic Ca2+ from extracellular sources. The resulting increases in free cytosolic Ca2+, rather than in cyclic nucleotides, appear to be involved in transcellular Cl- secretion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binder H. J., Filburn C., Volpe B. T. Bile salt alteration of colonic electrolyte transport: role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Gastroenterology. 1975 Mar;68(3):503–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., McRoberts J. A., Mandel K. G., Dharmsathaphorn K. Synergistic action of cyclic adenosine monophosphate- and calcium-mediated chloride secretion in a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1837–1842. doi: 10.1172/JCI112176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick V. S., Gaginella T. S., Carlson G. L., Debongnie J. C., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Effect of molecular structure on bile acid-induced alterations in absorptive function, permeability, and morphology in the perfused rabbit colon. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Nov;94(5):661–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Cohn J., Beuerlein G. Multiple calcium-mediated effector mechanisms regulate chloride secretory responses in T84-cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):C1224–C1230. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.6.C1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Mandel K. G., Masui H., McRoberts J. A. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-induced chloride secretion by a colonic epithelial cell line. Direct participation of a basolaterally localized Na+,K+,Cl- cotransport system. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):462–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI111721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., McRoberts J. A., Mandel K. G., Tisdale L. D., Masui H. A human colonic tumor cell line that maintains vectorial electrolyte transport. Am J Physiol. 1984 Feb;246(2 Pt 1):G204–G208. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.2.G204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Pandol S. J. Mechanism of chloride secretion induced by carbachol in a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):348–354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz M., Cusolito S., Battisti L., Sharp G. W. Dantrolene and basal ileal sodium and chloride transport: involvement of calcium stores. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):G780–G785. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.6.G780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farack U. M., Loeschke K. Inhibition by loperamide of deoxycholic acid induced intestinal secretion. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;325(3):286–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00495957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forth W., Rummel W., Glasner H. Zur resorptionshemmenden Wirkung von Gallensäuren. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol Exp Pathol. 1966;254(4):364–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A. Active chloride secretion by rabbit colon: calcium-dependent stimulation by ionophore A23187. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jun 30;35(2):175–187. doi: 10.1007/BF01869948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T. S., Phillips S. F., Dozois R. R., Go V. L. Stimulation of adenylate cyclase in homogenates of isolated intestinal epithelial cells from hamsters. Effects of gastrointestinal hormones, prostaglandins, and deoxycholic and ricinoleic acids. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jan;74(1):11–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goerg K. J., Nell G., Rummel W. Effect of deoxycholate on the perfused rat colon. Concentration dependence of the effect on net fluid and electrolyte transfer and the correlation with paracellular permeability. Digestion. 1983;26(3):105–113. doi: 10.1159/000198876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Poley J. R. Role of bile acid malabsorption in pathogenesis of diarrhea and steatorrhea in patients with ileal resection. I. Response to cholestyramine or replacement of dietary long chain triglyceride by medium chain triglyceride. Gastroenterology. 1972 May;62(5):918–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huott P. A., Liu W., McRoberts J. A., Giannella R. A., Dharmsathaphorn K. Mechanism of action of Escherichia coli heat stable enterotoxin in a human colonic cell line. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):514–523. doi: 10.1172/JCI113626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlström L., Cassuto J., Jodal M., Lundgren O. The importance of the enteric nervous system for the bile-salt-induced secretion in the small intestine of the rat. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Jan;18(1):117–123. doi: 10.3109/00365528309181570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krag E., Phillips S. F. Effect of free and conjugated bile acids on net water, electrolyte, and glucose movement in the perfused human ileum. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jun;83(6):947–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Dharmsathaphorn K. Occluding junction structure-function relationships in a cultured epithelial monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2124–2133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J., Dharmsathaphorn K., Carlson S. Structural analysis of a human intestinal epithelial cell line. Gastroenterology. 1987 May;92(5 Pt 1):1133–1145. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(87)91069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maenz D. D., Forsyth G. W. Ricinoleate and deoxycholate are calcium ionophores in jejunal brush border vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1982;70(2):125–133. doi: 10.1007/BF01870222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel K. G., Dharmsathaphorn K., McRoberts J. A. Characterization of a cyclic AMP-activated Cl-transport pathway in the apical membrane of a human colonic epithelial cell line. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):704–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel K. G., McRoberts J. A., Beuerlein G., Foster E. S., Dharmsathaphorn K. Ba2+ inhibition of VIP- and A23187-stimulated Cl- secretion by T84 cell monolayers. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):C486–C494. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.3.C486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRoberts J. A., Beuerlein G., Dharmsathaphorn K. Cyclic AMP and Ca2+-activated K+ transport in a human colonic epithelial cell line. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14163–14172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekjian H. S., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Colonic secretion of water and electrolytes induced by bile acids: perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1569–1577. doi: 10.1172/JCI106644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Tsien R. Y., Steinhardt R. A. Changes of free calcium levels with stages of the cell division cycle. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):147–149. doi: 10.1038/315147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahban S., Bonorris G. G., Marks J. W., Chung A., Schoenfield L. J. The effect of dihydroxy bile acids on intestinal secretion, cyclic nucleotides, and Na+-K+-ATPase. Am J Med Sci. 1980 May-Jun;279(3):141–146. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198005000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwiter E. J., Hepner G. W., Rose R. C. Effect of bile acids on electrical properties of rat colon: evaluation of an in-vitro model for secretion. Gut. 1975 Jun;16(6):477–481. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.6.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B., Cyzgan P., Stiehl A., Kather H. Human colonic adenylate cyclase: effects of bile acids. Eur J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;8(5):321–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1978.tb00849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J., Poenie M. Measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ in individual small cells using fluorescence microscopy with dual excitation wavelengths. Cell Calcium. 1985 Apr;6(1-2):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(85)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warhurst G., Higgs N. B., Lees M., Tonge A., Turnberg L. A. Activation of protein kinase C attenuates prostaglandin E2 responses in a colonic cell line. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 1):G27–G32. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.255.1.G27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I., Barrett K. E., Huott P. A., Beuerlein G., Kagnoff M. F., Dharmsathaphorn K. Immune-related intestinal Cl- secretion. I. Effect of histamine on the T84 cell line. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 1):C53–C62. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.1.C53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weymer A., Huott P., Liu W., McRoberts J. A., Dharmsathaphorn K. Chloride secretory mechanism induced by prostaglandin E1 in a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1828–1836. doi: 10.1172/JCI112175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate D. L., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Effect of glycine-conjugated bile acids with and without lecithin on water and glucose absorption in perfused human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1230–1236. doi: 10.1172/JCI107290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


