Abstract
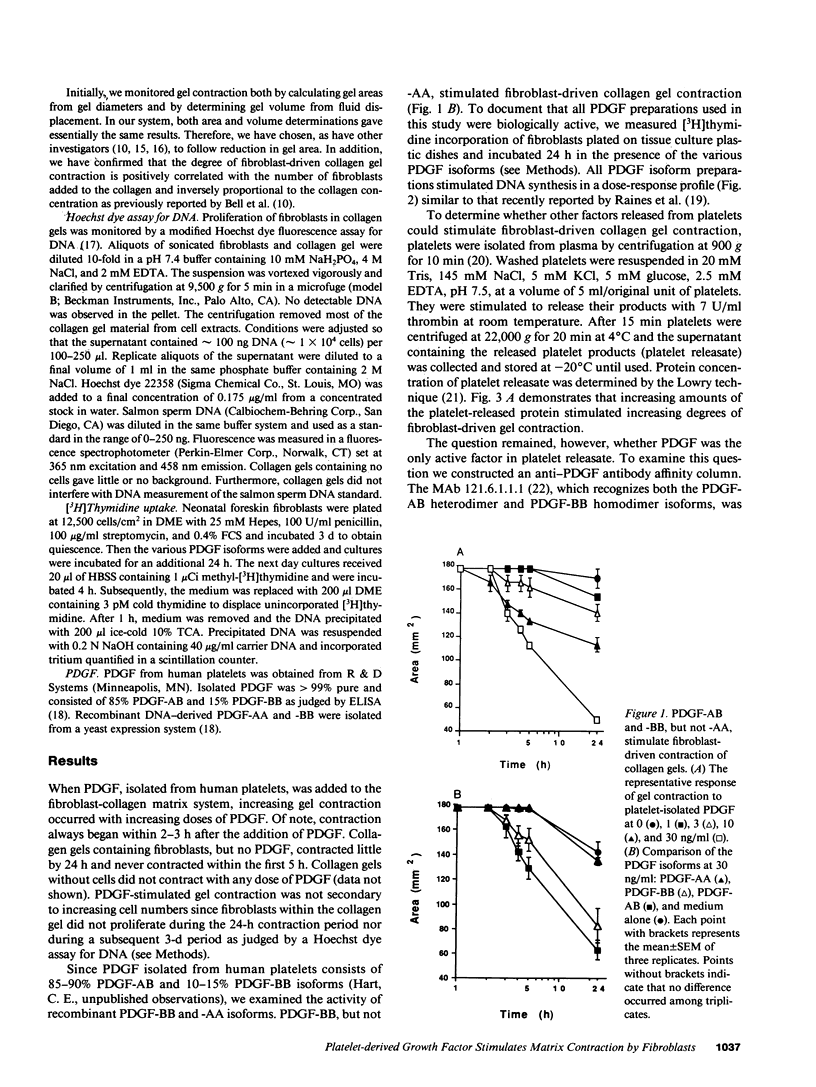
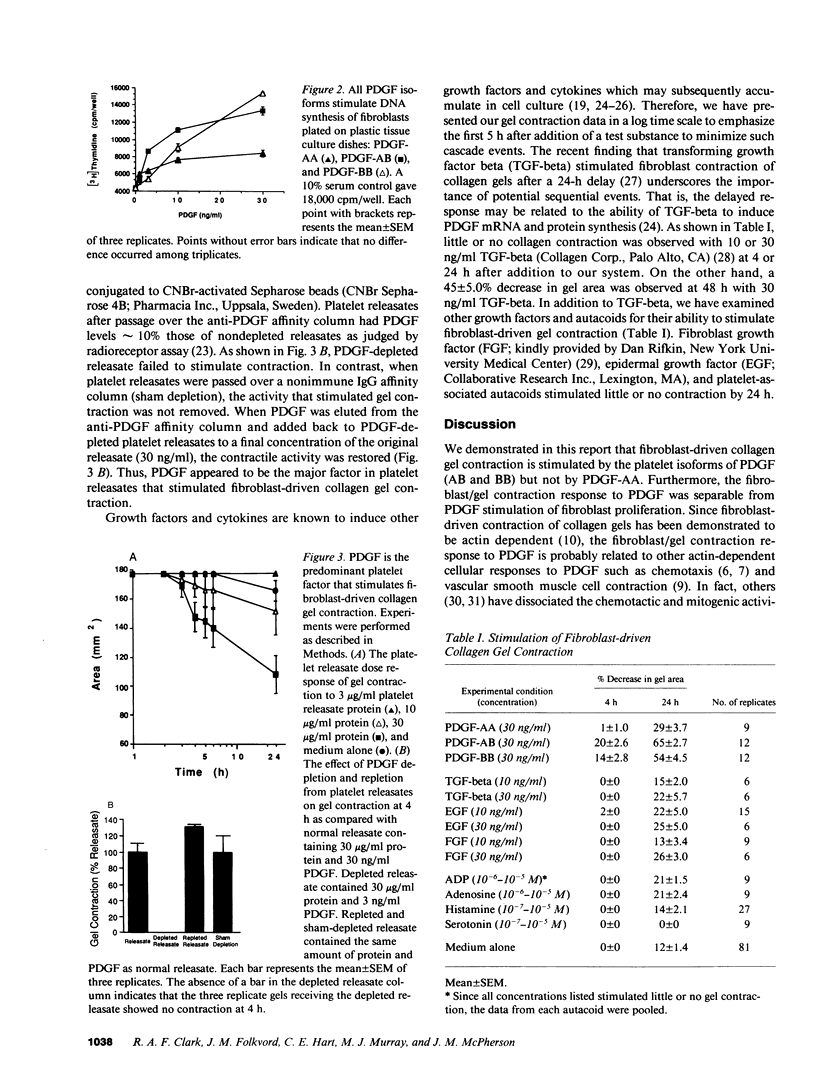
Fibroplasia and angiogenesis are essential components of tissue repair when substantial tissue has been lost at a site of injury. Platelets and monocyte/macrophages accumulate at these sites and release a variety of growth factors that are thought to initiate and sustain the repair. Often the involved tissue contracts, a process that can markedly reduce the amount of fibroplasia and angiogenesis necessary for the reestablishment of organ integrity. Such tissue contraction occurs over hours or days, a much slower time course than the rapid, reversible contraction of muscle tissue. Fibroblasts, which are rich in f-actin bundles, appear to be responsible for wound contraction. However, the signals that stimulate contraction are not known. Using cultured fibroblasts, which are also rich in f-actin bundles, we demonstrate the platelet and monocyte isoforms of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF; AB and BB) but not PDGF-AA, can stimulate fibroblasts to contract collagen matrix in a time course similar to that of wound contraction. In addition, PDGF appears to be the predominant fibroblast/collagen gel contraction activity released from platelets. Vasoactive agonists known to stimulate smooth and striated muscle contraction do not stimulate fibroblast-driven collagen gel contraction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell E., Ehrlich H. P., Buttle D. J., Nakatsuji T. Living tissue formed in vitro and accepted as skin-equivalent tissue of full thickness. Science. 1981 Mar 6;211(4486):1052–1054. doi: 10.1126/science.7008197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E., Ivarsson B., Merrill C. Production of a tissue-like structure by contraction of collagen lattices by human fibroblasts of different proliferative potential in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Alexander R. W., Brock T. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Webb R. C. Vasoconstriction: a new activity for platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.3485309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. II. Specific binding to cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5161–5171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A. Z., Pentland A. P., Bauer E. A., Goldberg G. I. Behavior of epidermolysis bullosa fibroblasts in a hydrated collagen lattice. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Jun;88(6):741–746. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12470412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Chaponnier C., Hüttner I. Cytoplasmic filaments and gap junctions in epithelial cells and myofibroblasts during wound healing. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):561–568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Hirschel B. J., Ryan G. B., Statkov P. R., Majno G. Granulation tissue as a contractile organ. A study of structure and function. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):719–734. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart C. E., Forstrom J. W., Kelly J. D., Seifert R. A., Smith R. A., Ross R., Murray M. J., Bowen-Pope D. F. Two classes of PDGF receptor recognize different isoforms of PDGF. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1529–1531. doi: 10.1126/science.2836952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Bäckström G., Ostman A., Hammacher A., Rönnstrand L., Rubin K., Nistér M., Westermark B. Binding of different dimeric forms of PDGF to human fibroblasts: evidence for two separate receptor types. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1387–1393. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. Relationships between fibronectin (LETS protein) and actin. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. D., Raines E. W., Ross R., Murray M. J. The B chain of PDGF alone is sufficient for mitogenesis. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3399–3405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04096.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Proper J. A., Goustin A. S., Shipley G. D., DiCorleto P. E., Moses H. L. Induction of c-sis mRNA and activity similar to platelet-derived growth factor by transforming growth factor beta: a proposed model for indirect mitogenesis involving autocrine activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson J. M., Wallace D. G., Sawamura S. J., Conti A., Condell R. A., Wade S., Piez K. A. Collagen fibrillogenesis in vitro: a characterization of fibril quality as a function of assembly conditions. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Mar;5(2):119–135. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson J., Sage H., Bornstein P. Isolation and characterization of a glycoprotein secreted by aortic endothelial cells in culture. Apparent identity with platelet thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11330–11336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Orci L. Transforming growth factor beta stimulates collagen-matrix contraction by fibroblasts: implications for wound healing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4894–4897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nistér M., Hammacher A., Mellström K., Siegbahn A., Rönnstrand L., Westermark B., Heldin C. H. A glioma-derived PDGF A chain homodimer has different functional activities from a PDGF AB heterodimer purified from human platelets. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):791–799. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90421-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines E. W., Dower S. K., Ross R. Interleukin-1 mitogenic activity for fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells is due to PDGF-AA. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):393–396. doi: 10.1126/science.2783498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Raines E. W., Bowen-Pope D. F. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Rifkin D. B. Autocrine activities of basic fibroblast growth factor: regulation of endothelial cell movement, plasminogen activator synthesis, and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1199–1205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Huang J. S., Walz D. A., Deuel T. F. Chemotactic activity of platelet alpha granule proteins for fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;96(2):382–385. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Huang J. S., Griffin G. L., Deuel T. F. Dissociation of the chemotactic and mitogenic activities of platelet-derived growth factor by human neutrophil elastase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):351–356. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppä H., Grotendorst G., Seppä S., Schiffmann E., Martin G. R. Platelet-derived growth factor in chemotactic for fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):584–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyedin S. M., Thompson A. Y., Bentz H., Rosen D. M., McPherson J. M., Conti A., Siegel N. R., Galluppi G. R., Piez K. A. Cartilage-inducing factor-A. Apparent identity to transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5693–5695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I. I., Kawka D. W., Kazazis D. M., Clark R. A. In vivo co-distribution of fibronectin and actin fibers in granulation tissue: immunofluorescence and electron microscope studies of the fibronexus at the myofibroblast surface. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):2091–2106. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I. I. The fibronexus: a transmembrane association of fibronectin-containing fibers and bundles of 5 nm microfilaments in hamster and human fibroblasts. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):675–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., de Crombrugghe B. Some recent advances in the chemistry and biology of transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg B. M., Smith K., Colozzo M., Pollack R. Establishment and transformation diminish the ability of fibroblasts to contract a native collagen gel. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):304–308. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Antoniades H. N., Goetzl E. J. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates mouse 3T3 cell mitogenesis and leukocyte chemotaxis through different structural determinants. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1759–1763. doi: 10.1172/JCI111135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



