Abstract
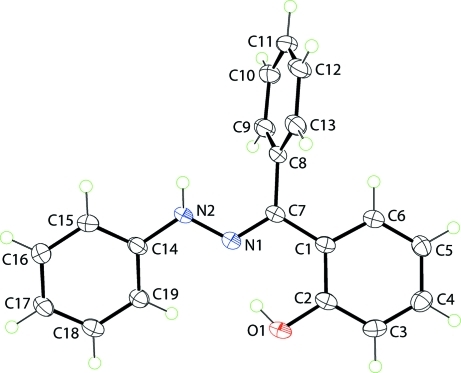
In the title hydrazone derivative, C19H16N2O, a twist is found between the hydroxyphenyl and N-bound phenyl rings [dihedral angle = 24.37 (7)°]. The C-bound phenyl ring is almost perpendicular to each of these planes [dihedral angles = 75.30 (7) and 86.00 (7)°, respectively]. The conformation about the imine bond [1.2935 (17) Å] is E. The hydroxy group forms an intramolecular hydrogen bond with the imine N atom. Zigzag chains along [001] mediated by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds feature in the crystal packing.
Related literature
For background on the influence of substituents upon the supramolecular structures of hydrazones, see: Glidewell et al. (2004 ▶); Ferguson et al. (2005 ▶); Wardell et al. (2007 ▶); Baddeley, de Souza França et al. (2009 ▶); Baddeley, Howie et al. (2009 ▶); de Souza et al. (2010 ▶); Howie, da Silva Lima et al. (2010 ▶); Howie, de Souza et al. (2010 ▶); Nogueira et al. (2011 ▶); Howie et al. (2011 ▶).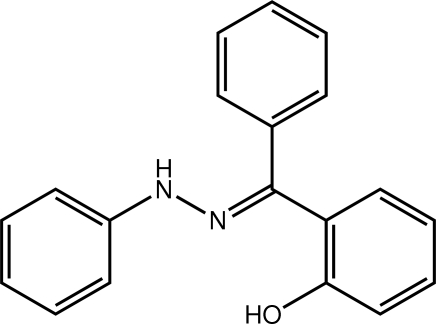
Experimental
Crystal data
C19H16N2O
M r = 288.34
Monoclinic,
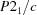
a = 9.6796 (3) Å
b = 15.3312 (5) Å
c = 10.3593 (2) Å
β = 108.149 (2)°
V = 1460.84 (7) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 120 K
0.49 × 0.38 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Bruker–Nonius Roper CCD camera on κ-goniostat diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.857, T max = 0.985
16532 measured reflections
3337 independent reflections
2624 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.044
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.051
wR(F 2) = 0.141
S = 1.06
3337 reflections
205 parameters
2 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3
Data collection: COLLECT (Hooft, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: DENZO (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶) and COLLECT; data reduction: DENZO and COLLECT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812005387/bt5814sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812005387/bt5814Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812005387/bt5814Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1O⋯N1 | 0.85 (1) | 1.76 (1) | 2.5678 (14) | 157 (2) |
| N2—H2N⋯O1i | 0.89 (2) | 2.43 (2) | 3.2517 (16) | 155 (1) |
Symmetry code: (i) 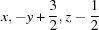 .
.
Acknowledgments
The use of the EPSRC X-ray crystallographic service at the University of Southampton, England, and the valuable assistance of the staff there is gratefully acknowledged. JLW acknowledges support from CAPES (Brazil). We also thank the Ministry of Higher Education (Malaysia) for funding structural studies through the High-Impact Research scheme (UM.C/HIR/MOHE/SC/12).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
For some time, we have been interested in the influence of substituents upon the supramolecular structures of hydrazones, especially of those having potential biological activities. These include substituted phenylhydrazines with substituted benzaldehydes (Glidewell et al., 2004; Ferguson et al., 2005) and 2-hydroxyacetophenone (Baddeley, de Souza França et al., 2009). Hydrazones derived from substituted benzaldehydes and (pyrazinecarbonyl)hydrazine (Baddeley, Howie et al., 2009; Howie, da Silva Lima et al., 2010), 2-hydrazinyl-benzothiazole (Nogueira et al., 2011), 7-chloroquinoline-4-hydrazide (Howie, de Souza et al., 2010; de Souza et al., 2010) and 2-hydrazinylacyl-N-isonicotine (Wardell et al., 2007) have also been investigated along with L-serinyl derivatives, (S)-2-hydroxy-1-[N-(benzylidene)-hydrazinylcarbonyl]ethylcarbamate esters (Howie et al., 2011). In continuation of these studies, herein the crystal and molecular structure of (E)-2-hydroxybenzophenone phenylhydrazone (I) is described.
In (I), Fig. 1, the hydroxy-benzene and N-bound phenyl rings are twisted, forming a dihedral angle of 24.37 (7)°. These planes form dihedral angles of 75.30 (7) and 86.00 (7)°, respectively, with the C-bound phenyl ring indicating an almost perpendicular relationship. The hydroxy group forms an intramolecular hydrogen bond with the imine-N1 atom, Table 1. The configuration about the imine bond N1═C7 [1.2935 (17) Å] is E.
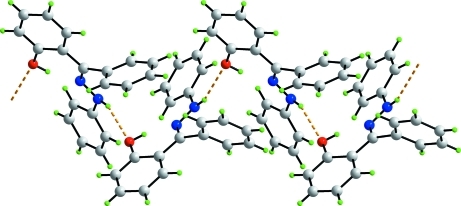
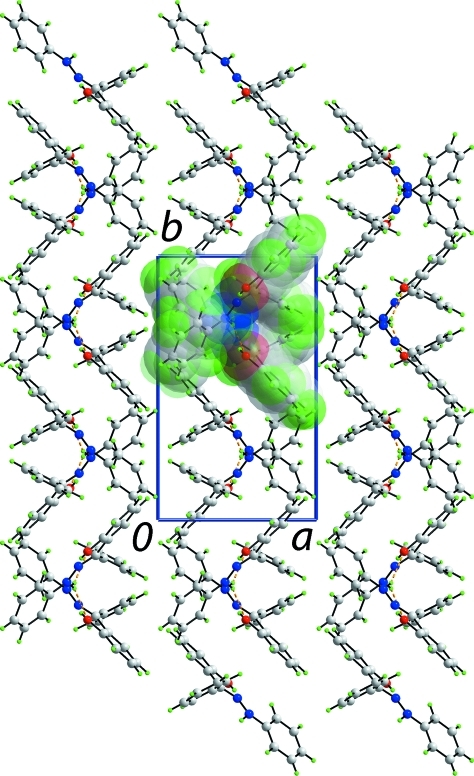
The most prominent feature of the crystal packing is the formation of zigzag chains along [001] generated by glide symmetry and mediated by N—H···O hydrogen bonds, Fig. 2 and Table 1. Chains pack in the crystal structure with no specific intermolecular interactions between them, Fig. 3.
Experimental
A solution of phenylhydrazine and 2-hydroxybenzophenone (1 mmol each) in ethanol (20 ml) was refluxed for 1 h, rotary evaporated and the residue recrystallized from ethanol. IR (KBr, cm-1): ν 3302, 1600, 1557. Analysis found: C 78.78, H 5.81, N 9.47%; calculated for C19H16N2O: C 79.14, H 5.59, N 9.71%.
Refinement
The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.95 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The O- and N-bound H atoms were located from a difference map and refined with the distance restraints O—H = 0.84±0.01 and N—H = 0.88±0.01 Å, and with Uiso(H) = zUeq(carrier atom); z = 1.5 for O and z = 1.2 for N.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing the atom-labelling scheme and displacement ellipsoids at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A view of the supramolecular zigzag chain in (I) sustained by N—H···O (orange dashed lines) hydrogen bonds.
Fig. 3.
A view in projection down the c axis of the packing of supramolecular chains in (I). The N—H···O hydrogen bonds are shown as orange dashed lines. One chain is highlighted in space-filling mode.
Crystal data
| C19H16N2O | F(000) = 608 |
| Mr = 288.34 | Dx = 1.311 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 9588 reflections |
| a = 9.6796 (3) Å | θ = 2.9–27.5° |
| b = 15.3312 (5) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| c = 10.3593 (2) Å | T = 120 K |
| β = 108.149 (2)° | Slab, yellow |
| V = 1460.84 (7) Å3 | 0.49 × 0.38 × 0.18 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker–Nonius Roper CCD camera on κ-goniostat diffractometer | 3337 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Bruker–Nonius FR591 rotating anode | 2624 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.044 |
| Detector resolution: 9.091 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.4° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −12→12 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2007) | k = −19→19 |
| Tmin = 0.857, Tmax = 0.985 | l = −13→13 |
| 16532 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.051 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.141 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0846P)2 + 0.1552P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3337 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 205 parameters | Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.55543 (11) | 0.62061 (7) | 0.67432 (9) | 0.0305 (3) | |
| H1O | 0.5167 (19) | 0.6457 (11) | 0.5981 (12) | 0.046* | |
| N1 | 0.49781 (12) | 0.67646 (7) | 0.42953 (11) | 0.0245 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.42408 (13) | 0.73657 (8) | 0.33672 (11) | 0.0279 (3) | |
| H2N | 0.4722 (16) | 0.7602 (10) | 0.2854 (14) | 0.033* | |
| C1 | 0.68370 (14) | 0.57283 (9) | 0.51935 (12) | 0.0219 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.65661 (15) | 0.56890 (9) | 0.64615 (13) | 0.0245 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.73482 (15) | 0.51112 (9) | 0.74555 (13) | 0.0275 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.7182 | 0.5098 | 0.8312 | 0.033* | |
| C4 | 0.83577 (16) | 0.45602 (9) | 0.72145 (14) | 0.0294 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.8872 | 0.4163 | 0.7900 | 0.035* | |
| C5 | 0.86344 (16) | 0.45784 (9) | 0.59745 (14) | 0.0268 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.9333 | 0.4196 | 0.5808 | 0.032* | |
| C6 | 0.78782 (15) | 0.51608 (9) | 0.49900 (13) | 0.0245 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.8073 | 0.5176 | 0.4146 | 0.029* | |
| C7 | 0.60591 (14) | 0.63406 (8) | 0.41159 (12) | 0.0225 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.65557 (15) | 0.64475 (9) | 0.28938 (13) | 0.0233 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.57166 (16) | 0.61134 (10) | 0.16460 (13) | 0.0295 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.4805 | 0.5848 | 0.1559 | 0.035* | |
| C10 | 0.62186 (17) | 0.61703 (10) | 0.05272 (14) | 0.0332 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.5659 | 0.5929 | −0.0319 | 0.040* | |
| C11 | 0.75214 (18) | 0.65735 (10) | 0.06393 (14) | 0.0342 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.7858 | 0.6608 | −0.0128 | 0.041* | |
| C12 | 0.83445 (17) | 0.69288 (10) | 0.18688 (15) | 0.0331 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.9230 | 0.7221 | 0.1939 | 0.040* | |
| C13 | 0.78680 (16) | 0.68548 (9) | 0.29963 (14) | 0.0286 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.8444 | 0.7084 | 0.3845 | 0.034* | |
| C14 | 0.31426 (15) | 0.78382 (9) | 0.36540 (12) | 0.0246 (3) | |
| C15 | 0.26578 (17) | 0.86137 (10) | 0.29652 (14) | 0.0335 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.3084 | 0.8820 | 0.2312 | 0.040* | |
| C16 | 0.15586 (17) | 0.90856 (11) | 0.32279 (15) | 0.0362 (4) | |
| H16 | 0.1232 | 0.9613 | 0.2749 | 0.043* | |
| C17 | 0.09268 (16) | 0.87973 (10) | 0.41823 (14) | 0.0319 (4) | |
| H17 | 0.0173 | 0.9124 | 0.4362 | 0.038* | |
| C18 | 0.14125 (15) | 0.80271 (10) | 0.48685 (14) | 0.0282 (3) | |
| H18 | 0.0990 | 0.7827 | 0.5528 | 0.034* | |
| C19 | 0.25048 (15) | 0.75439 (9) | 0.46098 (13) | 0.0253 (3) | |
| H19 | 0.2820 | 0.7013 | 0.5082 | 0.030* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0325 (6) | 0.0394 (6) | 0.0258 (5) | 0.0046 (4) | 0.0178 (4) | −0.0006 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0247 (6) | 0.0277 (6) | 0.0239 (5) | 0.0032 (5) | 0.0118 (5) | 0.0002 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0281 (7) | 0.0352 (7) | 0.0262 (6) | 0.0094 (5) | 0.0171 (5) | 0.0058 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0214 (7) | 0.0247 (7) | 0.0218 (6) | −0.0030 (5) | 0.0098 (5) | −0.0021 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0230 (7) | 0.0287 (7) | 0.0250 (6) | −0.0044 (5) | 0.0122 (5) | −0.0049 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0298 (8) | 0.0326 (8) | 0.0222 (6) | −0.0068 (6) | 0.0112 (5) | −0.0002 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0298 (8) | 0.0279 (7) | 0.0299 (7) | −0.0031 (6) | 0.0086 (6) | 0.0047 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0258 (7) | 0.0236 (7) | 0.0329 (7) | 0.0014 (5) | 0.0117 (6) | −0.0011 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0265 (7) | 0.0251 (7) | 0.0246 (6) | −0.0029 (5) | 0.0120 (5) | −0.0025 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0225 (7) | 0.0250 (7) | 0.0229 (6) | −0.0002 (5) | 0.0115 (5) | −0.0020 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0250 (7) | 0.0248 (7) | 0.0238 (6) | 0.0054 (5) | 0.0130 (5) | 0.0016 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0269 (8) | 0.0367 (8) | 0.0272 (7) | 0.0016 (6) | 0.0120 (6) | −0.0014 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0355 (9) | 0.0428 (9) | 0.0235 (7) | 0.0085 (7) | 0.0124 (6) | 0.0001 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0452 (9) | 0.0344 (8) | 0.0323 (7) | 0.0119 (7) | 0.0256 (7) | 0.0080 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0353 (9) | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0442 (8) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0274 (7) | 0.0032 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0286 (8) | 0.0283 (7) | 0.0330 (7) | 0.0018 (6) | 0.0156 (6) | −0.0020 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0225 (7) | 0.0314 (7) | 0.0218 (6) | 0.0029 (6) | 0.0094 (5) | −0.0035 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0356 (9) | 0.0429 (9) | 0.0278 (7) | 0.0102 (7) | 0.0181 (6) | 0.0083 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0359 (9) | 0.0428 (9) | 0.0347 (8) | 0.0160 (7) | 0.0180 (7) | 0.0112 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0266 (8) | 0.0409 (9) | 0.0320 (7) | 0.0093 (6) | 0.0147 (6) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C18 | 0.0254 (8) | 0.0346 (8) | 0.0291 (7) | −0.0012 (6) | 0.0151 (6) | −0.0023 (6) |
| C19 | 0.0248 (7) | 0.0263 (7) | 0.0271 (7) | −0.0004 (5) | 0.0114 (6) | −0.0007 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C2 | 1.3605 (17) | C9—C10 | 1.3920 (19) |
| O1—H1O | 0.853 (9) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C7 | 1.2935 (17) | C10—C11 | 1.376 (2) |
| N1—N2 | 1.3621 (16) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C14 | 1.3928 (17) | C11—C12 | 1.386 (2) |
| N2—H2N | 0.886 (9) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.3963 (19) | C12—C13 | 1.3875 (19) |
| C1—C2 | 1.4186 (17) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C7 | 1.4734 (18) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.390 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.391 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.372 (2) | C14—C19 | 1.3950 (19) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C15—C16 | 1.382 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.3917 (19) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C16—C17 | 1.387 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.3812 (19) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C17—C18 | 1.383 (2) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C7—C8 | 1.4966 (17) | C18—C19 | 1.3838 (19) |
| C8—C13 | 1.390 (2) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C8—C9 | 1.3924 (19) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C2—O1—H1O | 101.7 (13) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.1 |
| C7—N1—N2 | 120.53 (11) | C11—C10—C9 | 120.41 (13) |
| N1—N2—C14 | 117.92 (10) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.8 |
| N1—N2—H2N | 116.2 (11) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.8 |
| C14—N2—H2N | 119.7 (11) | C10—C11—C12 | 120.21 (13) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 117.62 (12) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| C6—C1—C7 | 120.35 (11) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| C2—C1—C7 | 122.03 (12) | C13—C12—C11 | 119.65 (14) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 118.34 (12) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.2 |
| O1—C2—C1 | 121.80 (12) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.2 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.86 (13) | C12—C13—C8 | 120.53 (13) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.79 (12) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.7 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C8—C13—H13 | 119.7 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.6 | C15—C14—N2 | 119.55 (12) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.54 (13) | C15—C14—C19 | 119.18 (12) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 | N2—C14—C19 | 121.27 (12) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C16—C15—C14 | 120.26 (13) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 118.98 (13) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.9 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.5 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.9 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.5 | C15—C16—C17 | 120.74 (14) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 122.19 (12) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 118.9 | C17—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 118.9 | C18—C17—C16 | 118.93 (13) |
| N1—C7—C1 | 117.18 (11) | C18—C17—H17 | 120.5 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 123.63 (12) | C16—C17—H17 | 120.5 |
| C1—C7—C8 | 119.19 (11) | C19—C18—C17 | 121.03 (13) |
| C13—C8—C9 | 119.42 (12) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.5 |
| C13—C8—C7 | 120.76 (12) | C17—C18—H18 | 119.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 119.79 (12) | C18—C19—C14 | 119.87 (13) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 119.73 (14) | C18—C19—H19 | 120.1 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.1 | C14—C19—H19 | 120.1 |
| C7—N1—N2—C14 | −176.29 (12) | N1—C7—C8—C9 | −72.19 (18) |
| C6—C1—C2—O1 | −178.88 (12) | C1—C7—C8—C9 | 108.42 (15) |
| C7—C1—C2—O1 | 1.1 (2) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | 1.7 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.25 (19) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −176.44 (13) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −178.79 (12) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −1.6 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | 178.47 (12) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.2 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.7 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 1.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.0 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −1.7 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.1 (2) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | −0.1 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.5 (2) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | 178.04 (12) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.2 (2) | N1—N2—C14—C15 | 161.37 (13) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | 179.83 (12) | N1—N2—C14—C19 | −19.38 (19) |
| N2—N1—C7—C1 | 177.56 (11) | N2—C14—C15—C16 | 179.33 (14) |
| N2—N1—C7—C8 | −1.8 (2) | C19—C14—C15—C16 | 0.1 (2) |
| C6—C1—C7—N1 | 171.04 (12) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.3 (2) |
| C2—C1—C7—N1 | −8.92 (19) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −0.1 (2) |
| C6—C1—C7—C8 | −9.52 (19) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | −0.4 (2) |
| C2—C1—C7—C8 | 170.52 (12) | C17—C18—C19—C14 | 0.7 (2) |
| N1—C7—C8—C13 | 109.69 (16) | C15—C14—C19—C18 | −0.5 (2) |
| C1—C7—C8—C13 | −69.71 (17) | N2—C14—C19—C18 | −179.78 (12) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1O···N1 | 0.85 (1) | 1.76 (1) | 2.5678 (14) | 157 (2) |
| N2—H2N···O1i | 0.89 (2) | 2.43 (2) | 3.2517 (16) | 155 (1) |
Symmetry code: (i) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5814).
References
- Baddeley, T. C., de Souza França, L., Howie, R. A., de Lima, G. M., Skakle, J. M. S., de Souza, J. D., Wardell, J. L. & Wardell, S. M. S. V. (2009). Z. Kristallogr. 224, 213–224.
- Baddeley, T. C., Howie, R. A., da Silva Lima, C. H., Kaiser, C. R., de Souza, M. V. N., Wardell, J. L. & Wardell, S. M. S. V. (2009). Z. Kristallogr. 224, 506–514.
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Ferguson, G., Glidewell, C., Low, J. N., Skakle, J. M. S. & Wardell, J. L. (2005). Acta Cryst. C61, o613–o616. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Glidewell, C., Low, J. N., Skakle, J. M. S. & Wardell, J. L. (2004). Acta Cryst. C60, o19–o23. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hooft, R. W. W. (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Howie, R. A., da Silva Lima, C. H., Kaiser, C. R., de Souza, M. V. N., Wardell, J. L. & Wardell, S. M. S. V. (2010). Z. Kristallogr. 225, 349–358.
- Howie, R. A., de Souza, M. V. N., de Lima Ferreira, M., Kaiser, C. R., Wardell, J. L. & Wardell, S. M. S. V. (2010). Z. Kristallogr. 225, 440–447.
- Howie, R. A., de Souza, M. V. N., Pinheiro, A. C., Kaiser, C. R., Wardell, J. L. & Wardell, S. M. S. V. (2011). Z. Kristallogr. 226, 483–491.
- Nogueira, A., Vasconcelos, T. R. A., Wardell, J. L., Solange, M. S. V. & Wardell, S. M. S. V. (2011). Z. Kristallogr. 226, 846–861.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2007). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Souza, M. V. N. de, Howie, R. A., Tiekink, E. R. T., Wardell, J. L., Wardell, S. M. S. V. & Kaiser, C. R. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o698–o699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wardell, S. M. S. V., de Souza, M. V. N., Wardell, J. L., Low, J. N. & Glidewell, C. (2007). Acta Cryst. B63, 879–895. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812005387/bt5814sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812005387/bt5814Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812005387/bt5814Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report