Abstract
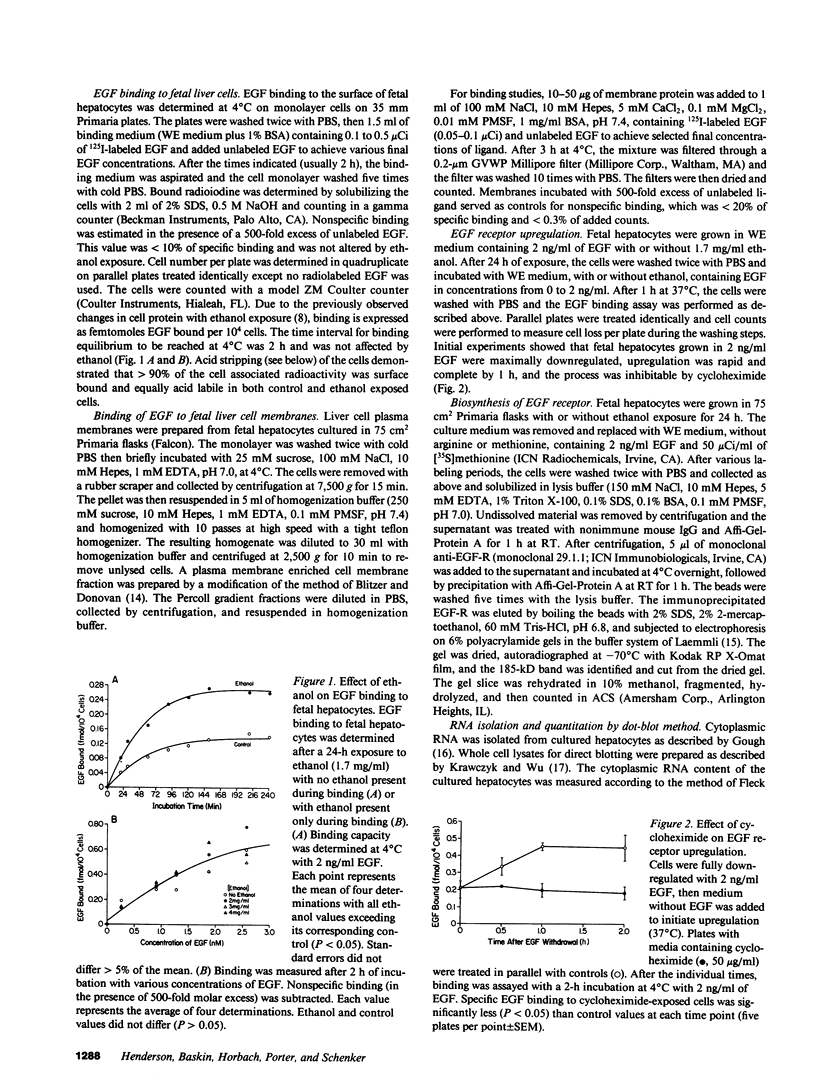
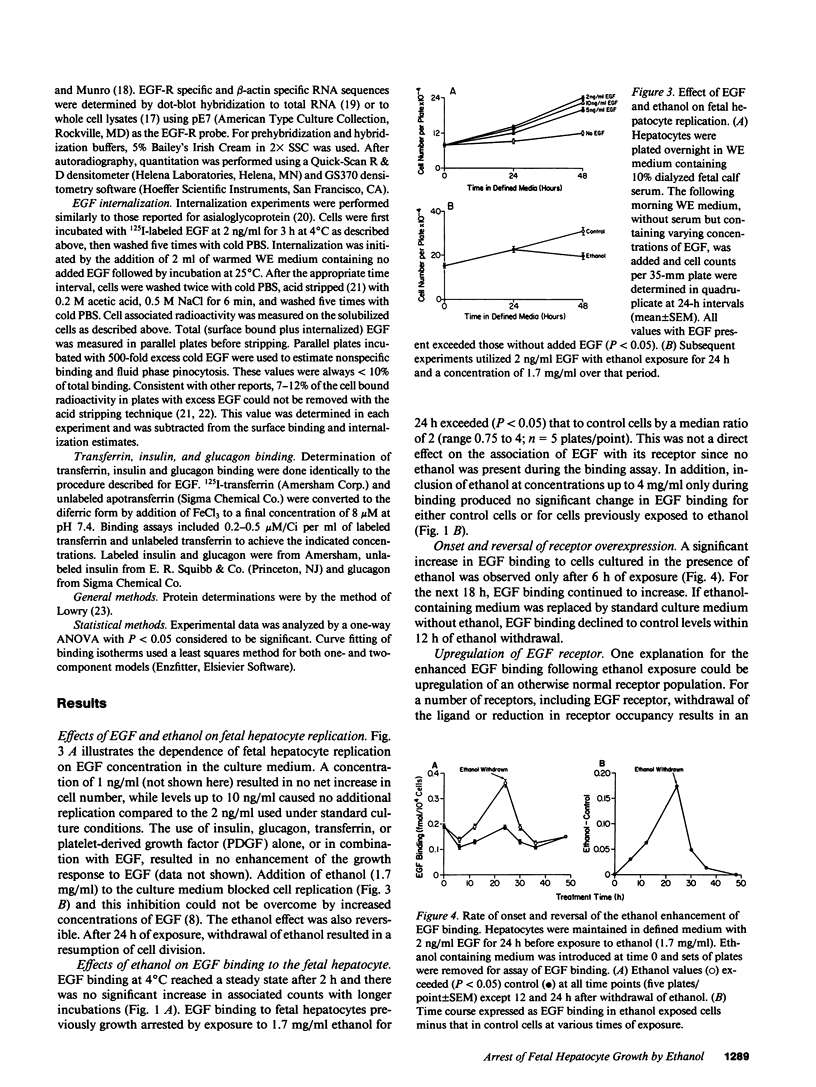
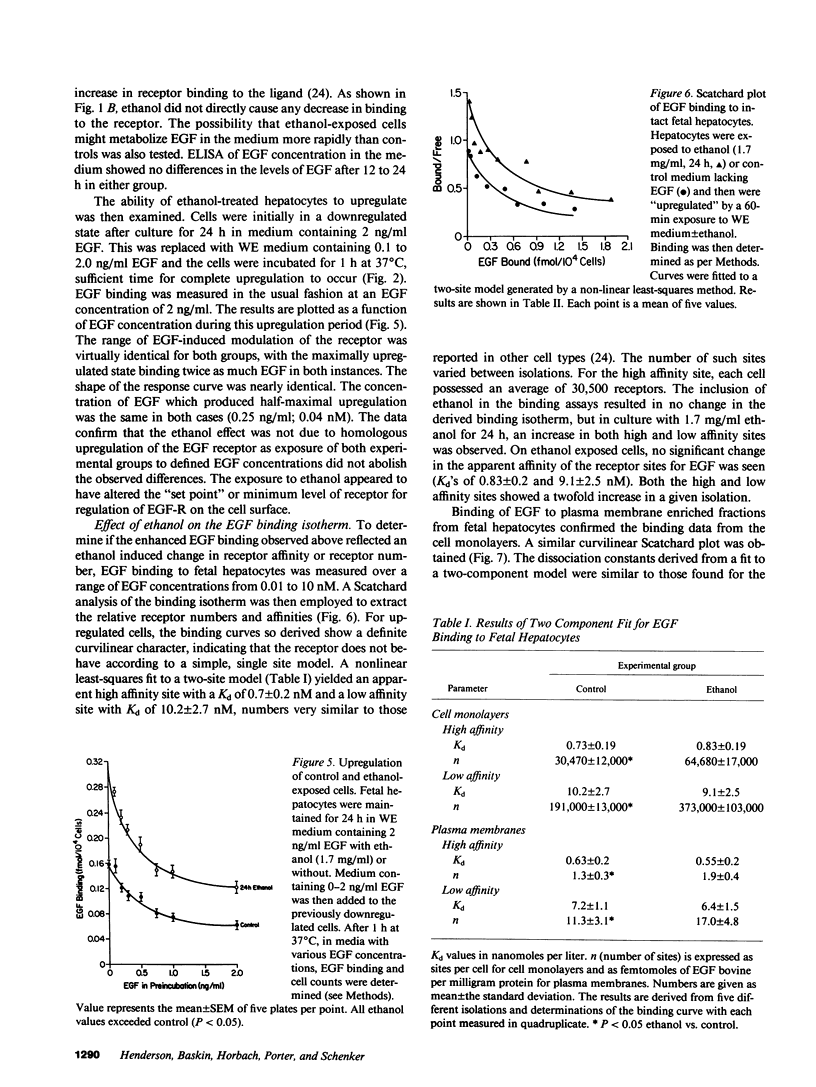
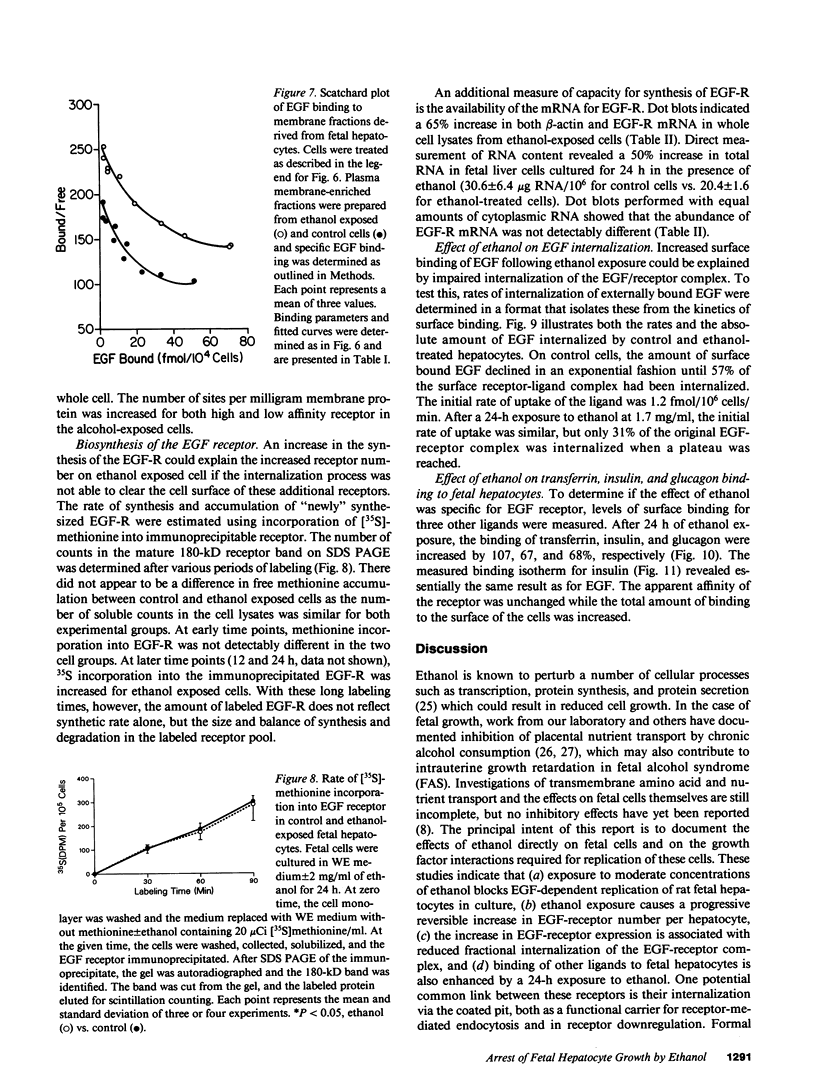
Exposure of the fetal rat hepatocyte to ethanol in vitro blocks epidermal growth factor (EGF)-dependent cell replication. To define possible mechanisms for this growth arrest, we determined the effects of ethanol on EGF binding and EGF receptor (EGF-R) levels. During a 24-h exposure to ethanol (1.7 mg/ml, 31 mM), cell replication was completely blocked while EGF binding per cell doubled. This effect was no specific for EGF, with variable degrees of increased binding noted for insulin, transferrin, and glucagon. Significantly increased EGF binding was seen after 6 h of ethanol exposure, and both growth arrest and enhanced EGF binding were reversed within 12 h of ethanol withdrawal. Increases in both "high" and "low" affinity sites were seen, with no changes in the apparent Kd's. Total RNA, beta-actin mRNA, and EGF-R mRNA were increased 50-70% in ethanol exposed cells. However, direct measurements of EGF-R synthesis rates by [35S]methionine incorporation revealed no differences between control and ethanol exposed cells. Internalization of EGF-R was significantly altered by ethanol exposure. A 2-h incubation resulted in the internalization of 57% of the ligand in control cells, while only 31% of bound EGF was internalized in the ethanol exposed cells. Thus, the enhanced EGF binding may be due to decreased efficiency of internalization.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abel E. L., Dintcheff B. A. Effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on growth and development in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Dec;207(3):916–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer B. L., Donovan C. B. A new method for the rapid isolation of basolateral plasma membrane vesicles from rat liver. Characterization, validation, and bile acid transport studies. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9295–9301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringman T. S., Lindquist P. B., Derynck R. Different transforming growth factor-alpha species are derived from a glycosylated and palmitoylated transmembrane precursor. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):429–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90194-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:881–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey C. A., Kragskow S. L., Sorrell M. F., Tuma D. J. Chronic ethanol administration impairs the binding and endocytosis of asialo-orosomucoid in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2704–2710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernoff G. F. The fetal alcohol syndrome in mice: an animal model. Teratology. 1977 Jun;15(3):223–229. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420150303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. H., Goldstein D. B. Membrane-disordering action of ethanol: variation with membrane cholesterol content and depth of the spin label probe. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 May;19(3):425–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draghi E., Armato U., Andreis P. G., Mengato L. The stimulation by epidermal growth factor (urogastrone) of the growth of neonatal rat hepatocytes in primary tissue culture and its modulation by serum and associated pancreatic hormones. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Apr;103(1):129–147. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041030118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis F. W., Pick J. R. An animal model of the fetal alcohol syndrome in beagles. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1980 Apr;4(2):123–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1980.tb05627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLECK A., MUNRO H. N. The precision of ultraviolet absorption measurements in the Schmidt-Thannhauser procedure for nucleic acid estimation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 14;55:571–583. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90836-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. E., Atkinson M., Van Thiel D. H., Rosenblum E., David R., Holzman I. Selective fetal malnutrition: the effect of ethanol and acetaldehyde upon in vitro uptake of alpha amino isobutyric acid by human placenta. Life Sci. 1981 Sep 21;29(12):1283–1288. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Calvin J. L., Saunders J. B., Crossley I. R., Dickenson C. J., Smith H. M., Tredger J. M., Williams R. Effects of ethanol administration on rat liver plasma membrane-bound enzymes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Aug 1;34(15):2685–2689. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90568-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M. Rapid and quantitative preparation of cytoplasmic RNA from small numbers of cells. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;173(1):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Dansylcadaverine inhibits internalization of 125I-epidermal growth factor in BALB 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1239–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman D. W., Frosto T. A., Schenker S., Henderson G. I. Stimulatory effects of ethanol on amino acid transport by rat fetal hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1987 Mar-Apr;7(2):307–314. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. I., Frosto T. A., Heitman D. W., Schenker S. Ethanol stimulates leucine uptake by rat fetal hepatocytes via trans-stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):G384–G389. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.2.G384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. I., Hoyumpa A. M., Jr, McClain C., Schenker S. The effects of chronic and acute alcohol administration on fetal development in the rat. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1979 Apr;3(2):99–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1979.tb05281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. I., Patwardhan R. V., Hoyumpa A. M., Jr, Schenker S. Fetal alcohol syndrome: overview of pathogenesis. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1981 Summer;3(2):73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. I., Patwardhan R. V., McLeroy S., Schenker S. Inhibition of placental amino acid uptake in rats following acute and chronic ethanol exposure. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1982 Fall;6(4):495–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1982.tb05013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. L., Smith D. W. Recognition of the fetal alcohol syndrome in early infancy. Lancet. 1973 Nov 3;302(7836):999–1001. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. L., Smith D. W., Ulleland C. N., Streissguth P. Pattern of malformation in offspring of chronic alcoholic mothers. Lancet. 1973 Jun 9;1(7815):1267–1271. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay D. G., Lai W. H., Uchihashi M., Khan M. N., Posner B. I., Bergeron J. J. Epidermal growth factor receptor kinase translocation and activation in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8473–8480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk Z., Wu C. Isolation of RNA for dot hybridization by heparin-DNase I treatment of whole cell lysate. Anal Biochem. 1987 Aug 15;165(1):20–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90195-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin J. M., Donzell W. C., Anderson R. G. Modulation of intracellular potassium and ATP: effects on coated pit function in fibroblasts and hepatocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Sep;124(3):372–378. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041240303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffert H. L., Paul D. Studies on primary cultures of differentiated fetal liver cells. J Cell Biol. 1972 Mar;52(3):559–568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.3.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Rodland K. D., Magun B. E. Disruption of intracellular processing of epidermal growth factor by methylamine inhibits epidermal growth factor-induced DNA synthesis but not early morphological or transcriptional events. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6908–6913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Davies P. J., Pastan I. Amines inhibit the clustering of alpha2-macroglobulin and EGF on the fibroblast cell surface. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):661–663. doi: 10.1038/277661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall C. L., Taylor J., Walker D. W. Ethanol-induced malformations in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1977 Jul;1(3):219–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1977.tb05876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raper S. E., Burwen S. J., Barker M. E., Jones A. L. Translocation of epidermal growth factor to the hepatocyte nucleus during rat liver regeneration. Gastroenterology. 1987 May;92(5 Pt 1):1243–1250. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(87)91084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S., Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Acidification of the cytosol inhibits endocytosis from coated pits. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):679–689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. J., Grant D. A. A differential effect between the acute and chronic administration of ethanol on the endocytotic rate constant, ke, for the internalisation of asialoglycoproteins by hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 6;862(1):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90483-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S. Anomalous binding of epidermal growth factor to A431 cells is due to the effect of high receptor densities and a saturable endocytic system. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):801–810. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. The endocytotic rate constant. A cellular parameter for quantitating receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4222–4229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Molecular analysis of signal transduction by growth factors. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3113–3119. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


