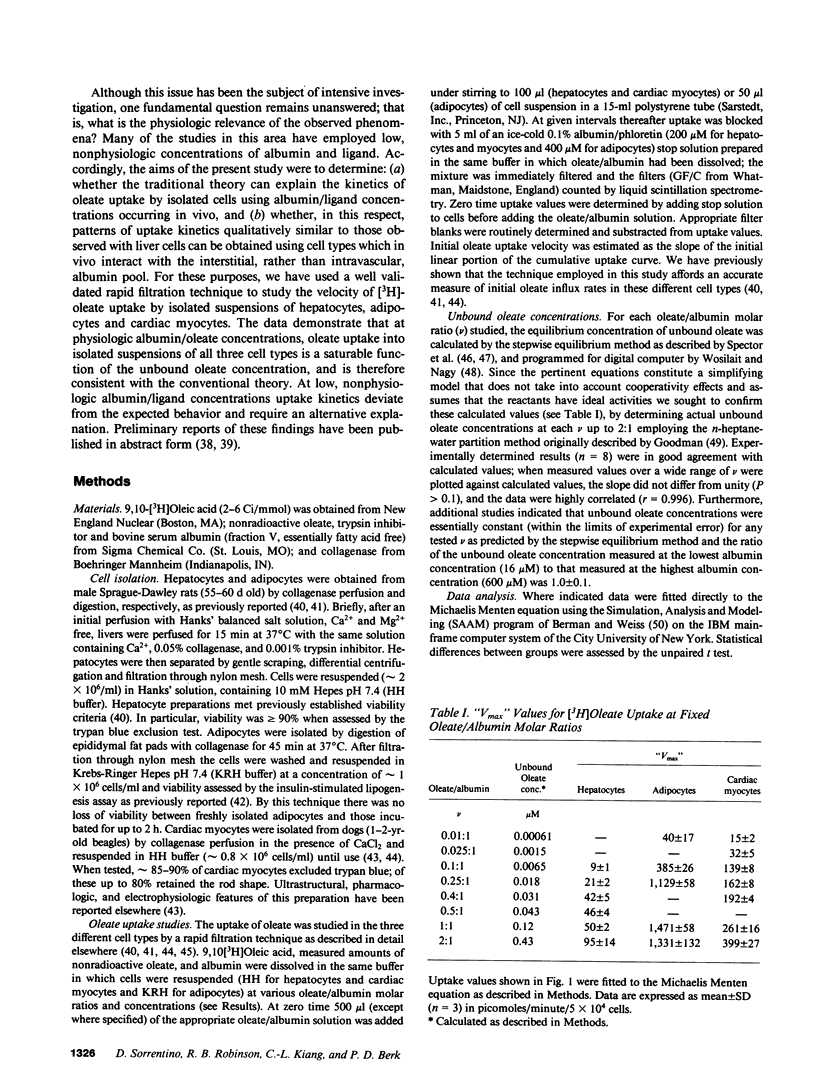
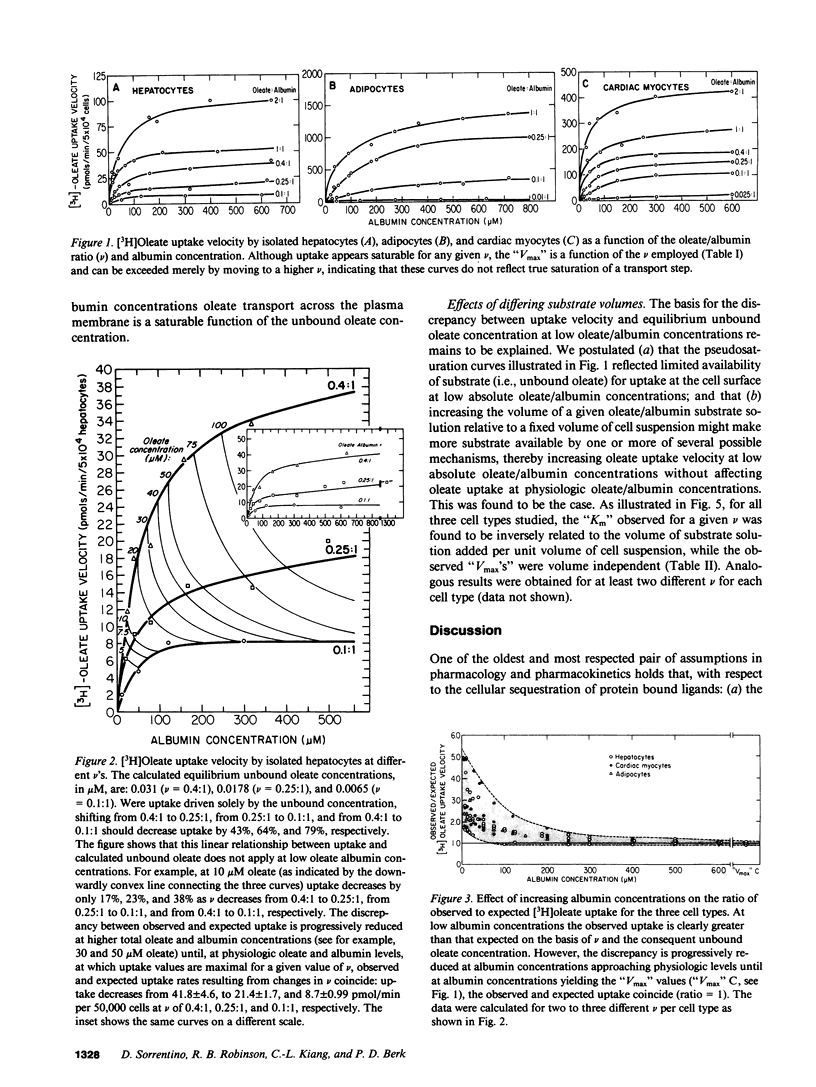
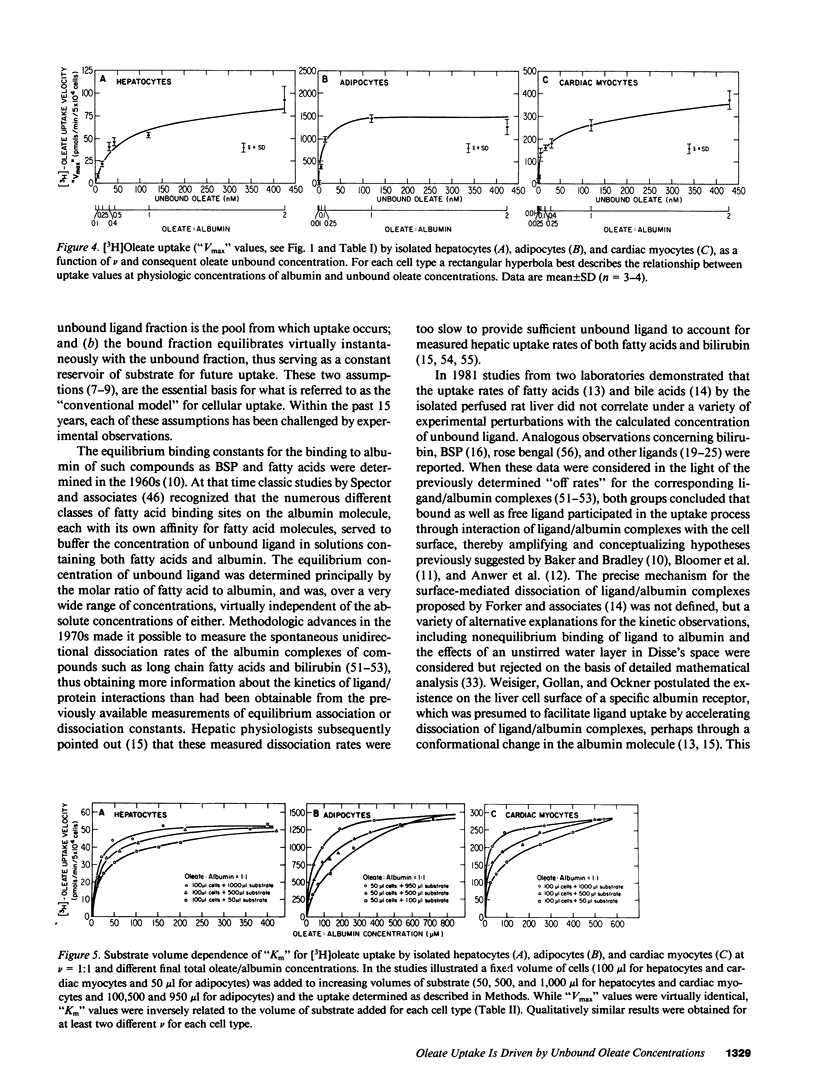
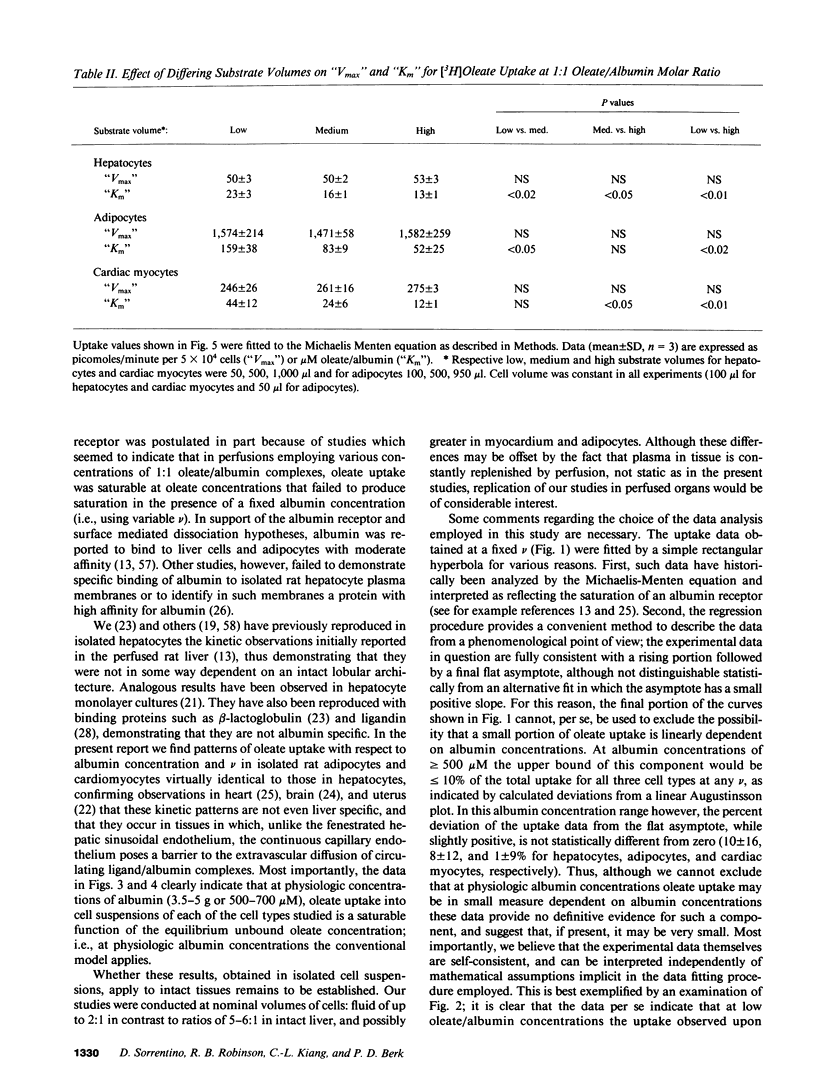
Abstract
To reexamine the role of albumin in cellular uptake of long chain fatty acids, we measured [3H]oleate uptake by isolated hepatocytes, adipocytes, and cardiac myocytes from incubations containing oleate/albumin complexes at molar ratios from 0.01:1 to 2:1. For each ratio the uptake was studied over a wide range of albumin concentrations. In all three cell types and at any given oleate/albumin ratio, the uptake appeared saturable with increasing concentrations of oleate:albumin complexes despite the fact that the unbound oleate concentration for each molar ratio is essentially constant. However, the "Km" but not the "Vmax" of these pseudosaturation curves was influenced by substrate availability. At low albumin concentrations, uptake velocities did not correlate with unbound oleate concentrations. However, observed and expected uptake velocities coincided at albumin concentrations approaching physiologic levels and were a saturable function of the oleate/albumin ratios and the consequent unbound oleate concentrations employed. Hence, under the experimental conditions employed in this study using a variety of suspended cell types, oleate uptake kinetics were consistent with the conventional theory at physiologic concentrations of albumin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abumrad N. A., Perkins R. C., Park J. H., Park C. R. Mechanism of long chain fatty acid permeation in the isolated adipocyte. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9183–9191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwer M. S., Kroker R., Hegner D. Effect of albumin on bile acid uptake by isolated rat hepatocytes. Is there a common bile acid carrier? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Nov 8;73(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90497-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUER R. W., PESSOTTI R. L. The removal of bromsulphthalein from blood plasma by the liver of the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1949 Nov;97(3):358–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker K. J., Bradley S. E. Binding of sulfobromophthalein (BSP) sodium by plasma albumin. Its role in hepatic BSP extraction. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):281–287. doi: 10.1172/JCI105341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnhart J. L., Clarenburg R. Factors determining clearance of bilirubin in perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1973 Aug;225(2):497–507. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.2.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnhart J. L., Witt B. L., Hardison W. G., Berk R. N. Uptake of iopanoic acid by isolated rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):G630–G636. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.6.G630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry P. H., Diamond J. M. Effects of unstirred layers on membrane phenomena. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jul;64(3):763–872. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.3.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein L. H., Ezzer J. B., Gartner L., Arias I. M. Hepatic intracellular distribution of tritium-labeled unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin in normal and Gunn rats. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jul;45(7):1194–1201. doi: 10.1172/JCI105425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomer J. R., Berk P. D., Vergalla J., Berlin N. I. Influence of albumin on the hepatic uptake of unconjugated bilirubin. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Oct;45(4):505–516. doi: 10.1042/cs0450505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandes R., Ockner R. K., Weisiger R. A., Lysenko N. Specific and saturable binding of albumin to rat adipocytes: modulation by epinephrine and possible role in free fatty acid transfer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 14;105(3):821–827. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faerch T., Jacobsen J. Determination of association and dissociation rate constants for bilirubin--bovine serum albumin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer A. B., Shurmantine W. O., Luxon B. A., Forker E. L. Palmitate uptake by hepatocyte monolayers. Effect of albumin binding. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):964–970. doi: 10.1172/JCI112397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L., Ghiron C. ESR, albumin, and the riddle of organic anion uptake by the liver. Am J Physiol. 1988 Apr;254(4 Pt 1):G463–G464. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.4.G463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L., Luxon B. A. Albumin helps mediate removal of taurocholate by rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1517–1522. doi: 10.1172/JCI110182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L., Luxon B. A. Albumin-mediated transport of rose bengal by perfused rat liver. Kinetics of the reaction at the cell surface. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1764–1771. doi: 10.1172/JCI111136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L., Luxon B. A., Sharma V. S. Hepatic transport and binding of rose bengal in the presence of albumin and gamma globulin. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 1):G702–G708. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.6.G702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L., Luxon B. A., Snell M., Shurmantine W. O. Effect of albumin binding on the hepatic transport of rose bengal: surface-mediated dissociation of limited capacity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):342–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORESKY C. A. INITIAL DISTRIBUTION AND RATE OF UPTAKE OF SULFOBROMOPHTHALEIN IN THE LIVER. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jul;207:13–26. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goresky C. A., Bach G. G., Wolkoff A. W., Rose C. P., Cousineau D. Sequestered tracer outflow recovery in multiple indicator dilution experiments. Hepatology. 1985 Sep-Oct;5(5):805–814. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goresky C. A., Daly D. S., Mishkin S., Arias I. M. Uptake of labeled palmitate by the intact liver: role of intracellular binding sites. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jun;234(6):E542–E553. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.6.E542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grausz H., Schmid R. Reciprocal relation between plasma albumin level and hepatic sulfobromophthalein removal. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jun 24;284(25):1403–1406. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197106242842504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett K., Legato M. J., Danilo P., Jr, Robinson R. B. Isolated myocytes from adult canine left ventricle: Ca2+ tolerance, electrophysiology, and ultrastructure. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):H830–H839. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.245.5.H830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie T., Mizuma T., Kasai S., Awazu S. Conformational change in plasma albumin due to interaction with isolated rat hepatocyte. Am J Physiol. 1988 Apr;254(4 Pt 1):G465–G470. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.4.G465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Okajima K., Nagase S., Morino Y. Plasma clearance of sulfobromophthalein and its interaction with hepatic binding proteins in normal and analbuminemic rats: is plasma albumin essential for vectorial transport of organic anions in the liver? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7654–7658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. A. Influence of plasma protein binding kinetics on hepatic clearance assessed from a "tube" model and a "well-stirred" model. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1981 Feb;9(1):15–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01059340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer L. R., Gambone J. C., Chaudhuri G., Pardridge W. M., Judd H. L. The effect of membrane permeability and binding by human serum proteins on sex steroid influx into the uterus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jun;56(6):1282–1287. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-6-1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody A. J., Stan M. A., Stan M., Gliemann J. A simple free fat cell bioassay for insulin. Horm Metab Res. 1974 Jan;6(1):12–16. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. J., Jones D. B., Smallwood R. A. Modeling of substrate elimination by the liver: has the albumin receptor model superseded the well-stirred model? Hepatology. 1985 Nov-Dec;5(6):1231–1235. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes R., Kiang C. L., Sorrentino D., Berk P. D. 'Albumin-receptor' uptake kinetics do not require an intact lobular architecture and are not specific for albumin. J Hepatol. 1988 Dec;7(3):293–304. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(88)80001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie S., Yang Y. H. Effect of altered albumin concentrations on elimination of unbound prazosin in vivo in the rat and in the isolated perfused rat liver. J Pharm Sci. 1988 Nov;77(11):948–951. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600771110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M. Transport of nutrients and hormones through the blood-brain barrier. Fed Proc. 1984 Feb;43(2):201–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paumgartner G., Reichen J. Kinetics of hepatic uptake of unconjugated bilirubin. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Aug;51(2):169–176. doi: 10.1042/cs0510169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter B. J., Stump D., Schwieterman W., Sorrentino D., Jacobs L. N., Kiang C. L., Rand J. H., Berk P. D. Isolation and partial characterization of plasma membrane fatty acid binding proteins from myocardium and adipose tissue and their relationship to analogous proteins in liver and gut. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1370–1376. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80283-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch B., Bode C., Piper H. M., Hütter J. F., Zimmermann R., Braunwell E., Hasselbach W., Kübler W. Palmitate uptake in calcium tolerant, adult rat myocardial single cells--evidence for an albumin mediated transport across sarcolemma. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1987 Feb;19(2):159–166. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(87)80558-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reider H., Ramadori G., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Opsonic activity of human ascitic fluid. Hepatology. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):545–546. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roda E., Aldini R., Roda A. Role of albumin in liver uptake. Gastroenterology. 1987 Apr;92(4):1097–1097. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)91001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose C. P., Goresky C. A., Bach G. G. The capillary and sarcolemmal barriers in the heart. An exploration of labeled water permeability. Circ Res. 1977 Oct;41(4):515–533. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.4.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose C. P., Goresky C. A. Constraints on the uptake of labeled palmitate by the heart. The barriers at the capillary and sarcolemmal surfaces and the control of intracellular sequestration. Circ Res. 1977 Oct;41(4):534–545. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.4.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheider W. Dissociation rate of serum albumin-fatty acid complex from stop-flow dielectric study of ligand exchange. Biophys J. 1978 Oct;24(1):260–262. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85371-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwieterman W., Sorrentino D., Potter B. J., Rand J., Kiang C. L., Stump D., Berk P. D. Uptake of oleate by isolated rat adipocytes is mediated by a 40-kDa plasma membrane fatty acid binding protein closely related to that in liver and gut. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):359–363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smallwood R. H., Morgan D. J., Mihaly G. W., Smallwood R. A. Lack of linear correlation between hepatic ligand uptake rate and unbound ligand concentration does not necessarily imply receptor-mediated uptake. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1988 Aug;16(4):397–411. doi: 10.1007/BF01062553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Grossbard M., Gordon E. R., Boyer J. L. Taurocholate uptake by isolated skate hepatocytes: effect of albumin. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 1):G479–G484. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.4.G479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino D., Berk P. D. Mechanistic aspects of hepatic bilirubin uptake. Semin Liver Dis. 1988 May;8(2):119–136. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino D., Stump D., Potter B. J., Robinson R. B., White R., Kiang C. L., Berk P. D. Oleate uptake by cardiac myocytes is carrier mediated and involves a 40-kD plasma membrane fatty acid binding protein similar to that in liver, adipose tissue, and gut. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):928–935. doi: 10.1172/JCI113700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., Fletcher J. E., Ashbrook J. D. Analysis of long-chain free fatty acid binding to bovine serum albumin by determination of stepwise equilibrium constants. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 17;10(17):3229–3232. doi: 10.1021/bi00793a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., John K., Fletcher J. E. Binding of long-chain fatty acids to bovine serum albumin. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):56–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollman Y. R., Gärtner U., Theilmann L., Ohmi N., Wolkoff A. W. Hepatic bilirubin uptake in the isolated perfused rat liver is not facilitated by albumin binding. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):718–723. doi: 10.1172/JCI111021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stremmel W., Berk P. D. Hepatocellular influx of [14C]oleate reflects membrane transport rather than intracellular metabolism or binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3086–3090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stremmel W., Lotz G., Strohmeyer G., Berk P. D. Identification, isolation, and partial characterization of a fatty acid binding protein from rat jejunal microvillous membranes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):1068–1076. doi: 10.1172/JCI111769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stremmel W., Potter B. J., Berk P. D. Studies of albumin binding to rat liver plasma membranes. Implications for the albumin receptor hypothesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 15;756(1):20–27. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stremmel W., Strohmeyer G., Berk P. D. Hepatocellular uptake of oleate is energy dependent, sodium linked, and inhibited by an antibody to a hepatocyte plasma membrane fatty acid binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3584–3588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stremmel W., Strohmeyer G., Borchard F., Kochwa S., Berk P. D. Isolation and partial characterization of a fatty acid binding protein in rat liver plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):4–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson A., Holmer E., Andersson L. O. A new method for the measurement of dissociation rates for complexes between small ligands and proteins as applied to the palmitate and bilirubin complexes with serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 14;342(1):54–59. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisiger R. A. Dissociation from albumin: a potentially rate-limiting step in the clearance of substances by the liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1563–1567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisiger R. A., Gollan J. L., Ockner R. K. The role of albumin in hepatic uptake processes. Prog Liver Dis. 1982;7:71–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisiger R. A., Ma W. L. Uptake of oleate from albumin solutions by rat liver. Failure to detect catalysis of the dissociation of oleate from albumin by an albumin receptor. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1070–1077. doi: 10.1172/JCI112920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisiger R. A., Zacks C. M., Smith N. D., Boyer J. L. Effect of albumin binding on extraction of sulfobromophthalein by perfused elasmobranch liver: evidence for dissociation-limited uptake. Hepatology. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):492–501. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisiger R., Gollan J., Ockner R. Receptor for albumin on the liver cell surface may mediate uptake of fatty acids and other albumin-bound substances. Science. 1981 Mar 6;211(4486):1048–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6258226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolkoff A. W. The role of an albumin receptor in hepatic organic anion uptake: the controversy continues. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):777–779. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wosilait W. D., Nagy P. A method of computing drug distribution in plasma using stepwise association constants: clofibrate acid as an illustrative example. Comput Programs Biomed. 1976 Oct;6(3):142–148. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(76)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sluijs P., Postema B., Meijer D. K. Lactosylation of albumin reduces uptake rate of dibromosulfophthalein in perfused rat liver and dissociation rate from albumin in vitro. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):688–695. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



