Abstract
EMBO J 31 5, 1062–1079 (2012); published online January 17 2012
In this issue of The EMBO Journal, Garg et al (2012) delineate a signalling pathway that leads to calreticulin (CRT) exposure and ATP release by cancer cells that succumb to photodynamic therapy (PTD), thereby providing fresh insights into the molecular regulation of immunogenic cell death (ICD).
The textbook notion that apoptosis would always take place unrecognized by the immune system has recently been invalidated (Zitvogel et al, 2010; Galluzzi et al, 2012). Thus, in specific circumstances (in particular in response to anthracyclines, oxaliplatin, and γ irradiation), cancer cells can enter a lethal stress pathway linked to the emission of a spatiotemporally defined combination of signals that is decoded by the immune system to activate tumour-specific immune responses (Zitvogel et al, 2010). These signals include the pre-apoptotic exposure of intracellular proteins such as the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperon CRT and the heat-shock protein HSP90 at the cell surface, the pre-apoptotic secretion of ATP, and the post-apoptotic release of the nuclear protein HMGB1 (Zitvogel et al, 2010). Together, these processes (and perhaps others) constitute the molecular determinants of ICD.
In this issue of The EMBO Journal, Garg et al (2012) add hypericin-based PTD (Hyp-PTD) to the list of bona fide ICD inducers and convincingly link Hyp-PTD-elicited ICD to the functional activation of the immune system. Moreover, Garg et al (2012) demonstrate that Hyp-PDT stimulates ICD via signalling pathways that overlap with—but are not identical to—those elicited by anthracyclines, which constitute the first ICD inducers to be characterized (Casares et al, 2005; Zappasodi et al, 2010; Fucikova et al, 2011).
Intrigued by the fact that the ER stress response is required for anthracycline-induced ICD (Panaretakis et al, 2009), Garg et al (2012) decided to investigate the immunogenicity of Hyp-PDT (which selectively targets the ER). Hyp-PDT potently stimulated CRT exposure and ATP release in human bladder carcinoma T24 cells. As a result, T24 cells exposed to Hyp-PDT (but not untreated cells) were engulfed by Mf4/4 macrophages and human dendritic cells (DCs), the most important antigen-presenting cells in antitumour immunity. Similarly, murine colon carcinoma CT26 cells succumbing to Hyp-PDT (but not cells dying in response to the unspecific ER stressor tunicamycin) were preferentially phagocytosed by murine JAWSII DCs, and efficiently immunized syngenic BALB/c mice against a subsequent challenge with living cells of the same type. Of note, contrarily to T24 cells treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or dying from accidental necrosis, T24 cells exposed to Hyp-PDT activated DCs while eliciting a peculiar functional profile, featuring high levels of NO production and absent secretion of immunosuppressive interleukin-10 (IL-10) (Garg et al, 2012). Moreover upon co-culture with Hyp-PDT-treated T24 cells, human DCs were found to secrete high levels of IL-1β, a cytokine that is required for the adequate polarization of interferon γ (IFNγ)-producing antineoplastic CD8+ T cells (Aymeric et al, 2010). Taken together, these data demonstrate that Hyp-PDT induces bona fide ICD, eliciting an antitumour immune response.
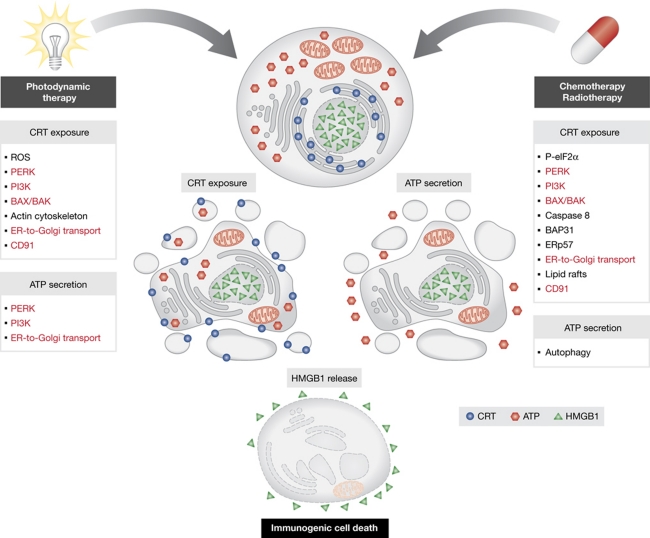
By combining pharmacological and genetic approaches, Garg et al (2012) then investigated the molecular cascades that are required for Hyp-PDT-induced CRT exposure and ATP release. They found that CRT exposure triggered by Hyp-PDT requires reactive oxygen species (as demonstrated with the 1O2 quencher L-histidine), class I phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K) activity (as shown with the chemical inhibitor wortmannin and the RNAi-mediated depletion of the catalytic PI3K subunit p110), the actin cytoskeleton (as proven with the actin inhibitor latrunculin B), the ER-to-Golgi anterograde transport (as shown using brefeldin A), the ER stress-associated kinase PERK, the pro-apoptotic molecules BAX and BAK as well as the CRT cell surface receptor CD91 (as demonstrated by their knockout or RNAi-mediated depletion). However, there were differences in the signalling pathways leading to CRT exposure in response to anthracyclines (Panaretakis et al, 2009) and Hyp-PDT (Garg et al, 2012). In contrast to the former, the latter was not accompanied by the exposure of the ER chaperon ERp57, and did not require eIF2α phosphorylation (as shown with non-phosphorylatable eIF2α mutants), caspase-8 activity (as shown with the pan-caspase blocker Z-VAD.fmk, upon overexpression of the viral caspase inhibitor CrmA and following the RNAi-mediated depletion of caspase-8), and increased cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations (as proven with cytosolic Ca2+ chelators and overexpression of the ER Ca2+ pump SERCA). Moreover, Hyp-PDT induced the translocation of CRT at the cell surface irrespective of retrograde transport (as demonstrated with the microtubular poison nocodazole) and lipid rafts (as demonstrated with the cholesterol-depleting agent methyl-β-cyclodextrine). Of note, ATP secretion in response to Hyp-PDT depended on the ER-to-Golgi anterograde transport, PI3K and PERK activity (presumably due to their role in the regulation of secretory pathways), but did not require BAX and BAK (Garg et al, 2012). Since PERK can stimulate autophagy in the context of ER stress (Kroemer et al, 2010), it is tempting to speculate that autophagy is involved in Hyp-PDT-elicited ATP secretion, as this appears to be to the case during anthracycline-induced ICD (Michaud et al, 2011).
Altogether, the intriguing report by Garg et al (2012) demonstrates that the stress signalling pathways leading to ICD depend—at least in part—on the initiating stimulus (Figure 1). Speculatively, this points to the coexistence of a ‘core’ ICD signalling pathway (which would be common to several, if not all, ICD inducers) with ‘private’ molecular cascades (which would be activated in a stimulus-dependent fashion). Irrespective of these details, the work by Garg et al (2012) further underscores the importance of anticancer immune responses elicited by established and experimental therapies.
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms of immunogenic cell death (ICD). At least three processes underlie the immunogenicity of cell death: the pre-apoptotic exposure of calreticulin (CRT) at the cell surface, the secretion of ATP, and the post-apoptotic release of HMGB1. ICD can be triggered by multiple stimuli, including photodynamic therapy, anthracycline-based chemotherapy, and some types of radiotherapy. The signalling pathways elicited by distinct ICD inducers overlap, but are not identical. In red are indicated molecules and processes that—according to current knowledge—may be required for CRT exposure and ATP secretion in response to most, if not all, ICD inducers. The molecular determinants of the immunogenic release of HMGB1 remain poorly understood. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; P-eIF2α, phosphorylated eIF2α; PI3K, class I phosphoinositide-3-kinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
Footnotes
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Aymeric L, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A, Martins I, Kroemer G, Smyth MJ, Zitvogel L (2010) Tumor cell death and ATP release prime dendritic cells and efficient anticancer immunity. Cancer Res 70: 855–858 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casares N, Pequignot MO, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Roux S, Chaput N, Schmitt E, Hamai A, Hervas-Stubbs S, Obeid M, Coutant F, Metivier D, Pichard E, Aucouturier P, Pierron G, Garrido C, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2005) Caspase-dependent immunogenicity of doxorubicin-induced tumor cell death. J Exp Med 202: 1691–1701 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fucikova J, Kralikova P, Fialova A, Brtnicky T, Rob L, Bartunkova J, Spisek R (2011) Human tumor cells killed by anthracyclines induce a tumor-specific immune response. Cancer Res 71: 4821–4833 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, El-Deiry WS, Fulda S, Gottlieb E, Green DR, Hengartner MO, Kepp O, Knight RA, Kumar S, Lipton SA, Lu X, Madeo F, Malorni W et al. (2012) Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ 19: 107–120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg AD, Krysko DV, Verfaillie T, Kaczmarek A, Ferreira GB, Marysael T, Rubio N, Firczuk M, Mathieu C, Roebroek AJM, Annaert W, Golab J, de Witte P, Vandenabeele P, Agostinis P (2012) A novel pathway combining calreticulin exposure and ATP secretion in immunogenic cancer cell death. EMBO J 31: 1062–1079 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroemer G, Marino G, Levine B (2010) Autophagy and the integrated stress response. Mol Cell 40: 280–293 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud M, Martins I, Sukkurwala AQ, Adjemian S, Ma Y, Pellegatti P, Shen S, Kepp O, Scoazec M, Mignot G, Rello-Varona S, Tailler M, Menger L, Vacchelli E, Galluzzi L, Ghiringhelli F, di Virgilio F, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2011) Autophagy-dependent anticancer immune responses induced by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. Science 334: 1573–1577 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panaretakis T, Kepp O, Brockmeier U, Tesniere A, Bjorklund AC, Chapman DC, Durchschlag M, Joza N, Pierron G, van Endert P, Yuan J, Zitvogel L, Madeo F, Williams DB, Kroemer G (2009) Mechanisms of pre-apoptotic calreticulin exposure in immunogenic cell death. EMBO J 28: 578–590 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zappasodi R, Pupa SM, Ghedini GC, Bongarzone I, Magni M, Cabras AD, Colombo MP, Carlo-Stella C, Gianni AM, Di Nicola M (2010) Improved clinical outcome in indolent B-cell lymphoma patients vaccinated with autologous tumor cells experiencing immunogenic death. Cancer Res 70: 9062–9072 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitvogel L, Kepp O, Kroemer G (2010) Decoding cell death signals in inflammation and immunity. Cell 140: 798–804 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]