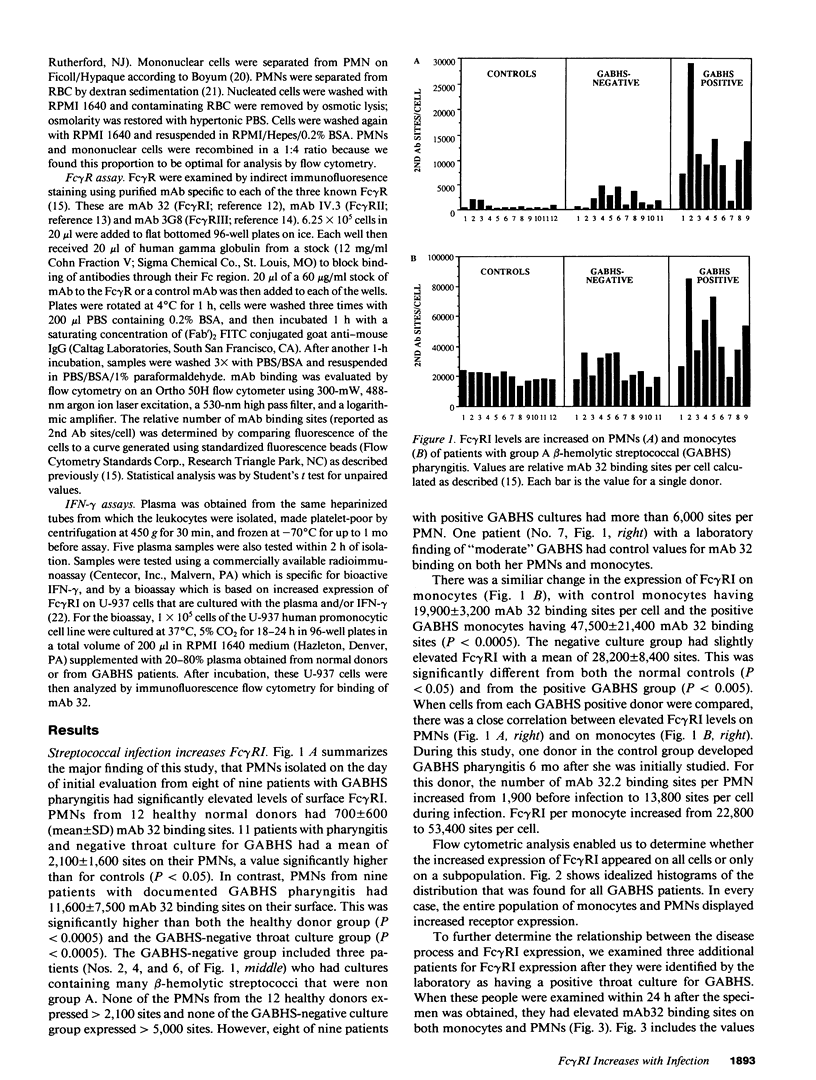
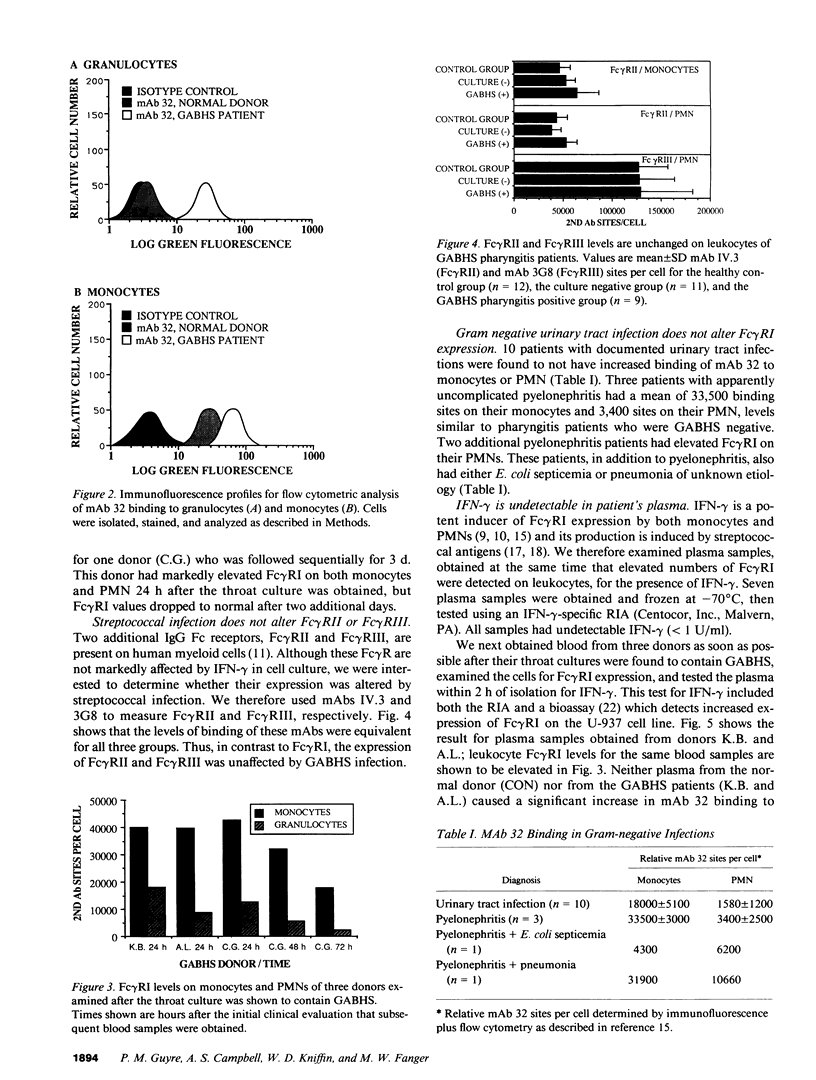
Abstract
Studies using cultured cells have shown that gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) induces the expression of Fc gamma RI (the type I Fc receptor for IgG) on human polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) and greatly increases the number of these receptors on human monocytes. Administration of rIFN-gamma in vivo also causes enhanced Fc gamma RI expression on these cell populations. Because streptococcal antigens are potent inducers of IFN-gamma in vitro, we postulated that IFN-gamma would be produced endogenously in vivo in patients with streptococcal infections. Such production of IFN-gamma in vivo, even at low levels, might be expected to induce the expression of Fc gamma RI on monocytes and neutrophils. To evaluate this possibility, we used monoclonal antibody 32 (mAb 32), which is specific for Fc gamma RI, to quantitate the expression of this receptor on human peripheral blood cells. We measured the binding of mAb 32 to monocytes and PMNs isolated from healthy donors and from patients with group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal (GABHS) pharyngitis. PMNs from healthy donors (n = 12) had 700 +/- 600 (mean +/- SD) mAb 32 binding sites. Patients with pharyngitis and negative throat culture for GABHS (n = 11) had 2,100 +/- 1,600 sites on their PMNs. In contrast, the PMNs from patients with documented GABHS pharyngitis (n = 12) had 11,600 +/- 7,500 mAb 32 binding sites on their surface. There was a similar change in the expression of Fc gamma RI on monocytes, with control monocytes having a mean of 19,900 +/- 3,200 mAb 32 binding sites per cell and the GABHS-positive monocytes having 47,500 +/- 21,400 sites. The GABHS-negative throat culture group had a slightly elevated number of Fc gamma RI with a mean of 28,200 +/- 8,400 sites. 10 patients with documented urinary tract infections and three patients with uncomplicated pyelonephritis had no elevation in Fc gamma RI expression. These studies demonstrate that a localized group A streptococcal infection can cause systemic activation of the entire circulating pool of phagocytes, and suggest that a similar level of activation is uncommon in localized gram-negative infections of the urinary tract.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. L., Guyre P. M., Whitin J. C., Ryan D. H., Looney R. J., Fanger M. W. Monoclonal antibodies to Fc receptors for IgG on human mononuclear phagocytes. Antibody characterization and induction of superoxide production in a monocyte cell line. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12856–12864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass D. A., Olbrantz P., Szejda P., Seeds M. C., McCall C. E. Subpopulations of neutrophils with increased oxidative product formation in blood of patients with infection. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):860–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Requirement of endogenous interferon-gamma production for resolution of Listeria monocytogenes infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7404–7408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centor R. M., Witherspoon J. M., Dalton H. P., Brody C. E., Link K. The diagnosis of strep throat in adults in the emergency room. Med Decis Making. 1981;1(3):239–246. doi: 10.1177/0272989X8100100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleit H. B., Wright S. D., Unkeless J. C. Human neutrophil Fc gamma receptor distribution and structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3275–3279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foon K. A., Sherwin S. A., Abrams P. G., Stevenson H. C., Holmes P., Maluish A. E., Oldham R. K., Herberman R. B. A phase I trial of recombinant gamma interferon in patients with cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1985;20(3):193–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00205575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano R. F., Fanger M. W. Fc gamma RI and Fc gamma RII on monocytes and granulocytes are cytotoxic trigger molecules for tumor cells. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3536–3541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyre P. M., Morganelli P. M., Miller R. Recombinant immune interferon increases immunoglobulin G Fc receptors on cultured human mononuclear phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):393–397. doi: 10.1172/JCI110980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Inoue T., Yamashita T., Midorikawa Y., Arai S., Sendo F. Production of factor(s) that render polymorphonuclear leukocytes cytostatic from spleen cells stimulated with a streptococcal preparation, OK-432. Cancer Res. 1987 Dec 1;47(23):6204–6209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Lymphokine-mediated activation of human monocytes: neutralization by monoclonal antibody to interferon-gamma. Cell Immunol. 1984 Apr 15;85(1):278–283. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90299-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Jerrells T. R., Spitalny G. L., Walker D. H. Gamma interferon as a crucial host defense against Rickettsia conorii in vivo. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1252–1255. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1252-1255.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney R. J., Abraham G. N., Anderson C. L. Human monocytes and U937 cells bear two distinct Fc receptors for IgG. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1641–1647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maluish A. E., Urba W. J., Longo D. L., Overton W. R., Coggin D., Crisp E. R., Williams R., Sherwin S. A., Gordon K., Steis R. G. The determination of an immunologically active dose of interferon-gamma in patients with melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 1988 Mar;6(3):434–445. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1988.6.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Rothermel C. D. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by lymphokine-stimulated human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence that interferon-gamma is the activating lymphokine. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1172/JCI111107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Spitalny G. L., Nathan C. F. Activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1619–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Horowitz C. R., de la Harpe J., Vadhan-Raj S., Sherwin S. A., Oettgen H. F., Krown S. E. Administration of recombinant interferon gamma to cancer patients enhances monocyte secretion of hydrogen peroxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8686–8690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Prendergast T. J., Wiebe M. E., Stanley E. R., Platzer E., Remold H. G., Welte K., Rubin B. Y., Murray H. W. Activation of human macrophages. Comparison of other cytokines with interferon-gamma. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):600–605. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Dayton E. T., Lazarus R., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Immune interferon induces the receptor for monomeric IgG1 on human monocytic and myeloid cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1092–1113. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petroni K. C., Shen L., Guyre P. M. Modulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte IgG Fc receptors and Fc receptor-mediated functions by IFN-gamma and glucocorticoids. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3467–3472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simms H. H., Frank M. M., Quinn T. C., Holland S., Gaither T. A. Studies on phagocytosis in patients with acute bacterial infections. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):252–260. doi: 10.1172/JCI113867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Orellana M. A., Schreiber R. D., Remington J. S. Interferon-gamma: the major mediator of resistance against Toxoplasma gondii. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):516–518. doi: 10.1126/science.3128869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. Function and heterogeneity of human Fc receptors for immunoglobulin G. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):355–361. doi: 10.1172/JCI113891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadhan-Raj S., Al-Katib A., Bhalla R., Pelus L., Nathan C. F., Sherwin S. A., Oettgen H. F., Krown S. E. Phase I trial of recombinant interferon gamma in cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 1986 Feb;4(2):137–146. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1986.4.2.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varesio L., Blasi E., Thurman G. B., Talmadge J. E., Wiltrout R. H., Herberman R. B. Potent activation of mouse macrophages by recombinant interferon-gamma. Cancer Res. 1984 Oct;44(10):4465–4469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Burg M., Edelstein M., Gerlis L., Liang C. M., Hirschi M., Dawson A. Recombinant interferon-gamma (immuneron): results of a phase I trial in patients with cancer. J Biol Response Mod. 1985 Jun;4(3):264–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


