An annual increase in Campylobacter infection in England and Wales begins in May and reaches a maximum in early June. This increase occurs in all age groups and is seen in all geographic areas. Examination of risk factors that might explain this seasonal increase identifies flies as a potential source of infection. The observed pattern of infection is hypothesized to reflect an annual epidemic caused by direct or indirect contamination of people by small quantities of infected material carried by flies that have been in contact with feces. The local pattern of human illness appears random, while having a defined geographic and temporal distribution that is a function of the growth kinetics of one or more fly species. The hypothesis provides an explanation for the seasonal distribution of Campylobacter infections seen around the world.
Campylobacter spp. are the most common bacterial causes of diarrhea in England and Wales (1). The epidemiologic features of Campylobacter infection have proved difficult to discover, and extensive strain typing has failed to clarify the main transmission routes. Testable hypotheses must be established to explain available evidence, particularly the reason for the observed seasonality. Relatively few outbreaks of Campylobacter gastroenteritis occur (2), and most cases are sporadic. In case-control and case-case studies of sporadic Campylobacter infections, most cases remain unexplained by recognized risk factors (3,4).
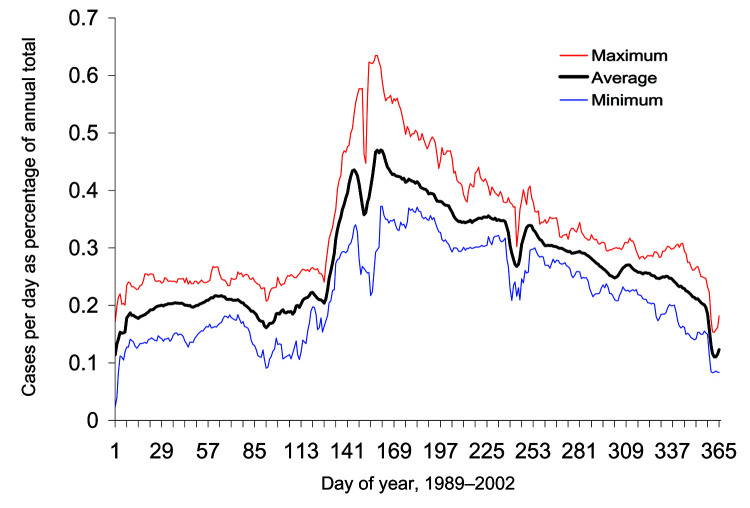
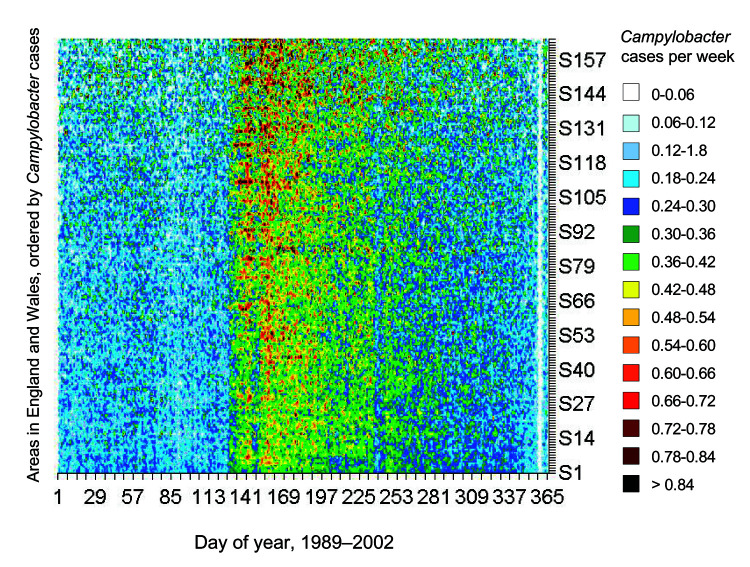
The annual increase in Campylobacter infections in England and Wales begins at approximately day 130 (May 9) and reaches a maximum at approximately day 160 (June 8) (Figure 1). Although this seasonal rise is seen in all ages, it is more marked in children (5). Cases in towns and cities across England and Wales show broadly similar seasonal changes in distribution (Figure 2). The relative geographic uniformity of the increase seen in May of most years has the temporal appearance of an annual national epidemic. Because person-to-person infection within the community is uncommon, it is likely that the epidemic is caused by a single main driver for human Campylobacter infection. The possible seasonal drivers were examined, and only vector transmission by flies appears to provide a convincing explanation for the observed seasonal trends (Table).
Figure 1.
Distribution of Campylobacter cases per day. When averaged for 1989 to 2002, the epidemic begins at approximately day 130, peaks at approximately day 160, and gradually declines through the rest of the year.
Figure 2.
Cases of Campylobacter infection in England and Wales based on the patient specimen date. Figure shows broadly similar changes in patterns of infection across the country as measured by laboratory reporting per town or city (cases as a percentage of the annual total) by day of year. Laboratories were ordered by the total number of cases reported over the 14-year period (Appendix).
The seasonal increase in Campylobacter infections in May and June in England and Wales is hypothesized to reflect an annual epidemic caused by direct or indirect exposure of humans to contaminated material carried by several fly species that have been in contact with human, bird, or animal feces or contaminated raw foods. Flies have been shown to carry Campylobacter and can infect both humans and animals (6–8). Intervention studies have demonstrated diarrheal disease reduction linked to control of flies (9–11), and deaths from diarrheal diseases have been linked to measurements of fly abundance (12). The local pattern of human Campylobacter infection appears random, while having a defined geographic and temporal distribution. This distribution is predicted to be linked to the growth kinetics of 1 or more fly species and their access to environmental sources of Campylobacter in feces or food. The seasonal increase in fly populations results from rainy weather and an increase in temperature that causes the development from egg to fly to occur in days rather than months. Individual flies can lay hundreds of eggs, which can result in a large increase in fly numbers in a short period. Fly numbers fluctuate through the summer and decline in October, but the decline is less dramatic and defined than the spring increase.
Disease transmission is hypothesized to occur through small quantities of contaminated material carried on the feet, proboscis, legs, and body hairs or from material regurgitated or defecated by flies. The variety, numbers, virulence and viability of organisms in the contaminated material will differ, and some contamination will include Campylobacter while others will not. Contamination will be distributed over a variety of food types. Contamination of food by flies could occur at any stage of the food supply chain, but Campylobacter counts within the contaminated material on foods will decrease over time; consequently, most infection will result from contamination close to consumption (e.g., in the domestic or catering environment). Because whether a fly has visited contaminated feces is unknown and how a person becomes infected is uncertain, epidemiologic investigation is difficult.
A number of synanthropic fly species could be involved, including houseflies (e.g., Musca spp., Fannia spp.), blowflies (e.g., Calliphora spp., Lucilia spp.), and other dung-related flies (e.g., Sarcophaga spp., Drosophila spp.) (13). These flies have individual behavioral patterns, ecology, physiology, and temporal and geographic distributions that will influence the likelihood of their being in kitchens, on human or animal feces, and on food. Although Musca domestica is the species most likely to be involved because it is commonly found in houses and food-processing establishments, larger flies (e.g., Calliphora spp.) may be able to transmit larger numbers of Campylobacter.
Flies contaminated through fecal contact will carry heterogeneous mixtures of organisms, including any pathogens that are present within the feces, and may be able to cause a variety of human infections, including infection by different Campylobacter species and types. This fact partially explains the lack of a clear epidemiologic picture arising from Campylobacter typing work. Gastrointestinal disease caused by flies is more likely to involve pathogens with a low infectious dose (e.g., Shigella, Campylobacter, Cryptosporidium, Giardia, Cyclospora, Escherichia coli O157), and some of these could have a seasonal component related to flies. Where high fly populations and poor hygiene conditions prevail, as in disasters or famines, or where pathogens can grow within fly-contaminated food, the potential exists for transmitting pathogens with a high infectious dose (e.g., Vibrio cholerae, Salmonella spp.). The access that flies have to human and animal feces will influence the degree to which they are contaminated with different enteric pathogens.
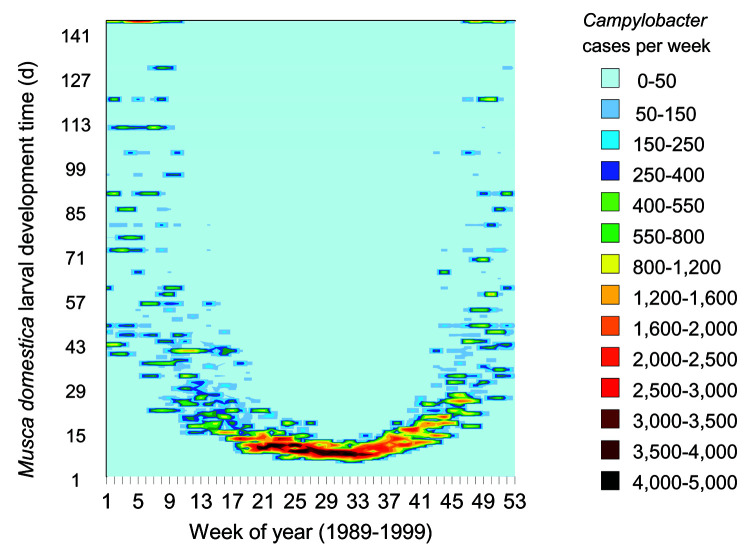
Contamination of a range of foods by flies will result in a pattern of infection that will not be amenable to identifying specific vehicles through standard case-control, case-case, or cohort studies, unless specific objective or subjective assessments of fly numbers can be obtained. Fly monitoring will need to be undertaken. An alternative approach could use estimates of fly population numbers based on climatic conditions to compare with data on human Campylobacter infections. This approach has the advantage of being able to use historical climatic and disease surveillance data. The broad relationship between Campylobacter cases and ambient temperature has not been explained in terms of disease causation. The time taken for the larvae of M. domestica to develop (13) was applied to temperature data for England and Wales and has been used to show a strong relationship between Campylobacter cases per week and M. domestica larval development time for 1989 to 1999 (Figure 3). Periods when Campylobacter cases exceed a 7-day average of 170 cases per day occurred when M. domestica larval development time was <3 weeks.
Figure 3.
Campylobacter cases by week and Musca domestica larval growth times. Campylobacter cases per day are plotted against the minimum M. domestica growth times for the 14 days before the date for weeks from January 1989 to December 1999. The time taken for M. domestica larvae to develop was based on understood growth temperatures (145 days divided by the number of degrees above 12°C, up to an optimum of 36°C) (8). The temperatures were based on a maximum temperature in 47 temperature sampling sites across England and Wales in the 2 weeks before (Appendix).
The hypothesis predicts that the Campylobacter infection rates will be higher in persons living close to animal production and lower in urban settings because fly numbers will be lower. Some evidence from the United Kingdom (1,14) and Norway (15) supports this hypothesis. Seasonal changes in Campylobacter incidence that are seen around the world may result from changes in fly populations and flies' access to human and animal feces. Much emphasis on foodborne disease reduction has rightly been on kitchen hygiene, since the low infectious dose of Campylobacter makes cross-transmission from raw meats to ready-to-eat foods a substantial risk in domestic and catering environments. Fly transmission may be the most important source of infection in kitchen transmission routes, and establishments that sell ready-to-eat foods may be sources of Campylobacter, if effective fly control is not in operation. Flies may also be important in transmitting Campylobacter in poultry flocks (16) and between other agricultural animals.
While flies are regarded as important mechanical vectors of diarrheal disease in developing countries, control has largely concentrated on improving drinking water and sewage disposal. In the industrialized world, flies are thought to play a minor role in the transmission of human diarrheal diseases. Immediately intervening in the transmission of Campylobacter gastroenteritis should be possible through increased public awareness and more effective fly control.
Appendix
Supplementary Information
Temperature Data
Temperature data were acquired from the British Atmospheric Data Centre (BADC), the Natural Environment Research Council's (NERC) Designated Data Centre for the Atmospheric Sciences based at the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory in Oxfordshire, part of the Central Laboratory of the Research Councils. Data are available on-line through a World Wide Web interface (http://badc.nerc.ac.uk) by prearranged agreement. Data were collated for the period 1989–1999, with 5 locations selected for each region to provide overall coverage of the region (except London, which had only 2 centers with data available for the given time period). Location of temperature stations is shown in the Figure A1.
There were a total of 47 sites. Some of the data series were missing data points. The maximum, minimum, and average temperatures were determined for all days between January 1, 1989, and December 31, 1999. Maximum temperatures across all sites were used to calculate the presumptive minimum Musca domestica larval development times.
Methods
The data represent patients who had fecal specimens examined by a microbiology laboratory in England and Wales between 1989 and 2003 where Campylobacter was isolated from the sample. Data were acquired through well-described surveillance processes, and analysis was conducted in Microsoft Access and Excel (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA). Daily cases were based on the patient specimen date, and a 7-day rolling mean was used to eliminate the weekly cycles that reflect reduced patient sampling on weekends.
Hypothesis generation was performed through a systematic review of known and suggested causes of Campylobacter infection, particularly reflecting on changes in these risks over the period of May and June and assessing their credibility as biological drivers for the observed seasonality.
Cities and Towns Included in Figure A1
S1, London; S2, Birmingham; S3, Bristol; S4, Nottingham; S5, Sheffield; S6, Manchester; S7, Leeds; S8, Leicester; S9, Reading; S10, Plymouth; S11, Portsmouth; S12, Colchester; S13, Bradford; S14, Southampton; S15, Poole; S16, Preston; S17, Cardiff; S18, Chelmsford; S19, Norwich; S20, Ipswich; S21, Truro; S22, Oxford; S23, Shrewsbury; S24, Dudley; S25, Taunton; S26, Newport; S27, Cambridge; S28, Newcastle; S29, Chester; S30, Gloucester; S31, Swindon; S32, Chertsey; S33, Coventry; S34, Welwyn; S35, Frimley Park; S36, High Wycombe; S37, Slough; S38, Exeter; S39, Swansea; S40, Luton; S41, Torquay; S42, Derby; S43, York; S44, Worcester; S45, Northampton; S46, Bishops Stortford; S47, Hull; S48, Basildon; S49, Stoke-on-Trent; S50, Worthing; S51, Stafford; S52, Harrogate; S53, Hereford; S54, Halifax; S55, Sunderland; S56, Chesterfield and N Derbyshire; S57, Lincoln; S58, Ashford Kent; S59, Stockport; S60, Blackpool; S61, Maidstone; S62, Liverpool; S63, Bangor; S64, Llandough; S65, Lancaster; S66, Sutton Coldfield; S67, Aylesbury; S68, Grimsby; S69, Doncaster; S70, Peterborough; S71, Brighton; S72, Gateshead; S73, Kettering; S74, Southend; S75, Rhyl; S76, Cheltenham; S77, Epsom; S78, Chichester; S79, Carlisle; S80, Milton Keynes; S81, Dorchester; S82, Durham; S83, Bury; S84, Great Yarmouth; S85, Bury St Edmunds; S86, Warwick; S87, Salisbury; S88, Wolverhampton; S89, Scarborough; S90, Pontefract; S91, Bath; S92, Winchester; S93, Bishop Auckland; S94, Watford; S95, Bolton; S96, Eastbourne; S97, Oldham; S98, North Shields; S99, Burnley; S100, Ashford Middlesex; S101, Kings Lynn; S102, Warrington; S103, Wakefield; S104, Keighley; S105, Crawley; S106, Barnstaple; S107, Abergavenney; S108, Boston; S109, Nuneaton; S110, Northallerton; S111, Wrexham; S112, Macclesfield; S113, Darlington; S114, Bedford; S115, Basingstoke; S116, Weston Supermare; S117, Middlesborough; S118, Dewsbury; S119, Sutton-in-Ashfield; S120, Rochdale; S121, Guildford; S122, Worksop; S123, Wigan; S124, Stevenage; S125, Bridgend; S126, Rotherham; S127, West Bromwich; S128, Solihull; S129, Burton-upon-Trent; S130, Haverford West; S131, Carmarthen; S132, Hemel Hempstead; S133, Stockton-on-Tees; S134, Huddersfield; S135, South Shields; S136, Barnsley; S137, Whitehaven; S138, Chatham; S139, Blackburn; S140, Redditch; S141, St Leonards-on-Sea; S142, Grantham and Kesteven; S143, Ormskirk; S144, Scunthorpe; S145, Canterbury; S146, Kidderminster; S147, Dartford; S148, Aberystwyth; S149, Hexham; S150, Barrow-in Furness; S151, Redhill; S152, Margate; S153, Walsall; S154, Ashington; S155, Salford; S156, Merthyr Tydfil; S157, Stourbridge; S158, Haywards Heath; S159, Banbury; S160, Hartlepool; S161, Prescot; S162, Otley; S163, Southport; S164, Yeovil; S165, Llanelli. The number of reported Campylobacter cases per city and town were based on reports from all laboratories serving the area and are ordered from highest (S1) to lowest (S165) case numbers. Results from towns reporting smaller numbers of cases were excluded from the analysis.
Factors Linked to Campylobacter Infection
The Table A1 provides evidence for seasonal associations between factors linked to human Campylobacter infections or outbreaks.
Supplementary Material
Table A1 in PDF format.
Acknowledgments
This hypothesis arose after a lecture by Professor Sandy Cairncross at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, in the spring of 2002. I thank Fay Burgess, Radha Patel, Chris Lane, Douglas Harding, and Erol Yousef for help in preparing the data; Jim McLauchlin, Barry Evans, Chris Little, and John Edmonds for critically commenting on versions of the paper; and André Charlett for statistical support.
Biography
Dr. Nichols is an epidemiologist in the Communicable Disease Surveillance Centre, which is part of the Health Protection Agency in London. His research interests include waterborne diseases, foodborne diseases, cryptosporidiosis, and enteric infections.
Figure A1.
Temperature station locations.
Table. Risk factors that might affect Campylobacter seasonality*.
| Risk factor | Outbreaks | Evidence of seasonality | Credibility as the main seasonal driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barbecuing | Yes | Medium | Low |
| Birds | Yes | Strong | Low |
| Bottled water | No | None | Low |
| Chicken | Yes | Medium | Medium |
| Cross-contamination | Yes | None | None |
| Domestic catering | No | None | None |
| Farm visit | Yes | None | None |
| Farm animals | Yes | Weak | Low |
| Flies | No | Strong | High |
| Food handlers | Yes | None | None |
| Food packaging | No | None | None |
| Immunologic response | No | Weak | None |
| Mains supply drinking water | Yes | None | None |
| Nosocomial | Yes | None | None |
| Pets | No | Weak | Low |
| Pools, lakes, streams | No | None | None |
| Private drinking water supplies | Yes | Weak | None |
| Protozoa | No | None | Low |
| Salads and fruit | Yes | Weak | Low |
| Stir-fried food | Yes | None | None |
| The countryside | No | Weak | Medium |
| Transmission in families | Yes | None | None |
| Travel abroad | No | None | None |
| Unpasteurized milk | Yes | Weak | None |
| Weather/climate | No | Medium | Medium |
*Evidence base provided in Appendix.
Table A1. Evidence for seasonal associations between factors linked to human Campylobacter infections or outbreaks. Download PDF(71Kb, 6 pages).
| Risk factor | Outbreaks | Evidence for factor causing seasonal increase | Evidence against factor causing seasonal increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chicken/turkey | (17–23) | Chicken is the food most commonly contaminated with Campylobacter. A substantial portion of infection probably derives from this source (17–22,24–26). Some evidence shows that Campylobacter contamination of chickens is seasonal. | Chicken is not the vehicle for most sporadic Campylobacter infections (24,27,28). Little evidence exists that the seasonal differences in Campylobacter in chickens are sufficient to drive the seasonality of human disease (29-34). |
| Salads and fruit | (35-37) | Untreated leaf salads and soft fruits might be potential sources of human campylobacteriosis (25, 35-37) because these raw products are eaten without any heat treatment. | In most of the outbreaks involving salad items, cross-contamination from contaminated raw foods was thought to be involved. While seasonal import of fresh fruit or vegetables from different countries might represent a potential source of infection it would be surprising if this manifested itself as an annual nationwide outbreak across the whole of England and Wales while remaining refractory to epidemiologic investigation. Fly transmission from animal feces may be important. |
| Cross-contamination from raw meats to ready-to-eat foods | (25) | Cross-contamination from raw meats to ready to eat foods within kitchens and retail premises probably contributes significantly to Campylobacter infection. | Why cross-contamination should be strongly influenced by the season is unclear, unless levels of raw meat contamination change with the seasons. |
| Unpasteurized or inadequately pasteurized milk | (22, 38-49) | Unpasteurized or badly pasteurized milk can be a source of Campylobacter infection (22,39, 42, 45, 49-52). Milk could cause the seasonality if the numbers of Campylobacter in raw milk changed with the season and other critical control points in milk production (pasteurization) are not tightly maintained. Infections related to consumption of unpasteurized milk appear to be seasonal, with a peak in May, which suggests seasonal changes in the Campylobacter contamination of unpasteurized milk. | No evidence shows that the seasonality of human disease is largely due to unpasteurized milk because this product is not commonly consumed. No evidence shows that pasteurization varies substantially by season. |
| Birds | (53,54) | Campylobacter is common in birds. Migratory birds result in large seasonal changes in the inputs to the environment from bird feces and could contribute to human Campylobacter exposure (55). Migratory birds could be a seasonally changing driver to human disease (56). The main likely exposure route if this were the case would be direct contact with contaminated bird feces in the garden, contamination of field-grown fruit and vegetables and contamination of source waters for drinking. Bird-pecked milk is a recognized route by which Campylobacter infection can be acquired (53,54). The contamination is thought to result from birds feeding consecutively on cow feces and milk in bottles. The infections related to bird-pecked milk appear to be seasonal in distribution with a marked increase in May (57). | Bird-pecked milk is unlikely to be the cause of the worldwide seasonal distribution of Campylobacter infections. Fly transmission from bird feces, particularly farmed poultry, may be important. Evidence from extensive monitoring of ready-to-eat foods sampled at retail businesses suggests little evidence of Campylobacter contamination (Little, pers. comm.). |
| Barbecue | (17) | Barbecue use might be a contributing factor to the total Campylobacter infection because standards of food safety associated with barbecue use are likely to be poorer (17,58, 59). Case-control studies have found associations between barbecue use and sporadic Campylobacter infection (60,61). | Barbecue use on its own is unlikely a big enough, or seasonal enough, driver of disease to account for seasonal changes in incidence. |
| Food packaging | The packaging around chickens is commonly contaminated with Campylobacter, which may represent a source of some infections through cross-contamination. | Strong seasonal changes in the extent of this contamination would have to exist for this factor to affect the disease epidemiology, and no evidence for these changes exists. | |
| Food handlers/hygiene | (62-66) | Infected food handlers might represent a source of infection in catering premises. | Infections in food handlers probably are seasonal, reflecting the seasonality of Campylobacter in general, but they are probably not the driver for the overall seasonality. |
| Food, stir-fried | (17) | Stir-fried food may be contaminated through inadequately cooking raw ingredients or cross-contamination. | A seasonal change in the contamination of raw ingredients would need to exist to explain the epidemiology. |
| Flies | Flies provide a biological explanation for the spring increase in Campylobacter cases through the increase in fly numbers. Campylobacter has been isolated from flies, and the low infectious dose required to cause human disease would make this route credible. Historical records link “summer diarrhea” to flies. | Little hard evidence exists for this transmission route. | |
| Mains drinking water | (44, 67-76) | With mains water supplies, the relatively even distribution of seasonal changes in the distribution of Campylobacter cases suggests that any contamination of public supplies must be systemic (a generic problem with all supplies) or a much bigger regional difference in the incidence would be seen. Potential seasonal differences in water quality that could explain why treatment might not prevent sporadic Campylobacter infection through mains water (e.g., viable noncultivable Campylobacter in chlorine-resistant protozoa) are not supported by evidence. The rarity of outbreaks associated with public water supplies suggests that drinking water is not a substantial source of Campylobacter infection. | |
| Private drinking water supplies/untreated surface water, rain water, or well water | (22, 75,77-86) | Waterborne infection associated with private water supplies can result in outbreaks of infection because many people drink the contaminated water (87). Campylobacter is the most common organism causing these outbreaks. A seasonal change in water quality could occur. | Seasonal changes in water contamination should trigger outbreaks rather than a national increase in sporadic disease. The comparative rarity of outbreaks associated with private supplies suggests that this source does not substantially contribute to the total illness that is seen to change dramatically with the season. Given the influence of surface water on the microbiologic quality of private water supplies, we expect that the seasonal occurrence of Campylobacter might be more influenced by rainfall than time of year, which does not appear to happen. |
| Bottled water | In a case-case study of Campylobacter, people with C. coli infection were more likely to have drunk bottled water than were those with C. jejuni infection (88). Natural mineral water is not disinfected and could be a widely dispersed product that experiences seasonal changes in contamination. | Sources of water that are used to produce natural mineral water and other bottled waters are relatively well protected. These groundwaters are unlikely to be contaminated with Campylobacter. If bottled water consumption is a risk factor, it should come up as such in analytic epidemiologic studies of Campylobacter infection. It is unclear why the seasonal pattern of infection should be so constant both geographically and annually if bottled water contamination is such a substantial contributor to human disease. | |
| Pools, lakes, and streams | Potential exists for illness after swallowing contaminated recreational water (89-92). Water sports in natural waters can be a source of exposure. If the contamination of water with Campylobacter is seasonal, then any seasonality in this group could be linked to either changes in water quality or behavior. | Illness associated with recreational water activity has not been established, and this is unlikely to be the source of the spring increase in campylobacteriosis. Little evidence shows that the change in recreational water activity in the spring is enough to explain the seasonal change in Campylobacter cases. | |
| Within-family transmission | (93) | Person-to-person transmission can occur. | No obvious reason explains why within-household transmission of Campylobacter should be seasonal, given that personal hygiene practices are not likely to change substantially over a matter of weeks. |
| Domestic catering | Domestic food preparation may contribute to human Campylobacter disease. | Fly transmission within kitchens may contribute to transmission, and this would likely be seasonal. Little else within the kitchen environment, other than the contamination of raw food ingredients, is likely to vary seasonally. | |
| Nursery/childcare/school | (94,95) | As Campylobacter is common in children, transmission may occur within the childcare setting. | No evidence shows that infections in childcare are common or that they vary through the year. |
| Nosocomial transmission | (96) | Nosocomial transmission cannot account for the national seasonal increase in cases. | |
| Pets | Pets, particularly kittens and puppies, have been postulated as a source of Campylobacter. Canine births, as recorded in Kennel Club and Guide Dogs for the Blind Association records, show a strong seasonal distribution, and this factor has been proposed as a driver for human disease (97). | Little evidence shows that the seasonal change in Campylobacter is directly related to pets, although fly transmission from animal feces may be important. | |
| Farm animals | (98) | Campylobacter strains isolated from cattle have been linked to strains from human infections (99,100). Cattle and sheep represent a reservoir of Campylobacter (101,102), and milkborne outbreaks (23, 39,42,45,49-55) suggest that other routes may occur. Fecal shedding by sheep may be more frequent around lambing (103). Seasonal differences in Campylobacter infections have also been demonstrated in rhesus monkeys, other agricultural animals, and birds (31, 32, 104-107). | Any seasonality of Campylobacter infection or colonization in animals could cause seasonality in humans, but this seasonality is most likely to result from the contamination of food. Fly transmission from animal feces may be important. |
| Farm visits | (108) | Visits to farms can expose children to common zoonotic enteric pathogens, including Campylobacter. | Any seasonality of farm visits is unlikely to contribute to the seasonal distribution of all cases. |
| The countryside | Direct environmental exposure could occur through walking in the country. | This activity may be seasonal but is unlikely to contribute to the strong seasonal distribution of cases. | |
| Travel | Campylobacter has been linked to overseas travel (109-111), including military service (112,113), and probably represents a significant percentage of all cases of travelers' diarrhea (114-117). In some countries, >50% of Campylobacter cases may be linked to foreign travel (118) | The seasonality of Campylobacter does not follow the seasonality of travel abroad. | |
| Weather/climate | In some developing countries a higher incidence was seen in the rainy season (119, 120), which suggests flies might be contributory. Although Campylobacter is more common during the summer months and has been linked to temperature (121), no direct relationship was seen between temperature and cases of human disease. The different seasonal distribution in different countries appears to be partly temperature-related | Little evidence shows that Campylobacter is associated with rainfall. There was no association between thermophilic Campylobacter in lambs at slaughter and rainfall (105). The main seasonal driver for Campylobacter infection is not likely to be rainfall itself, since the increase appears to occur annually, irrespective of when most rain falls. | |
| Immunologic response | The immunologic response to Campylobacter exposure could change throughout the year. This hypothesis has been studied in male rhesus monkeys (104). A marked seasonality was seen ,with the frequency of TH1-type cytokine synthesis in the summer being markedly greater than in the winter, whereas TH2-type cytokine expression did not vary between the seasons. | Current evidence suggests that seasonal changes in immunologic response to Campylobacter infection are unlikely to account for the major seasonal changes in Campylobacter incidence. |
Footnotes
Suggested citation for this article: Nichols GL. Fly transmission of Campylobacter. Emerg Infect Dis [serial on the Internet]. 2005 Mar [date cited]. Available from http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid1103.040460
References
- 1.Tam CC. Campylobacter reporting at its peak year of 1998: don't count your chickens yet. Commun Dis Public Health. 2001;4:194–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Frost JA, Gillespie IA, O'Brien SJ. Public health implications of campylobacter outbreaks in England and Wales, 1995–9: epidemiological and microbiological investigations. Epidemiol Infect. 2002;128:111–8. 10.1017/S0950268802006799 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Adak GK, Cowden JM, Nicholas S, Evans HS. The Public Health Laboratory Service national case-control study of primary indigenous sporadic cases of campylobacter infection. Epidemiol Infect. 1995;115:15–22. 10.1017/S0950268800058076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gillespie IA, O'Brien SJ, Frost JA, Adak GK, Horby P, Swan AV, et al. A case-case comparison of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni infection: a tool for generating hypotheses. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Louis VR, Gillespie IA, O'Brien SJ, Russek-Cohen E, Pearson AD, Colwell RR. Temperature driven Campylobacter seasonality in England and Wales. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005;71:85–92. 10.1128/AEM.71.1.85-92.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Khalil K, Lindblom GB, Mazhar K, Kaijser B. Flies and water as reservoirs for bacterial enteropathogens in urban and rural areas in and around Lahore, Pakistan. Epidemiol Infect. 1994;113:435–44. 10.1017/S0950268800068448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rosef O, Kapperud G. House flies (Musca domestica) as possible vectors of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983;45:381–3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shane SM, Montrose MS, Harrington KS. Transmission of Campylobacter jejuni by the housefly (Musca domestica). Avian Dis. 1985;29:384–91. 10.2307/1590499 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chavasse DC, Shier RP, Murphy OA, Huttly SR, Cousens SN, Akhtar T. Impact of fly control on childhood diarrhoea in Pakistan: community-randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;353:22–5. 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)03366-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cohen D, Green M, Block C, Slepon R, Ambar R, Wasserman SS, et al. Reduction of transmission of shigellosis by control of houseflies (Musca domestica). Lancet. 1991;337:993–7. 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92657-N [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Emerson PM, Lindsay SW, Walraven GE, Faal H, Bogh C, Lowe K, et al. Effect of fly control on trachoma and diarrhoea. Lancet. 1999;353:1401–3. 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)09158-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Niven J. Summer diarrhoea and enteric fever. Proc R Soc Med. 1910;III(Epidem. Sect.):131–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Kettle DS. Medical and veterinary entomology. 2nd ed. Wallingford (UK): CABI Publishing; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Skirrow MB. A demographic survey of campylobacter, salmonella, and shigella infections in England. A Public Health Laboratory Service survey. Epidemiol Infect. 1987;99:647–57. 10.1017/S0950268800066504 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kapperud G, Aasen S. Descriptive epidemiology of infections due to thermotolerant Campylobacter spp. in Norway, 1979–1988. APMIS. 1992;100:883–90. 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1992.tb04014.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hald B, Skovgard H, Bang DD, Pedersen K, Dybdahl J, Jespersen JB, et al. Flies and Campylobacter infection of broiler flocks. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:1490–2. 10.3201/eid1008.040129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Allerberger F, Al Jazrawi N, Kreidl P, Dierich MP, Feierl G, Hein I, et al. Barbecued chicken causing a multi-state outbreak of Campylobacter jejuni enteritis. Infection. 2003;31:19–23. 10.1007/s15010-002-3088-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Evans MR, Lane W, Frost JA, Nylen G. A campylobacter outbreak associated with stir-fried food. Epidemiol Infect. 1998;121:275–9. 10.1017/S0950268898001204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kessel AS, Gillespie IA, O'Brien SJ, Adak GK, Humphrey TJ, Ward LR. General outbreaks of infectious intestinal disease linked with poultry, England and Wales, 1992–1999. Commun Dis Public Health. 2001;4:171–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Murphy O, Gray J, Gordon S, Bint AJ. An outbreak of campylobacter food poisoning in a health care setting. J Hosp Infect. 1995;30:225–8. 10.1016/S0195-6701(95)90318-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pearson AD, Greenwood MH, Donaldson J, Healing TD, Jones DM, Shahamat M, et al. Continuous source outbreak of campylobacteriosis traced to chicken. J Food Prot. 2000;63:309–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pebody RG, Ryan MJ, Wall PG. Outbreaks of campylobacter infection: rare events for a common pathogen. Commun Dis Rep CDR Rev. 1997;7:R33–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shandera WX, Tormey MP, Blaser MJ. An outbreak of bacteremic Campylobacter jejuni infection. Mt Sinai J Med. 1992;59:53–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rodrigues LC, Cowden JM, Wheeler JG, Sethi D, Wall PG, Cumberland P, et al. The study of infectious intestinal disease in England: risk factors for cases of infectious intestinal disease with Campylobacter jejuni infection. Epidemiol Infect. 2001;127:185–93. 10.1017/S0950268801006057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of Campylobacter enteritis associated with cross-contamination of food—Oklahoma, 1996. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1998;47:129–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Layton MC, Calliste SG, Gomez TM, Patton C, Brooks S. A mixed foodborne outbreak with Salmonella heidelberg and Campylobacter jejuni in a nursing home. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1997;18:115–21. 10.1086/647565 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Neal KR, Slack RC. Diabetes mellitus, anti-secretory drugs and other risk factors for campylobacter gastro-enteritis in adults: a case-control study. Epidemiol Infect. 1997;119:307–11. 10.1017/S0950268897008224 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Adak GK, Cowden JM, Nicholas S, Evans HS. The Public Health Laboratory Service national case-control study of primary indigenous sporadic cases of campylobacter infection. Epidemiol Infect. 1995;115:15–22. 10.1017/S0950268800058076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wilson IG. Salmonella and campylobacter contamination of raw retail chickens from different producers: a six-year survey. Epidemiol Infect. 2002;129:635–45. 10.1017/S0950268802007665 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hanninen ML, Perko-Makela P, Pitkala A, Rautelin H. A three-year study of Campylobacter jejuni genotypes in humans with domestically acquired infections and in chicken samples from the Helsinki area. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:1998–2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hudson JA, Nicol C, Wright J, Whyte R, Hasell SK. Seasonal variation of Campylobacter types from human cases, veterinary cases, raw chicken, milk and water. J Appl Microbiol. 1999;87:115–24. 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1999.00806.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wallace JS, Stanley KN, Currie JE, Diggle PJ, Jones K. Seasonality of thermophilic Campylobacter populations in chickens. J Appl Microbiol. 1997;82:219–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Humphrey TJ, Henley A, Lanning DG. The colonization of broiler chickens with Campylobacter jejuni: some epidemiological investigations. Epidemiol Infect. 1993;110:601–7. 10.1017/S0950268800051025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kapperud G, Skjerve E, Vik L, Hauge K, Lysaker A, Aalmen I, et al. Epidemiological investigation of risk factors for campylobacter colonization in Norwegian broiler flocks. Epidemiol Infect. 1993;111:245–55. 10.1017/S0950268800056958 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kirk M, Waddell R, Dalton C, Creaser A, Rose N. A prolonged outbreak of Campylobacter infection at a training facility. Commun Dis Intell. 1997;21:57–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Roels TH, Wickus B, Bostrom HH, Kazmierczak JJ, Nicholson MA, Kurzynski TA, et al. A foodborne outbreak of Campylobacter jejuni (O:33) infection associated with tuna salad: a rare strain in an unusual vehicle. Epidemiol Infect. 1998;121:281–7. 10.1017/S0950268898001174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ronveaux O, Quoilin S, Van Loock F, Lheureux P, Struelens M, Butzler JP. A Campylobacter coli foodborne outbreak in Belgium. Acta Clin Belg. 2000;55:307–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of Campylobacter jejuni infections associated with drinking unpasteurized milk procured through a cow-leasing program—Wisconsin, 2001. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2002;51:548–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Evans MR, Roberts RJ, Ribeiro CD, Gardner D, Kembrey D. A milk-borne campylobacter outbreak following an educational farm visit. Epidemiol Infect. 1996;117:457–62. 10.1017/S0950268800059112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fahey T, Morgan D, Gunneburg C, Adak GK, Majid F, Kaczmarski E. An outbreak of Campylobacter jejuni enteritis associated with failed milk pasteurisation. J Infect. 1995;31:137–43. 10.1016/S0163-4453(95)92160-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jones PH, Willis AT, Robinson DA, Skirrow MB, Josephs DS. Campylobacter enteritis associated with the consumption of free school milk. J Hyg (Lond). 1981;87:155–62. 10.1017/S0022172400069357 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kalman M, Szollosi E, Czermann B, Zimanyi M, Szekeres S, Kalman M. Milkborne campylobacter infection in Hungary. J Food Prot. 2000;63:1426–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Korlath JA, Osterholm MT, Judy LA, Forfang JC, Robinson RA. A point-source outbreak of campylobacteriosis associated with consumption of raw milk. J Infect Dis. 1985;152:592–6. 10.1093/infdis/152.3.592 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lind L, Sjogren E, Melby K, Kaijser B. DNA fingerprinting and serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from epidemic outbreaks. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:892–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Morgan D, Gunneberg C, Gunnell D, Healing TD, Lamerton S, Soltanpoor N, et al. An outbreak of Campylobacter infection associated with the consumption of unpasteurised milk at a large festival in England. Eur J Epidemiol. 1994;10:581–5. 10.1007/BF01719576 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Porter IA, Reid TM. A milk-borne outbreak of Campylobacter infection. J Hyg (Lond). 1980;84:415–9. 10.1017/S0022172400026942 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Robinson DA, Edgar WJ, Gibson GL, Matchett AA, Robertson L. Campylobacter enteritis associated with consumption of unpasteurised milk. BMJ. 1979;1:1171–3. 10.1136/bmj.1.6172.1171 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Robinson DA, Jones DM. Milk-borne campylobacter infection. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1981;282:1374–6. 10.1136/bmj.282.6273.1374 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wood RC, MacDonald KL, Osterholm MT. Campylobacter enteritis outbreaks associated with drinking raw milk during youth activities. A 10-year review of outbreaks in the United States. JAMA. 1992;268:3228–30. 10.1001/jama.1992.03490220072031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lehner A, Schneck C, Feierl G, Pless P, Deutz A, Brandl E, et al. Epidemiologic application of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis to an outbreak of Campylobacter jejuni in an Austrian youth centre. Epidemiol Infect. 2000;125:13–6. 10.1017/S0950268899004318 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Djuretic T, Wall PG, Nichols G. General outbreaks of infectious intestinal disease associated with milk and dairy products in England and Wales: 1992 to 1996. Commun Dis Rep CDR Rev. 1997;7:R41–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Public Health Laboratory Service Study Group. Cryptosporidiosis in England and Wales: prevalence and clinical and epidemiological features. BMJ. 1990;300:774–7. 10.1136/bmj.300.6727.774 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Riordan T, Humphrey TJ, Fowles A. A point source outbreak of campylobacter infection related to bird-pecked milk. Epidemiol Infect. 1993;110:261–5. 10.1017/S0950268800068187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Stuart J, Sufi F, McNulty C, Park P. Outbreak of campylobacter enteritis in a residential school associated with bird-pecked bottle tops. Commun Dis Rep CDR Rev. 1997;7:R38–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Waldenstrom J, Broman T, Carlsson I, Hasselquist D, Achterberg RP, Wagenaar JA, et al. Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter lari, and Campylobacter coli in different ecological guilds and taxa of migrating birds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002;68:5911–7. 10.1128/AEM.68.12.5911-5917.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Broman T, Palmgren H, Bergstrom S, Sellin M, Waldenstrom J, Danielsson-Tham ML, et al. Campylobacter jejuni in black-headed gulls (Larus ridibundus): prevalence, genotypes, and influence on C. jejuni epidemiology. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:4594–602. 10.1128/JCM.40.12.4594-4602.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sopwith W, Ashton M, Frost JA, Tocque K, O'Brien S, Regan M, et al. Enhanced surveillance of campylobacter infection in the north west of England 1997–1999. J Infect. 2003;46:35–45. 10.1053/jinf.2002.1072 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Butzler JP, Oosterom J. Campylobacter: pathogenicity and significance in foods. Int J Food Microbiol. 1991;12:1–8. 10.1016/0168-1605(91)90043-O [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kapperud G. Campylobacter infection. Epidemiology, risk factors and preventive measures. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1994;114:795–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ikram R, Chambers S, Mitchell P, Brieseman MA, Ikam OH. A case control study to determine risk factors for campylobacter infection in Christchurch in the summer of 1992–3. N Z Med J. 1994;107:430–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kapperud G, Skjerve E, Bean NH, Ostroff SM, Lassen J. Risk factors for sporadic Campylobacter infections: results of a case-control study in southeastern Norway. J Clin Microbiol. 1992;30:3117–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Fitzgerald C, Helsel LO, Nicholson MA, Olsen SJ, Swerdlow DL, Flahart R, et al. Evaluation of methods for subtyping Campylobacter jejuni during an outbreak involving a food handler. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:2386–90. 10.1128/JCM.39.7.2386-2390.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Olsen SJ, Hansen GR, Bartlett L, Fitzgerald C, Sonder A, Manjrekar R, et al. An outbreak of Campylobacter jejuni infections associated with food handler contamination: the use of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:164–7. 10.1086/317657 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Gent RN, Telford DR, Syed Q. An outbreak of campylobacter food poisoning at a university campus. Commun Dis Public Health. 1999;2:39–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Wight JP, Rhodes P, Chapman PA, Lee SM, Finner P. Outbreaks of food poisoning in adults due to Escherichia coli O111 and campylobacter associated with coach trips to northern France. Epidemiol Infect. 1997;119:9–14. 10.1017/S0950268897007620 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Winquist AG, Roome A, Mshar R, Fiorentino T, Mshar P, Hadler J. Outbreak of campylobacteriosis at a senior center. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001;49:304–7. 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2001.4930304.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Alary M, Nadeau D. An outbreak of Campylobacter enteritis associated with a community water supply. Can J Public Health. 1990;81:268–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Engberg J, Gerner-Smidt P, Scheutz F, Moller NE, On SL, Molbak K. Water-borne Campylobacter jejuni infection in a Danish town—a 6-week continuous source outbreak. Clin Microbiol Infect. 1998;4:648–56. 10.1111/j.1469-0691.1998.tb00348.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Godoy P, Artigues A, Nuin C, Aramburu J, Perez M, Dominguez A, et al. Outbreak of gastroenteritis caused by Campylobacter jejuni transmitted through drinking water. Med Clin (Barc). 2002;119:695–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hanninen ML, Haajanen H, Pummi T, Wermundsen K, Katila ML, Sarkkinen H, et al. Detection and typing of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli and analysis of indicator organisms in three waterborne outbreaks in Finland. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003;69:1391–6. 10.1128/AEM.69.3.1391-1396.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Jones IG, Roworth M. An outbreak of Escherichia coli O157 and campylobacteriosis associated with contamination of a drinking water supply. Public Health. 1996;110:277–82. 10.1016/S0033-3506(96)80089-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Holme R. Drinking water contamination in Walkerton, Ontario: positive resolutions from a tragic event. Water Sci Technol. 2003;47:1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Maurer AM, Sturchler D. A waterborne outbreak of small round structured virus, campylobacter and shigella co-infections in La Neuveville, Switzerland, 1998. Epidemiol Infect. 2000;125:325–32. 10.1017/S0950268899004495 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Melby K, Gondrosen B, Gregusson S, Ribe H, Dahl OP. Waterborne campylobacteriosis in northern Norway. Int J Food Microbiol. 1991;12:151–6. 10.1016/0168-1605(91)90064-V [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Miettinen IT, Zacheus O, von Bonsdorff CH, Vartiainen T. Waterborne epidemics in Finland in 1998–1999. Water Sci Technol. 2001;43:67–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Sacks JJ, Lieb S, Baldy LM, Berta S, Patton CM, White MC, et al. Epidemic campylobacteriosis associated with a community water supply. Am J Public Health. 1986;76:424–8. 10.2105/AJPH.76.4.424 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Duke LA, Breathnach AS, Jenkins DR, Harkis BA, Codd AW. A mixed outbreak of cryptosporidium and campylobacter infection associated with a private water supply. Epidemiol Infect. 1996;116:303–8. 10.1017/S0950268800052614 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Furtado C, Adak GK, Stuart JM, Wall PG, Evans HS, Casemore DP. Outbreaks of waterborne infectious intestinal disease in England and Wales, 1992–5. Epidemiol Infect. 1998;121:109–19. 10.1017/S0950268898001083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Melby KK, Svendby JG, Eggebo T, Holmen LA, Andersen BM, Lind L, et al. Outbreak of Campylobacter infection in a subartic community. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000;19:542–4. 10.1007/s100960000316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Rautelin H, Koota K, von Essen R, Jahkola M, Siitonen A, Kosunen TU. Waterborne Campylobacter jejuni epidemic in a Finnish hospital for rheumatic diseases. Scand J Infect Dis. 1990;22:321–6. 10.3109/00365549009027054 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Stehr-Green JK, Nicholls C, McEwan S, Payne A, Mitchell P. Waterborne outbreak of Campylobacter jejuni in Christchurch: the importance of a combined epidemiologic and microbiologic investigation. N Z Med J. 1991;104:356–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Campylobacter among attendees of the Washington County Fair—New York, 1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1999;48:803–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Bopp DJ, Sauders BD, Waring AL, Ackelsberg J, Dumas N, Braun-Howland E, et al. Detection, isolation, and molecular subtyping of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Campylobacter jejuni associated with a large waterborne outbreak. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:174–80. 10.1128/JCM.41.1.174-180.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Millson M, Bokhout M, Carlson J, Spielberg L, Aldis R, Borczyk A, et al. An outbreak of Campylobacter jejuni gastroenteritis linked to meltwater contamination of a municipal well. Can J Public Health. 1991;82:27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Aho M, Kurki M, Rautelin H, Kosunen TU. Waterborne outbreak of Campylobacter enteritis after outdoors infantry drill in Utti, Finland. Epidemiol Infect. 1989;103:133–41. 10.1017/S0950268800030430 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Merritt A, Miles R, Bates J. An outbreak of Campylobacter enteritis on an island resort, north Queensland. Commun Dis Intell. 1999;23:215–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Said B, Wright F, Nichols GL, Reacher M, Rutter M. Outbreaks of infectious disease associated with private drinking water supplies in England and Wales 1970–2000. Epidemiol Infect. 2003;130:469–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Gillespie IA, O'Brien SJ, Frost JA, Adak GK, Horby P, Swan AV, et al. A case-case comparison of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni infection: a tool for generating hypotheses. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:937–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Moore J, Caldwell P, Millar B. Molecular detection of Campylobacter spp. in drinking, recreational and environmental water supplies. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2001;204:185–9. 10.1078/1438-4639-00096 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Moore JE, Caldwell PS, Millar BC, Murphy PG. Occurrence of Campylobacter spp. in water in Northern Ireland: implications for public health. Ulster Med J. 2001;70:102–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Savill MG, Hudson JA, Ball A, Klena JD, Scholes P, Whyte RJ, et al. Enumeration of Campylobacter in New Zealand recreational and drinking waters. J Appl Microbiol. 2001;91:38–46. 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01337.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Hernandez J, Fayos A, Alonso JL, Owen RJ. Ribotypes and AP-PCR fingerprints of thermophilic campylobacters from marine recreational waters. J Appl Bacteriol. 1996;80:157–64. 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1996.tb03204.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Minaev VI, Cherkasskii BL, Volokhovich TT, Minaeva NZ, Pertin OS, Gorelov AV, et al. The leading pathways and factors in the transmission of the causative agents of campylobacteriosis under current conditions. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1995; (2):39–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Goossens H, Giesendorf BA, Vandamme P, Vlaes L, Van den BC, Koeken A, et al. Investigation of an outbreak of Campylobacter upsaliensis in day care centers in Brussels: analysis of relationships among isolates by phenotypic and genotypic typing methods. J Infect Dis. 1995;172:1298–305. 10.1093/infdis/172.5.1298 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Vandamme P, Pugina P, Benzi G, Van Etterijck R, Vlaes L, Kersters K, et al. Outbreak of recurrent abdominal cramps associated with Arcobacter butzleri in an Italian school. J Clin Microbiol. 1992;30:2335–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Morooka T, Umeda A, Fujita M, Matano H, Fujimoto S, Yukitake K, et al. Epidemiologic application of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis to an outbreak of Campylobacter fetus meningitis in a neonatal intensive care unit. Scand J Infect Dis. 1996;28:269–70. 10.3109/00365549609027170 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Evans SJ. The seasonality of canine births and human campylobacteriosis: a hypothesis. Epidemiol Infect. 1993;110:267–72. 10.1017/S0950268800068199 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Ellis A, Irwin R, Hockin J, Borczyk A, Woodward D, Johnson W. Outbreak of Campylobacter infection among farm workers: an occupational hazard. Can Commun Dis Rep. 1995;21:153–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Schouls LM, Reulen S, Duim B, Wagenaar JA, Willems RJ, Dingle KE, et al. Comparative genotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by amplified fragment length polymorphism, multilocus sequence typing, and short repeat sequencing: strain diversity, host range, and recombination. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:15–26. 10.1128/JCM.41.1.15-26.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Nielsen EM, Engberg J, Fussing V, Petersen L, Brogren CH, On SL. Evaluation of phenotypic and genotypic methods for subtyping Campylobacter jejuni isolates from humans, poultry, and cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:3800–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Savill M, Hudson A, Devane M, Garrett N, Gilpin B, Ball A. Elucidation of potential transmission routes of Campylobacter in New Zealand. Water Sci Technol. 2003;47:33–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Stanley K, Jones K. Cattle and sheep farms as reservoirs of Campylobacter. J Appl Microbiol. 2003;94(Suppl):S104–13. 10.1046/j.1365-2672.94.s1.12.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Jones K, Howard S, Wallace JS. Intermittent shedding of thermophilic campylobacters by sheep at pasture. J Appl Microbiol. 1999;86:531–6. 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1999.00702.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Mann DR, Akinbami MA, Gould KG, Ansari AA. Seasonal variations in cytokine expression and cell-mediated immunity in male rhesus monkeys. Cell Immunol. 2000;200:105–15. 10.1006/cimm.2000.1623 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Stanley KN, Wallace JS, Currie JE, Diggle PJ, Jones K. Seasonal variation of thermophilic campylobacters in lambs at slaughter. J Appl Microbiol. 1998;84:1111–6. 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1998.00450.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Stanley KN, Wallace JS, Currie JE, Diggle PJ, Jones K. The seasonal variation of thermophilic campylobacters in beef cattle, dairy cattle and calves. J Appl Microbiol. 1998;85:472–80. 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1998.853511.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Willis WL, Murray C. Campylobacter jejuni seasonal recovery observations of retail market broilers. Poult Sci. 1997;76:314–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Srour SF, Rishpon S, Rubin L, Warman S. An outbreak of Campylobacter jejuni enteritis after farm visit in Haifa subdistrict. Harefuah. 2002;141:683–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Beecham HJ III, Lebron CI, Echeverria P. Short report: impact of traveler's diarrhea on United States troops deployed to Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997;57:699–701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Mattila L, Siitonen A, Kyronseppa H, Simula I, Oksanen P, Stenvik M, et al. Seasonal variation in etiology of travelers' diarrhea. Finnish-Moroccan Study Group. J Infect Dis. 1992;165:385–8. 10.1093/infdis/165.2.385 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Pearson AD, Healing TD. The surveillance and control of campylobacter infection. Commun Dis Rep CDR Rev. 1992;2:R133–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Beecham HJ III, Lebron CI, Echeverria P. Short report: impact of traveler's diarrhea on United States troops deployed to Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997;57:699–701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Haberberger RL Jr, Mikhail IA, Burans JP, Hyams KC, Glenn JC, Diniega BM, et al. Travelers' diarrhea among United States military personnel during joint American-Egyptian armed forces exercises in Cairo, Egypt. Mil Med. 1991;156:27–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Black RE. Epidemiology of travelers' diarrhea and relative importance of various pathogens. Rev Infect Dis. 1990;12(Suppl 1):S73–9. 10.1093/clinids/12.Supplement_1.S73 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Black RE. Pathogens that cause travelers' diarrhea in Latin America and Africa. Rev Infect Dis. 1986;8(Suppl 2):S131–5. 10.1093/clinids/8.Supplement_2.S131 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Brasseur D, Casimir G, Goyens P. Campylobacter jejuni and infantile traveller's diarrhoea. Eur J Pediatr. 1986;144:517–8. 10.1007/BF00441757 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Echeverria P, Blacklow NR, Sanford LB, Cukor GG. Travelers' diarrhea among American Peace Corps volunteers in rural Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1981;143:767–71. 10.1093/infdis/143.6.767 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Kapperud G, Lassen J, Ostroff SM, Aasen S. Clinical features of sporadic Campylobacter infections in Norway. Scand J Infect Dis. 1992;24:741–9. 10.3109/00365549209062459 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Pazzaglia G, Bourgeois AL, Araby I, Mikhail I, Podgore JK, Mourad A, et al. Campylobacter-associated diarrhoea in Egyptian infants: epidemiology and clinical manifestations of disease and high frequency of concomitant infections. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1993;11:6–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Bichile LS, Saraswati K, Popat UR, Nanivadekar SA, Deodhar LP. Acute Campylobacter jejuni enteritis in 385 hospitalised patients. J Assoc Physicians India. 1992;40:164–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Louis V, Russek-Cohen E, Rubinstein MI, O'Brien SJ, Pearson AD, Colwell RR. Seasonality of Campylobacter cases in England and Wales (1990–1999) [abstract]. Presented at the 103rd General Meeting of the American Society for Microbiology; 2003. May 17–22; Washington, DC. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table A1 in PDF format.