Abstract
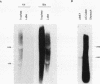
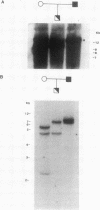
A cystic fibrosis trachea cDNA library was constructed and probed with a synthetic oligonucleotide containing a consensus sequence recently identified in human intestinal mucin. One of the isolated clones, AMN-22, has been characterized extensively. The cDNA sequence of this 884-bp fragment was determined, and revealed a tandem repeat structure rich in threonine and proline residues. The repeating sequence of AMN-22 was similar but not identical to that determined for gut mucin. When examined by Northern analysis, the mRNA hybridizing to AMN-22 is extremely polydisperse in cystic fibrosis (CF) trachea, with apparent message length varying from approximately 2 kb to greater than 10 kb. A similar pattern was observed, with less abundant message, in CF bronchiectatic lung parenchyma. The lung cDNA hybridized to a similarly polydisperse message in ulcerative colitis colon RNA, but did not hybridize to control RNA from U937 lymphoma cells or stomach RNA. Pedigree analysis of restriction digests of genomic DNA revealed a pattern indicating a single polymorphic locus for the mucin gene expressed in the lung and the intestine. Southern analyses of human:mouse somatic cell hybrid cell lines allow a chromosomal localization for the mucin gene to human chromosome II, within the region 11p13-11pTer. Taken together, these data demonstrate that a polymorphic gene encodes a mucin core polypeptide expressed in both lung and intestine.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruffo A., Seed B. Molecular cloning of a CD28 cDNA by a high-efficiency COS cell expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8573–8577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlstedt I., Sheehan J. K., Corfield A. P., Gallagher J. T. Mucous glycoproteins: a gel of a problem. Essays Biochem. 1985;20:40–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chace K. V., Flux M., Sachdev G. P. Comparison of physicochemical properties of purified mucus glycoproteins isolated from respiratory secretions of cystic fibrosis and asthmatic patients. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7334–7341. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng P. W., Boat T. F., Cranfill K., Yankaskas J. R., Boucher R. C. Increased sulfation of glycoconjugates by cultured nasal epithelial cells from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):68–72. doi: 10.1172/JCI114171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M., Bhaskar K. R., Horton J. R., Das I., Lopez-Vidriero M. T., Reid L. The separation and characterization of bronchial glycoproteins by density-gradient methods. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):557–569. doi: 10.1042/bj1670557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt A. E., Timpte C. S., Abernethy J. L., Toumadje A., Johnson W. C., Jr, Hill R. L. Structural properties of porcine submaxillary gland apomucin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11339–11344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldhoff P. A., Bhavanandan V. P., Davidson E. A. Purification, properties, and analysis of human asthmatic bronchial mucin. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2430–2436. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendler S., Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Duhig T., Rothbard J., Burchell J. A highly immunogenic region of a human polymorphic epithelial mucin expressed by carcinomas is made up of tandem repeats. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12820–12823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gum J. R., Byrd J. C., Hicks J. W., Toribara N. W., Lamport D. T., Kim Y. S. Molecular cloning of human intestinal mucin cDNAs. Sequence analysis and evidence for genetic polymorphism. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6480–6487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. D., Jr, Schwyzer M., Steinman H. M., Hill R. L. Ovine submaxillary mucin. Primary structure and peptide substrates of UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine:mucin transferase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3799–3804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. C., Lynn W. S., Kaufman B. Resolution of the major components of human lung mucosal gel and their capabilities for reaggregation and gel formation. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 4;18(18):4030–4037. doi: 10.1021/bi00585a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Brown J. A., Haley L. L., Byers M. G., Eddy R. L., Cooper E. S., Goggin A. P. Assignment of the beta-glucuronidase structural gene to the pter leads to q22 region of chromosome 7 in man. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;21(1-2):99–104. doi: 10.1159/000130882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L. Mapping the human genome, cloned genes, DNA polymorphisms, and inherited disease. Adv Hum Genet. 1982;12:341–452. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8315-8_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T., Eddy R., Haley L., Byers M., Henry M., Fujita T., Matsui H., Taniguchi T. Interleukin 2 (IL2) is assigned to human chromosome 4. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 May;10(3):315–318. doi: 10.1007/BF01535253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam P. Y., Verdugo P. Control of mucus hydration as a Donnan equilibrium process. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):340–342. doi: 10.1038/292340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesley A., Mantle M., Man D., Qureshi R., Forstner G., Forstner J. Neutral and acidic species of human intestinal mucin. Evidence for different core peptides. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7955–7959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward H., Horsey B., Bhavanandan V. P., Davidson E. A. Isolation, purification, and properties of respiratory mucus glycoproteins. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 16;21(4):694–701. doi: 10.1021/bi00533a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]