This surveillance can help in assessments of the prevalence of wild animal-to-human transmission.
Keywords: Avian influenza, wild ducks, migratory waterfowl, surveillance, Texas, waterfowl, wintering grounds, zoonoses, research
Abstract
We studied the prevalence of influenza A virus in wintering waterfowl from the Central Flyway on the Gulf Coast of Texas. Of 5,363 hunter-harvested migratory and resident waterfowl and wetland-associated game birds sampled during 3 consecutive hunting seasons (September–January 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008–09), real-time reverse transcription–PCR detected influenza A matrix sequences in 8.5% of samples, H5 in 0.7%, and H7 in 0.6%. Virus isolation yielded 134 influenza A viruses, including N1–N9, H1–H7, H10, and H11 subtypes. Low-pathogenicity H7 subtype was isolated during January, September, and November 2007 and January 2008; low-pathogenicity H5 subtype was isolated during November and December 2007.
Wild waterfowl, primarily species in the orders Charadriiformes and Anseriformes (1), are natural reservoirs for type A influenza viruses. These viruses, which are occasionally transmitted to other species, including humans, poultry, and swine, result in subclinical to highly pathogenic diseases. Two subtypes (H5 and H7) have been most frequently associated with high pathogenicity in poultry and are of considerable interest to the poultry industry and to researchers who study avian influenza viruses (AIVs) (2–4). The migratory nature of many waterfowl species and the persistence of AIV in them present a potential vehicle for global dissemination of influenza viruses, as well as a constant source of viruses and genetic material for new pandemic strains. Preventing the introduction and adaptation of wild bird–origin AIVs to other susceptible species is an efficient strategy for minimizing the effects of AIV on global health and the global economy (5,6). Thus, surveillance in reservoir species is crucial for identifying viruses and gene pools with interspecies and intraspecies transmission potential.
In North America, migratory birds use 4 major flyways: Pacific, Central, Mississippi, and Atlantic (www.flyways.us). Three flyways (Pacific, Mississippi, and Atlantic) are well represented in the literature that addresses AIV surveillance (summarized in [7]); however, data are limited for the Central Flyway (8–10). Approximately 90% of waterfowl that use the Central Flyway winter in Texas. Of these, ≈10 million ducks and geese winter in wetlands throughout the state, whereas 1–3 million ducks and >1 million geese winter along the Texas Gulf Coast (11). Before the implementation of surveillance programs to detect subtype H5N1 highly pathogenic AIV, few surveillance studies included migratory waterfowl on their wintering grounds or nonmigratory waterfowl during winter, particularly for the Texas–Louisiana Gulf Coast, where most studies were limited to just a few waterfowl species and limited by time of year and number of years studied (8,9,12,13). Although the US Interagency Strategic Plan for the Early Detection of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1 has extensively sampled waterfowl across all flyways, the program focuses on detection of subtype H5N1 virus; thus, only information pertaining to this subtype is publicly available (14). To understand the ecology, natural history, and evolution of influenza viruses, long-term surveillance studies are needed, particularly those that investigate waterfowl in understudied areas, such as wintering grounds. Long-term surveillance is even more important in areas where commercial poultry operations and migratory waterfowl stopover or wintering areas overlap (15).
We recently reported AIV prevalence, as determined by real-time reverse transcription–PCR (rRT-PCR) and virus isolation, from a multiyear surveillance project (September 2005–January 2009) of hunter-harvested waterfowl in the Texas mid–Gulf Coast region (16). We found little variation in overall AIV prevalence within or between seasons, except for 1 season (2007–08) when the overall prevalence was higher (16). The objectives of the current study were to 1) determine subtype diversity of AIV in both migratory and resident waterfowl populations (mostly ducks and geese) to which humans may be exposed and 2) compare prevalence and subtype diversity of AIV among species, according to age and sex, focusing on the Texas mid–Gulf Coast region during early fall and winter, which coincides with the regional hunting season.
Methods
Sample Collection and Analysis
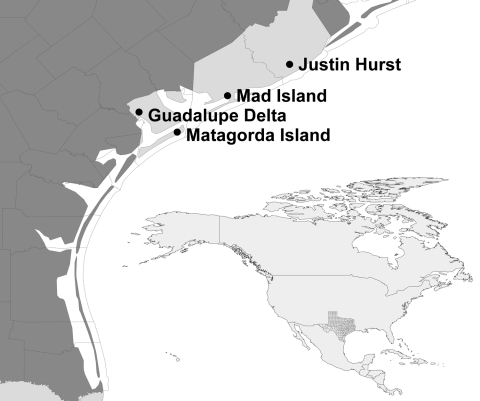
During 2006–09, cloacal swab samples were collected from hunter-harvested waterfowl (17) and other wetland-associated game birds (18) during 3 consecutive hunting seasons: September 2006–January 2007 (season 1), September 2007–January 2008 (season 2), and September 2008–January 2009 (season 3) at 4 state wildlife management areas (WMAs) along the Gulf Coast of Texas: Justin Hurst WMA in Brazoria County, Mad Island WMA in Matagorda County, Guadalupe Delta WMA in Calhoun County, and Matagorda Island WMA in Calhoun County (Figure). Trained field personnel identified the species, sex, and age (when possible) of the bird on the basis of plumage (19). The bird’s age was recorded as adult, if it was not the bird’s hatch-year, and juvenile, if it was the bird’s hatch-year. Waterfowl species and areas sampled reflected hunters’ choices and personnel available to collect swabs on sampling days. Data from all 4 WMAs were combined for analysis.
Figure.
Locations of state wildlife management areas where samples were collected from waterfowl for avian influenza virus surveillance, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, September–January 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008–09. Inset shows location of Texas (shaded).
All samples were collected, processed, and tested as previously described (8,16). Briefly, all samples (N = 5,363) were screened for AIV by AIV-matrix rRT-PCR, and virus isolation was performed on all 455 rRT-PCR–positive samples and 3,664 rRT-PCR–negative samples. All rRT-PCR–positive samples were screened for H5 and H7 subtypes by rRT-PCR by using the AgPath-ID One-Step RT-PCR Kit (Ambion, Inc., Austin, TX, USA) and an ABI 7500Fast Real-time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Inc., Foster City, CA, USA) in a 25-µL final reaction volume. Primers and probes for the M and H5 (20,21) and H7 subtypes (21,22) were those previously described. All AIV isolates were submitted to the National Veterinary Services Laboratory (NVSL; Ames, IA, USA) for subtyping by hemagglutination (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) inhibition tests and screening for the presence of the N1 gene by rRT-PCR. Additionally, all H5 and H7 isolates were pathotyped at NVSL by analysis of the amino acid sequence at the HA protein cleavage site.
Statistical Analysis
We previously documented that prevalence estimates calculated on virus isolation following a positive AIV-matrix rRT-PCR provided results nearly identical to those obtained by performing both tests in parallel (16); for this reason, we calculated apparent prevalence by dividing the number of virus isolation–positive samples (after a positive rRT-PCR result) by the total number of samples collected and tested by rRT-PCR (16).
Pearson χ2 analyses were used to evaluate differences in AIV-infected proportion by sex (drake vs. hen), age (adult vs. juvenile), species of waterfowl, and hunting season of collection (seasons 1, 2, 3). Fisher exact test was used instead of χ2 when >1 cells were expected to have a frequency of <5. A p value <0.05 was considered significant. Wald 95% confidence intervals were calculated for all proportions of AIV infections (i.e., sex, age, species).
A multivariate main effects logistic regression model was also constructed to assess differences in AIV detection by using rRT-PCR by age, sex, and bird species. Species were categorized as blue-winged teal, green-winged teal, gadwall, northern shoveler, or other species. We chose the 4 species-specific categories because they represented the largest numbers of tested birds. Sample records with missing rRT-PCR results or age, sex, or species data were removed from this analysis. We analyzed all data using Intercooled Stata version 9 (Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA).
Results
Sampling Overview
A total of 5,363 cloacal swab samples were collected from 33 different potential host species, including a variety of waterfowl and other wetland-associated game birds (Table A1; Table A2; and Table A3) during 3 consecutive hunting seasons (season 1: 2,171 birds; season 2: 2,424 birds; and season 3: 768 birds). Most samples (3,138 [58.5%]) were from teal (blue-winged [Anas discors] and green-winged [A. crecca]), followed by northern shovelers (A. clypeata; 703 [13.1%]), gadwall (A. strepera; 437 [8.2%]), and American wigeon (A. americana; 238 [4.4%]); the remaining samples (847 [15.8%]) were from a variety of other species (Table A1–3). Adults accounted for 2,759 (51.5%) samples; 1,504 (28.0%) were collected from juveniles, and 1,100 (20.5%) from birds of undetermined age. Additionally, 2,445 (45.6%) samples were from drakes, 2,262 (42.2%) from hens, and 656 (12.2%) from birds of undetermined sex.
Table 3. Comparison of apparent prevalence of avian influenza virus in hunter-harvested waterfowl, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, September–January 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008–09*.
| Hunting season | Juvenile waterfowl† |
Adult waterfowl† |
p value |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. tested | rRT-PCR | VI | No. tested | rRT-PCR | VI | rRT-PCR | VI | |||
| 2006–07 | 518 | 8.30 (5.92–10.68) | 3.28 (1.75–4.82) | 1,081 | 5.46 (4.10–6.81) | 0.74 (0.23–1.25) | 0.029 | <0.001 | ||
| 2007–08 | 763 | 13.80 (11.30–16.20) | 5.50 (3.89–7.12) | 1,189 | 10.51 (8.77–12.20) | 3.28 (2.27–4.29) | 0.030 | 0.022 | ||
| 2008–09 |
222 |
8.56
(4.88–12.24) |
1.80
(0.49–4.55) |
|
489 |
4.70
(2.82–6.58) |
0.20
(0.01–1.13) |
|
0.043 |
0.035 |
| Total‡ | 1,503 | 11.10 (9.52–12.69) | 4.06 (3.06–5.06) | 2,759 | 1.74 (1.25–2.23) | 1.74 (1.25–2.23) | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
*rRT-PCR, real-time reverse transcription–PCR; VI, virus isolation. †Values for rRT-PCR and VI are apparent prevalence, % (95% confidence interval). ‡Total = the 3 hunting seasons combined (September–January, 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008–09).
Subtype Prevalences
Of 4,119 samples processed for virus isolation, influenza A viruses were isolated from 134. All 9 NA subtypes (N1–9) were isolated, whereas only 9 of the 16 different HA subtypes (H1–7, 10, and 11) were isolated. Thirty-two different HA and NA subtype combinations were identified (Table A4), and for 8 isolates, either the HA (n = 7) or NA (n = 1) was not identified.
The most frequently identified HA subtypes during season 1 were H3 and H6 (8 [25.0%] and 9 [28.1%], respectively), whereas for season 2, H4 and H10 were predominant (26 [26.8%] and 17 [17.5%], respectively); the H4 subtype (4 [80.0%]) remained predominant in season 3. With respect to NA subtypes, N1 and N8 were most common in season 1 (8 [18.8%] and 10 [31.3%], respectively), whereas N6, N7, and N8 (19 [19.6%]; 16 [16.5%], and 19 [19.6%], respectively) were predominant in season 2, with N6 and N8 (2 [40.0%] each) remaining predominant in season 3. The most frequent HA and NA subtype combinations identified during season 1 were subtype H3N8 (n = 7) and H6N1 (n = 4) viruses, whereas H4N6 (n = 17), H3N8 (n = 9), and H10N7 (n = 9) viruses were the most common subtype combinations identified in season 2, and H4N6 (n = 2) and H4N8 (n = 2) were most common in season 3 (Table A4).
H7 subtype was identified by rRT-PCR during all 3 hunting seasons (n = 2, 28, and 2, respectively). Additionally, H5 subtype was detected by rRT-PCR for all 3 seasons (n = 14, 21, and 2, respectively). Yet, H5 viruses were isolated only during season 2, whereas H7 viruses were isolated during all 3 hunting seasons (Tables 1, 2). All H5 and H7 viruses were determined to be low-pathogenicity AIVs by analysis of the amino acid sequence at the HA protein cleavage site.
Table 1. Subtypes of avian influenza viruses isolated in the fall (September and November) from selected species during 3 consecutive hunting seasons, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008–09.
| Species* | Subtype (no. isolated) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| September† |
November |
||||||
| 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | ||
| Fulvous whistling duck (Dendrocygna bicolor) | – | – | – | H6N1 | – | – | |
| Mottled duck × mallard (Anas fulvigula × A. platyrhynchos) | – | – | – | – | H6N8 | – | |
| Mottled duck (A. fulvigula) | – | – | – | H6N5 | – | – | |
| Northern pintail (A. acuta) | – | – | – | – | H4N8 | – | |
| Northern shoveler (A. clypeata) | – | – | – | H2N9, H3N8, H4N2, H4N6, H4N8 | H4N2, H5N2, H5N3, H6N2, H10N2, H11N9 (2) | H7N2 | |
| Teal, blue-winged (A. discors) | H1N1, H3N6, H3N8 (6) | H1N1 (2), H2N8, H3N4, H3N6, H3N8 (9), H4N1, H4N6 (17), H4N8 (6), H6N1, H7N1, H7N1/4, H7N7 (2), H10N7 (5) | H4N6, H4N8 | H2N9, H4N2 H4N6, H4N8 H6N1 (3), H6N1/4, H6N5, H6N6, H6N8 | H3N6, H5N2 (2), H5N3 (2), H7N4, H7N7 (3), H10N7, H11N9 (3) | H4N8 | |
| Teal, green-winged (A. crecca) | H6N2 | H10N7 | – | H1N1 | H5N2, H7N1/4, H11N9 | – | |
*Species selected by significance as determined by prevalence, uniqueness to the area, or native, nonmigratory species. †Teal are the only species hunted during September on the Texas mid–Gulf coast.
Table 2. Subtypes of avian influenza viruses isolated in the winter (December–January) from selected species during 3 consecutive hunting seasons, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008–
| Species* | Subtype (no. isolated) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| December |
January |
||||||
| 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | ||
| Northern pintail (Anas acuta) | – | H10N3/7 | H4N6 | – | H10N3 | – | |
| Northern shoveler (A. clypeata) | – | H5N2, H6N2, H10N7 | – | – | – | – | |
| Teal, blue-winged (A. discors) | – | – | – | – | H10N3 (3) | – | |
| Teal, green-winged (A. crecca) | H10N7, H11N3 | – | – | H7N3 | H7N3, H10N3 (2) | – | |
*Species selected by significance as determined by prevalence, uniqueness to the area, or native, nonmigratory species.
Prevalence by Sex, Age, and Species
Apparent AIV prevalence did not differ significantly between hens and drakes by rRT-PCR or virus isolation during any of the 3 hunting seasons or all seasons combined (Table A5). Prevalence as determined by rRT-PCR and virus isolation differed significantly between juvenile and adult birds during the 3 hunting seasons and for all seasons combined (Table 3). However, when data were analyzed on the basis of samples for which both sex and age of the birds were known, results differed significantly between adult drakes and hens according to rRT-PCR results during season 1 and between juvenile hens and drakes by virus isolation during season 3 and for all 3 seasons combined (Table A6).
To determine whether a species effect existed for age differences, we assessed apparent AIV prevalence by age for species for which >100 samples from adult birds and >100 samples from juvenile birds were tested (i.e., blue-winged teal, green-winged teal, gadwall, and northern shoveler; Table 4; Table A7; and Table A8). When data from all 3 hunting seasons were combined, significantly more juvenile than adult birds were positive for AIV by virus isolation for 3 of the predominant host species analyzed (blue-winged teal, green-winged teal, and northern shoveler); no significant difference was observed for gadwall (Table A7–8). However, apparent AIV prevalence by rRT-PCR was significantly higher only for juvenile blue-winged teal and northern shovelers (Table A 7, 8). According to multivariate logistic regression, rRT-PCR results were associated with age and species but not with sex (Table 4).
Table 4. Multivariate logistic regression model to identify variables associated with a positive real-time RT-PCR result, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008–09*.
| Variable | Odds ratio (95% CI) | p value |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Drake | 1.0† | |
| Hen |
1.07 (0.859–1.320) |
0.558 |
| Age | ||
| Adult | 1.0 | |
| Juvenile |
1.45 (1.17–1.81) |
0.001
|
| Species | ||
| Other species | 1.0 | |
| Gadwall | 0.407 (0.120–0.825) | 0.013 |
| Northern shoveler | 1.51 (0.987–2.320) | 0.057 |
| Blue-winged teal | 2.18 (1.52–3.13) | <0.001 |
| Green-winged teal | 1.12 (0.742–1.680) | 0.592 |
*Results for a total of 4,187 samples, collected during September–January for each season. RT-PCR, reverse transcription–PCR; CI, confidence interval. Boldface indicates significant result. †Reference category.
Blue-winged teal and northern shovelers had the greatest diversity in subtypes, followed by green-winged teal (Tables 1, 2; Table A1–3). Nine HA (H1–7, 10, and 11) and all 9 NA (N1–9) subtypes were identified in blue-winged teal, 8 HA (H2–7, 10, and 11) and 6 NA (N2, N3, and N6–9) subtypes were identified in northern shovelers, whereas 6 HA (H1, 5–7, 10, and 11) and 6 NA (N1–4, N7, and N9) subtypes were identified in green-winged teal.
Discussion
The Texas Gulf Coast provides winter habitat for ≈2–3 million ducks and >1 million geese (11). In this region, migratory waterfowl intermingle with resident wild species such as the mottled duck, and are in close contact with poultry operations and humans, primarily hunters (15,17). Recently, we reported prevalence for the first multiyear study of AIV that covered waterfowl wintering grounds along the Texas Gulf Coast (16), a previously understudied area. Unlike results of previous studies, we found little to no variation in apparent AIV prevalence by month within wintering seasons (September–January) with the exception of rRT-PCR during December 2007–January 2008 and virus isolation during 2005–06 and 2006–07 (16). Additionally, AIV prevalence, as determined by rRT-PCR or virus isolation, varied little among the 4 consecutive hunting seasons studied (September–January 2005–06 through 2008–09), except for the 2007–08 season, during which overall AIV prevalence was higher than the other 3 seasons as determined by both rRT-PCR and virus isolation (16). Detection of AIV at low levels throughout the wintering season supports the contention that AIV can persist in wild-bird populations through continuous circulation in a proportion of the population (1). The low rate of virus isolation observed in the current study (29.9% of rRT-PCR–positive samples) is consistent with findings of other studies and is not surprising (2,23). Real-time RT-PCR is considered more sensitive than virus isolation, enabling the detection of genome fragments and viruses that do not grow in embryonated chicken eggs. Also, consistent with other surveillance studies, no differences were noted in AIV prevalence based on sex, and AIV was more prevalent in juvenile birds than in adults (1,7,23). The latter finding supports the assumption that immunologically immature (juvenile) birds are more susceptible to AIV than are mature (adult) birds (24,25).
The most commonly identified HA and NA subtype combinations during season 1 were H3N8 and H6N1; during season 2, H3N8 remained, but it was not detected during season 3. During season 2, H4N6 and H10N7, which have been reported on the Gulf Coast (8,13), were the predominant subtype combinations; H4N6 also was detected during season 3. The annual variations in AIV subtype prevalence observed in this study show the need for continued annual surveillance in domestic and migratory avian species, particularly in areas of high poultry and waterfowl density, such as the Texas Gulf Coast (15).
Outbreaks of H5 AIV have been documented previously in Texas. In 1993, an outbreak of H5N2 occurred in emus, in 2002 H5N3 was detected in chickens, and in 2004 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (H5N2) was reported in a commercial poultry operation (26–28). We isolated subtype H5N2 and H5N3 viruses from apparently healthy free-roaming waterfowl only during season 2. Although no data are available on subtypes circulating in waterfowl on the Texas coast before the 3 outbreaks noted above, our data document the presence of these subtypes in migratory waterfowl near commercial poultry operations (15). Molecular characterization of the subtype H5N2 and H5N3 viruses we isolated should help clarify the relation between these viruses and those isolated from commercial species.
Our isolation of AIVs from resident (nonmigratory) mottled ducks and mottled duck/mallard hybrids suggests AIV transmission on the wintering ground and is consistent with previous reports (13). Mallards interbreed with mottled ducks and are sister species phylogenetically (29). Before the isolation of H6 AIVs from a mottled duck/mallard hybrid in November 2006 and a mottled duck in November 2007, we isolated H6 subtypes from migratory teals and northern shovelers (September and November 2006 and 2007). Additional support for AIV transmission on wintering grounds included isolation of an H6 virus from a fulvous whistling duck, a species that breeds on the Texas–Louisiana coast and leaves during late summer to winter further south in Mexico; nearly all whistling ducks are gone by late January (17). Although circulation of AIVs within fulvous whistling ducks, mottled ducks, and mottled duck hybrids throughout the year cannot be ruled out, such circulation seems unlikely. Hanson et al. were unable to isolate AIVs from mottled ducks collected on the Texas Gulf Coast during August (9); additionally, we did not detect AIV by rRT-PCR in samples collected during June–August 2007 (n = 155, S. Rollo et al., unpub. data), which suggests that these viruses are not readily circulating in these resident populations during summer. Genetic characterization of these H6 isolates will help determine whether these isolates are related and help clarify the role of waterfowl wintering grounds in the transmission and perpetuation of AIVs in nature. Further studies focused on AIV prevalence and immune responses to AIV in these resident populations also are needed to clarify the maintenance and transmission of AIVs in the wintering grounds.
Before singling out a particular species on which to focus surveillance efforts, one must consider the technique used for subject selection (hunter-harvest vs. live-capture) as well as the area under study (e.g., breeding grounds vs. wintering grounds; fresh water vs. salt water) and which populations are prevalent within the study areas. Mallards have become a primary species of interest not only because of their susceptibility to H5 and H7 subtypes but also because of their abundance and relative ease of capture (2,17,23,30–32). During our study, few mallard samples were collected because most Texas mallards winter in the playa lakes and sorghum fields of the Texas Panhandle with few (<4%) wintering along the Gulf Coast (17). Our data indicate that mallards, although appropriate focal species for AIV monitoring in some portions of North America, are not as suitable as blue-winged teal or northern shoveler in other regions, such as the Texas mid–Coast (8,9,13). In many studies that found mallards as a high-prevalence species for AIV infection, they were captured live for testing and dominated the samples (2,23). The few studies in which other species were more frequently sampled and tested positive for AIV were conducted on hunter-harvested waterfowl (8,13,33).
Our study supports the consensus that dabbling ducks are more likely than diving ducks to be positive for AIV; however, as others have documented, not all dabbling ducks are equally likely to be AIV positive (2,23,33). We found blue-winged teal to be the species with the highest prevalence, followed by northern shoveler and green-winged teal. Gadwalls, also a dabbling duck from which we collected substantial numbers of samples, were the least likely to test positive for AIV. Blue-winged teal are generally the first ducks to fly south in the fall, first arriving on wintering grounds in September, and the last to pass through Texas in late February–March on their return north (17). They also make exceedingly long flights compared with other dabbling ducks between feeding and resting areas during migrations (17). On the other hand, gadwalls are short-distance migrants and migrate later, generally beginning their southward migration in early September and their return north starting in February (17). The physiologic demands of long-distance migration can suppress the immune system (34); thus, blue-winged teal might be more susceptible to infection than some other dabbling ducks because of their long-distance migration. More extensive studies are needed incorporating more ecologic factors such as food resources, body mass, and immune status to more fully understand how AIV persists in nature and why the prevalence of AIV is higher in particular species.
Although our samples were not collected probabilistically (i.e., the samples reflect hunters’ choices, as well as the relative abundance of each species), use of hunter-harvested waterfowl was convenient for obtaining large number of samples with which to estimate the prevalence of AIV subtypes carried by waterfowl in the Gulf Coast of Texas. In addition, because hunters have been identified as the human population most at risk for exposure to AIV (35) and antibodies to H11 subtype have been identified in hunters and wildlife professionals (36), continued monitoring of AIV in waterfowl and humans exposed to them should provide useful information about the prevalence and significance of wild animal-to-human transmission.
AIV surveillance studies over time in the same region are critical, particularly in understudied areas. Although studies in areas of low AIV prevalence are inconvenient because of the large sample sizes required to isolate substantial numbers of AIVs, such surveys are critical to gain more knowledge of the ecology of influenza viruses. Our data contribute temporal information about AIV prevalence and subtype diversity for a historically understudied area of North America, the waterfowl wintering grounds of the Texas Gulf Coast.
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the cooperation and patience of the waterfowl hunters of the Texas Gulf Coast who graciously allowed us to sample their harvested waterfowl. We thank everyone who assisted in sample collecting over the years. We also appreciate the help of biologists and technicians from the Texas Parks and Wildlife Department. For assistance with molecular testing, we thank the Animal Health Solutions Group at Ambion, Inc., for subtyping and pathotyping of the influenza isolates and the Avian Section in the Diagnostic Virology Laboratory at the NVSL. The work was completed in the laboratory of B. Lupiani at Texas A&M University.
This research was supported by the National Research Initiative of the US Department of Agriculture Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service AICAP grant 2005-3560515388 (Z507201), awarded to B.L.
Biography
Ms Ferro is a PhD candidate in veterinary microbiology in the College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences at Texas A&M University. Her primary research interests include wildlife disease ecology, particularly pathogens at the exotic/wild–domestic animal interface, such as avian influenza virus, and diagnostics associated with viruses of veterinary importance.
Table A1. Apparent prevalence of avian influenza virus in various waterfowl and wetland-associated game bird species as determined by VI and real-time RT-PCR from cloacal swabs collected from hunter-harvested waterfowl, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, September 2006–January 2007*.
| Species |
No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR,†
no. (%) |
VI,† no. (%) |
Isolate‡ |
| American wigeon (Anas americana) | 171 | 4 (2.3) | 0 | – |
| Fulvous whistling duck (Dendrocygna bicolor) | 18 | 2 (11.1) | 1 (5.6) | H6N1 |
| Lesser scaup (Aythya affinis) | 60 | 1 (1.7) | 1 (1.7) | H10N7 |
| Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos) | 5 | 1 (20.0) | 0 | – |
| Mottled duck (Anas fulvigula) | 33 | 2 (6.1) | 1 (3.0) | H6N5 |
| Northern pintail (Anas acuta) | 72 | 5 (6.9) | 0 | – |
| Northern shoveler (Anas clypeata) | 360 | 23 (6.4) | 5 (1.3) | H2N9, H3N8, H4N2, H4N6, H4N8 |
| Redhead (Aythya amercana) | 51 | 2 (3.9) | 0 | – |
| Ring-necked duck (Aythya collaris) | 35 | 1 (2.9) | 0 | – |
| Ruddy duck (Oxyura jamaicensis) | 31 | 2 (6.5) | 0 | – |
| Teal, blue-winged (Anas discors) | 610 | 65 (10.7) | 19 (3.1) | H1N1, H2N9, H3N6, H3N8 (6), H4N2, H4N6, H4N8, H6N1 (3), H6N1/4, H6N5, H6N6, H6N8 |
| Teal, green-winged (Anas crecca) | 358 | 31 (8.7) | 5 (1.4) | H1N1, H6N2, H7N3, H10N7, H11N3 |
| Snow goose (Chen eaerulescens) |
46 |
2 (4.4) |
0 |
– |
| Total§ | 2,171 | 141 (6.5) | 32 (1.5) | – |
*VI, virus isolation; RT-PCR, reverse transcription–PCR. †Number positive (apparent prevalence). Numbers and apparent prevalences for VI are after RT-PCR result. ‡Isolates typed by the National Veterinary Services Laboratory. Included are VI that were RT-PCR negative on the original sample. §Other species sampled that were negative for AI by RT-PCR and VI, number sampled: American coot (Fulica americana), 25; black-bellied whistling duck (Dendrocygna autumnalis), 6; bufflehead (Bucephala albeola), 2; canvasback (Aythya valisineria), 16; cinnamon teal (Anas cyanoptera), 1; common goldeneye (Bucephala clangula), 1;common moorhen (Gallinula chloropus), 1; common snipe (Gallinago gallinago), 1; gadwall (Anas strepera), 247; greater white-front goose (Anser albifrons), 3; hooded merganser (Laphodytes cucullatus), 11; mottled duck x mallard hybrid (Anas fulvigula x Anas platyrhynchos), 1; Ross’s goose (Anser albifrons), 2; sandhill crane (Grus candensis), 1; wood duck (Aix sponsa), 1; and unidentified teal, 2.
Table A2. Apparent prevalence of avian influenza virus in various waterfowl and wetland-associated game bird species as determined by VI and real-time RT-PCR from cloacal swabs collected from hunter-harvested waterfowl, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, September 2007–January 2008*.
| Species |
No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR,†
no. (%) |
VI,† no. (%) |
Isolate‡ |
| American wigeon (Anas americana) | 51 | 8 (15.7) | 0 | – |
| Fulvous whistling duck (Dendrocygna bicolor) | 14 | 1 (7.1) | 0 | – |
| Gadwall (Anas strepera) | 160 | 10 (6.3) | 1 (0.6) | H6N1 |
| Mottled duck (Anas fulvigula) | 26 | 1 (3.9) | 0 | – |
| Mottled duck x Mallard (A. fulvigula x A. platyrhynchos) | 2 | 1§ | 1§ | H6N8 |
| Northern pintail (Anas acuta) | 62 | 13 (21.0) | 3 (4.8) | H4N8, H10N3, H10N3/7 |
| Northern shoveler (Anas clypeata) | 239 | 38 (15.9) | 10 (4.2) | H4N2, H5N2 (2), H5N3, H6N2 (2), H10N2, H10N7, H11N9 (2) |
| Ring-necked duck (Aythya collaris) | 17 | 1 (5.9) | 0 | – |
| Ruddy duck (Oxyura jamaicensis) | 36 | 2 (5.6) | 1 (2.8) | H2N3 |
| Teal, blue-winged (Anas discors) | 1,213 | 155 (12.8) | 73 (6.0) | H1N1 (2), H2N8, H3N4, H3N6 (2), H3N8 (9), H4N1, H4N6 (17), H4N8 (6), H5N2 (2), H5N3 (2), H6N1, H7N1, H7N1/4, H7N4, H7N7 (5), H10N?, H10N3 (2), H10N3/7, H10N7 (7), H11N9 (3) |
| Teal, cinnamon (Anas cyanoptera) | 2 | 1§ | 1§ | H7N3 |
| Teal, green-winged (Anas crecca) | 464 | 38 (8.2) | 7 (1.5) | H5N2, H7N1/4, H7N3, H10N3, H10N3/7, H10N7, H11N9 |
| Snow goose (Chen eaerulescens) |
43 |
3 (7.0) |
0 |
– |
| Total¶ | 2,424 | 272 (11.2) | 97 (4.0) | – |
*VI, virus isolation; RT-PCR, reverse transcription–PCR. †Number positive (apparent prevalence). Numbers and apparent prevalence for VI are after RT-PCR result. ‡Isolates typed by the National Veterinary Services Laboratory. Seven isolates were confirmed as avian influenza but were unable to be subtyped. Included are virus isolates that were RT-PCR negative on the original sample. §Apparent prevalence not calculated due to the small sample size. ¶Other species sampled that were negative for AI by RT-PCR and VI, number sampled: American coot (Fulica americana), 27; Black-bellied whistling duck (Dendrocygna autumnalis), 9; Canvasback (Aythya valisineria), 3; Common snipe (Gallinago gallinago), 2; Greater white-front goose (Anser albifrons), 3; Hooded merganser (Laphodytes cucullatus), 3; Least grebe (Tachybaptus dominicus), 1; Lesser Scaup (Aythya affinis), 26; Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos), 4; Redhead (Aythya amercana), 3; Ross’s goose (Anser albifrons), 5; Sandhill crane (Grus candensis), 8; and unidentified teal, 1.
Table A3. Apparent prevalence of avian influenza virus in various waterfowl and wetland-associated game bird species as determined by VI and real-time RT-PCR from cloacal swabs collected from hunter-harvested waterfowl, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, September 2008–January 2009*.
| Species |
No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR,† no. (%) |
VI,† no. (%) |
Isolate‡ |
| American wigeon (Anas americana) | 16 | 1 (6.3) | 0 | – |
| Northern pintail (A. acuta) | 28 | 2 (7.1) | 1 (3.6) | H4N6 |
| Northern shoveler (A. clypeata) | 104 | 5 (4.8) | 1 (1.0) | H7N2 |
| Teal, blue-winged (A. discors) | 176 | 21 (11.9) | 3 (1.7) | H4N6, H4N8 (2) |
| Teal, green-winged (A. crecca) |
314 |
13 (4.1) |
0 |
– |
| Total§ | 768 | 42 (5.5) | 5 (0.7) | – |
*VI, virus isolation; RT-PCR, reverse transcription–PCR. †Number positive (apparent prevalence). ‡Isolates typed by the National Veterinary Services Laboratory. §Other species sampled that were negative for AI by RT-PCR and VI, number sampled: Common ground dove (Columbina passerina), 1; Gadwall (Anas strepera), 30; Greater white-front goose (Anser albifrons), 6; Hooded merganser (Laphodytes cucullatus), 4; Lesser Scaup (Aythya affinis), 1; Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos), 4; Mottled duck (Anas fulvigla), 23; Mottled duck x Mallard hybrid (Anas fulvigula x Anas platyrhynchos), 1; Ring-necked duck (Aythya collaris), 1; Ross’s goose (Anser albifrons), 1; Sandhill crane (Grus candensis), 1; Snow goose (Chen eaerulescens), 56; and Wood duck (Aix sponsa), 1.
Table A4. Hemagglutinin and neuramindase subtype combinations for all avian influenza viruses isolated from hunter-harvested waterfowl, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, September–January 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008–09.
| Neuraminidase |
Hunting season |
Hemagglutinin* |
|||||||||
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
10 |
11 |
Total |
||
| 1 |
2006–07 | 2 | – | – | – | – | 5 | – | – | – | 7 |
| 2007–08 |
2 |
– |
– |
1 |
– |
2 |
3 |
– |
– |
8 |
|
| 2 |
2006–07 | – | – | – | 2 | – | 1 | – | – | – | 3 |
| 2007–08 | – | – | – | 1 | 5 | 2 | – | 1 | – | 9 | |
| 2008–09 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1 |
– |
– |
1 |
|
| 3 |
2006–07 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | 1 | 2 |
| 2007–08 |
– |
1 |
– |
– |
3 |
– |
2 |
7 |
– |
13 |
|
| 4 |
2006–07 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 |
| 2007–08 |
– |
– |
1 |
– |
– |
– |
1 |
– |
– |
2 |
|
| 5 |
2006–07 | – | – | – | – | – | 2 | – | – | – | 2 |
| 2007–08 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
0 |
|
| 6 |
2006–07 | – | – | 1 | 2 | – | 1 | – | – | – | 4 |
| 2007–08 | – | – | 2 | 17 | – | – | – | – | – | 19 | |
| 2008–09 |
– |
– |
– |
2 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
2 |
|
| 7 |
2006–07 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2 | – | 2 |
| 2007–08 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
5 |
9 |
– |
14 |
|
| 8 |
2006–07 | – | – | 7 | 2 | – | 1 | – | – | – | 10 |
| 2007–08 | – | 1 | 9 | 7 | – | 1 | – | – | – | 18 | |
| 2008–09 |
– |
– |
– |
2 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
2 |
|
| 9 |
2006–07 | – | 2 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2 |
| 2007–08 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
6 |
6 |
|
| Total | 2006–07 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 32 |
| 2007–08 | 2 | 2 | 12 | 26 | 8 | 5 | 11 | 17 | 6 | 89† | |
| 2008–09 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 | |
| Total | 4 | 4 | 20 | 36 | 8 | 15 | 13 | 19 | 7 | 126 | |
*No H8, H9, or H12–16 were identified in this study. †Eight isolates not recorded because of inability to subtype the hemagglutinin and/or neuraminidase. All isolates included regardless of real-time reverse transcription–PCR result.
Table A5. Comparison of apparent prevalence of avian influenza virus by sex and detection method in hunter-harvested waterfowl, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, September–January 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008–09.
| Hunting season |
Hen |
|
Drake |
p value for
rRT-PCR, VI |
||||
| No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR* |
VI† |
No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR* |
VI |
|||
| 2006–07 | 967 | 7.14 (5.51–8.76) | 1.24 (0.54–1.94) | 1,083 | 6.10 (4.67–7.53) | 1.48 (0.76–2.20) | 0.343, 0.645 | |
| 2007–08 | 895 | 13.30 (11.10–15.50) | 4.69 (3.31–6.08) | 1,059 | 10.70 (8.89–12.60) | 3.77 (2.62–4.92) | 0.084, 0.312 | |
| 2008–09 |
400 |
5.00 (2.86–7.14) |
0.25 (0.01–1.38) |
|
303 |
7.26 (4.34–10.18) |
1.32 (0.36–3.35) |
0.210, 0.171 |
| Total‡ | 2,262 | 9.20 (8.00–10.39) | 2.39 (1.76–3.02) | 2,445 | 8.26 (7.17–9.35) | 2.41 (1.80–3.02) | 0.255, 0.956 | |
*RT-PCR, reverse transcription–PCR. Apparent prevalence, % (95% confidence interval). †VI, virus isolation. Apparent prevalence, % (95% confidence interval). ‡Total = all 3 seasons combined (September−January 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008−09).
Table A6. Apparent prevalence of avian influenza virus by age, sex, and detection method in hunter-harvested waterfowl, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, September–January 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008–09.
| Age/sex |
Hunting season |
Total, 2006–09 |
||||||||||||
| 2006–07 |
|
2007–08 |
|
2008–09 |
||||||||||
| No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR* |
VI† |
No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR* |
VI |
No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR* |
VI |
No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR* |
VI |
|||
| Adult | ||||||||||||||
| Hen | 483 | 34 (7.0) | 5 (1.0) | 468 | 55 (11.8) | 20 (4.3) | 259 | 10 (3.9) | 1 (0.4) | 1,210 | 99 (8.2) | 26 (2.2) | ||
| Drake | 580 | 24 (4.1) | 3 (0.5) | 704 | 69 (9.8) | 19 (2.7) | 221 | 13 (5.9) | 0 | 1,505 | 106 (7.0) | 22 (1.5) | ||
| Total | 1,063 | 58 (5.5) | 8 (0.8) | 1,172 | 124 (10.6) | 39 (3.3) | 480 | 23 (4.8) | 1 (0.2) | 2,715 | 205 (7.6) | 48 (1.8) | ||
| p value |
– |
0.038
|
0.33 |
|
– |
0.288 |
0.141 |
|
– |
0.301 |
0.355 |
– |
0.264 |
0.177 |
| Juvenile | ||||||||||||||
| Hen | 250 | 15 (6.0) | 5 (2.0) | 409 | 60 (14.7) | 20 (4.9) | 136 | 10 (7.4) | 0 | 795 | 85 (10.7) | 25 (3.1) | ||
| Drake | 254 | 27 (10.7) | 12 (4.7) | 344 | 45 (13.1) | 20 (5.8) | 80 | 9 (11.3) | 4 (5.0) | 678 | 81 (12.0) | 36 (5.3) | ||
| Total | 504 | 42 (8.3) | 17 (3.4) | 753 | 105 (13.9) | 40 (5.3) | 216 | 19 (8.8) | 4 (1.9) | 1,473 | 166 (11.3) | 61 (4.1) | ||
| p value | – | 0.060 | 0.090 | – | 0.531 | 0.573 | – | 0.329 | 0.008 | – | 0.448 | 0.038 | ||
*RT-PCR, reverse transcription–PCR. No. positive (apparent prevalence, %). †VI, virus isolation. No. positive (apparent prevalence, %). Boldface indicates significance.
Table A7. Comparison of apparent prevalence of avian influenza virus in blue-winged and green-winged teal from hunter-harvested waterfowl, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, September–January 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008–09.
| Age/sex |
Blue-winged teal |
|
Green-winged teal |
||||
| No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR* |
VI† |
No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR* |
VI† |
||
| Adult | 910 | 11.00 (8.97–13.04) | 3.85 (2.60–5.10) | 790 | 6.33 (4.63–8.03) | 0.38 (0.08–1.11) | |
| Juvenile | 620 | 15.48 (12.64–18.33) | 6.94 (4.94–8.94) | 251 | 7.57 (4.30–10.84) | 1.99 (0.26–3.72) | |
| p value |
|
0.010
|
0.007
|
|
|
0.491 |
0.011
|
| Hen | 772 | 13.73 (11.30–16.16) | 4.40 (2.96–5.85) | 548 | 6.57 (4.50–8.64) | 0.91 (0.12–1.71) | |
| Drake | 894 | 11.30 (9.22–13.37) | 4.92 (3.50–6.34) | 581 | 7.75 (5.57–9.92) | 0.86 (0.11–1.61) | |
| p value | 0.133 | 0.618 | 0.444 | 0.926 | |||
*RT-PCR, reverse transcription–PCR. Apparent prevalence, % (95% confidence interval). †VI, virus isolation. Apparent prevalence, % (95% confidence interval). Boldface indicates significance.
Table A8. Apparent prevalence of avian influenza virus in gadwall and northern shoveler from hunter-harvested waterfowl, Texas mid–Gulf Coast, USA, September–January 2006–07, 2007–08, and 2008–09.
| Age/sex |
Gadwall |
|
Northern shoveler |
||||
| No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR* |
VI† |
No. tested |
Real-time RT-PCR* |
VI† |
||
| Adult | 233 | 2.15 (0.29–4.01) | 0.43 (0.01–2.37) | 363 | 7.16 (4.51–9.82) | 1.38 (0.18–2.58) | |
| Juvenile | 144 | 3.47 (0.48–6.46) | 0 | 258 | 12.40 (8.38–16.43) | 3.88 (1.52–6.23) | |
| p value |
|
0.436 |
0.431 |
|
|
0.027
|
0.046
|
| Hen | 221 | 1.36 (0.28–3.92) | 0.45 (0.01–2.50) | 373 | 10.99 (7.82–14.17) | 2.68 (1.04–4.32) | |
| Drake | 216 | 3.24 (0.88–5.60) | 0 | 330 | 7.58 (4.72–10.43) | 1.52 (0.20–2.83) | |
*RT-PCR, reverse transcription–PCR. Apparent prevalence, % (95% confidence interval). †VI, virus isolation. Apparent prevalence, % (95% confidence interval). Boldface indicates significance.
Footnotes
Suggested citation for this article: Ferro PJ, Budke CM, Peterson MJ, Cox D, Roltsch E, Merendino T, et al. Multiyear surveillance for avian influenza virus in waterfowl from wintering grounds, Texas coast, USA. Emerg Infect Dis [serial on the Internet]. 2010 Aug [date cited]. http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid1608.091864
References
- 1.Webster RG, Bean WJ, Gorman OT, Chambers TM, Kawaoka Y. Evolution and ecology of influenza A viruses. Microbiol Rev. 1992;56:152–79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dusek RJ, Bortner JB, DeLiberto TJ, Hoskins J, Franson JC, Bales BD, et al. Surveillance for high pathogenicity avian influenza virus in wild birds in the Pacific Flyway of the United States, 2006–2007. Avian Dis. 2009;53:222–30. 10.1637/8462-082908-Reg.1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Munster VJ, Wallensten A, Baas C, Rimmelzwaan GF, Schutten M, Olsen B, et al. Mallards and highly pathogenic avian influenza ancestral viruses, northern Europe. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:1545–51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Reperant LA, Rimmelzwaan GF, Kuiken T. Avian influenza viruses in mammals. Rev Sci Tech. 2009;28:137–59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.US Department of Agriculture. Wild Bird Plan: an early detection system for highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza in wild migratory birds. US Interagency Strategic Plan 2006. March 14 [cited 2009 Dec 1]. http://www.usda.gov/wps/portal/usdahome?contentidonly=true&contentid=2006/03/0094.xml
- 6.Capua I, Alexander DJ. The challenge of avian influenza to the veterinary community. Avian Pathol. 2006;35:189–205. 10.1080/03079450600717174 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Krauss S, Walker D, Pryor SP, Niles L, Chenghong L, Hinshaw VS, et al. Influenza A viruses of migrating wild aquatic birds in North America. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2004;4:177–89. 10.1089/vbz.2004.4.177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ferro PJ, El-Attrache J, Fang X, Rollo SN, Jester A, Merendino T, et al. Avian influenza surveillance in hunter-harvested waterfowl from the Gulf Coast of Texas (November 2005–January 2006). J Wildl Dis. 2008;44:434–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hanson BA, Swayne DE, Senne DA, Lobpries DS, Hurst J, Stallknecht DE. Avian influenza viruses and paramyxoviruses in wintering and resident ducks in Texas. J Wildl Dis. 2005;41:624–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kocan AA, Hinshaw VS, Daubney GA, Influenza A. Viruses isolated from migrating ducks in Oklahoma. J Wildl Dis. 1980;16:281–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ducks Unlimited Texas. CARE. Conserving Agricultural Resources and the Environment. 2008. [cited 2009 Dec 7]. http://www.ducks.org/Page379.aspx
- 12.Stallknecht DE, Senne DA, Zwank PJ, Shane SM, Kearney MT. Avian paramyxoviruses from migrating and resident ducks in coastal Louisiana. J Wildl Dis. 1991;27:123–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Stallknecht DE, Shane SM, Zwank PJ, Senne DA, Kearney MT. Avian influenza viruses from migratory and resident ducks of coastal Louisiana. Avian Dis. 1990;34:398–405. 10.2307/1591427 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.U.S. Geological Survey National Wildlife Health Center. Highly pathogenic avian influenza early detection data system [cited 2009 Dec 1]. http://wildlifedisease.nbii.gov/ai/index.jsp
- 15.Miller R. Analysis identifies areas, populations for Asian H5N1 HPAI surveillance. NAHSS Outlook Quarter Two 2007. [cited 2009 Dec 4]. http://www.usda.gov/wps/portal/!ut/p/_s.7_0_A/7_0_1OB?navid=SEARCH&mode=simple&q=ryan+miller&x=0&y=0&site=usda
- 16.Ferro PJ, Peterson MJ, Merendino T, Nelson M, Lupiani B. Comparison of real-time RT-PCR and virus isolation for estimating prevalence of avian influenza in hunter-harvested wild birds at waterfowl wintering grounds along the Texas mid–Gulf Coast (2005–2006 through 2008–2009). Avian Dis. 2010;54(Suppl):655–9. 10.1637/8810-040109-ResNote.1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bellrose FC. Ducks, geese, and swans of North America, 2nd ed. Harrisburg (PA): Stackpole Books; 1978. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tacha TC, Braun CE, eds. Migratory shore and upland game bird management in North America. Washington: International Association of Fish and Wildlife Agencies; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Braun CE, ed. Techniques for wildlife investigations and management. 6th ed. Bethesda (MD): The Wildlife Society by Port City Press; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Spackman E, Senne DA, Bulaga LL, Myers TJ, Perdue ML, Garber LP, et al. Development of real-time RT-PCR for the detection of avian influenza virus. Avian Dis. 2003;47(Suppl):1079–82. 10.1637/0005-2086-47.s3.1079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Spackman E, Senne DA, Myers TJ, Bulaga LL, Garber LP, Perdue ML, et al. Development of a real-time reverse transcriptase PCR assay for type A influenza virus and the avian H5 and H7 hemagglutinin subtypes. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:3256–60. 10.1128/JCM.40.9.3256-3260.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Spackman E, Ip HS, Suarez DL, Slemons RD, Stallknecht DE. Analytical validation of a real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction test for Pan-American lineage H7 subtype Avian influenza viruses. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2008;20:612–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Munster VJ, Baas C, Lexmond P, Waldenstrom J, Wallensten A, Fransson T, et al. Spatial, temporal, and species variation in prevalence of influenza A viruses in wild migratory birds. PLoS Pathog. 2007;3:e61. 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030061 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stallknecht DE, Brown JD. Wild birds and the epidemiology of avian influenza. J Wildl Dis. 2007;43:S15–20. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Stallknecht DE, Shane SM. Host range of avian influenza virus in free-living birds. Vet Res Commun. 1988;12:125–41. 10.1007/BF00362792 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lee CW, Senne DA, Linares JA, Woolcock PR, Stallknecht DE, Spackman E, et al. Characterization of recent H5 subtype avian influenza viruses from US poultry. Avian Pathol. 2004;33:288–97. 10.1080/0307945042000203407 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lee CW, Swayne DE, Linares JA, Senne DA, Suarez DL. H5N2 avian influenza outbreak in Texas in 2004: the first highly pathogenic strain in the United States in 20 years? J Virol. 2005;79:11412–21. 10.1128/JVI.79.17.11412-11421.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pelzel AM, McCluskey BJ, Scott AE. Review of the highly pathogenic avian influenza outbreak in Texas, 2004. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2006;228:1869–75. 10.2460/javma.228.12.1869 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Omland KE. Character congruence between a molecular and a morphological phylogeny for dabbling ducks (Anas). Syst Biol. 1994;43:369–86. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jourdain E, Gunnarsson G, Wahlgren J, Latorre-Margalef N, Brojer C, Sahlin S, et al. Influenza virus in a natural host, the mallard: experimental infection data. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e8935. 10.1371/journal.pone.0008935 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Olsen B, Munster VJ, Wallensten A, Waldenstrom J, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Global patterns of influenza A virus in wild birds. Science. 2006;312:384–8. 10.1126/science.1122438 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wallensten A, Munster VJ, Latorre-Margalef N, Brytting M, Elmberg J, Fouchier RA, et al. Surveillance of influenza A virus in migratory waterfowl in northern Europe. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:404–11. 10.3201/eid1303.061130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Siembieda J, Johnson C, Cardona C, Anchell NL, Dao N, Reisen W, et al. Influenza A viruses in wild birds of the Pacific Flyway. [Epub ahead of print]. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005–2008;2010:8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Weber TP, Stilianakis NI. Ecologic immunology of avian influenza (H5N1) in migratory birds. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1139–43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Siembieda J, Johnson CK, Boyce W, Sandrock C, Cardona C. Risk for avian influenza virus exposure at human-wildlife interface. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:1151–3. 10.3201/eid1407.080066 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gill JS, Webby R, Gilchrist MJ, Gray GC. Avian influenza among waterfowl hunters and wildlife professionals. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:1284–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]